CH 7 & 8 - Prokaryotic Genomes and Gene Expression
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
A phenotype generally results from the functioning of one or more:
Genes
can have genotype but wont see phenotype all the time
DNA —→RNA—→Protein
Central Dogma
Transcription
DNA—→RNA
RNA polymerase; mRNA
Translation
RNA—→Protein
genetic code, transfer RNA’s; ribosomal RNA’s
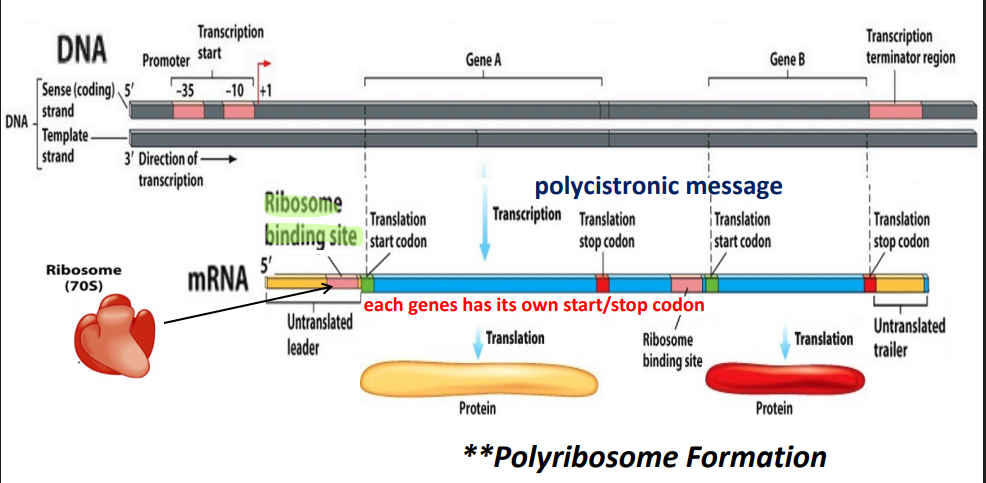
Transcription and translation are ______ in prokaryotes
coupled

