CS330 Midterm
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
Information
Data which has been turned into a meaningful and useful form
Data
Raw facts before being turned into meaningful information
Information System
Set of interrelated components that collect or retrieve, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making in an organization
What are the three dimensions of information systems?
Information Technology (IT), Organizations, Management
Understanding all the dimensions of information systems is referred to as what?
Information systems literacy
Define Information Technology
All the hardware, software, data management technologies, networking, etc. needed to achieve business objectives
Management needs to…
Needs to make informed decisions to design and deliver new products and services
What is Management Information Systems (MIS)
A field where the goal is to develop broader information systems literacy. It encompasses both technical and behavioural issues within an organization surrounding the development, use, and impact of information systems.
What is a bit?
Binary digit; smallest unit of data in a computer system. With n bits, you have 2^n possible values. Binary - can only have one of two values (0 or 1)
What is a byte?
1 byte = 8 bits; this is enough information to specify one English letter. There are 2^8 = 256 possible values from 00000000 to 11111111.
In measurements like KB, Mb, Gb, GB: B represents bytes, b represents bits.
Order of magnitude when measuring data?
KMGT - KB MB GB TB - 1024 bytes, 1024², 1024³, 1024^4 bytes respectively.
What are the eight basic hardware components?
1) Processor
2) Main Memory
3) Secondary Storage
4) Input Devices
5) Output Devices
6) Communication Devices
Processors are also known as _____
Central Processing Units (CPU)
What are processors?
Where symbols, characters, and numbers are manipulated. This part of the computer does computation and only executes very simple instructions such as:
Arithmetic and logic: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and/or/not
Inequalities/comparisons: greater than, less than, equals, does not equal
Accessing data: loading and storing from RAM
Flow control: implement function calls, for loops, while loops, etc.
Known as the “brains” of the computer
What is the program counter’s (PC) function?
Stores the address of the current or next instruction; first step of CPU
What is the instruction register’s (IR) function?
Stores the instruction that is being (or is about to be) executed.
What is the control unit’s function?
Read the instruction from the instruction register and turn other components on/off to execute the instruction.
What is the function of the arithmetic logic unit (ALU)?
Performs arithmetic and logic operations, based on commands given by the control unit.
What is the function of other (non-specified) registers?
Small, temporary, fast storage. Data comes from or gets stored here before/after being processed by the ALU.
What is the function of cache?
Store recently used data and instructions for quick access.
What are the three typical levels of cache?
L1 - 32KB, L2 - 256KB, L3 - 2MB
Moving from L1 to L3, as storage gets larger, cache gets slower and usage decreases
Most frequently used data and instructions would be in L1, then L2, etc.
What is the function of Random Access Memory (RAM)?
Stores data that you are actively using (like open files or programs); data can be read in any order
What does the word size of a processor measure?
How many bits it can transfer or manipulate in parallel (32 bit or 64 bit)
Programs optimized for a 64-bit architecture would be faster since it can handle more data at once.
64-bit architectures can still handle programs that were created for 32-bit architectures.
What is backwards compatability?
When the new version of one component is designed to work with remaining old components (think of new game consoles that can play games from older models)
What are cores?
Each one acts like a separate processor, but may share resources with each other (cache, ram).
Common multicore processors are duo-core and quad-core, which can execute 2 or 4 instructions simultaneously, respectively.
What is clock speed?
How quickly the CPU can retrieve and interpret instructions.
MHz: 1 million clock ticks per second
GHz: 1 billion clock ticks per second
Used as a way of reporting performance
How is data stored?
Computers have multiple storage devices.
In the CPU, there are registers, caches, and RAM.
Together, these make up main memory.
What is main memory?
Where data and program instructions are stored TEMPORARILY during processing.
ie. parts of a software program being executed, data the program is using, etc.
It is faster, expensive, and volatile: contents disappear when there is no power.
What is main memory composed of?
Registers, caches, RAM
What is Static RAM (SRAM)?
