MGT173 midterm
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
style d
the driver, solution than problem, getting things done
style I
expressive, social, customer service
style s
steadiness, supportive, harmony, therapist
style c
analytical; compliance, cautious, conscientiousness
4 essential elements for cultivating trust
competence, connection, communication, honesty
competence
get the job done, effective decision making
being careless and unreliable is the easiest way to lose trust
honesty
answer later with full picture, open conversation about how realistic
promise too much and trust is broken
connection
see them as individuals and spend time understanding them
basics of empathy
communication
communicate clearly and effectively
what makes situations challenging?
there is a lot at stake
there are opposing ideas
there are strong emotions from one or both sides
4 strategies for preparing for challenging convos
build self-awareness: most challenging, reflect on past, current and future projects, objective as you can on this part
prepare for the conversation: think through how differently the conversation could go
seek first to understand then to be understood: open and curious attitude
respond rather than react: breathe and slow down
primary stakeholder
people or groups that stand to be directly affected by an effort of an institution
may hurt one but benefit another
particular population, residents, people experiencing problem in an organization
secondary stakeholder
people or groups that are indirectly affected by an effort or the actions of an institution
parents, spouse, of the people, social workers, health and human services, community volunteers
police, emergency room personnel, teachers, landlords, contractors, employers
key stakeholders
those who can have a positive or negative impact on an effort or who are important within or to an institution
when to identify stakeholders and interests
involve stakeholders in a participatory process, should be apart of every phase of the work; allows for transparency
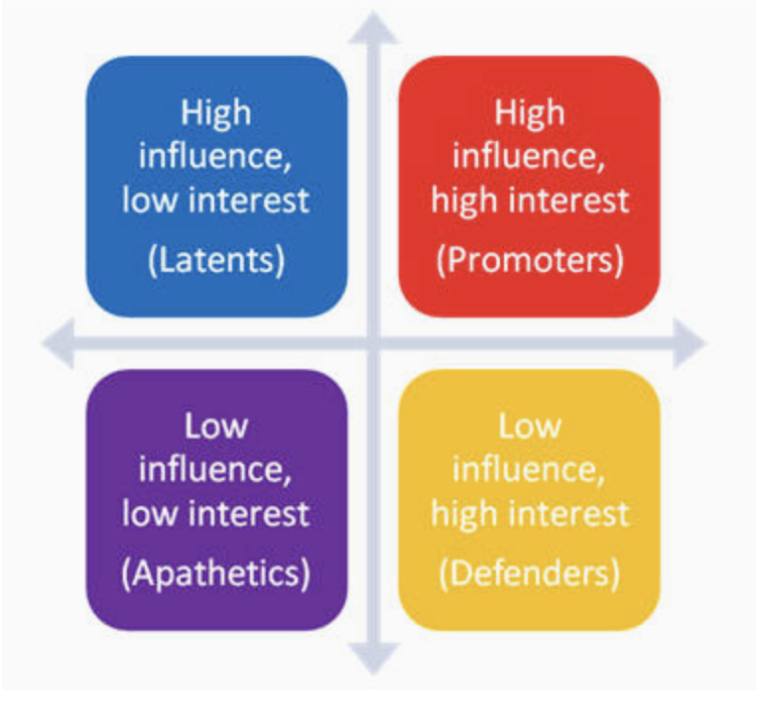
promoters
high influence, high interest; have both great interest in the effort and the power to help make it successful
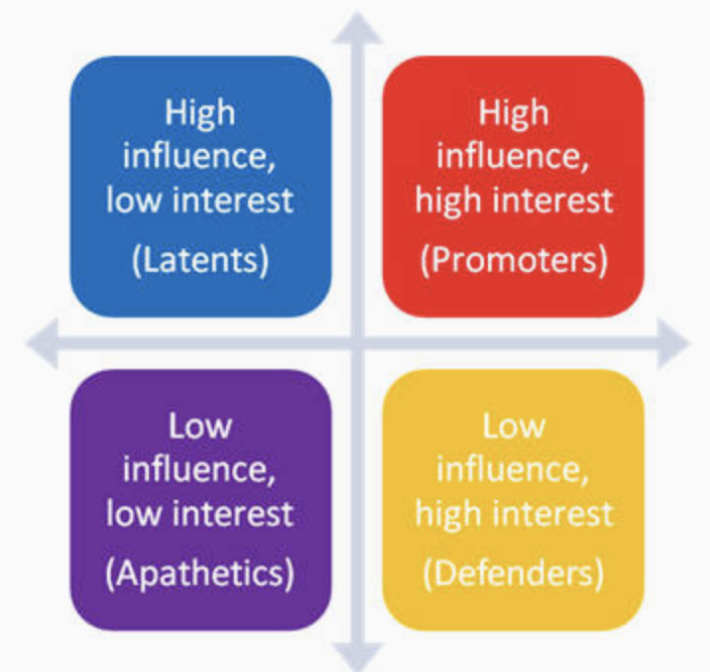
defenders
have vested interest and can voice their support in the community but have little actual power to influence the effort in any way; low influence high interest
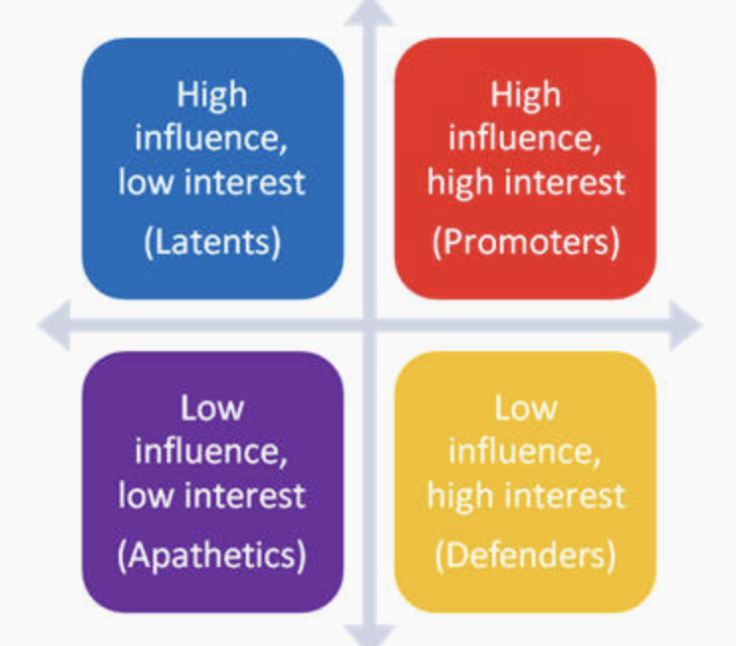
latents
no particular interest or involvement in the effort but have the power to influence it greatly if they become interested; high influence, low interest
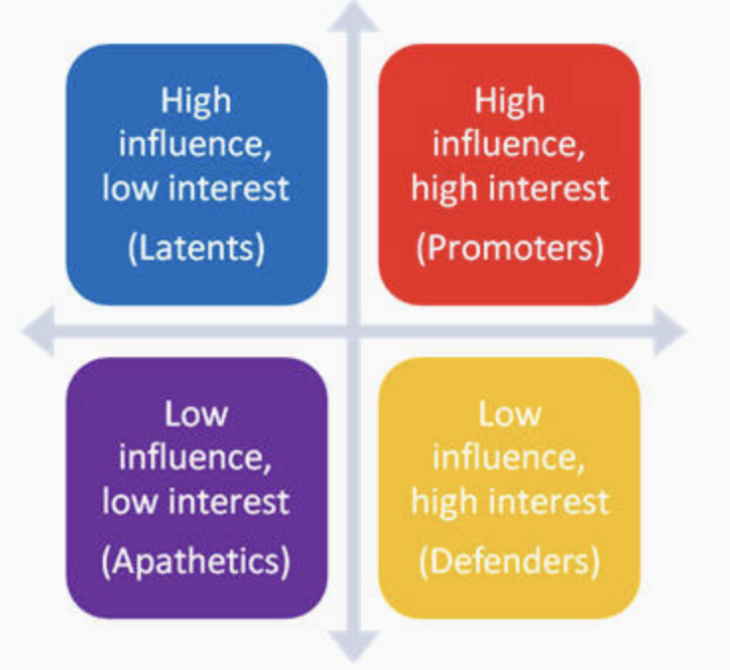
apathetics
little interest and little power, may not even know the effort exists
the 5 typologies
felt needed, expressed need, normative need, comparative need, latent or unmet need
felt needed
what people experience as need
