HSCI LAB FINAL
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What are the main differences between EKG and Echocardiogram
EKG Electrical, Echo mechanical
EKG produces a wave diagram, Echo produces a picture
EKG has eelctrodes that connect to a machine
Echo: cool gel on chest + transducer that releases sound waves
Sound waves echo back and produce picture
What are the main types of Echocardiogram
TTE (Transthoracic Echocardiogram)
TEE (Transesophageal Echocardiogram
Stress Echo
What is TTE and what can it be used for
Transthoracic echocardiogram
most common type, minimally/noninvasive
Used to
Check the health of heart valves
determine how well the heart is pumping blood
measure blood pressure
measure the size and shape of the heart chambers
What is TEE and what is it used for
Transesophageal Echocardiogram
invasive, has to slide an endoscope down esophagus
photos within the body
up to 90 minutes
Used to
Follow up a TTE to help diagnose/manage heart prolem
Useful in emergency and critical care
check for blood clots before a procedure
successful surgery confirmation
real-time imaging for some catheter-based procedures
What is a stress echo and what is it used for
Used to assess heart’s function while beating fast
What are the different options for echos?
Two dimensional vs three dimensional
Doppler vs color doppler
Strain imaging vs contrast imaging
What is the difference between two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasounds?
Two dimensional ultrasound
Slices on a computer screen
can be stacked to be 3d
Three dimensional ultrasound
Allows to view heart from different angles
shows how well heart pumps blood
What is the difference between a doppler ultrasound and a color doppler
Doppler: shows how fast blood flows and in what directions
Color doppler: same thing but uses different colors to highlight the different directions of blood flow
What is the difference between strain imaging and contrast imaging
Strain: shows changes in how the heart muscle moves
Contrast: substance is injected into vein, helps show details of the heart
What are the different types of tranducers?
Linear, Curvilinear, phased array
When is a linear transducer used for?
Looking at arteries and veins
what is a curvilinear transducer used for?
Looking at the abdominal aorta
What is a phased array transducer for
echocardiography
how does a tranducer work
produces soundwaves that bounce off body tissues and make echoes. send them to a computer to create a sonogram
How would you get a sagittal plane view of the heart?
transducer placed over the chest
indicator points to patient’s head
How would you get a transverse plane of the heart
transducer placed subcostally (below the rib cage
indicator points toward the right side of transverse plane
how would you get a coronal plane of the heart
transducer is placed along the mid-axillary line
indicator on the transducer is pointing toward the patient’s axillary region
When is a long axis/short axis used for
when structures do not lie in the classic planes
how does the ultrasound beam shine
near field to far field
what view is this
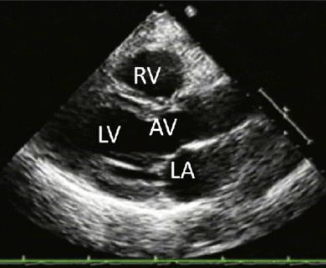
Parasternal long axis
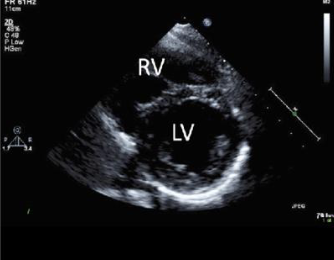
what view is this
parasternal short axis
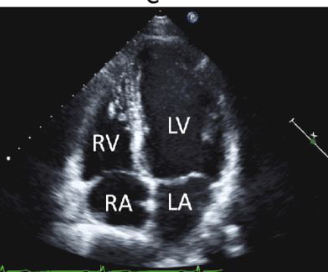
what view is this
apical 4 chamber
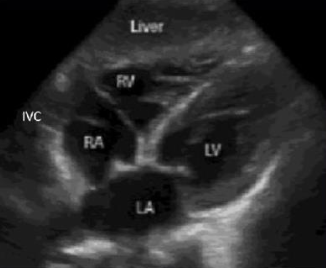
what view is this
subcostal 4 chamber
how is the transducer placed for parasternal long axis view
placed to left of the sternum in the 3rd, 4th, or 5th intercostal space
indicator towrds right clavicle (11’oclock)
what does plax allow you to see
everything but the right ventricle
what does parasternal short axis view allow you to see
shape and size of the ventricles
how is the transducer placed on psax
3 4 5 ics
but rotated 90 of the plax
how should the ventricles look like in psax
lv is round
rv is d
what can the a4c see and identify
pericardial effucion
what is pleural effusion
buildup of fluid between the lungs and pleural membrane
can occur due to inflammation or CHF
what is pericardial effusion
buildup of fluid between heart and pericardial membranes
can occur due to pericarditis
what is cardiac pericardial tamponade
pericardial effusion puts pressure on the heart which prevents it from filling properly
causes blood pressure to drop
how do you calculate ejection fraction
(Stroke Volume/End Diastolic Volume) * 100
What is normal rate for Ejection Fraction
>50%
what is a moderately depressed ejection fraction
30-50%
what is congestive heart failure
occurs when heart cannot pump or fill adequately
what can a leftsided chf lead to
left ventricle dysfunction, results in a decreased af
what can cause a decreased Ef
left sided chf
aortic regurgitation
mitral valve stenosis
what is a patent foramen ovale?
