Topic 2 - Cobalt-60 Therapy & Brachytherapy
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 234 - Therapeutic and Imaging Equipment. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
before WWII, radium was attempted to be used for radiotherapy because it could create energies of 2 MeV. Why was it not used?
it has a half-life of 1600 years, and there was limited amounts of it available
where were the first two cobalt-60 units built?
Saskatoon, Saskatchewan and London, Ontario
When was the first patient treated with cobalt-60 radiation
1957 in London, Ontario
How is Cobalt-60 Produced
59Co(n,y)60Co
bombarding stable Co59 with neutrons
t1/2 of Co60
5.3 years
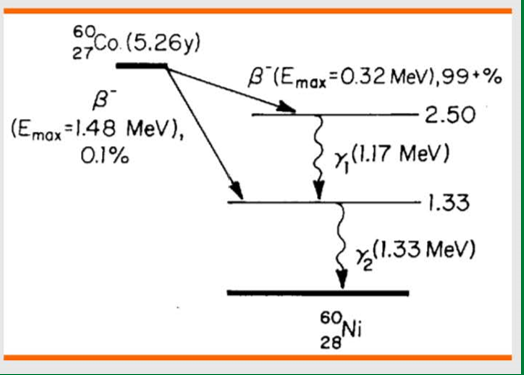
Co60 decay process
Beta minus decay
produces 1.17 MeV and 1.33 MeV gamma
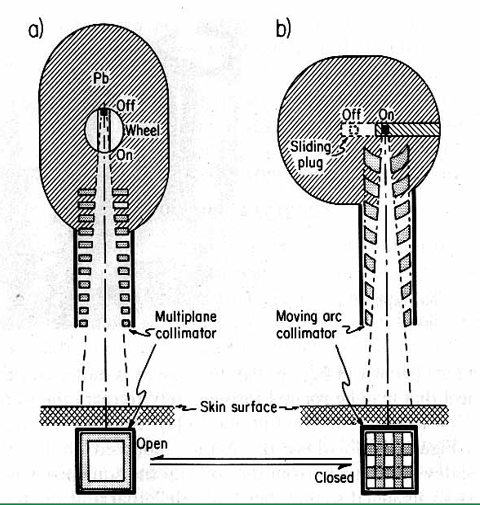
What are the two ways to turn the cobalt beam ‘on and off’
rotating cylinder
rotate the gamma beam 180 degrees into a lead shielding area
sliding drawer
most popular: push the source into lead shielding area
what is contained in a cobalt-60 unit’s source head
a steel shell with lead lining
a mechanism to bring the source in front of collimator
collimators to prevent unwanted scatter
What is a Co-60 fail safe device?
At the end of exposure or a breakdown, there is a mechanism to interrupt the beam and take it out of the ‘on’ position
if the source fails to return to the off position with the fail safe device, how is exposure interruption
using a manual return system
how does the size of a Co-60 machine compare to today’s LINACs
Co60 machines are smaller as there is much less electronics involved
no magnetron, klystron, accelerating chamber.
