Honors Biology: Genetics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Genetics
The study of genes and how they function.
Gergor Mendel
The father of modern genetics
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
Chromosome
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
Locus
The location of genes on a chromosome
Allele
Different forms of a gene
Dominate Allele
An allele that will be observed if one or both gene copies are this version.
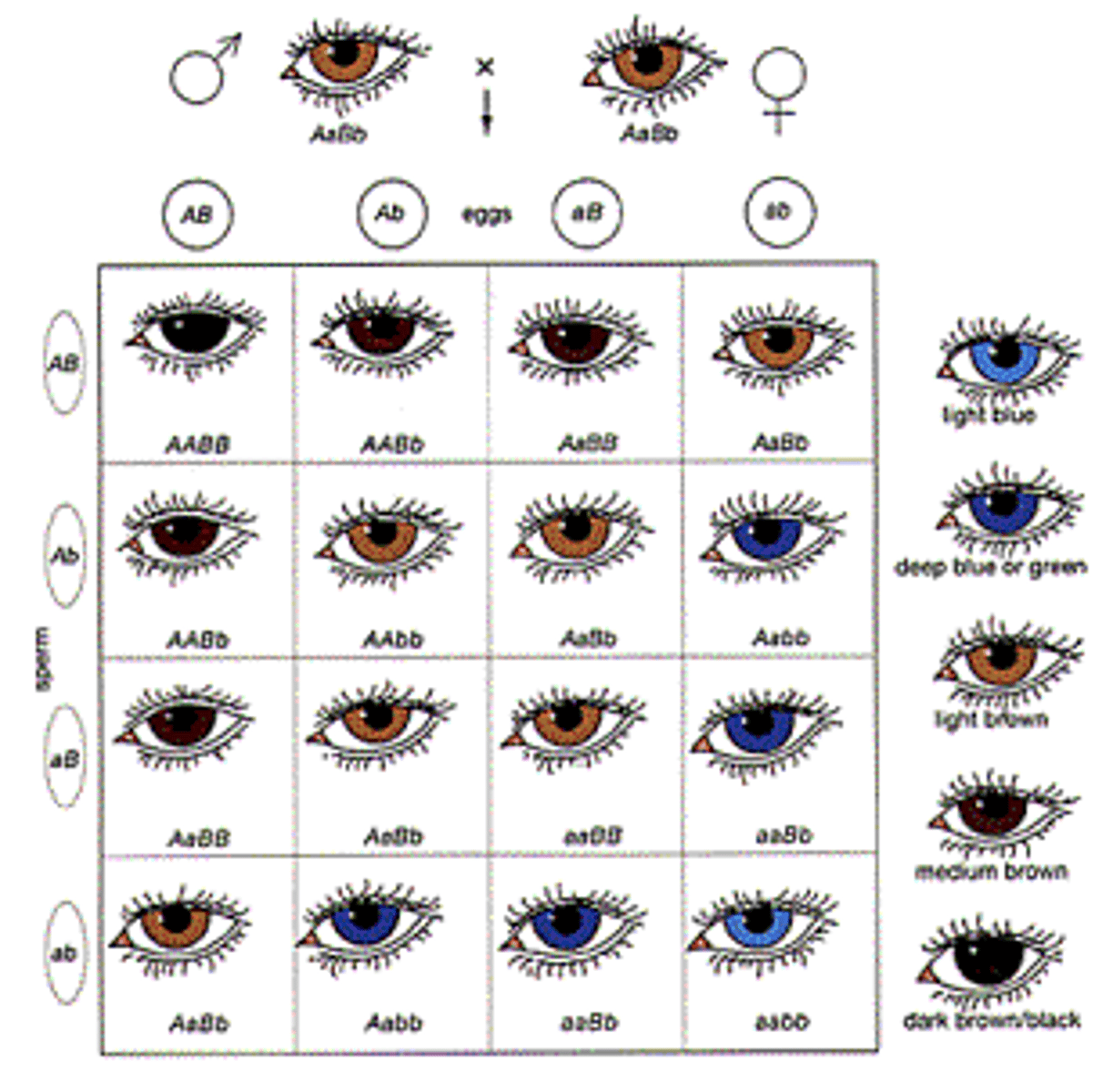
Recessive Allele
An allele that will be observed only if both gene copies are this form
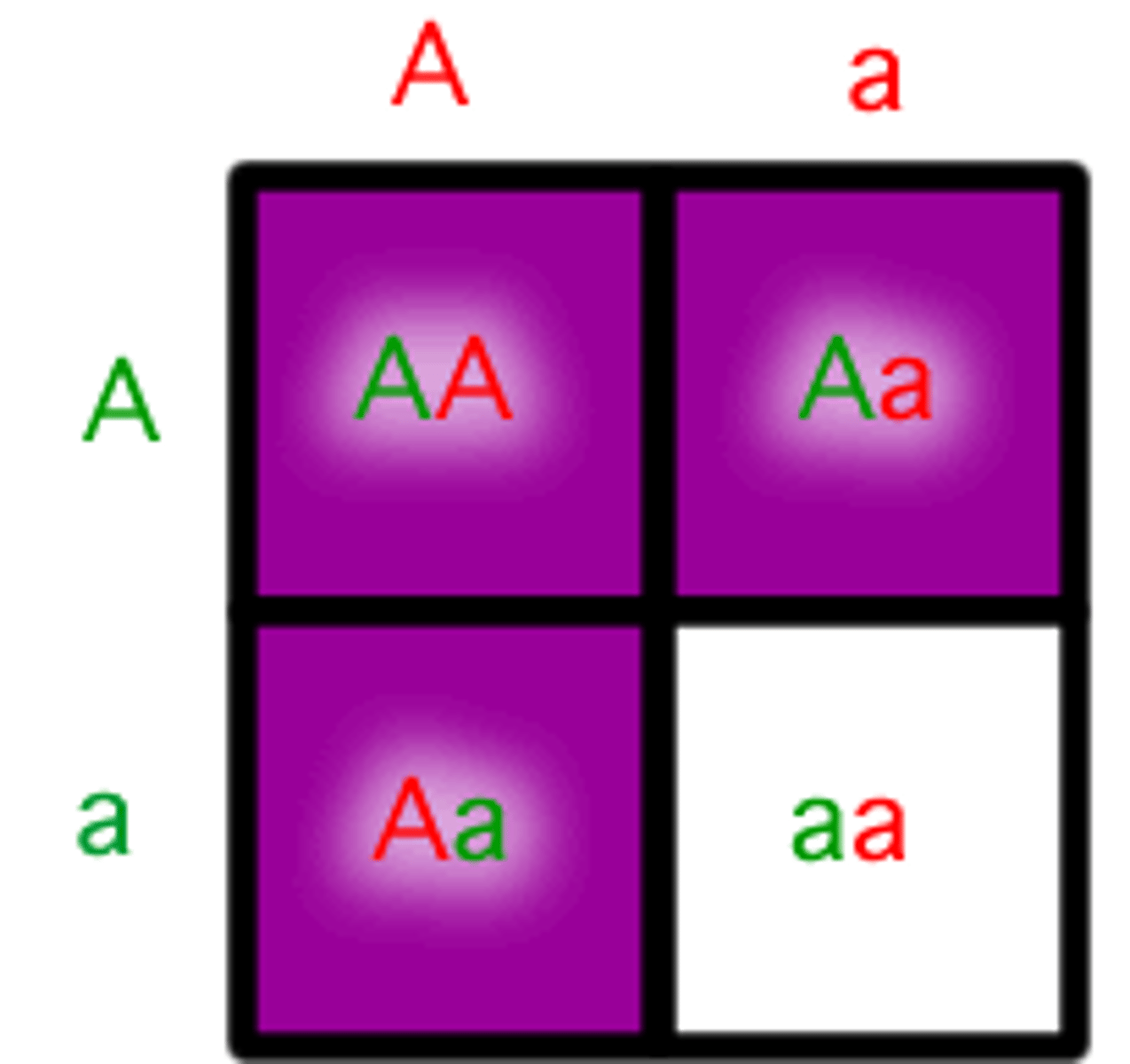
Homozygous Genotype
Both alleles are the same (AKA a hybrid)

Genotype
An allele inherited from the egg cell and the allele inherited from the sperm cell for a particluar gene
