UNIT 6 REVIEW HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Created in 2023 for P. Hammond's AP Human Geography course.
Last updated 4:30 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
3 Characteristics of Urban Hearths
**-agricultural surplus:** irrigation, farming improvements domestication
**-social stratification:** a permanent leadership class or urban elite
**-job specialization:** craftsmen, soldiers, officials, scribes, religious leaders
(6.1)
**-social stratification:** a permanent leadership class or urban elite
**-job specialization:** craftsmen, soldiers, officials, scribes, religious leaders
(6.1)
2
New cards
Industrial Revolution’s Impact on Cities
\-urban population growth boomed
\-transportation improved
\-increased availability of services
\-governments encouraged urbanization (6.1)
\-transportation improved
\-increased availability of services
\-governments encouraged urbanization (6.1)
3
New cards
Site
the exact location of a city on a map; the physical character of a place
EX characteristics: climate, water sources, energy sources, barriers to invasion, climate (6.1)
EX characteristics: climate, water sources, energy sources, barriers to invasion, climate (6.1)
4
New cards
Situation
the surrounding features, both man-made and natural; the location of a place relative to another place (6.1)
5
New cards
Urbanization
the process of developing towns and cities; an ongoing process that does not end when the city is formed (6.1)

6
New cards
Suburbanization
the process of people moving, usually from cities, to residential areas on the outskirts of cities; typically the suburban communities are connected to the city for jobs and services, but are often less densely populated (6.1)

7
New cards
Urban/Suburban/Rural
urban– cities with high concentrations of people
suburban– primarily residential areas near cities
rural– farms and villages with low concentrations of people (6.1)
suburban– primarily residential areas near cities