just cobalt sources in head
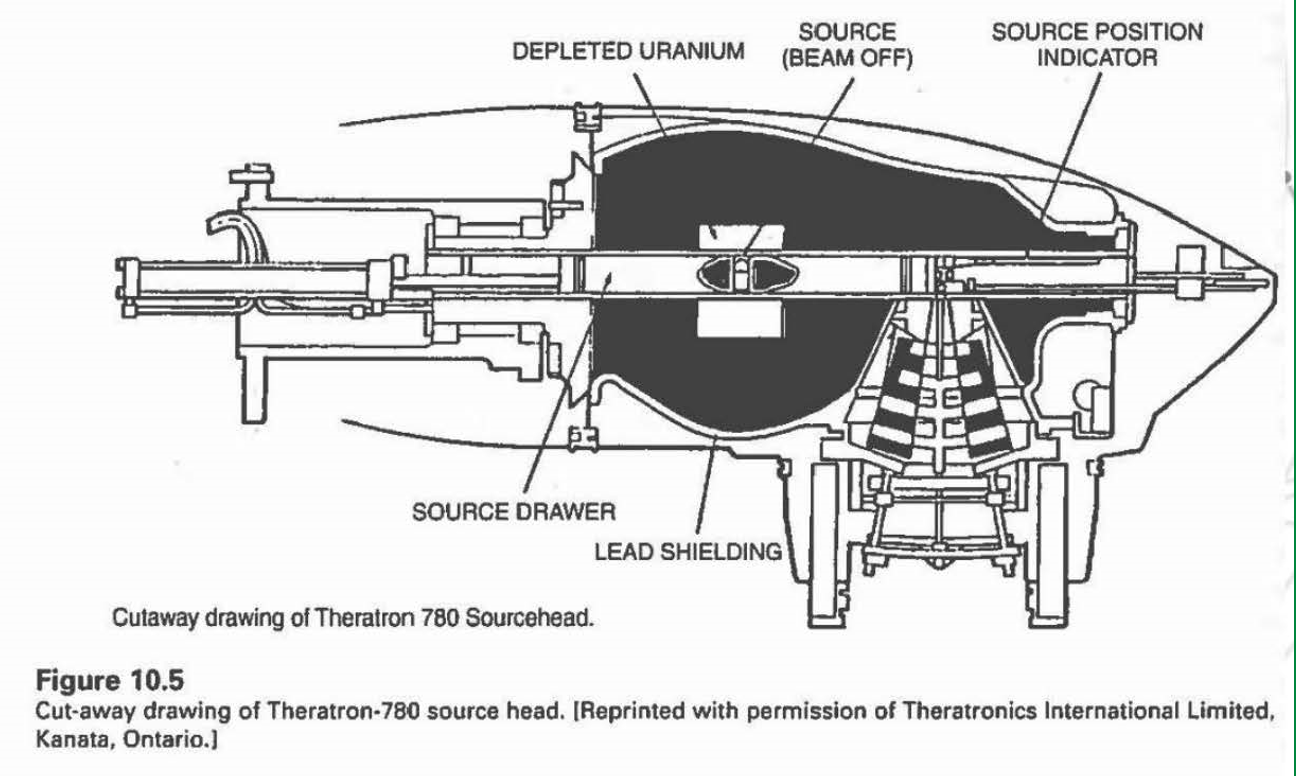
what is the purpose of the depleted uranium in this Theratron-780 source head?
it works like lead, absorbing radiation
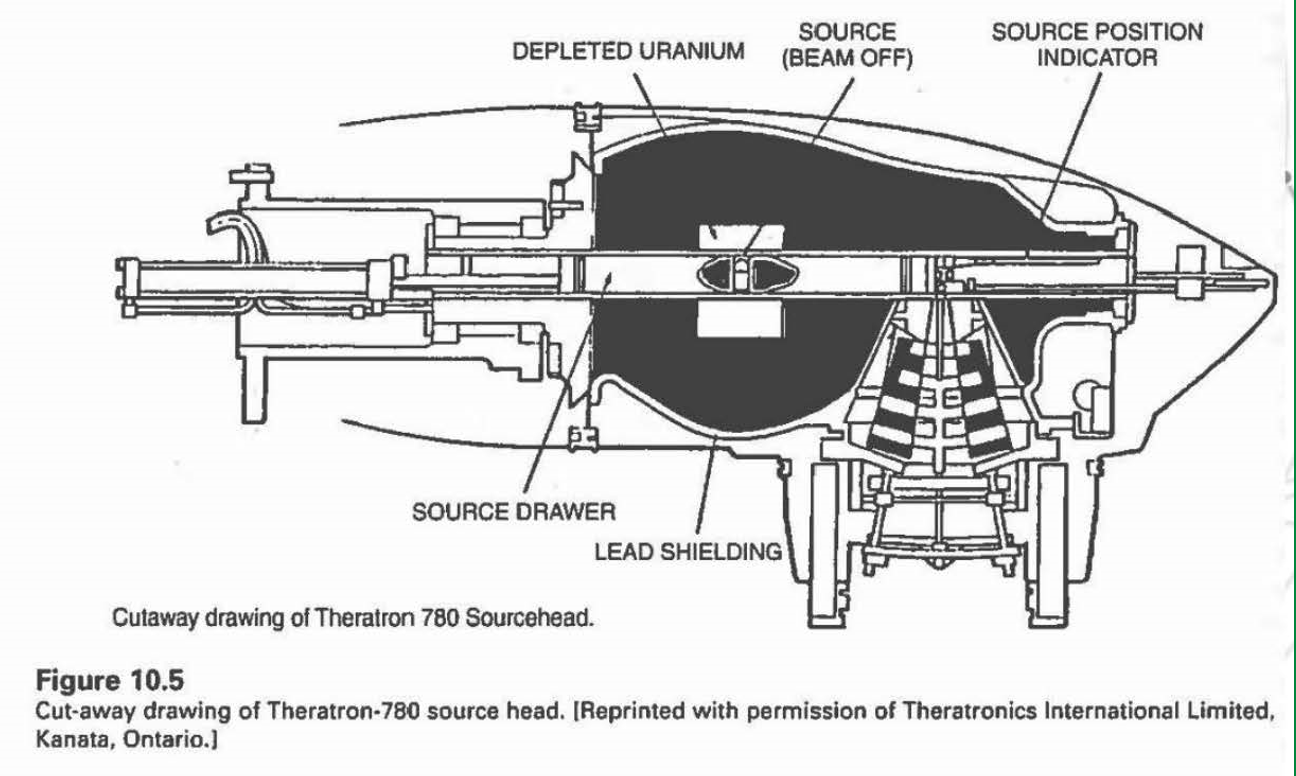
how is the cobalt machine put into the ‘on’ position