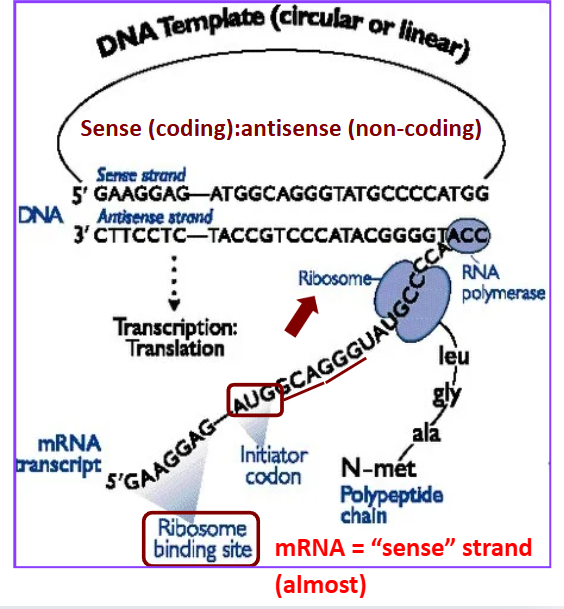
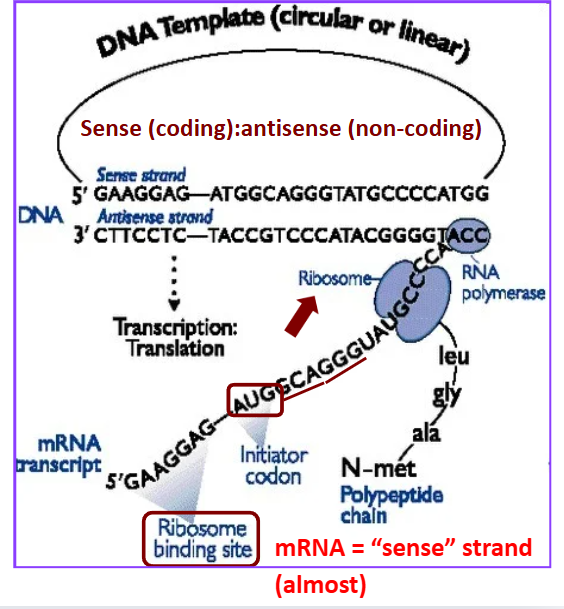
Sense strand
coding strand
mRNA = “sense” strand (almost) —→ due to uracil
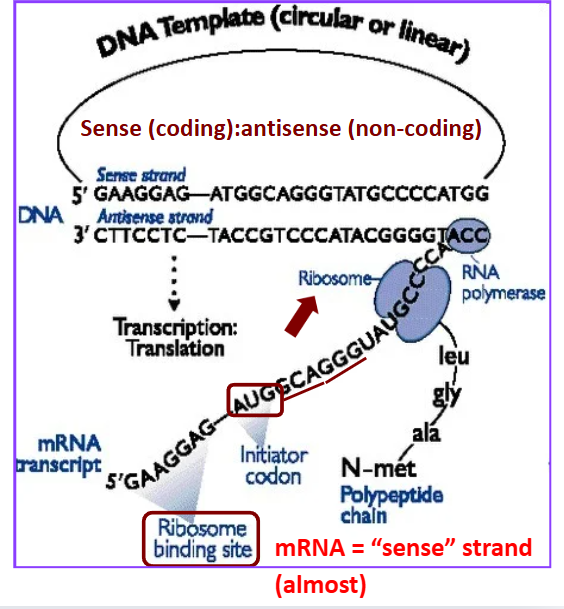
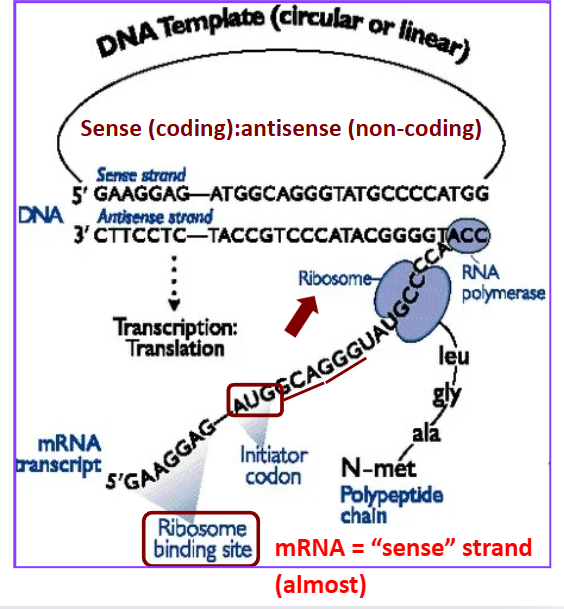
Antisense strand
non-coding template strand

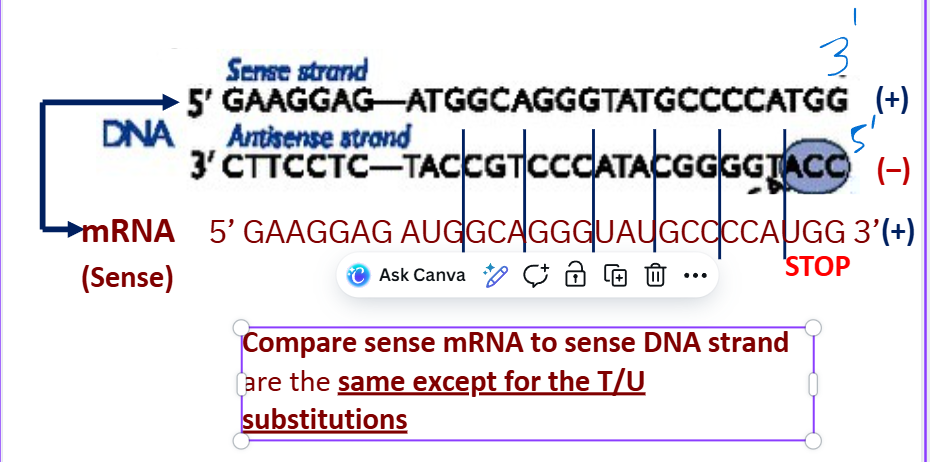
Compare sense mRNA to sense DNA strand are the same except _______
for the T/U substitutions