rural– farms and villages with low concentrations of people (6.1)

8
New cards
Percent Urban
statistic used to indicate the proportion of the population that lives in cities and towns compared to those that live in rural areas; typically broken down on a national scale of analysis (6.1)
9
New cards
Municipality
one way of referring to the political and legal aspect of a city (6.1)
10
New cards
Metropolitan Area
the city and adjacent cities, also referred to as the “metro” (6.1)
11
New cards
Reurbanization
when suburbanites **return** to live in the city (6.1)
12
New cards
Satellite City
when an established town near a very large city grows into a city independent of the larger one (6.1)
13
New cards
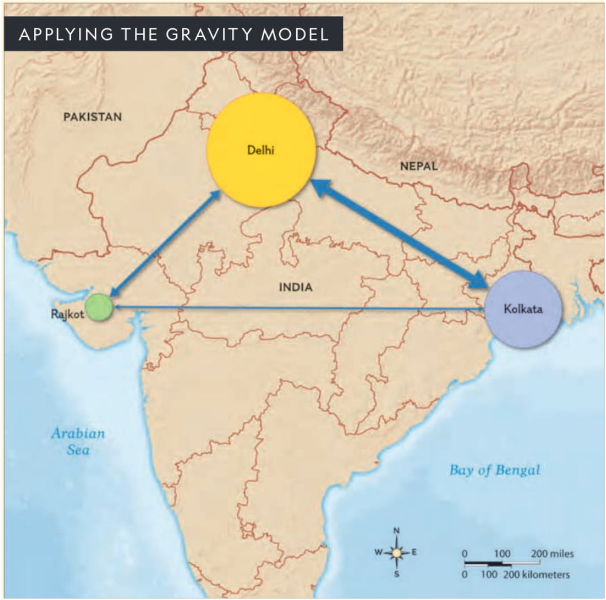
Gravity Model
places that are larger and closer will have a greater interaction than places that are smaller and farther away from each other; can be used to predict the flow of workers, shoppers, vacationers, mail, migrants, and nearly anything that flows into and between cities (6.1)