the source drawer is pushed in line with the collimator
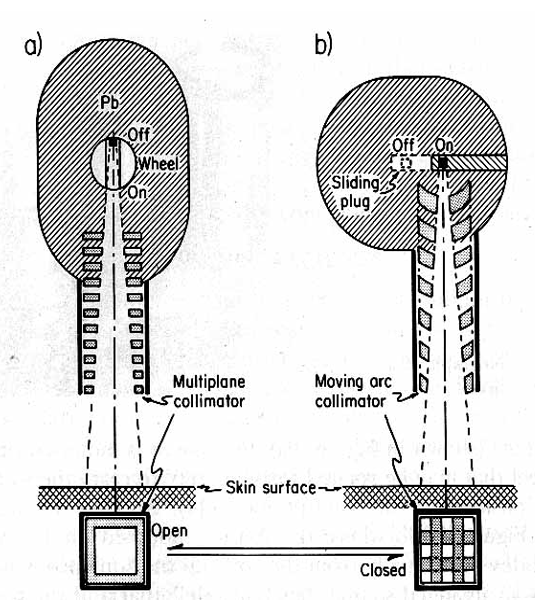
Did the Saskatoon Co60 machine have a treatment head like a or b?
a
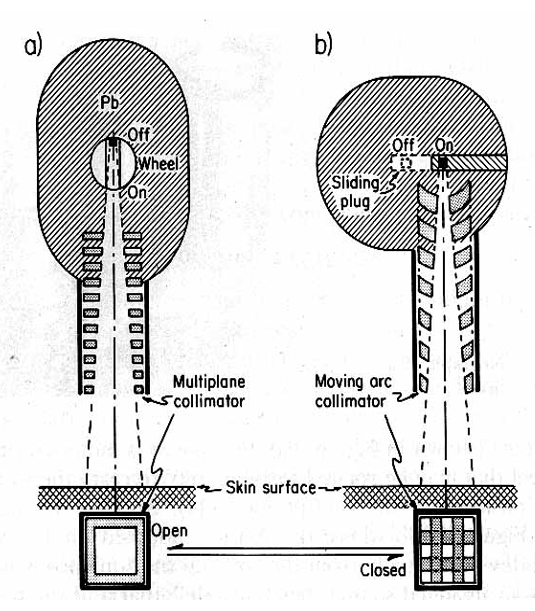
did A.E.C.L units have a treatment head like a or b?