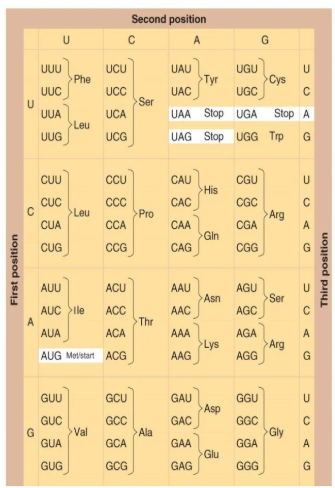
Genetic Code
redundant: 64 codons (20 amino acids)
start/stop codons
represents mRNA
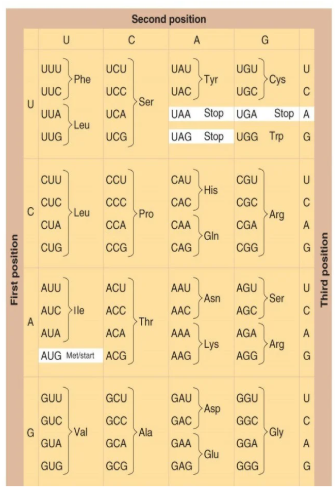

Codons process
The “A” in AUG start codon is not the first base in the transcript

Prokaryotic Genomes
Genome
Transcriptome
Proteome
Genome
the totality of DNA in a cell
chromosome and plasmids
PROKARYOTES are HAPLOID (1 chromosome)
Transcriptome
total transcripts present at a given time
transcripts DISAPPEAR QUICKLY
Proteome
all the types and numbers of proteins expressed at a given time
Prokaryotic genome organization
Most possess a single circular chromosome
Size: 500,000 to 9,000,000 bp (order of magnitude < eukaryotes)
May also possess small, circular, extra-chromosomal segments called plasmids (1000 – 25,000 bp)
operon vs. regulon
operon - single regulatory sequence
regulon - a collection of operons
Cistron
gene
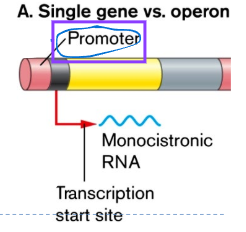
Monocistronic: one prmoter, one gene
Polycistronic: one promoter, multiple genes
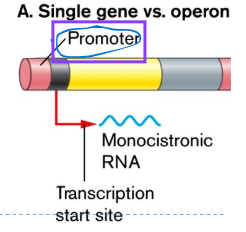
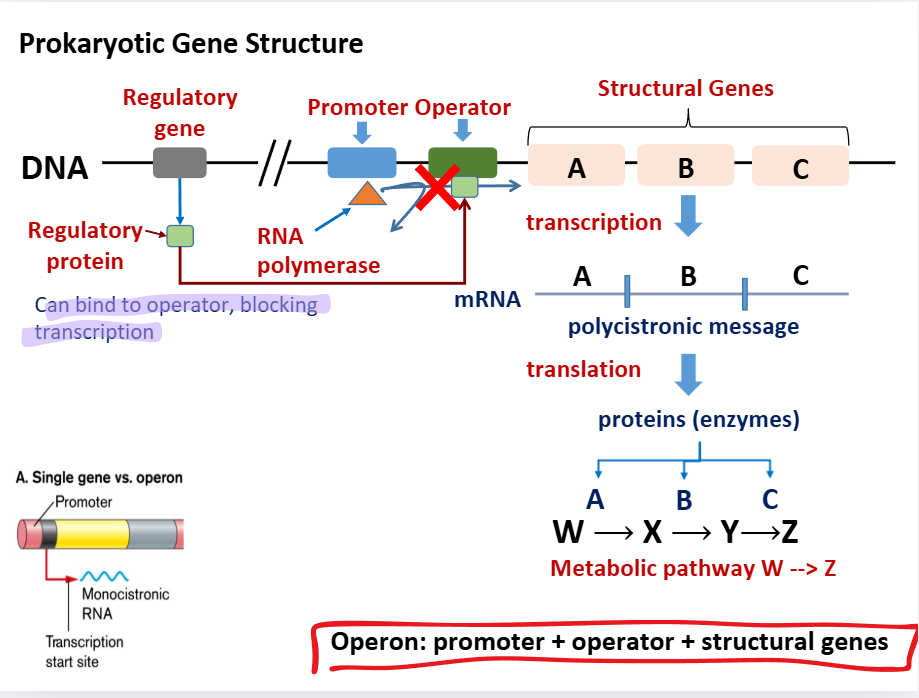
Operon basic structure
promoter
defines the start of the gene (common to prokaryotes and eukaryotes)
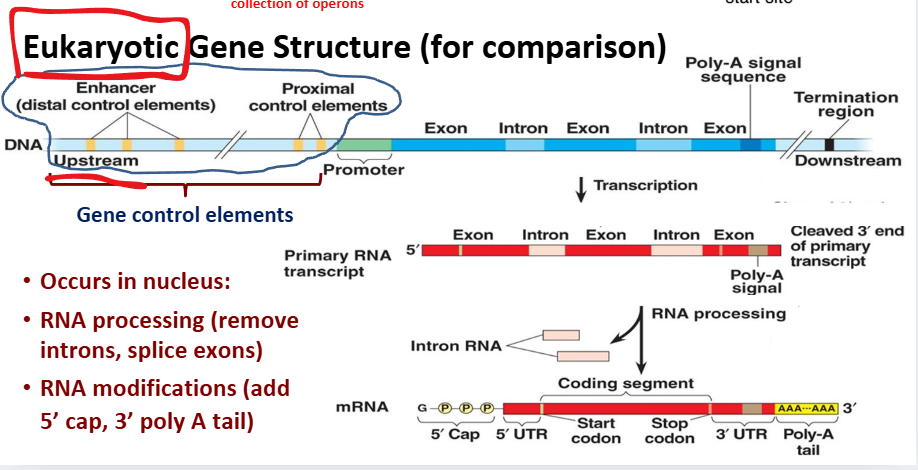
Eukaryotic Gene Structure (for comparison)