Expensive but faster
Flip-flop circuits to manage state (0 or 1), making them “static”
Used for registers and caches
What is Dynamic RAM (DRAM)?
Cheaper but slower
Capacitors store electric charge or not (1 or 0) and need to be recharged periodically, making them “dynamic”
Used for RAM
What are the types of memory, from fastest to slowest?
Registers, caches, ram, SSD, hard drive
What is Secondary Storage?
Where programs or files are stored when not being used.
It is typically a hard drive (HDD) or solid state drive (SSD), but can also include other flash drives (SD, USB) and other optical drives (CD, DVD, Blu-Ray).
It is slower and cheaper than main memory.
It is non-volatile: contents do NOT disappear when there is no power.
Data is copied into main memory so the processor can access it.
What are the components of a hard drive?
Platters, actuator arms, read/write heads
What are platters/what do they do?
One component of a hard drive;
They are discs with thin, magnetic coating on both sides. Hard drives will usually have one or more of these stacked on top of each other.
Actuator arms will move across the platter disc to position read/write heads.
RPM: rotations per minute; represents how quickly the platters spin
What do read/write heads do?
Writing: Change the orientation of the magnetic field to write 0s or 1s, represented as magnetic North or South on the platter.
Reading: to write data, it will return to the same spots and read the magnetic pole to read back data as bits.
What is the mean time between failures (MTBF)?
Also referred to as MTTF; the average time a system/component will work before it fails.
Failure Rate Time graph has a U shape - more likely to fail right at the beginning of lifetime (due to manufacturer error), or at the end of lifetime (due to components wearing out).
Given the AFR → MTBF = 8766/AFR
What is the Annualized Failure Rate (AFR)?
The probability that a system/component will fail during a full year.
How can you approximate the AFR?
100% x (8766/MTBF)
What are Solid State Drives (SSD)?
An alternative to a hard disk; uses electronic circuits to read/write data
What are the pros of solid state drives?
Around 10x faster than HDDs
Last longer
No moving parts that can wear out
What are the cons of solid state drives?
More expensive
Data can fade over time if not connected to power
Limited number of “writes” (endurance)
can wear out sooner if you are frequently writing a lot of data
How is endurance of an SSD measured?
One of two ways: DW/D (drive writes per day) or TBW (terabytes written)
What are Hybrid Drives?
Combine smaller SSDs with larger HDDs
Move common files from the HDD to the SSD for speed.
What are Optical Drives?
Similar to a hard drive (spinning disk), but uses a laser and a mirror
Laser will create “pits” on the aluminum surface, which scatters light, to represent a 1
Slower and have less capacity than a hard drive, but are cheap and durable.
ie. CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray
What do Input Devices do?
Convert data and instructions from the outside world into an electronic form that a computer can understand
Keyboards, cameras, microphones, touch screens, laptop touchpads, etc.
What do Output Devices do?
Coverts electronic data produced by the computer into a form that humans and the outside world can understand.
Display monitors
Audio from devices
Printers
What do Communication Devices do?
Enables connections between the computer and communications networks.
What are mainframe speciality computers?
High performance computers that are optimized for simple but simultaneous data processing on a MASSIVE scale.
Processing bank or credit card transactions, airline reservations.
Centralized system, controlled by operators either directly or via terminals.
Designed to be very reliable with redundant parts.
Achieved through hot swapping
Were very expensive in the 1950s; owned only by the largest corporations (like banks and insurance companies)

What is Hot Swapping?
Replacing a part while the computer is still running and processing (no need to shut down)
What is a super computer?
Fastest computer in the world.
Mainly used for fast, floating point calculations
ie. for simulations, weather forecasting, artificial intelligence, and other scientific computations.
What is a Microcontroller?
Very simple processors, RAM and input/output (I/O) capabilities, very cheap.
Used in embedded systems.
Examples: home appliances, robots, cars
What are embedded systems?