pregnant women may feel the need for more information on childbirth and potential complications
expressed need
an actual request for services or programs - a felt need expressed in the form of demand for services (people seeking the service) or through community action
the need for a place to exercise in a local community may be expressed as a demand for excersie classes, long waiting lists etc
normative need
expert or professional views on what is needed, determined on the basis of research, professional opinion, value judgements or established standards
the advisable levels of flouride in water or the daily recs allowances of nutrients in food
comparative need
level of need is inferred by benchmarking against the volume of services or programs in comparable settings
by comparing access to supportive care and education for patients with diabetes in different geographic locations
latent or unmet need
usually seen as a gap between known levels of need and actual take-up or avaliablity of services or programs
the difference between the number diagnosed diabetes in a region and the number who access care, the gap between demand for emergency admissions and the capacity of local hospitals
VMOSA
vision, mission, objectives, strategies and action plans; practival planning process used to help community groups define a vision and develop practical ways to enact change
vision should be….
understood and shared by members of the community
broad enough to encompass a variety of local perspectives
inspiring and uplifting to everyone involved of local perspectives
easy to communicate (tshirt saying)
mission…
concise: one sentence
outcome-oriented: overarching outcomes
inclusive: broad
objectives…
behavioral objectives: look at changing behaviors of people and the products
EX: neighborhood improvement increased amount of home repair taking place
community-level outcome objectives: community level instead of individual level
process objectives: refer to the implementation of activities necessary to achieve other objectives
strategies
explain how the initiative will reach its objectives
the five types of strategies
providing information and enhancing skills
enhancing services and support
modify access, barriers, and opportunities
change the consequences of efforts
modify policies
action plan
describes in great detail exactly how strategies will be implemented to accomplish the objectives developed earlier in this process
plan refers to a) specific changes to be cought b) specific action steps necessary to bring about changes in all of the revelant sectors or parts of the community
what the plan includes
action steps: what will happen
persons responsible: who will do what
date to be completed: timing of each action step
resources required: resources and support
barriers or resistance and a plan to overcome them
collaborators: who else should know about this action