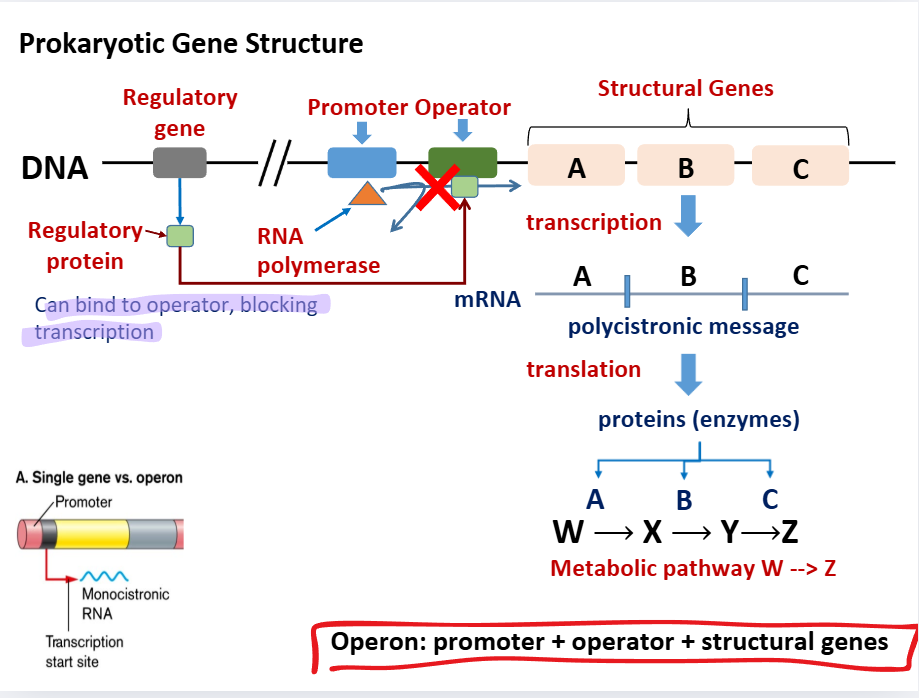
Operon gene structure
Operon: promoter + operator + structural genes
Regulatory gene is upstream
Regulatory gene —→ regulatory protein —→ binds to operator and prevents transcription
If regulatory gene is inactive: structural genes —→ transcription into polycistronic message —→ translation into enzymes (proteins) which guide metabolic pathways
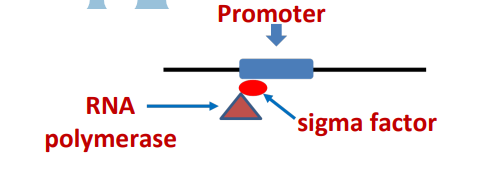
Sigma factors
interacting w/different promoters; sigma factors guide RNA polymerase to the promoters

