CFB 19: Amino Acids (Biochemistry)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
T/F: There are storage forms of amino acids/proteins.
False
The carbons of excess amino acids from dietary protein are converted to what?
Fat or carbohydrate or CO2
What is positive vs. negative nitrogen balance?
Positive: gaining protein in body
Negative: losing protein from body
What is another name for amino acid metabolism?
Nitrogen metabolism
Where is the amino acid pool maintained?
Blood
The amount of urea in urine is proportional to what?
Dietary protein
Under conditions of constant weight (nitrogen balance), only the ____ level changes as a result of changed protein intake.
Urea
Where are acid and pepsinogen secreted?
Glands of the stomach
What does acid denature?
Proteins
What does pepsin produce?
Peptides
What does the pancreas secrete?
Bicarbonate and zymogens
Activated enzymes in the first part of the small intestine digest ________.
Peptides
What are the enzymes in the duodenum?
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
Elastase
Carboxypeptidase
What is the final stage of dietary protein digestion?
Enzymes of intestinal lumen and villi produce mostly amino acids for absorption
Where does intracellular (body) protein degradation occur?
26S proteasome (mini stomach)
What enzymes add ubiquitin to target proteins?
E3
Poly-ubiquitinated proteins are ________.
Degraded
Abundant aminoopeptidases inside most cells degrade the short peptides to what?
Amino acids
Essential amino acids are obtained from what?
Degradation of body protein or the diet
What supplies AAs?
Amino acid pool of blood
Pepsin in the stomach is active at what pH?
1.5
Where are trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase located?
Lumen of small intestine
What do carboxypeptidase and aminopeptidases produce?
Amino acids
Intracellular proteins are tagged by _________ and degraded by what?
Ubiquitin; proteosome
Body protein is degraded with insufficient or incomplete _______ _______.
Dietary protein
The carbons of excess amino acids are used, the ________ is waste.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is removed in 3 steps:
Transfer to a common carrier
Ammonia is regenerated in liver
Ammonia is incorporated into urea
What is the essential first step in the catabolism of amino acids?
Amino acids transfer their nitrogen via amino transfer reactions to a common carrier
All ____________ utilize α-ketoglutarate as the acceptor for the amino group or glutamate as the donor.
Transaminases
Aspartate amino transferase does...
Aspartate + α-ketoglutarate → oxaloacetate + glutamate
Alanine amino acid transferase does...
Alanine + α-ketoglutarate → pyruvate + glutamate
Removal of nitrogens occurs via ______.
Ammonia (ammonium ion)
What catalyzes the release of ammonia from glutamate?
Glutamate dehydrogenase
The ammonia is secreted in the form of ____ through the ____ cycle.
Urea
What does glutaminase do?
Converts glutamine to glutamate
What is the sum of the reactions catalyzed by transaminases and glutamate dehydrogenase?
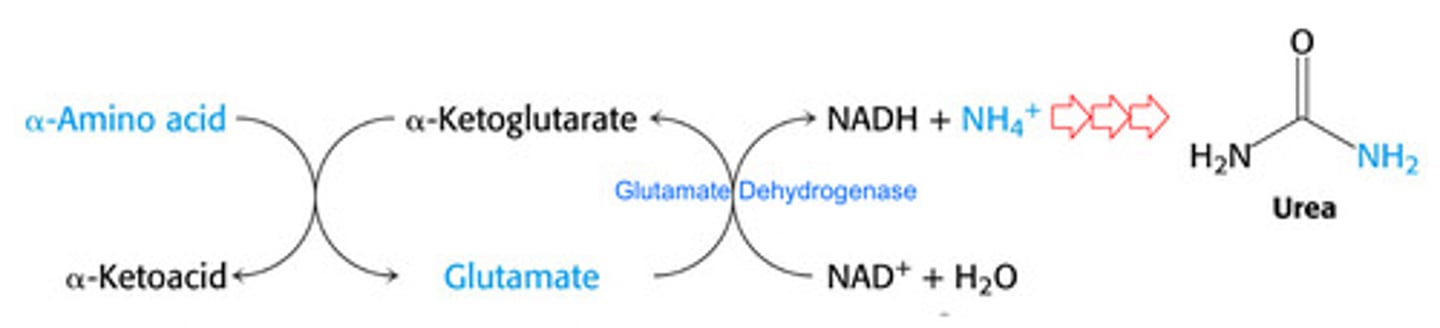
Where is urea synthesized?
Liver
Two atoms of ________ are needed for the synthesis of one molecule of urea.
Nitrogen
Where does nitrogen enter the urea cycle?