b
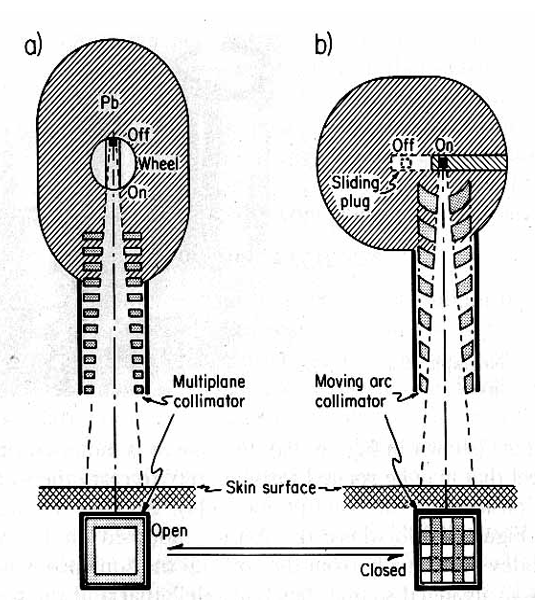
how was the collimator used to prevent excess radiation from coming through if machine was stuck in on posiiton
it would make criss-cross pattern
How did the Co60 machine compare to 200 kV x-ray machine in terms of isodose and depth
dose was much better at depth
200 kV: at 10 cm depth we got 35% of surface dose