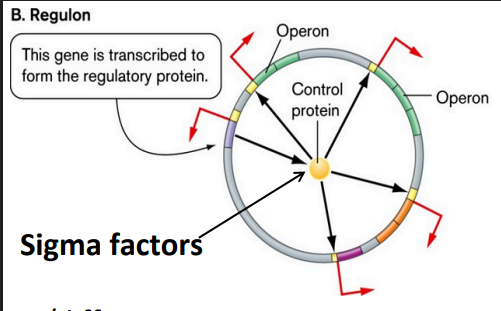
Regulon
controls multiple operons
collectively control operons common to particular metabolism via specific sigma factor
Plasmids
small, extra-chromosomal, circular DNA segments 2 – 25 kbp in size.
Plasmids NOT necessary for survival
Autonomous; possess an ori
Some can integrate into chromosome
Some are transferable
How do low copy number plasmids and high copy number plasmids affect the latter?
High copy number plasmids provide higher gene expression and protein yields, but can lead to a metabolic burden, protein aggregation, and lower cell growth. Conversely, low copy number plasmids are less of a burden and are better for expressing toxic proteins, studying genes at a more physiological level, or maintaining a more stable phenotype.
R factor, catabolic plasmids, F factor
resistance to antibiotics, catabolic pathway, fertility (transfer of plasmids - conjugation)
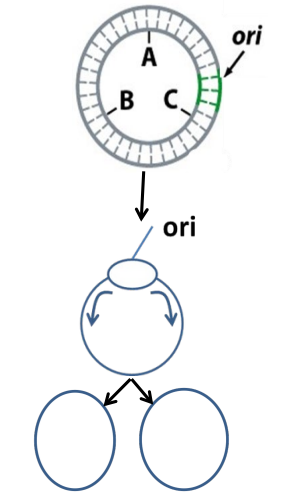
Bidirectional replication (plasmids)
same as chromosomal replication
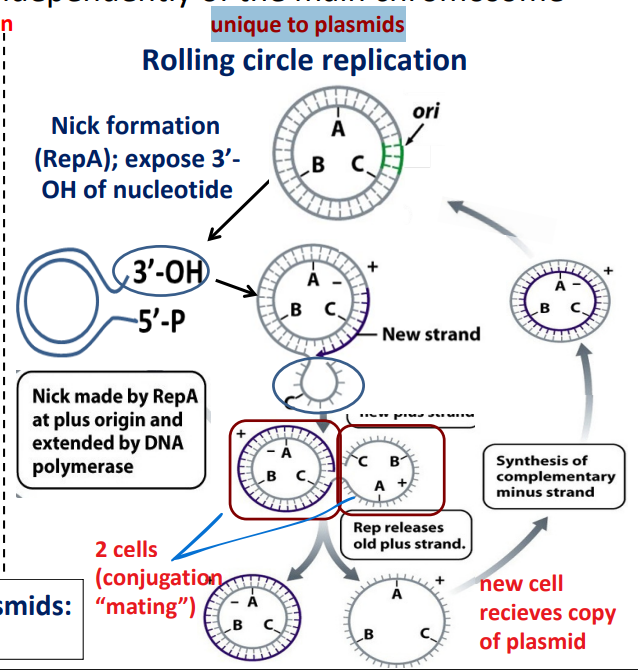
Rolling circle replication
unique to plasmids
Nick formation (RepA); exposes 3’- OH of nucleotide
Nick made by RepA at ori extended by RNA polymerase
Rep releases old (+) strand and new cell recieves copy of plasmid
synthesis of complementary (-) strand for plasmid in new cell

Plasmid Inheritance
Plasmids do not carry essential* genes how are they maintained in the host cell?
Possess plasmid genes that benefit the host under certain conditions *antibiotic resistance (Selective pressure)
Integrate plasmid into the chromosome
High/Low copy # of plasmids
High copy # plasmids
Low copy # plasmids
possess a partitioning system (par proteins)
Par proteins - guide plasmid to opposite end (requires energy); serve to segregate and partition plasmid and its copy
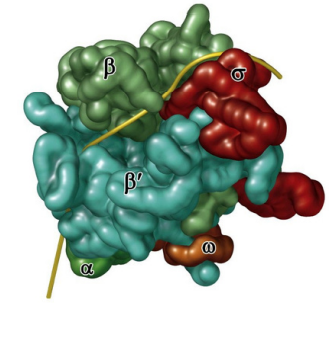
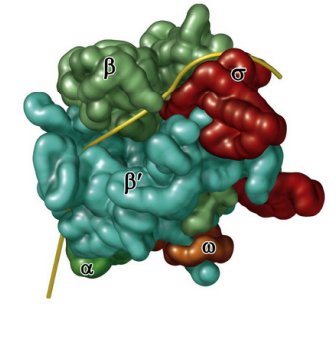
Bacterial RNA Polymerase
Bacterial RNA polymerase “holoenzyme”: a core polymerase that synthesizes mRNA : has 4 subunits: 2 alpha (α)subunits, 1 β, and 1 β’
Sigma factor guides RNA polymerase to the promoter, then unbinds from core polymerase