14
New cards
Rank-Size Rule
describes one way in which the size of cities in a region may develop in relation to one another
FORMULA: the **nth** largest city in any region will be **1/n** the size of the largest city (6.1)
FORMULA: the **nth** largest city in any region will be **1/n** the size of the largest city (6.1)
15
New cards
Primate City
if the largest city in a state is **more than twice** as large as the next largest city, the largest city is said to be this
EX: London, Mexico City, Asmara (6.1)
EX: London, Mexico City, Asmara (6.1)
16
New cards
Forward Capital
a symbolically relocated capital city usually because of either economic or strategic reasons, like dispersing power
EX: Washington DC, USA; Brasilia, Brazil; Abuja, Nigeria (6.1)
EX: Washington DC, USA; Brasilia, Brazil; Abuja, Nigeria (6.1)
17
New cards
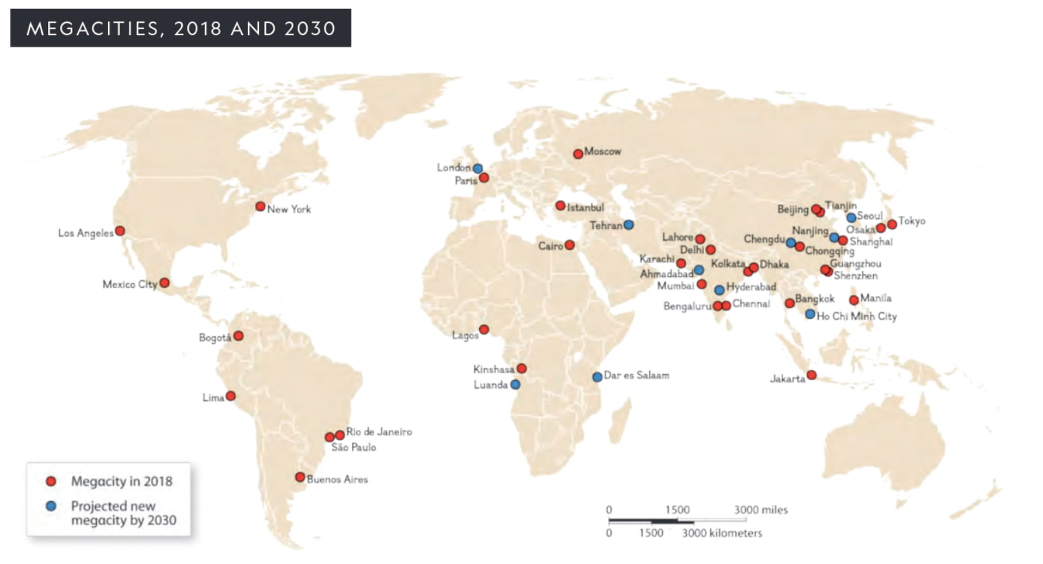
Megacities
the world’s largest cities whose population exceeds 10 million