Systems that have a very specific function within a larger system
What are the five primary eras of IT Infrastructure since the 1950s?
1) Mainframe and minicomputer
2) Personal computer
3) Client/Server
4) Enterprise computing
5) Cloud and mobile computing
What are minicomputers (1950s)?
Introduced after mainframe computer as cheaper, smaller, but powerful computers.
Made decentralization possible; could be customized to suit specific needs of individual departments or companies.
A large university could have several minicomputers shared by many people.
What are personal computers? When were they introduced?
Computers used by one person, introduced in the 1980s.
Very expensive initially (around $4000 with inflation adjustment), but became cheaper with time.
Users were technically sophisticated.
Windows OS Intel processor (Wintel), IBM 1981, was commonly used in businesses.
What was the interface progression of the personal computer?
Initially started with text-based user interfaces, then evolved to graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that used a mouse.
Mouse became commercialized in the late 70s/early 80s, but were invented prior.
Personal productivity software was launched.
What happened when operating systems improved?
Enabled personal computers to be connected to each other through networks (client-server relationship introduced; 1980s)
What are client computers and what do they do?
Typically inexpensive computers that will request and use services provided by servers.
What are server computers and what do they do?
Typically more expensive computers that will run an application and provide it to others over a network.
ie. google search, streaming.
sometimes we use the term “server” to refer to software like a “server application”
Why was the emergence of the client/server relationship important?
Important for increased redundancy, reduced latency, and load balancing.
large companies could have millions of servers placed around the world
What is the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) client-server relationship?
Every machine consumes and provides services at the same time,
Decentralized; each device acts as a client and a server at the same time
Torrenting is a good example of P2P
What is Enterprise Computing? When did it emerge?
Emerged in the 1990s.
In this, applications and networks may be disparate.
Achieves integration; linking together different networks and applications.
Does this by creating standards for data and using software to translate between different formats
Connected through internet protocols (IP)
What is Cloud Computing? When did it emerge?
Emerged in the 2000s.
Similar to client-server, but instead of having a server, clients can consume a shared pool of resources.
Clusters of computers, software, storage.
Enabled by the growing bandwidth of the Internet.
Several business models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
What is mobile computing and when did it emerge?
Emerged in the 2000s; refers to the use of portable computing devices (ie. smartphones) to access or process information
Internet access can happen anywhere
These devices are taking over the function of many others
What are the Five Drivers of Technology that have driven the evolution of IT Infrastructure?
1) Moore’s Law
2) The Law of Mass Digital Storage
3) Metcalfe’s Law
4) Declining Communications Costs
5) The Creation of Technology Standards
What are Transistors?
Considered one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century; an electrical component that acts as a building block to make computer chips.
Can amplify or switch electronic current and power.
What is Moore’s Law (1956)?
The number of transistors that can fit on a chip doubles every 2 years.
Means that processing and computing power doubles every two years
Consequently, price of computing halves every two years.
Moore’s Law should be considered as a trend, not a law.
The trend held up since 1956, but the rate slowed down significantly around 2010 due to limitations of technology.
What is the Law of Mass Digital Storage?
The amount of digital information is roughly doubling every year.
Storage capacity is growing exponentially (roughly 65% per year).
The amount of data that can be stored per dollar doubles every 15 months.
Consequently, cost of storing a gigabyte is cut by half every 15 months.
What is Metcalfe’s Law?
The financial value of a network grows exponentially as more members are added.
ie. consider owning a cellphone or fax machine - this is useless if you are the only one who owns it.
What are the implications of Declining Communication Costs?
There is an increased reliance on communication costs to conduct business.
What are technology standards?
Specifications that establish the compatibility of technology and products.
They act as a common language for interoperability, consistency, and increased quality.
Having technology standards enables competition and reduces costs.
What is the significance of the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) standard?
Enabled computers made by different manufacturers to represent alphabets in a consistent way.
What is the significance of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) standard?