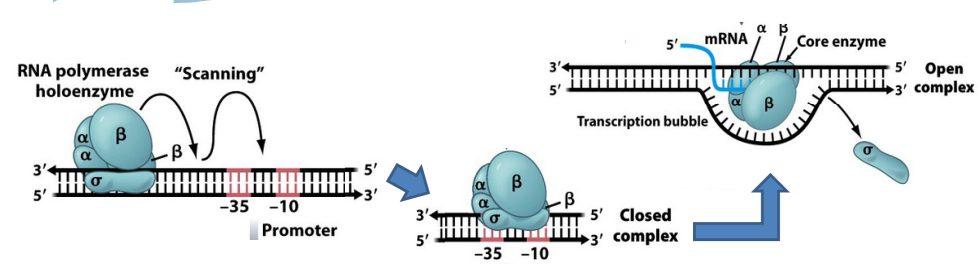
-35 and -10 bp
Most sigma factors recognize promoter sequences at positions -35 bp, -10 bp upstream of transcription start.
Consensus sequences are conserved sequences
rich in T, A bonds b/c it has 2 DB compared to 3 in G, C (less energy to break)

σ70 sigma factor
common for most bacterial genes

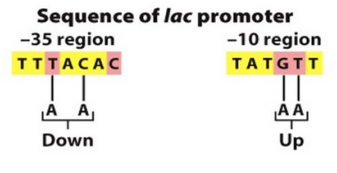
Changes in promoter sequence:
up (increase activity) or down (decrease activity)

Promoter strength:
strong (high expression) v. weak (low expression)
strong vs weak binding (weak promoters are NOT BAD, they just code for less genes)

Ribosome (70S)
large subunit (50S) + small subunit (30S)
30 S includes —→ 16 S - rRNA and proteins

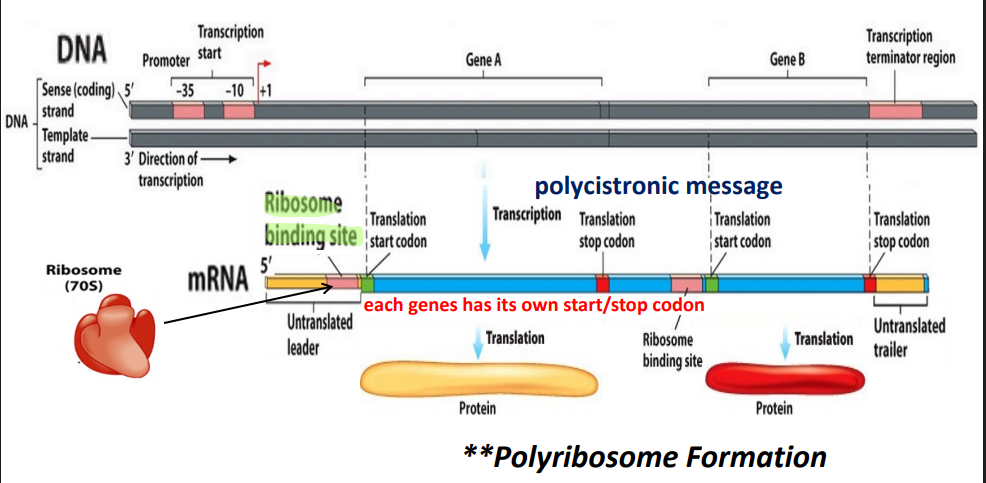
Shine-Delgarno sequence:
ribosome binding site; binds to 16S ribosomal RNA of small (30S) ribosomal subunit;ribosome binding followed by translation of transcript toform polypeptide