objectives
specific measurable results of the intiative
types of objectives
process objectives: provide the groundwork necessary to achieve your other objectives
behavioral objectives: changing the behaviors of people and the products of their behaviors
community-level outcome objectives: the product or result of behavior change in many people
SMART + C
specific, measurable, achieveable, relevant, timed, challenging
logic model
presents a picture of how your effort or initiative is supposed to work
logic model needs
purpose or mission what needs to change
contact or conditions
inputs or resources or infrastructure
activities or interventions
outputs
in VMOSA the vision and mission statements should be engthy and detailed to ensure comprehensive understanding
flase
evidence-based public health interventions can be indentified through consensus of opinion among informed experts
true
why is action plan an important component of VMOSA
it outlines how strategies will be implemented to achieve objectives
what signifies the effectiveness of an evidence-based public health intervention
documentation in reputable sources of information
what are the 3 basic types of objectives in VMOSA
behavoiral, community level outcome, process
project management
systematic approach to planning, executing and closing projects, ensuring aligh=nment with organizational goals and objectives
iron triangle
model highlighting three constraints of project management: scope, time and cost
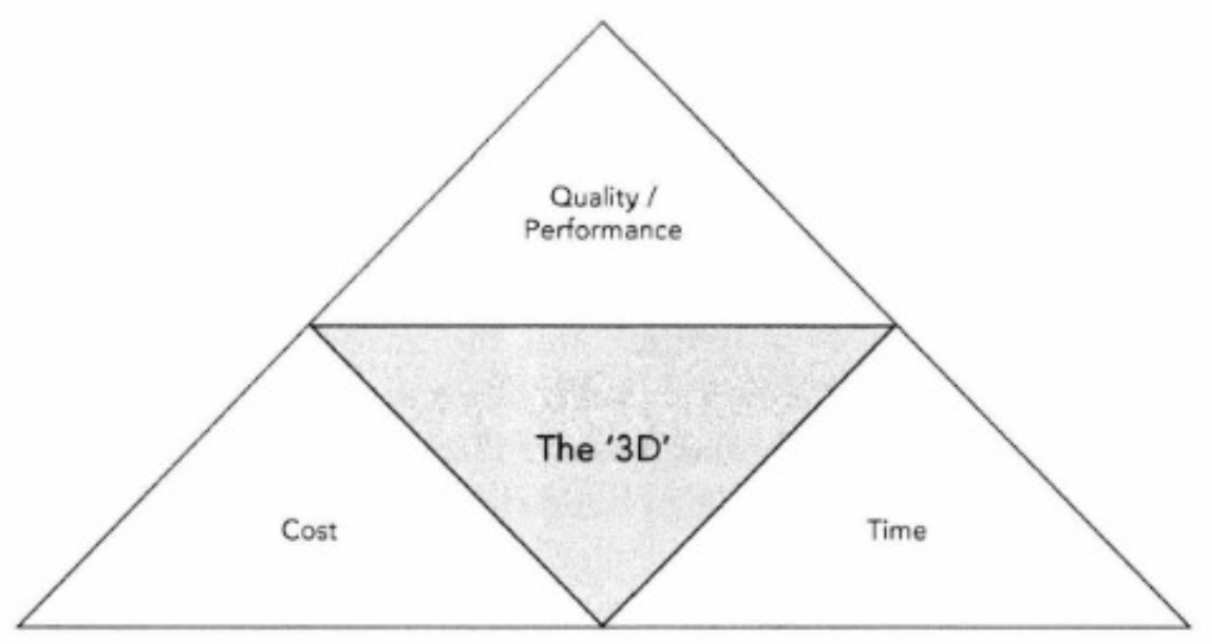
program vs. project
programs are more ongoing and aim to provide long-term benefit, projects have specific start and end dates and achieve a particular objective
project life cycle
4-phase proces of initiating, planning, executing and closing a project
significance of project management in health
understanding the unique challeneges, requirements and importance of effective management in the health sector
social determinants of health
conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age influencing health risks and outcomes. understanding its ink to health service program development ensures more targeted and effective service delivery
delieverable
any unique and verifiable product
unique characteristics of projects
each project is novel, require the involvement of many fields, complex, managing dynamic situation
project managers
critical role in monitoring progress, identifying problems or variations, modifying the plan and taking action accoridingly
health project management methods
development of new servces
to improve existing services
implementation of new organizational structures
conduct of procurement process
construction of new equipment and facilities
to conduct research projects
project success is defined from 3 perspectives
project sponsor
project managers
key stakeholders
critical sucess factors
project mission