Co60: at 10 cm depth, we got 55% of surface dose
compared to modern LINAC: 80%
radiation output was steady, easier to predict, and more controlled
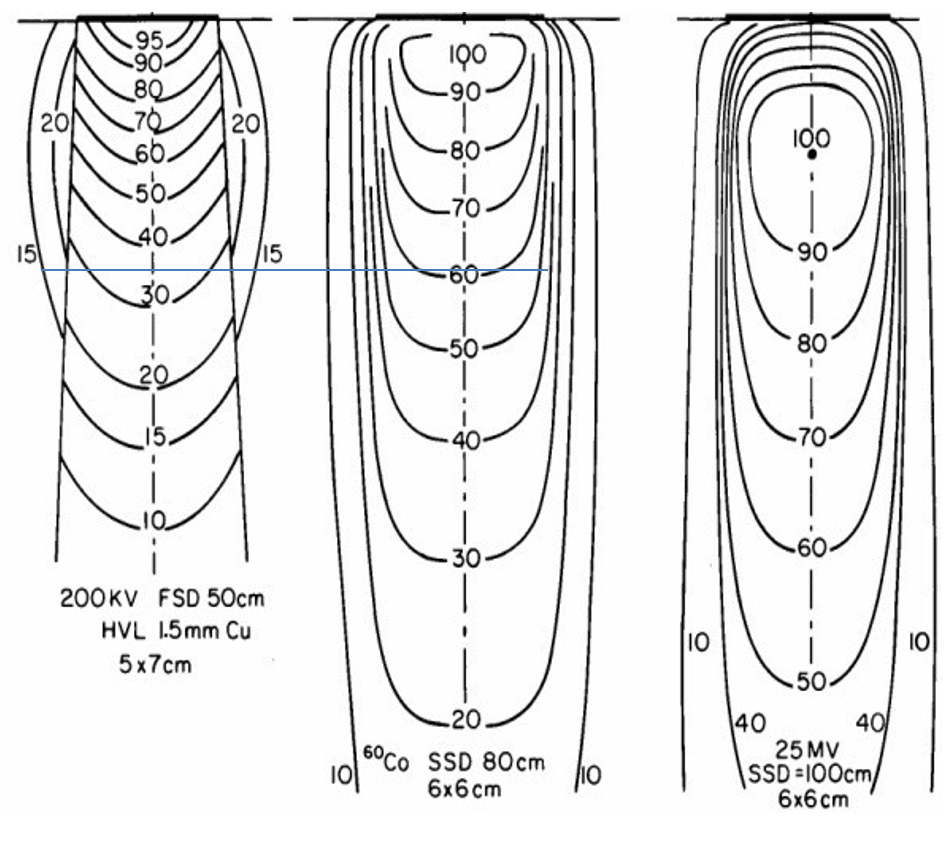
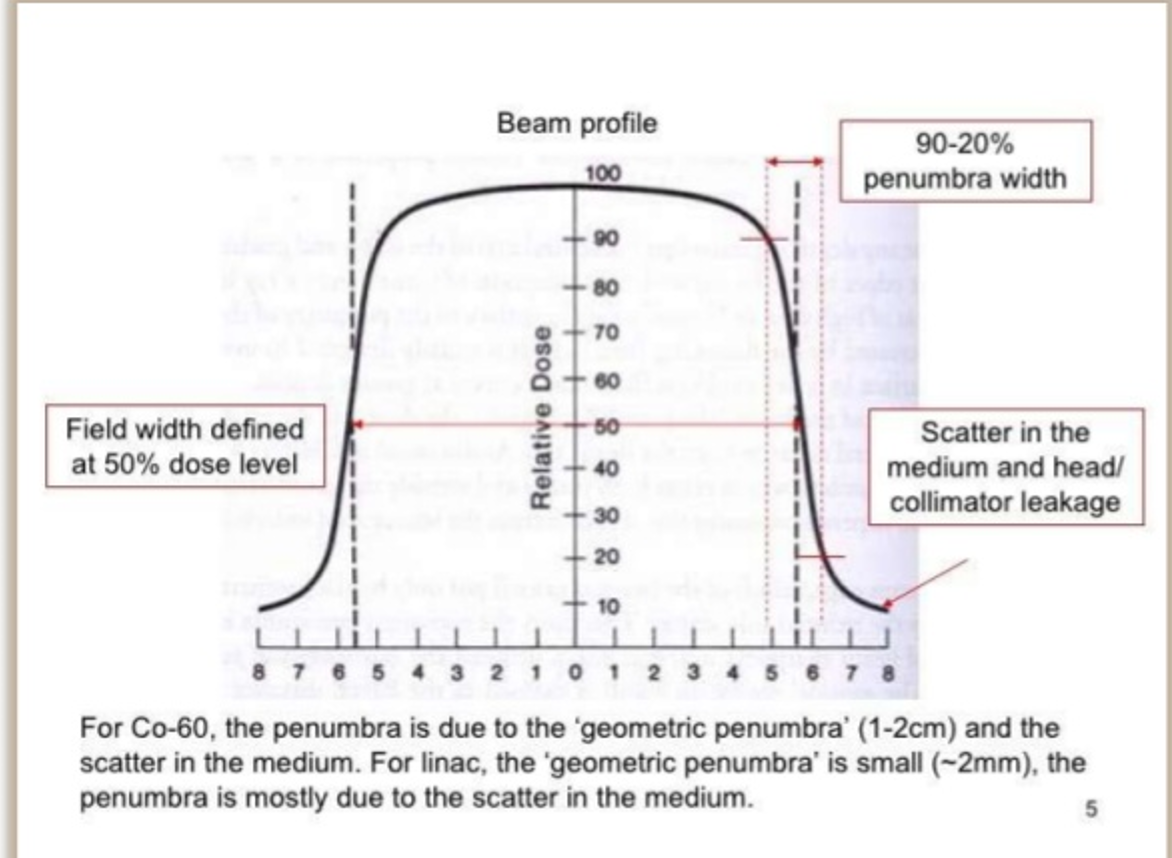
How does the penumbra of the Co60 machine compare to LINAC
Co60 penumbra is much worse due to geometric penumbra
What are two modern applications of Cobalt therapy?