Homozygous dominant genotypes
Two alles that are the same and are both dominate
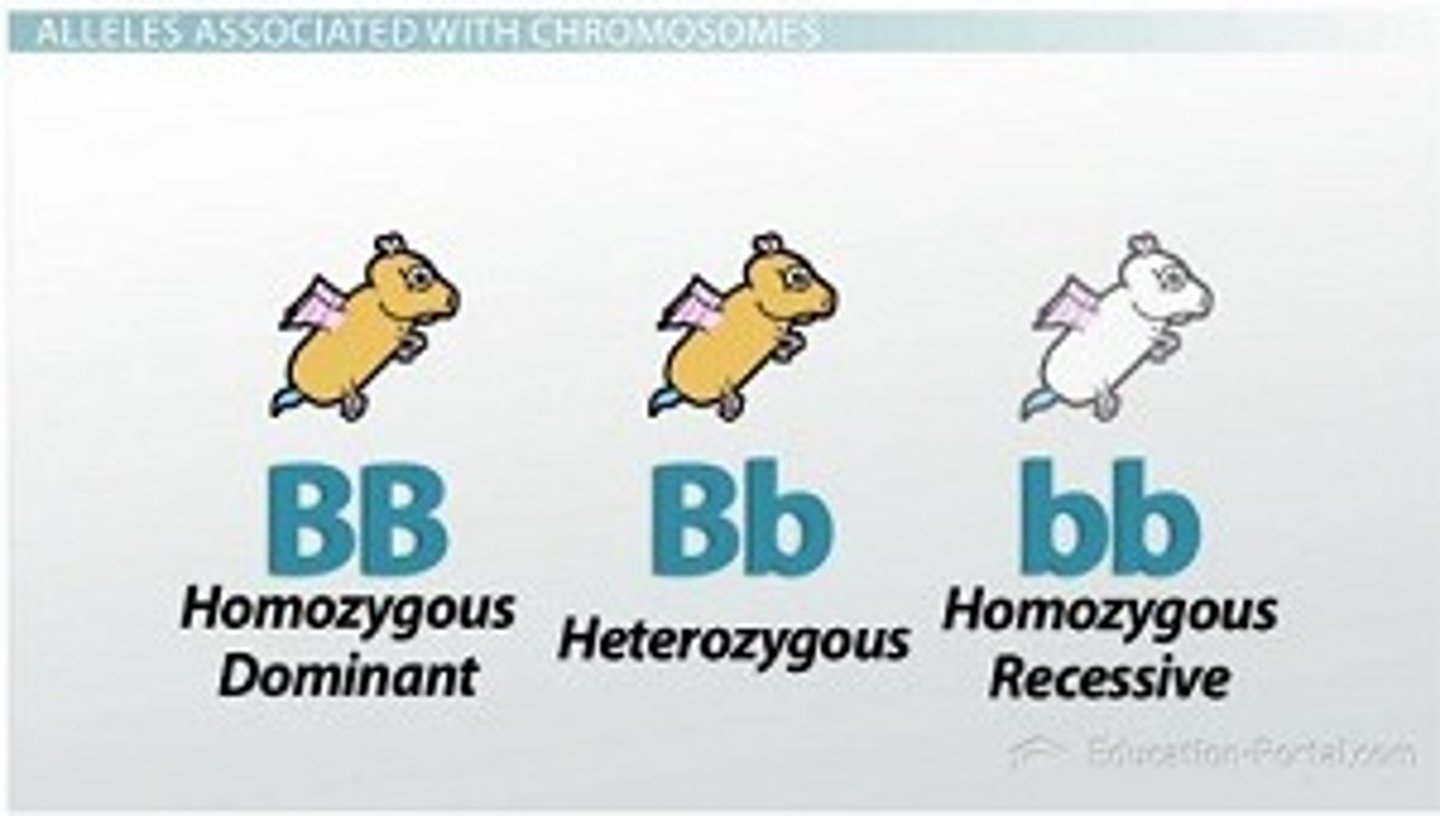
Homozygous recessive genotypes
Two alles that are the same and are both recessive
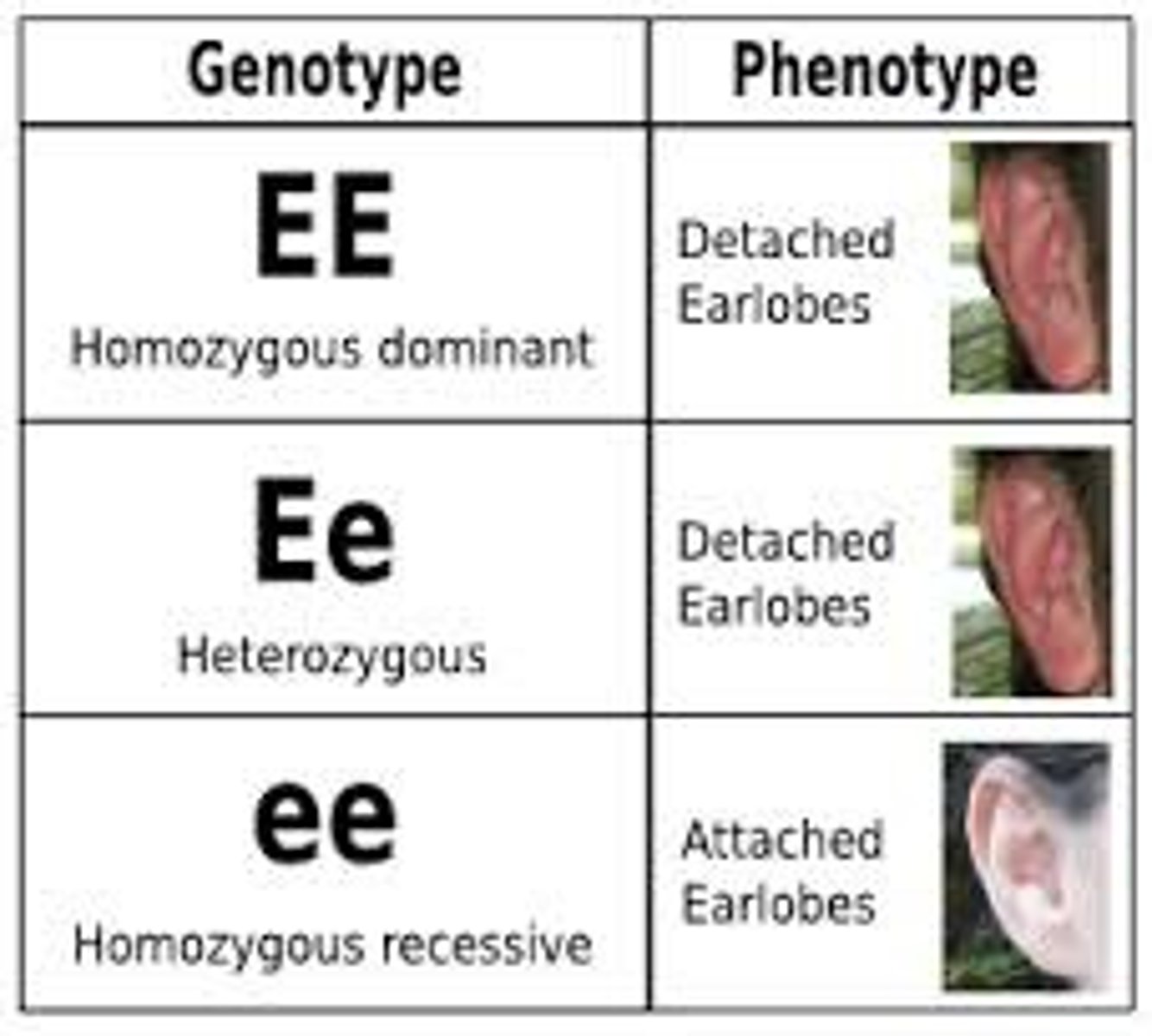
Heterozygous Genotype
A genotype with two different alleles

Phenotype
The appearance of a measurable trait resulting from the genotype of a particular gene