top management support
project planning
client consultation
people management
techinical tasks
client accpetance
monitoring and feeback
communication
trouble shooting
4 phases of project life cycle
inittate: concept and start up
plan: definition, scope, plan, and budget
implement: kickoff, track and control, pratcical completion
close
value proposition
positioning statement that explains what benefit you provide for who and how you di it unqiuely well
comprehensive position assessment
business/servive/product mix
access
price/cost
quality
customer experience
customer segementation
groups individuals into segments on the basis of their needs and how those needs are expressed or acted on
organizational structure
division of the business as whole into departments or units
organizational deisgn
encompasses the process, roles, and formal reporting relationships of the business
functional departmentalization
subdivides work and workers into separate units reposibvle for business
sales, HR
functional departmentalization advantages
allows work to be done by highly qualiffied specialists
lowers cost and expenses by reducing duplication
functional departmentalization disadvanatges
cross department coordination is complicated
slower and less effective deicision making
produce workers and managers with narrow expertise
product departmentalization
divides and organizes work and workers into separate units responsible for particular products or services
product departmentalization advantage
specialization of skills and expertise
easy for managers to assess workers and work-unit performance
more effective and efficient
product departmentalization disadvantage
duplication
difficult to coordinate and communicate across departments
geographic departmentalization
divides and organizes work and workers into separate units responsible for certain geographic areas
geographic departmentalization advantage
respond to the needs of different markets
geographic departmentalization disadvantage
duplication
difficulty in establishing effective communication and coordination
customer departmentalization
divides and organizes work and workers into separate units responsible for certain kinds of customers
customer departmentalization advantage
focuses on the needs of the customer
customer departmentalization disadvantage
duplication of resources
difficult to establish effective communication across departments
unbalanced decision making
matrix departmentalization
hybrid structure, combines two or more forms of departmentalization
matrix departmentalization attributes
most employees report to 2 bosses
more cross functional interaction
significant amounts of communication and coordination are typical
matrix departmentalization advantage
allows companies to gather employees from different functional areas with varying expertise and experience to manage large complex projects