Consistent communication between different devices over a network.
What is the significance of the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) standard?
Consistent structure of web content that is displayed using a web browser.
What are the seven components of typical IT infrastructure?
1) Computer Hardware Platforms
2) Operating System (OS) Platforms
3) Enterprise Applications
4) Data Management and Storage
5) Network and Telecom Platforms
6) Internet Platforms
7) Service Platforms
What are Server Farms?
A type of computer hardware platform; collections of hundreds of thousands of rack or blade servers stored in racks in large, windowless, temperature-controlled rooms.
Optimized to take up the least amount of space.
What are Operating Systems (OS)?
Manage hardware and software resources like the processor, memory, peripheral devices, files, applications, etc.
Popular OS are Windows (for laptops and desktops), Android (for smartphones and tablets), and Linux (for servers)
What are Enterprise Applications?
Computer programs that integrate business applications and services across many different departments.
The largest suppliers of enterprise software are SAP, Oracle, IBM, and Microsoft.
What is a Database Management System (DBSM)?
Organizes and stores company data. You may need a database server if you want it to be accessed by multiple machines or through the internet.
What are tape drives?
A method of data storage that used to be common because of its portability.
Works similarly to an HDD: magnetic film coating along the tape and read/write system that relies on magnetizing or interpreting magnetic poles as 0s or 1s.
Uses sequential access (not random access), so it is slower.
What is Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)?
Can be used to improve hard drive performance; involves using multiple drives together to achieve improvements in reliability, availability, performance, and capacity.
there are many ways to do this, and each achieves a different balance of the aforementioned categories.
7 official levels: 0 to 6
What is RAID 0?
Disk Stripping; with this method, there is a tradeoff between performance and reliability.
Performance is improved since we can read data more simultaneously.
Reliability is decreased since if one HDD fails, all files become corrupted.
This method is not really used for important data.
RAID 0 and RAID 1 can be combined.
What is RAID 1?
Disk Mirroring; stores the same data on multiple disks. Improved reliability and read performance, but capacity is decreased.
Reliability is improved because if one drive fails, it can use the copy stored on another drive.
Read performance is improved because if one drive is busy, it can read from another.
Uses more space to store a single file, so capacity is decreased.
RAID 0 and RAID 1 can be combined.
What is a parity bit?
A single bit added to the end of a binary string;
What is even parity?
An error detecting technique.
Maintaining an even number of 1s; add a 0 or 1 to achieve this.
ie. if we have 1001, we would add a 0 to maintain the even number of ones → 10010
ie. if we have 1011, we would add a 1 to obtain an even number of ones → 10111
If even parity is being used and the server receives data correctly, the resulting binary strings will have an even number of 1s. I
If even parity is being used and the server does not receive data correctly, the string that was incorrectly received would have an odd number of 1s.
Even parity has limitations; if two bits change, the error would be undetected for example.
What is odd parity?
An error detecting technique.
Maintaining an odd number of ones, otherwise similar to even parity.
What is data backup? What are the two ways?
Making a copy of data so it can be used if data is lost and needs to be restored.
Two ways: online (also called hot backup) and offline,
What is an online (or hot) backup?
Done instantly and in real-time
Protects against a failing hard drive
What is an offline backup?
Done at the end of the day; copy and transfer the data to another location
Cloud or tape
Full vs. Incremental
Protect against a complete failure but only from the day before.
What is a network?
A group of computers linked together to share data or resources.