Punnett Sqaure
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
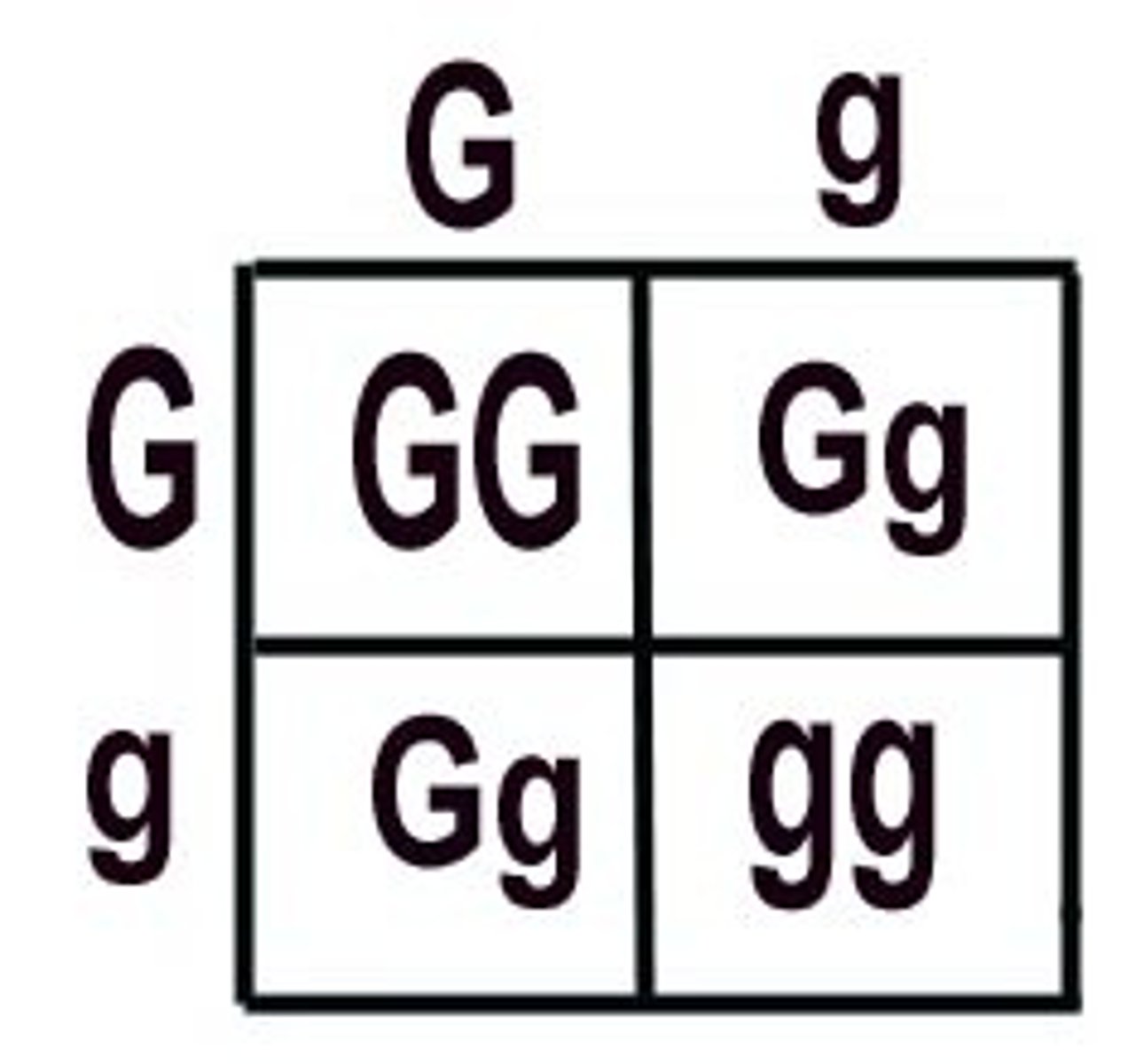
Mendel's Law of Segregation
The two copies of a gene segregate from each other during transmission from parent to offspring
Diploid Cells
Cells that have pairs of chromosomes
Haploid Cells
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes.