Cobalt-MRI
Gamma Knife
Cobalt-MRI system
cobalt source inside MRI magnet allows for simultaneous imaging and radiation for image radiation guidance

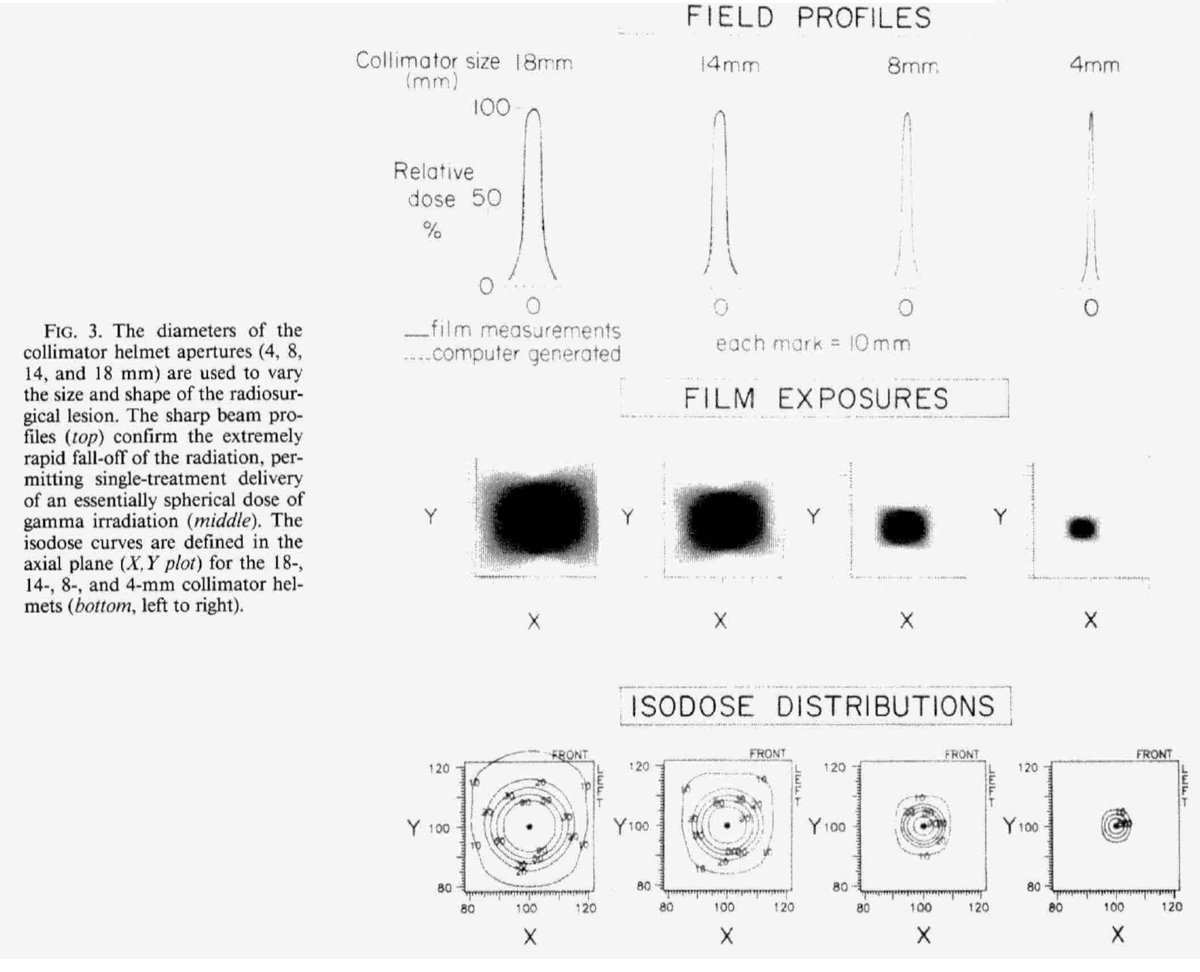
Gamma Knife
contains 201 Co60 sources in a circular array which converge to focus a narrow high dose beam of 0.5 mm on to a small tumor volume
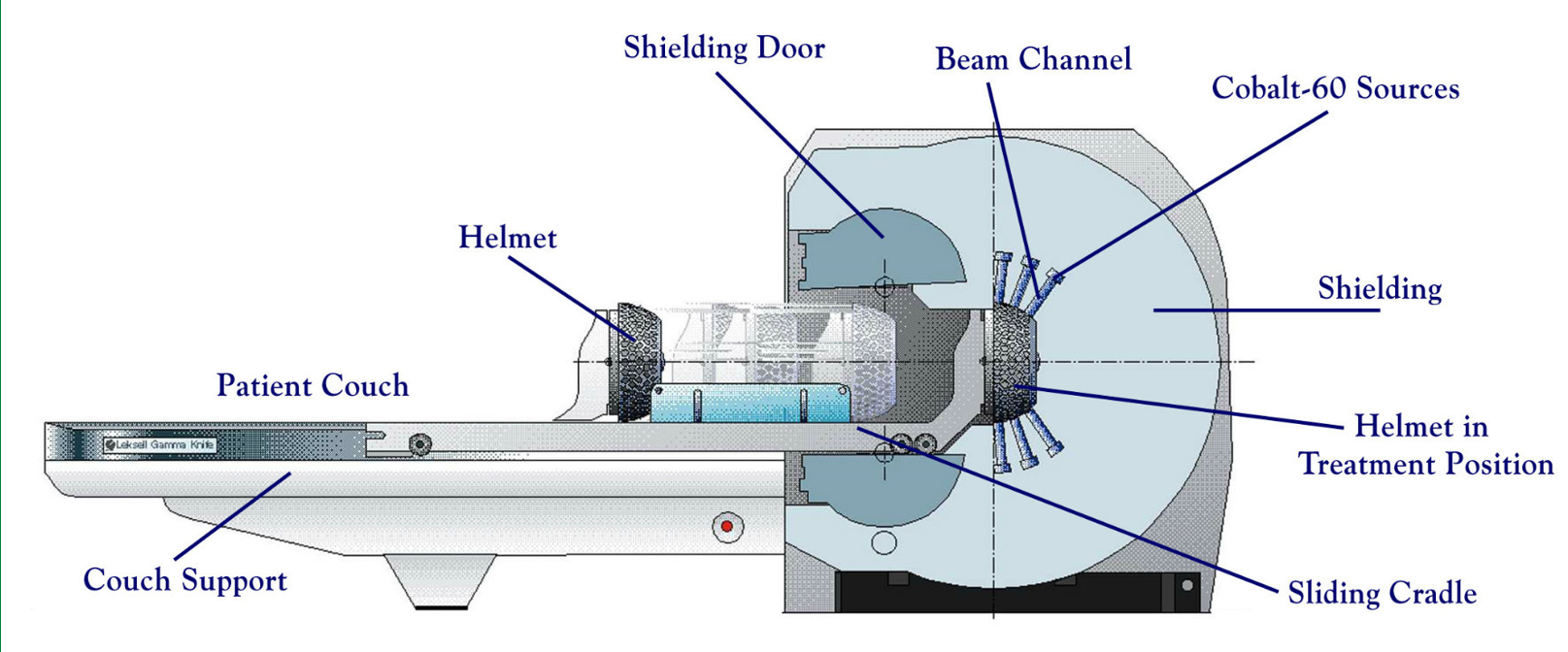
what treatments can the gamma knife be used for?
deep brain tumors and brain radiosurgery
radiosurgery = 1 fraction
tumors = multiple longer fractions
Why is the gamma knife great for small lesions?
due to narrowing of beam, the isodose can be very small
Brachytherapy Definition
a method of treatment in which sealed radioactive sources are used to deliver radiation at a short distance by interstitial, intracavitary, or surface application
Where does the term ‘brachy’ come from
from the greek word brachys meaning ‘short distance’
what cancers is brachytherapy commonly used to treat
cervical, prostate, breast, skin
interstitial brachytherapy
the sources are placed directly in the target tissue of the affected site such as the prostate or breast
contact brachytherapy
placement of radiation source in a space next to the target tissue. this space may be
a body cavity (intracavitary)
a body lumen (intraluminal)
externally (surface
intravascular brachytherapy
a radiation source placed in blood vessels for the treatment of coronary stenosis
interstitial brachytherapy catheter technique
uses several flexible catheters inserted into treated tissue
catheters are then attached to afterloader to deliver treatment
intracavitary brachytherapy catheter technique
involves placement of a single baloon catheter into the cavity left after the removal of the tumor.