Can be achieved using different components:
hubs
bridges
switches
modems
routers
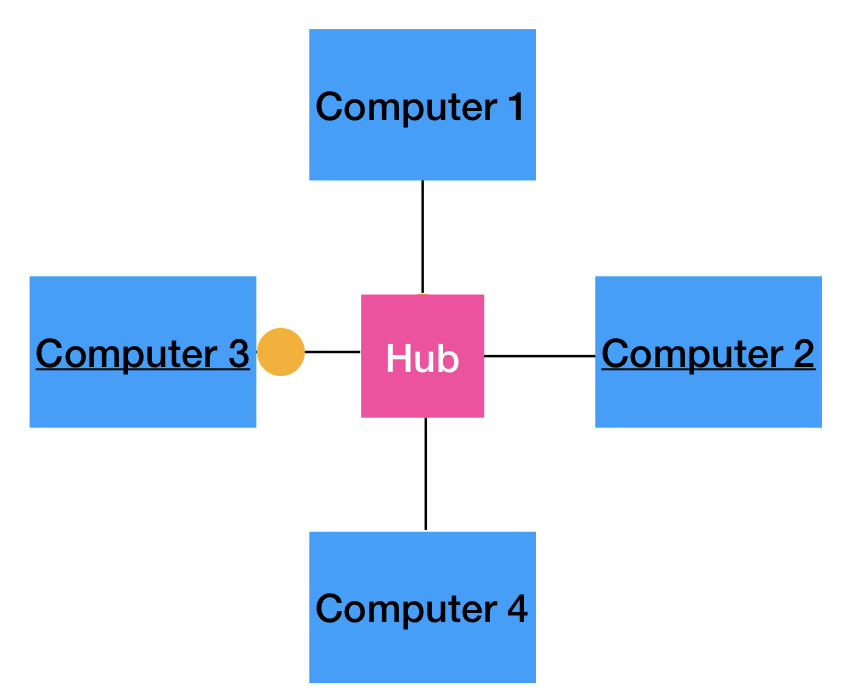
How does a hub work?
Any received data is sent to all connected devices.
Suppose a message is being sent from computer 3 to computer 2. The message would go through the hub and be sent to computers 1, 2, and 4.
This is inefficient and can cause security issues.
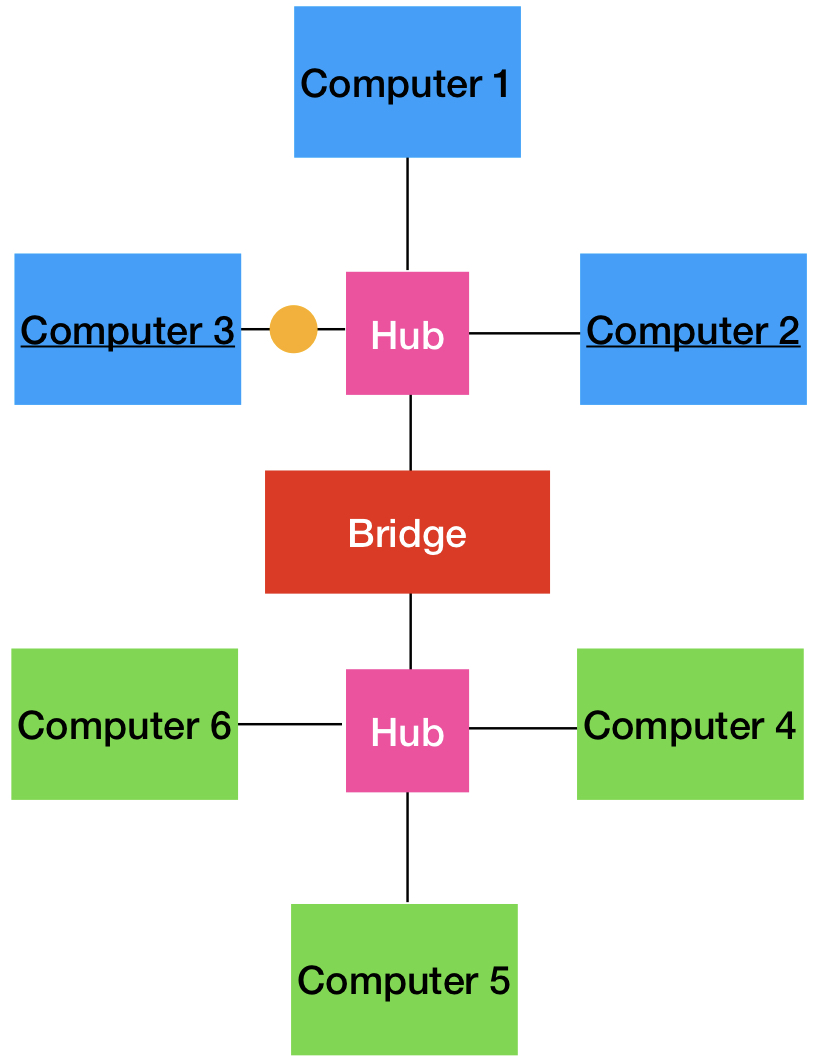
What is a bridge?