ability to executive large and complex tasks
matrix departmentalization disadvantage
consumption of time and resources
confusion and disagreements
managers must havefinely honed management skills and the ability to work within the constricts of a matrix structure
organizational authority
responsibility for certain areas of activity including the right to make decisions, take action and give directions and orders to achieve organizational objectives
delegation of authority
process of assigning direct authority and responsibility to a subordinate
delegation of authority transfers
manager must take full responsibility for the transfer of work activity
manager must transfer full authority over necessary resources
transfer of accountability
Taylors key principles of scientific management
in order for an org to improve its efficiency it would need to recognize and adopt the most effective way to perform workplace tasks
work process, techniques, and routines must be based on scientific study of the task
employees must be scientifically selected, trained and developed
employees must be provided detailed instruction and supervision on assigned workplace tasks
work should be divided between managers and employees with managers planning the work and employees performing workplace tasks
coercive leaders
demand immediate compliance; do what i tell you
coercive leaders EQ
drive to achieve, initiative, self-control
coercive leaders climate impact
negative
coercive leaders works best when
in a crisis to kick start a turnaround or with problem employees
authoritative leaders
mobilize people toward a vision ; come with me
authoritative leaders EQ
elf-confidence, empathy, change catalyst
authoritative leaders works best when / impact
changes require a nre vision or when a clear direction is needed
impact: most strongly positive
affiliative leaders
create harmony and builds emotional bonds
people come first
affiliative leaders EQ
empathy, building relationships, communication
affiliative leaders works best when / impact
health rifts in a team or to motivate people during stressful circumstances
impact: positive
democratic leaders
forge consensus through participation
what do you think
democratic leaders EQ
EQ: collaboration, team leadership, communication
democratic leaders works best when / impact
build buy-in or consensus, to get input from employees
impact: positive
pacesetting leaders
set high standards for performance
do as I do now
pacesetting leaders EQ
conscientiousness, drive to achieve ,intiiative
pacesetting leaders works best when / impact
get quick results from a highly motivated and competent team
impact: negative
coaching leaders
develop people for the future
try this
coaching leaders EQ
developing others, empathy, self-awareness
coaching leaders works best when / impact
help employee improve performance or develop long term strengths
impact: positive