examples on map (6.1)
examples on map (6.1)
18
New cards
Metacities
describes groups of large cities that merge and have a total population exceeding 20 million residents
EX: the Bos-Wash Corridor (east coast of US); Tokyo-Yokohama; Coastal California; Jing-Jin-Ji (Beijing, Tianjin, HeBei) (6.1)
EX: the Bos-Wash Corridor (east coast of US); Tokyo-Yokohama; Coastal California; Jing-Jin-Ji (Beijing, Tianjin, HeBei) (6.1)
19
New cards
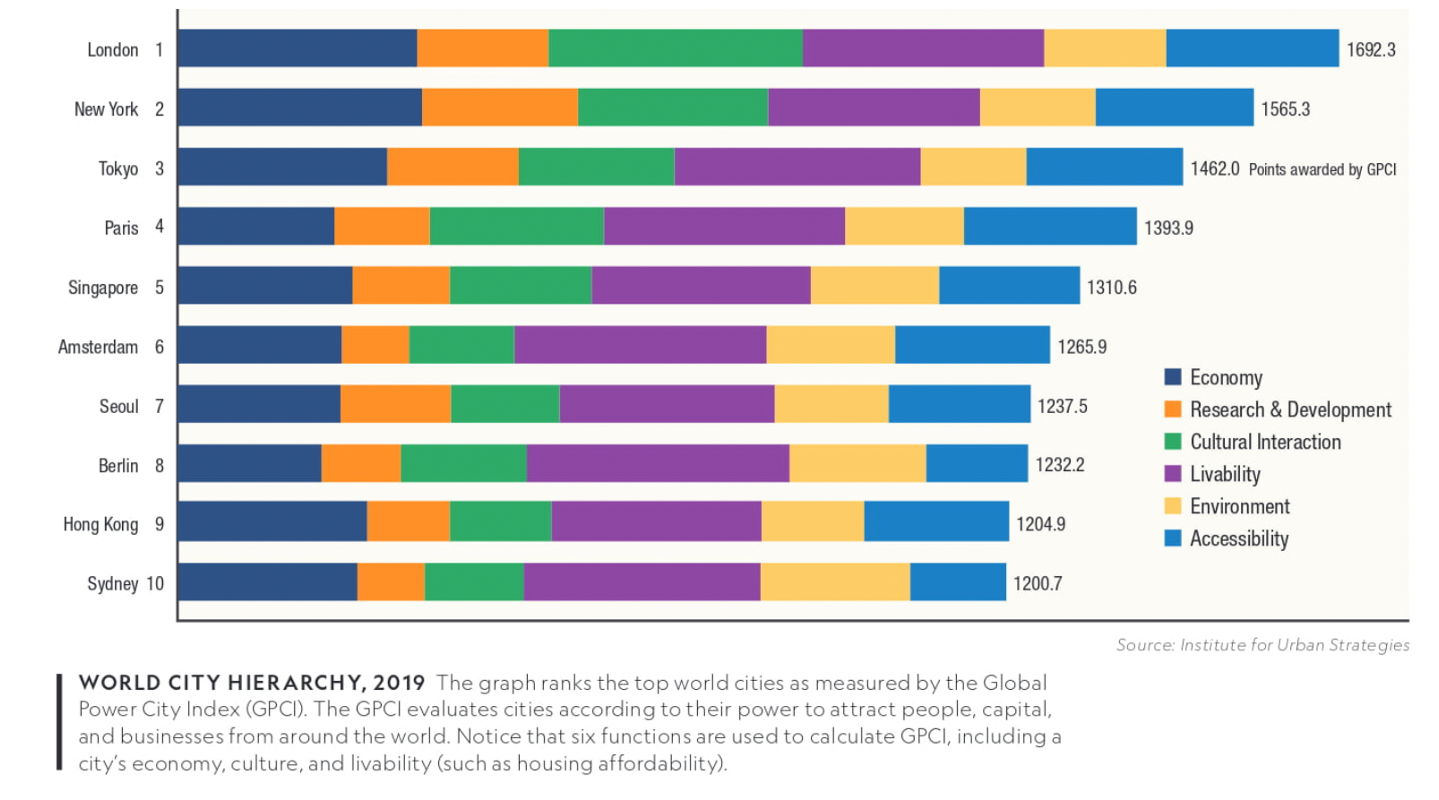
World Cities
cities that exert influence far beyond their national boundaries
examples on chart (6.1)
examples on chart (6.1)
20
New cards
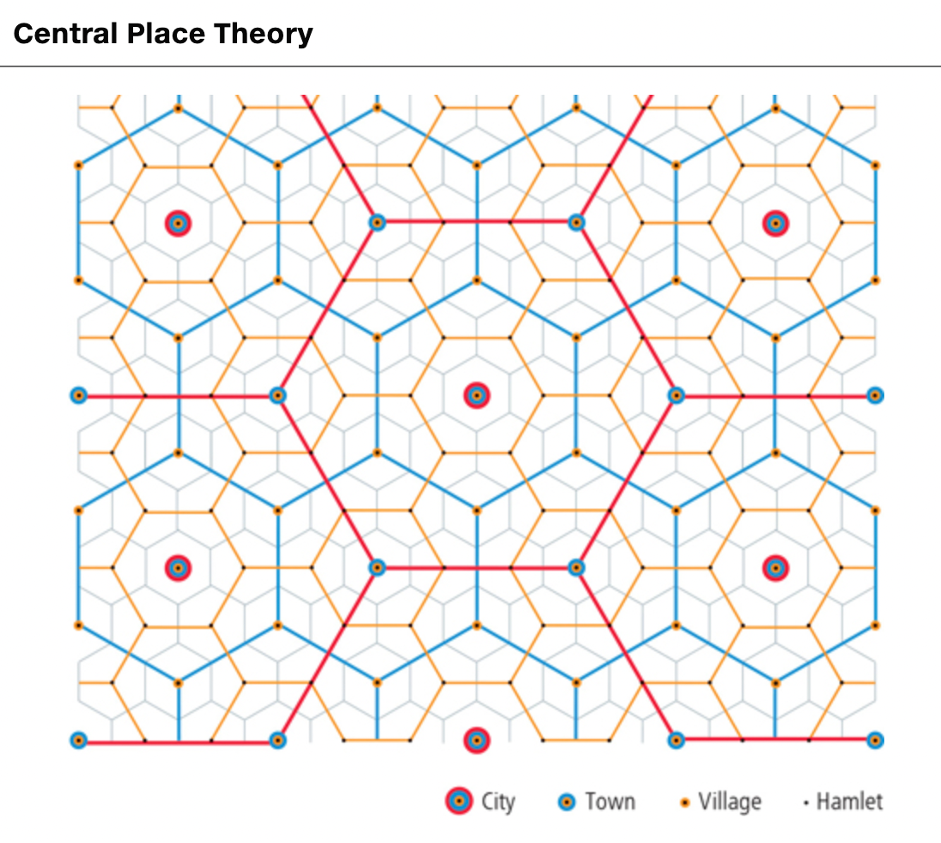
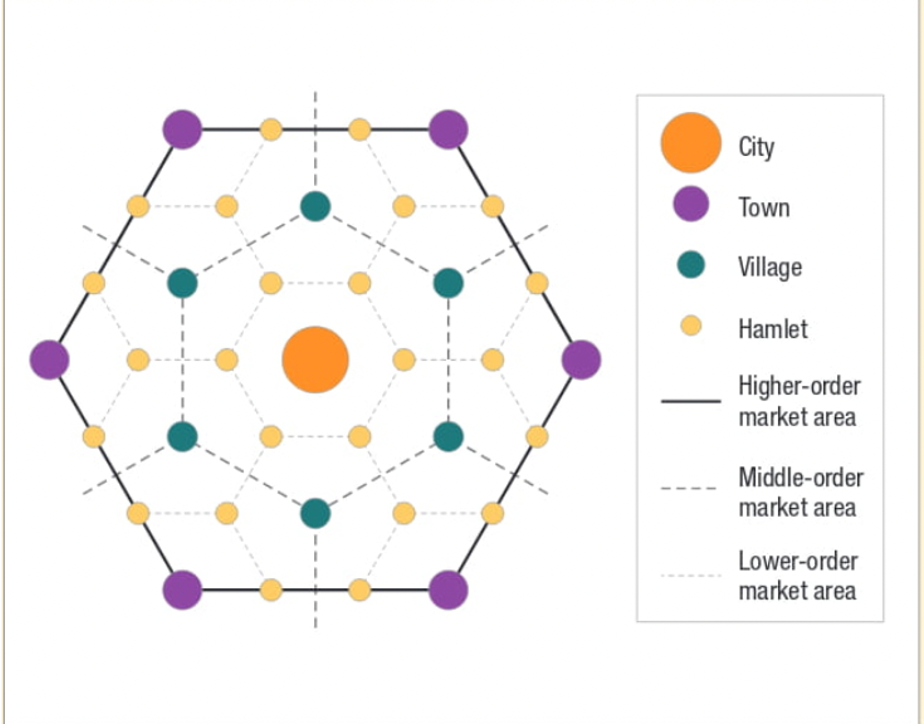
Central Place (Theory)
a location where people go to receive goods and services; varies in size from tiny community to major city; market area is depicted as surrounding hexagon (6.2)
21
New cards
Threshold
part of Central Place Theory; the size of a population necessary for any particular service to exist and remain profitable; think *minimum* distance required