They split the network into two segments and receiving data can only cross if it is intended for a device on the other side.
If we want to send something from computer 3 to computer 2, the data will not cross the bridge because the bridge knows that computer 2 is still on the blue side.
The information would be received by computers 1, 2, and 3.
If we want to send something from computer 3 to computer 5, the data will cross the bridge because the bridge knows computer 5 is on the other side.
the information would be received by all of the computers on the network (1, 2, 4, 5, 6)
Bridges are nice to reduce network traffic, but they only connect two segments so they are not widely used.
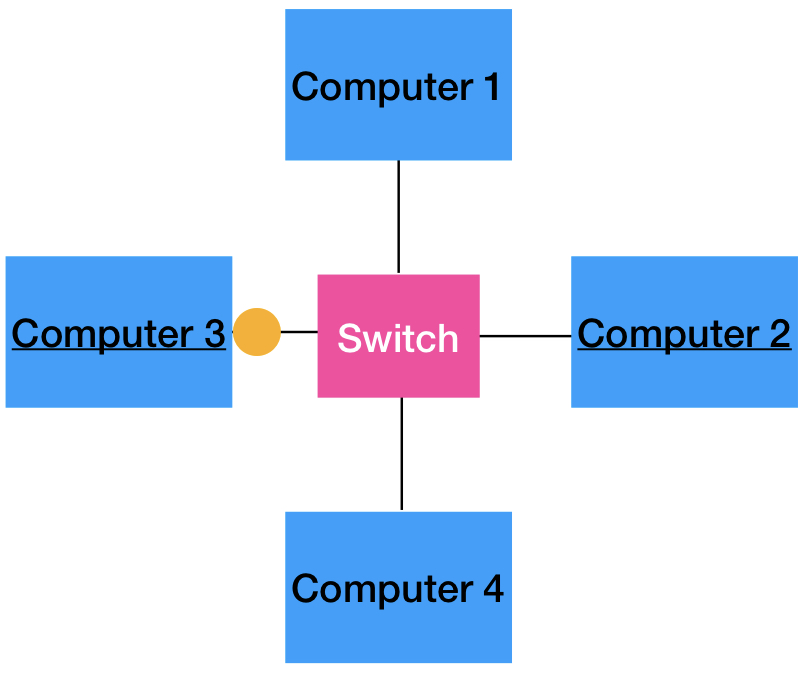
What are switches?
These combine properties of both hubs and bridges - they can send data only to the intended recipient.
They act like hubs in that all devices are connected to it, but also act like bridges because it knows whether data should be passed through to other devices.
If a message is being sent from computer 3 to computer 2, the switch will be able to send the data directly to computer 2 and the other computers will NOT receive it, unlike the other methods.