At two points, one as carbamoyl phosphate synthesized from free ammonia, the other as the amino group of aspartate
What is the key regulatory step of the urea cycle?
The first irreversible reaction, catalyzed by CPSI
What is the first regulatory step of the urea cycle controlled primarily by?
Cofactor N-acetylglutamate (NAG)
Where is the NAG cofactor formed?
Only in mitochondria
What is NAG synthesized from?
Acetyl-CoA and glutamate (stimulated by arginine)
Feed the excess nitrogen into which AA?
Glutamate
Where is NH4+ made?
Mitochondria of liver cells
Where is NH4+ incorporated?
Carbamoyl phosphate (and eventually, urea)
What combines with carbamoyl phosphate in the mitochondria?
Ornithine
What catalyzes ornithine + carbamoyl phosphate?
Ornithine transcarbamoylase
Whta edoes ornithine + carbamoyl phosphate exit as?
Citrulline
Production of carbamoyl phosphate is controlled by ___.
NAG
What activates NAG?
Arginine
What does arginine produce?
Urea
What catalyzes arginine to urea?
Arginase
What are the two fates of the amino acids?
Glycogenic or ketogenic
T/F: You can get blood glucose from lysine and leucine.
False
T/F: In mitochondria, almost all AAs are degraded into TCA cycle compounds.
True
Breakdown of _______ begins like other branched-chain AAs, then diverges to...
Leucine; acetyl-CoA
Why would someone's urine smell of maple syrup/burnt sugar?
Some individuals lack the ketoacid dehydrogenase and build up the keto acids
Which amino acids are involved in maple syrup urine disease?
I L V
Where are reduced NADH and FADH found?
Mitochondria
When amino acids are broken down, their carbons form either ________ or ___ _____ intermediates.
Pyruvate or TCA cycle intermediates
If these intermediates can form OAA, you can make _______.
Glucose
What do branched chain amino acids form?
Branched chain keto acids
Which compounds are involved in the synthesis of catecholamines (dopamine)?
Tetrahydrobiopterin (in hydroxylase reaction)
PLP (in decarboxylase reaction)
What converts Dopa to Dopamine?
DOPA decarboxylase (PLP)
Epinephrine is made from ________.
Dopamine
What is the intermediate between dopamine and epinephrine?
Norepinephrine
Melanin is synthesized from ________.
Tyrosine
What do patients with Albinism lack?
Tyrosinase (leading to a lack of melanin pigments in skin and eyes)
Depending on the tissue, what 3 compounds can tyrosien form?
Dopamine
Epinephrine (adrenalin)
Melanin
The synthesis of glycine, serine, cysteine, methionine, and other molecules requires _-carbon transfers.
1
What group does Biotin and PLP transfer?
CO2
What group does cofactor SAM transfer?
Methyl
Tetrahydrofolate derives from dietary _______.
Folate
T/F: Folates can carry out essential methylation reactions.
True
Where are folates found?
Green leafy vegetables
Folate is required for synthesis of what?
Nucleic acid
T/F: All forms of folate interconvert.
False; the methyl form does not
What are these forms of THF known as?
One-carbon pool
What can be made from glycine using the methylene form?
Serine
This reaction is reversible
What is the methyl donor?
S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM)
THF (tetrahydrofolate) comes in different forms.
True
Using Methylene THF/THF, _______ can be interconverted with ______.
Glycine, serine
SAM is used in making what?
Epinephrine (from norepinephrine)
Oxaloacetate is the TCA cycle entry point for the breakdown of which amino acids?
Asparagine and aspartate
Conversion of glycine to serine requires which of the following enzymatic processes?
One carbon addition from N5,N10-methylene tetrahydrofolate
What is the glycolysis/TCA cycle intermediate that is transaminated to form glutamate?
α-ketoglutarate
Which precursors does mitochondrial carbamoyl phosphate synthase use?
NH4+, ATP, and CO2
One of the nitrogens for urea biosynthesis comes from aspartate. Aspartate is regenerated by the transamination of which TCA cycle intermediate?
Oxaloacetate
Which enzyme functions best at low pH (around 1.5)?
Pepsin
Body protein that is degraded is tagged with what molecule and is degraded by which cellular structure?
Ubiquitin, proteosome
An individual is on a diet that is deficient in leucine. They will lose muscle mass because leucine is...
An essential amino acid
An individual who is deficient in ornithine transcarbamoylase will most likely present with low levels of urea, and low levels of what other compound?
Citrulline
Which one of the following enzymes or compounds is not directly in the pathway from tyrosine to epinephrine?
Melanin