__low threshold places__*–* gas stations, convenience stores, fast food joints
__medium threshold places__*–* restaurants, hospitals, high schools, department stores
__high threshold places__*–* stock market exchanges, sports teams, symphony orchestras (6.2)
__low threshold places__*–* gas stations, convenience stores, fast food joints
__medium threshold places__*–* restaurants, hospitals, high schools, department stores
__high threshold places__*–* stock market exchanges, sports teams, symphony orchestras (6.2)
22
New cards
Range
part of Central Place Theory; the distance people will travel to obtain specific goods or services; think *maximum* distance required (6.2)
23
New cards
Functional Zonation
the idea that portions of an urban area have distinct and specific purposes, sometimes specified with zoning ordinances
__3 categories__: residential, commercial, and industrial (6.2)
__3 categories__: residential, commercial, and industrial (6.2)
24
New cards
Central Business District (CBD)
a vital part of any urban model often located near the physical center and is the commercial heart of the city; high property values; often called “downtown” (6.2)
25
New cards
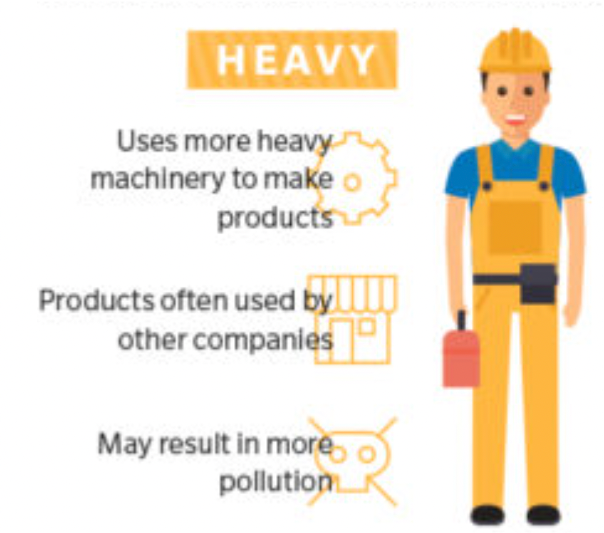
Heavy Manufacturing
industry that is expensive and requires heavy machinery, large buildings, large machine tools, and a large investment to create and maintain; often create high levels of pollution
EX: coal, oil, steel, shipping (6.2)
EX: coal, oil, steel, shipping (6.2)
26
New cards
Light Manufacturing
industry that does not need as much land or investment; usually sold directly to a consumer
EX: clothing, shoes, furniture, electronics (6.2)
EX: clothing, shoes, furniture, electronics (6.2)

27
New cards
Residential Density Gradient
as one moves from the inner city, population density declines along with the density of housing units (6.2)

28
New cards
Disamenity Zones