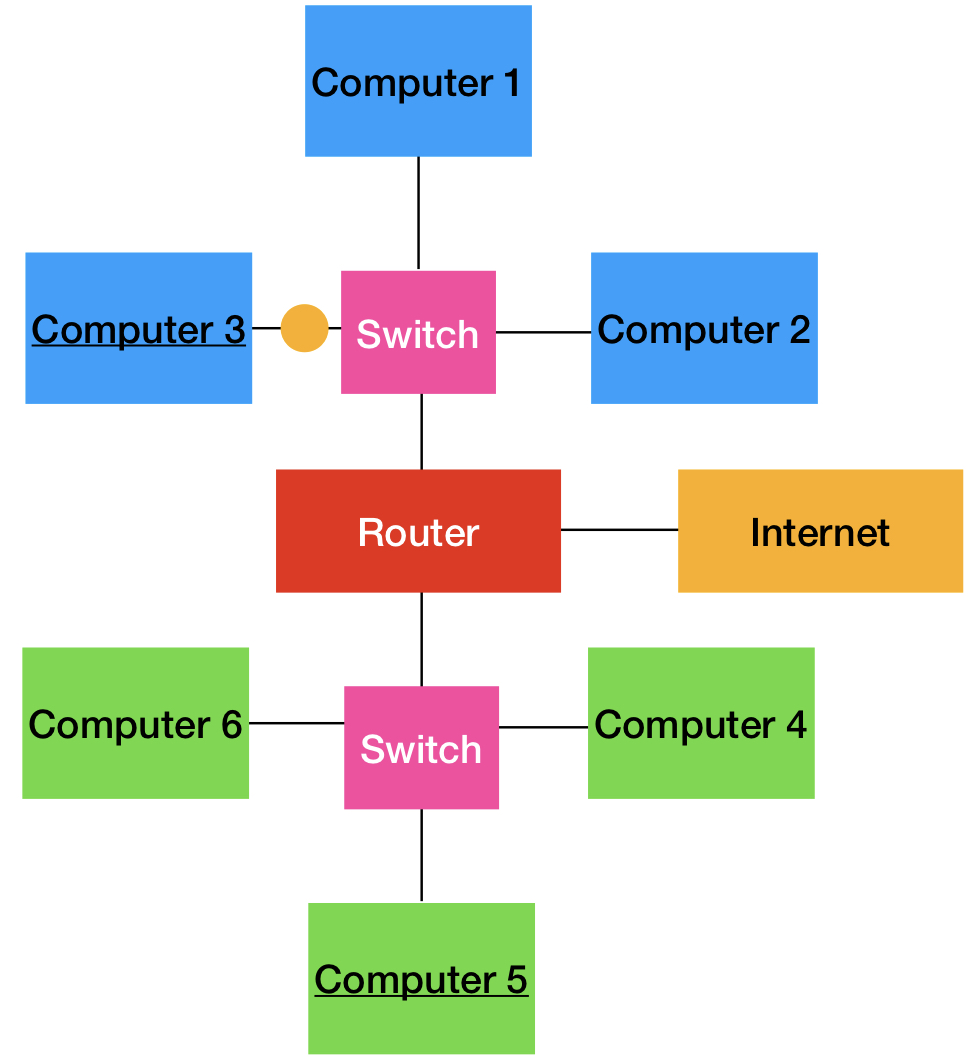
What is the difference between hubs-bridges-switches and routers?
Unlike hubs, bridges, and switches which connect computers within a single network, routers connect between multiple networks (and the Internet).
What are routers?
They connect multiple networks and the internet. If we want to send something from computer 3 to computer 5, the router will redirect to the right network.
For a home network, the switches will be contained within the router.
For work networks, you would have separate switches.
What is a MODEM?
MOdulator-DEModulator.
These convert data from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) into a format that your computer can understand.
What is a firewall?
Hardware or software between the internal network and the Internet to prevent outsiders from obtaining unauthorized access to your network.
the firewall will use a set of rules to evaluate whether the traffic is allowed or not
What is a network interfacing card?
Computers have network interfacing cards; ethernet, wifi, bluetooth .
Allows the computer to be connected to the network
What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
These provides the link from your home or company network to the rest of the internet.
ie. Rogers, Bell, Shaw
Smaller ISPs lease the network from these larger ISPs and have their own customer service, tech support, etc.