Medel's Law of Independent Assortment
Each pair of factors segregates independently of the other pairs
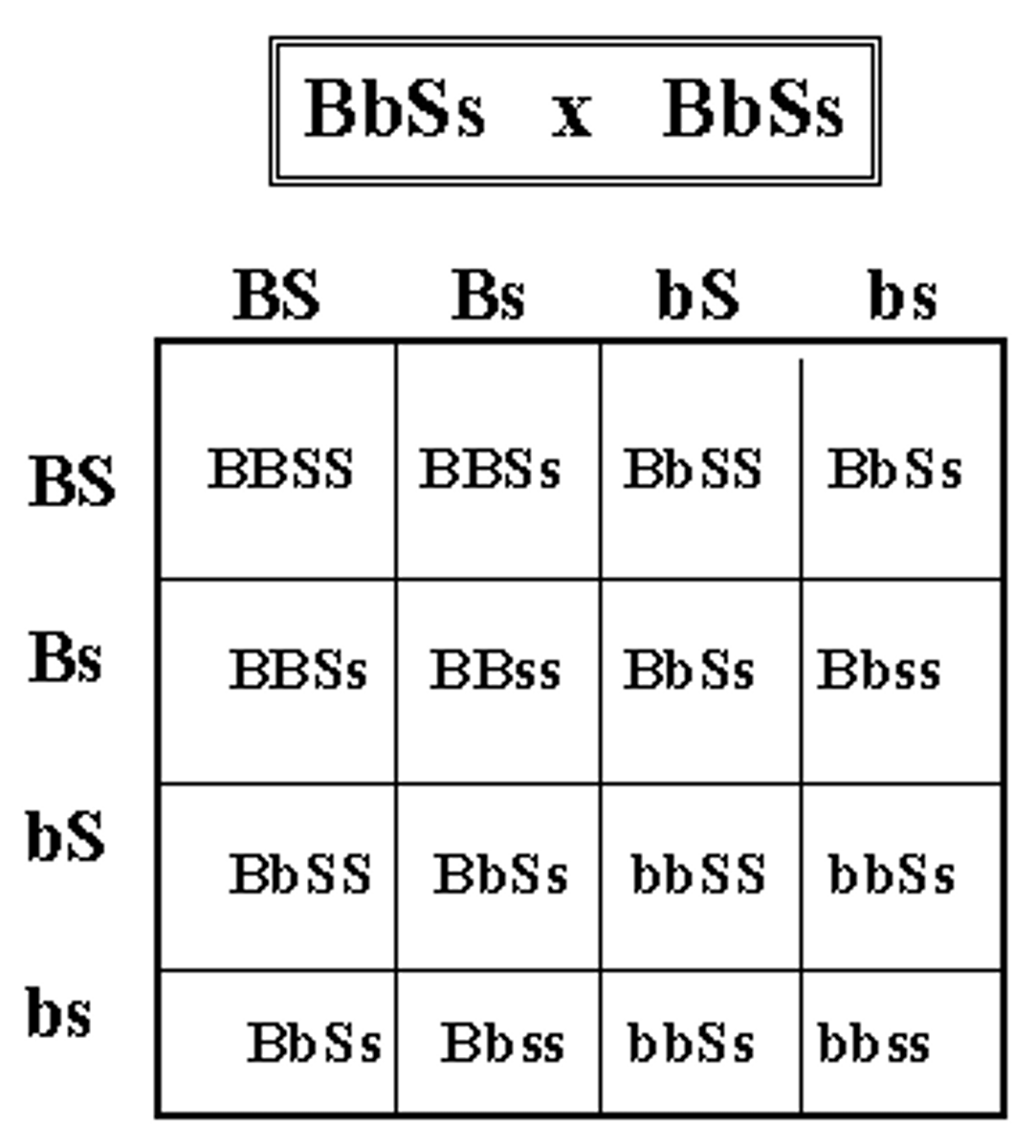
Dihybrid Cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
Autosomal Traits
Traits influenced by a gene found on any of the autosomes