a hole in the interatrial septum separating the two atrium
what is atherosclerosis
plaque within the arteries
what are some risk factors for atherosclerosis
hyperlipidemia, hypertension, smoking
how can atherosclerotic plaques be detected
in a carotid artery scan
what is a bicuspid aortic valve
aortic valve contains two cusps
what can a bav lead to
aortic regurgitation
aortuc stenosis
both lead to heart failure
what vessel is used for measuring blood pressure
brachial artery
what are the five phases of korotkoff sounds
1: appreance of faint tapping sound (systolic)
2: louder + swishing
3: distinct loud
4: sound becomes muffled and softer
5: sound dissappears
what phases do you listen for while the person is at rest
phase one, phase five
what phases do you listened to while the person is in motion
phase one, phase four
what happens if the cuff is too big/loose
erroneously low blood pressure
what happens if the cuff is too small/tight
systolic blood pressure increases
what happens if a cuff is too wide
underestimate bp
what happens if the cuff is too narrow?
overestimate bp
what is normal blood pressure
<120/<80
what is elevated blood pressure
120-129/<80
what high blood pressure stage one
130-139/80-89
what is range of high blood pressure stage 2
>140/>90
what is hypertensive crisis
>180/>120
what is the treatment for high blood pressure
healthy diet and exercise
diuretics
ace inhibitors
beta blockers
vasodilators
what is the normal bp response to exercise
systolic elevates, dyastolic remains the same/decrreases
what is an abnormal bp responses to exercise
systolic fails to elevate, diastolic elevates
what does a 0 rating pulse quality mean
no pulse
what does a 1+ pulse rating mean
weak pulse
what does a 2+ pulse quality mean
normal pulse
what is a 3+ pulse quality
bounding pulse
what can an irregular pulse indicate
cardiac disease
what is a normal respiratory rate for an adult
12-20 minutes
what can labored preathing lead to
respiratory muscle fatigue→ respiratory failure
what is a heart rate over 100 bpm called
tachycardia
what is the term for a heart rate below 60bpm
bradycardia
what can a white skin color indicate
vasoconstriction, blood loss, shock, heart attack, fright, anemia, fainting, emotional distress
what can pale cool and clammy skin indicate?
inadequate oxygenation, hypoxia, hypoxemia
what does a blue skin tone mean
inadeqyate oxygenation/perfusion/ inadequate respiration, suffocation, hypoxia, hypoxemia, heart attack, or poisoning
what does a red skin color mean
heat exposure, peripheral vasodilation, carbon monoxide poisoning
what does a yellow skin color indicate
liver disease
what does a geay skin color indicate
shock patients/ blood poolingwhat
what could a longer capillary refill time indicate
shock
what could a <90% SpO2 reading indicate
hypoxia
What are the Different levels of consciousness from least concerning to most
alert
verbal stimulus
painful stimulus
how would you apply a central painful stimulus
trapezius pinch or sternal rub
how would you apply a peripheral painful stimulus
thumb, index finger pinch
what does perla stand for
pupils equal, responsive to light, accomodating
what can dilated pupils be a symptom of
cardiac arrest
drug use (LSD, amphetamines, cocaine
what could constricted pupils be a symptom of
CNS disorder
narcotics
what could unequal pupils be a symptom of
stroke, head injury, brain trauma
what could nonreactive pupils be a symptom of
cardiac arrest, brain injury, drug overdose
what does the markle test assess
abdominal pain
stand on ballf of foot, drop onto heels
what is the babinski reflex
firmly stroking the plantar surface of foot
what is a positive markle?
if they grimace in pain
what is a positive babinski
if toes fan out
what is a normal babinski response
negative for adults
positive for infants
what can a positive babinski be a symptom of (for an adult)
cns disorders
what coulda. pronator arm drift be a symptom of
stroke
what questions would u ask to assess an individuals pain
who: do they have pain (acute/chronic)
what: how bad is it (1-10)
where: location of the pain
when: when did it start
why: what were they doing
how: characteristics/qualities, does anything make it worse/better
how would you calculate minute ventillation
tidal volume x breaths ina minute
what is the average minute ventilation for an adult
500ml * 12/min = 6000ml/min
what is alveolar ventilation
amount of air moved in and out of alveoli in a minute
how would you calculate alveolar ventilation
(TV-Dead Space) * Breaths in 1 min
what has a greater effect on inspiration: tidal volume or breath rate?
tidal volume, breathing rate short term but, respiratory muscles are weak
what is the range of borg rating of perceived exertion (RPE) scale
6-20
what are the average values in adults at rest for
respiration
heart rate
blood pressure
RPE
Respiration: 12-20 breaths/min
heart rate: 60-100 beats/min
blood pressure: systolic 120 mmHg/80mmHg
RPE: 6