balloon is inflated and catheter is then connected to afterloader to deliver radiation into the balloon
LDR (Low Dose Rate) Brachytherapy
sources that emit radiation up to 2 Gy/hr
used in oral cavity, sarcomas, prostate
MDR (medium dose rate) brachytherapy
rate of dose deliver between 2-12 Gy/hr
HDR (high dose rate) brachytherapy
rate of dose delivery exceeds 12 Gy/hr
used in cervix, lungs, breast, prostate
why must automatic afterloading be used for HDR
because of the radiation source’s high activity
PDR (pulse dose rate) brachytherapy
short pulses of radiation given once an hour to stimulate rate and effectiveness of LDR treatment
used in gynaecological and H+N cancers
Permanent implant brachytherapy
delivers a high total dose of 150 Gy at a very low dose rate over several months
Afterloading Unit
after applicator/catheter is placed into target position, the radioactive sources are loaded after by a machine
the applicator cable containing the sources is preloaded, then moved by a stepping motor into the catheter
Remote HDR afterloader
used to deliver a single source of high activity (like IR192)
how is the remote afterloader tested for QA?
before the active source is placed into the catheter, a dummy wire is placed to ensure no obstruction occurs
advantages of brachytherapy
high localized dose to small volume
reduced radiation to healthy organs
shorter treatment time
hypoxic tumor targeted easier
Disadvantages of brachytherapy
invasive
requires expertise, experience, equipment
time consuming
Radium t1/2
1600 years
What series is radium apart of?
uranium series
starts with U238, ends with Pb206
radium decay mode
alpha decay
what does radium decay into?
Radon (a gas)
Radon half-life
3.83 days
how many gamma decays does it take to decay radon
49
what does radon decay into?
lead
Radium Source Encapsulation
radium sources have two capsules, as after radium decays, it decays into radon gas
we don’t want this to break inside the patient
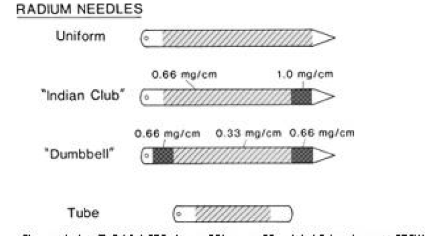
Iodine-125 half life
59.3 days
iodine-125 decay mode
electron (k) capture
what tumors is I-125 used in brachytherapy for?
prostate cancer
can also be used in diagnostic nuclear medicine
Iridium-192 half life
73.8 days
is iridium a sealed or open source?
sealed
Is Ir-192 used for HDR or LDR therapy
HDR and also PDR
Ir-192 decay mode
Beta minus (95%)
K capture (5%)
Co-60 half life
5.26 years
when is Co-60 used in radiotherapy
rarely used, but can be used to replace Rad-226
what kind of afterloader is needed for Co-60
a remote afterloader, since it is HDR
Co-60 decay mode
beta minus
Cs-137 half life
30 years
when is Cs-137 used in therapy
LDR interstitial or intracavitary brachytherapy
Cs-137 decay mode
Beta minus
I-131 half life
8 days
is I-131 a sealed or unsealed source
unselaed, it is given orally for nuclear medicine
I-131 decay mode
beta minus
Sr-90 half life
29 years
is Sr-90 a sealed or unsealed source?
unsealed
how is Sr-90 used in brachytherapy
used to treat superficial ocular (eye) malignancies
Sr-90 decay mode
Beta minus
Pd-103 half life
17 days
When is Pd-103 used in brachytherapy
used similarly to I-125: prostate treatment
Pd-103 decay mode
K capture
temporary prostate implant method
radioisotopes like Ir-192 are implanted during surgery and left in for three days
patients are hospitalized for this
permanent prostate implant medthod
radioisotopes with short half lives like I-125 or Pd-103 emit low energy photons are are left in the patient forever
guided through TRUS
intravascular brachytherapy
used to reduce rate of restenosis to below 10% with high energy beta sources like Sr-90 or gamma sources like Ir-192