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome (1-22)
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes.
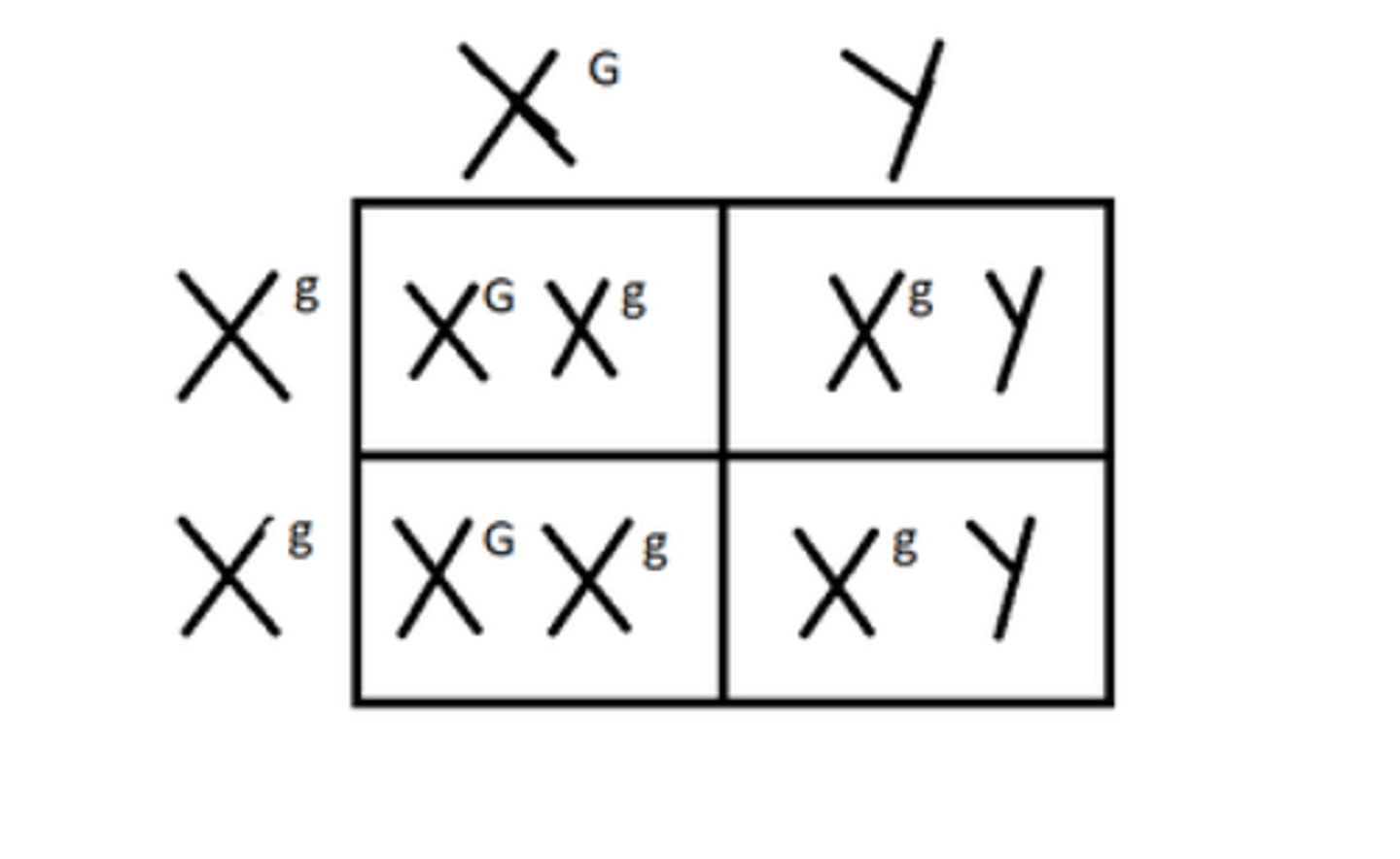
X-linked
A gene located on the X chromosome
y-Linked
A gene located on the Y chromosome
Incomplete Dominance
The situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
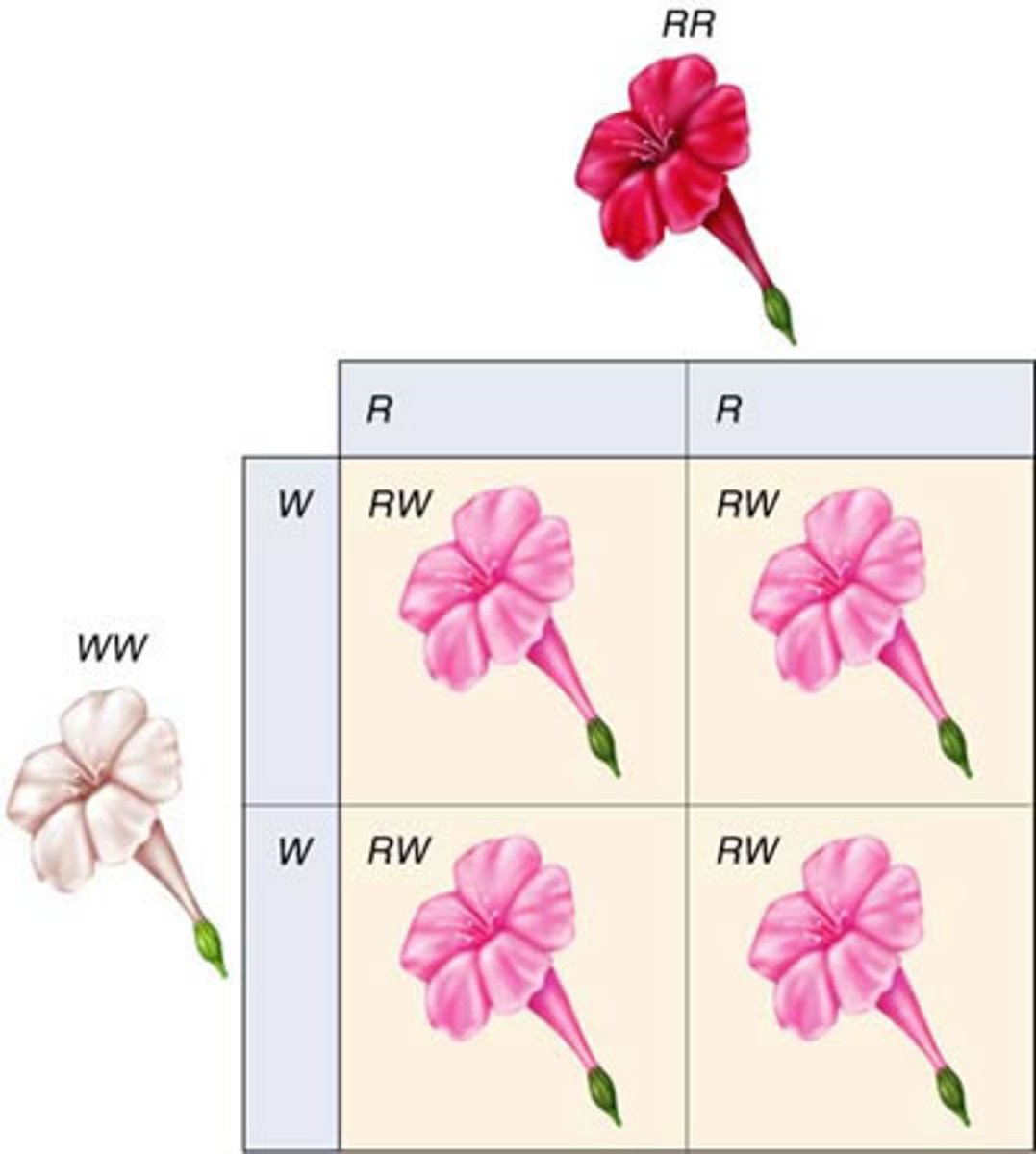
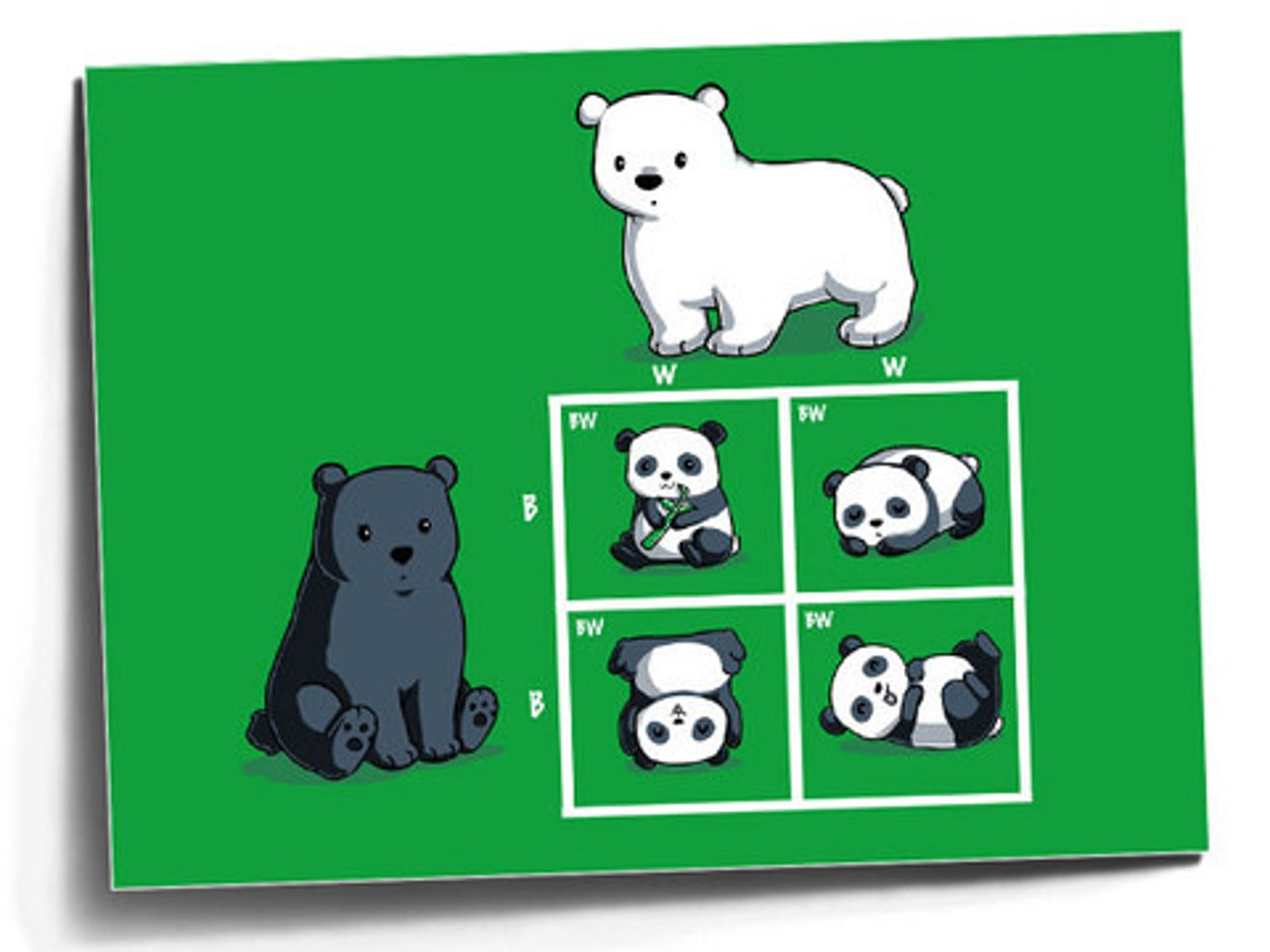
Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive.
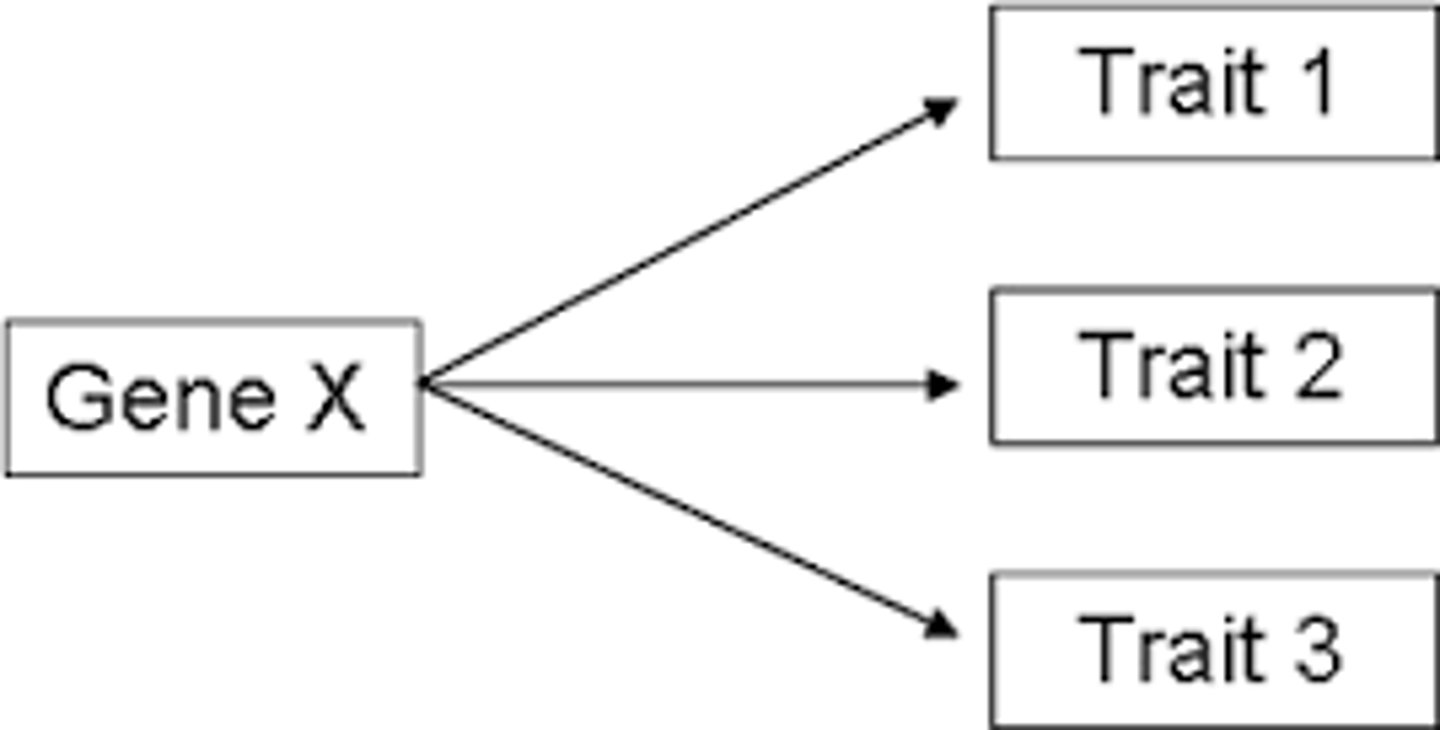
Pleiotropy
The ability of a single gene to have multiple effects.
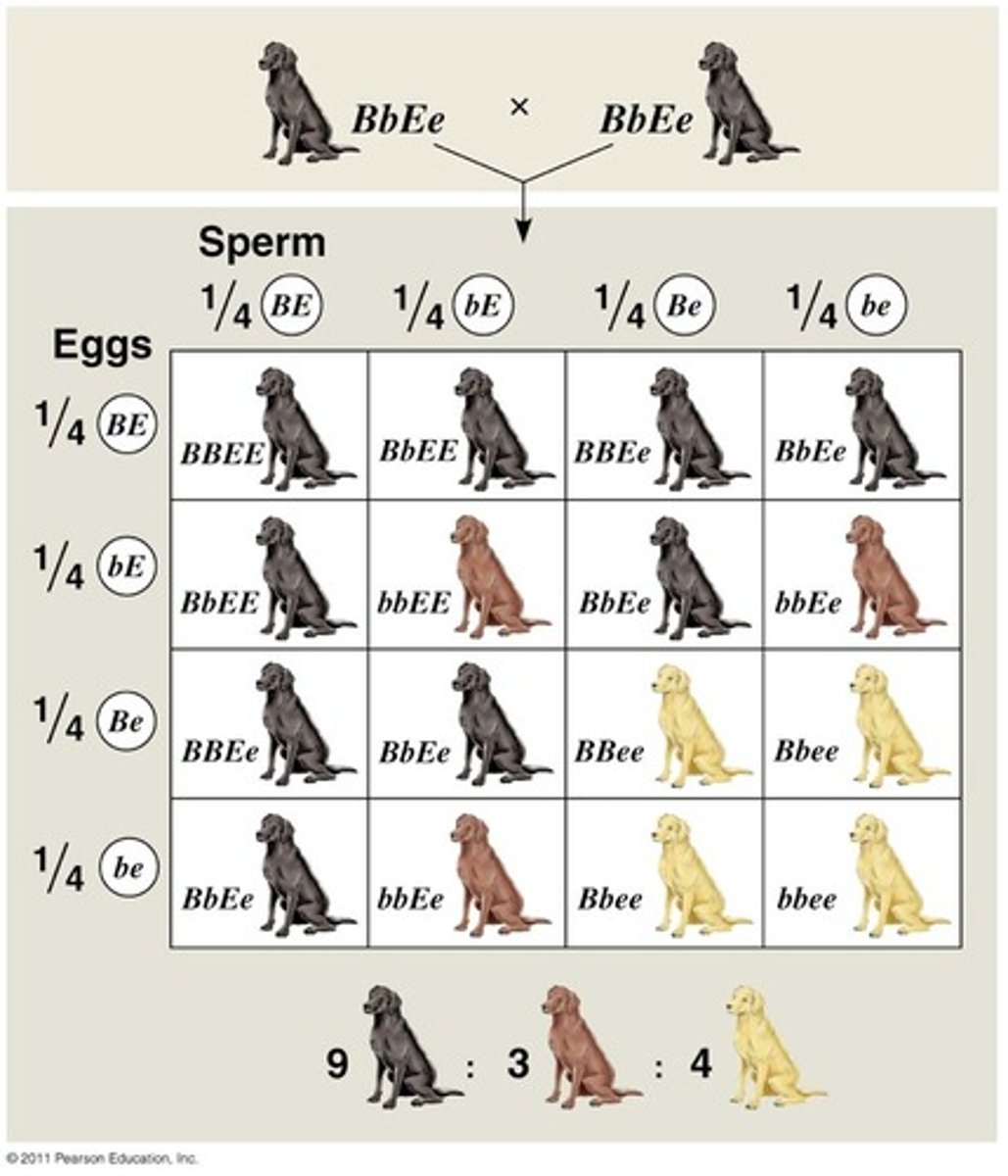
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
Polygenic Trait
A trait controlled by two or more genes