the poorest areas of a city; often the location of slums, not connected to traditional urban infrastructure, and are prevalent in gang activity (6.2)
29
New cards
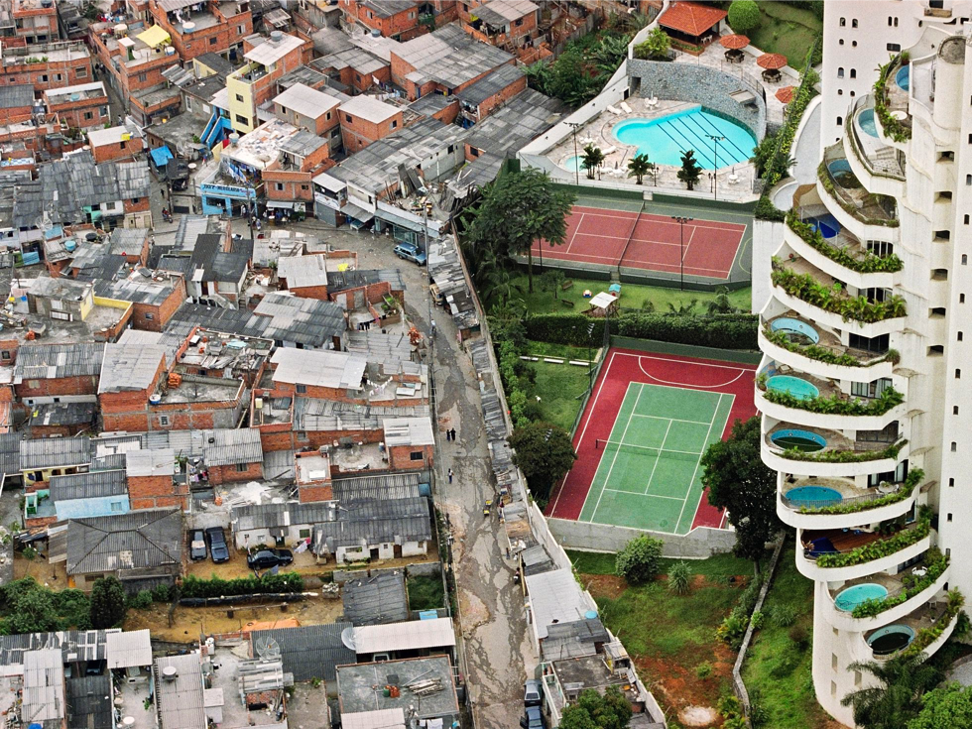
Squatter Settlements
an informal housing area beset with overcrowding and poverty that features temporary homes often made of wood scraps or metal sheeting
AKA favelas, barrios, shantytowns, slums (6.2)
AKA favelas, barrios, shantytowns, slums (6.2)

30
New cards
Bid-Rent Theory
attempts to explain land-use patterns as distance grows to the CBD; commercial development is willing to pay more for land, followed by industry, warehousing, and then residential (6.2)
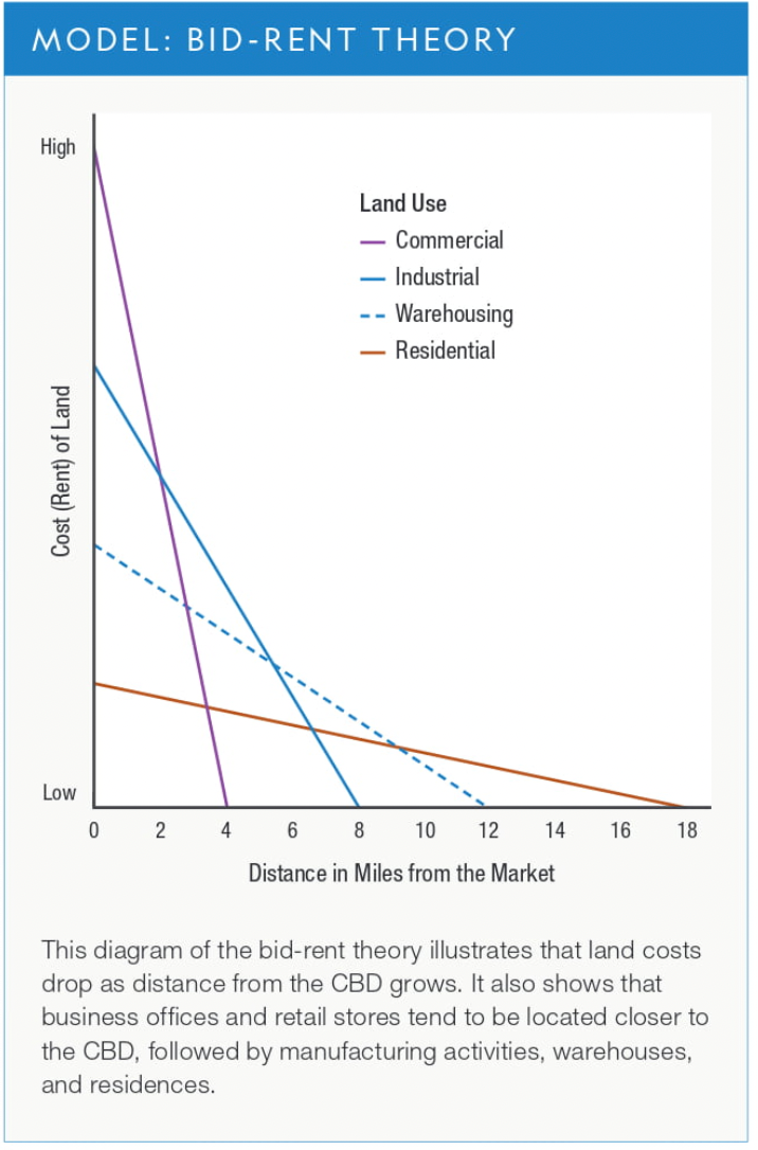
31
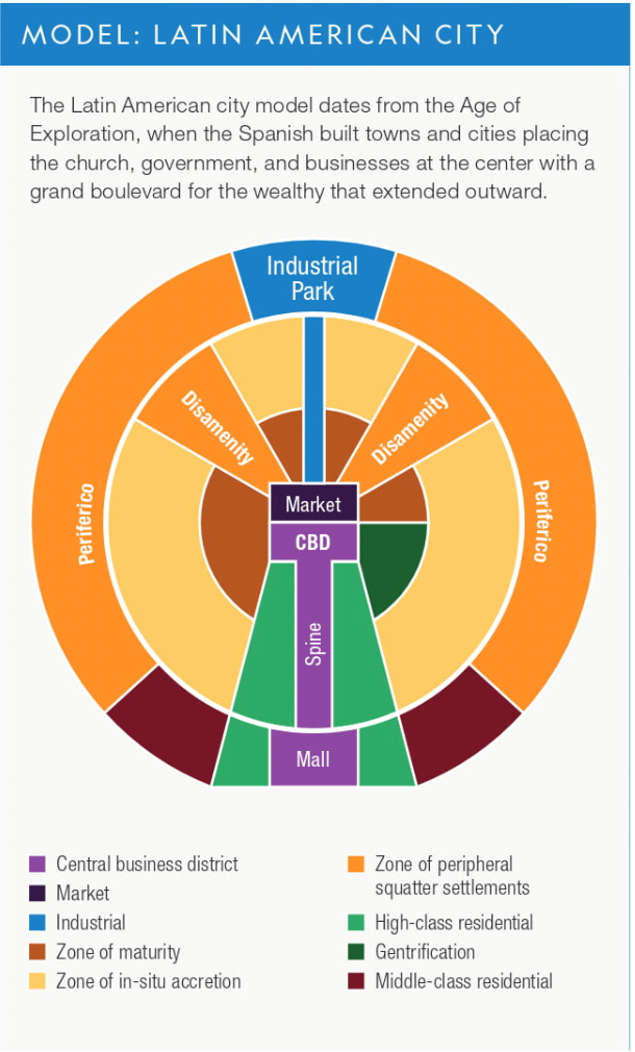
New cards
Latin American Urban Model
(6.2)
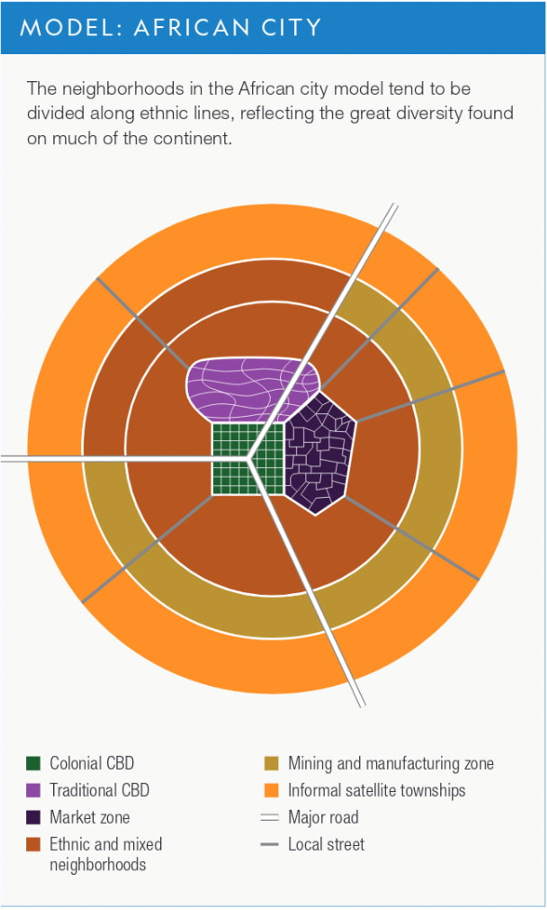
32
New cards
African City Urban Model
(6.2)
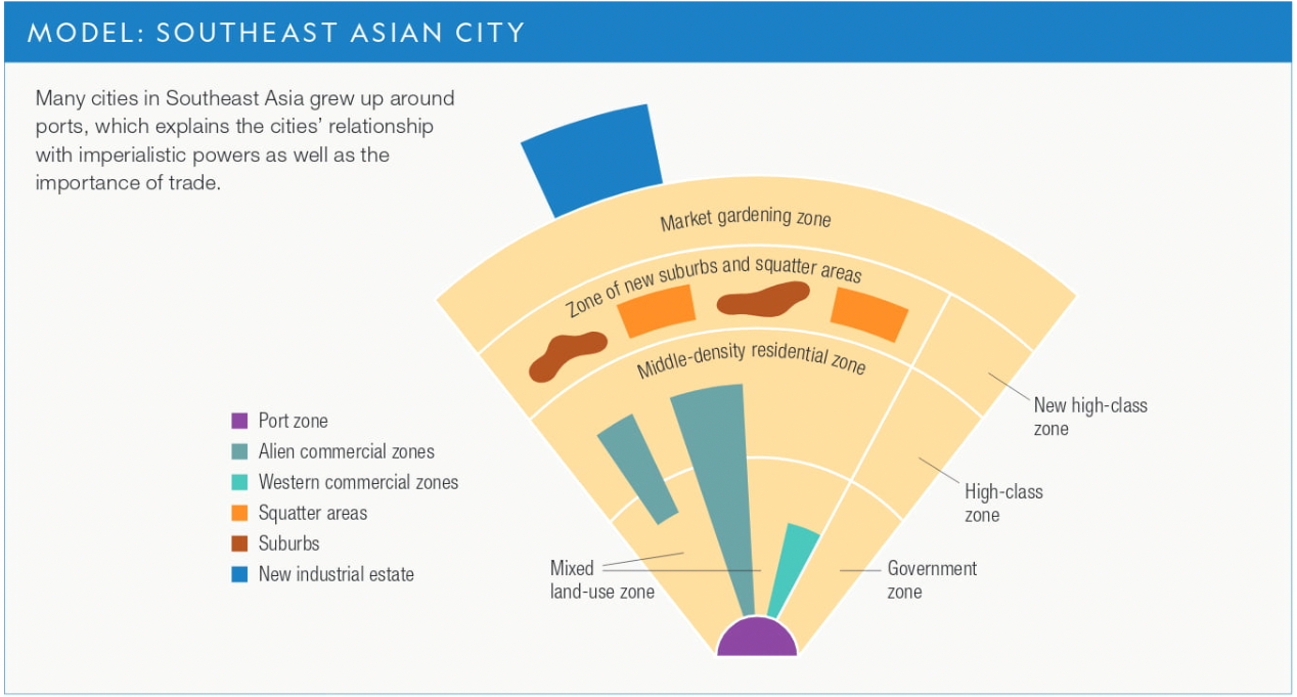
33
New cards
Southeast Asian City
(6.2)
34
New cards
Burgess Concentric Zone Urban Model
(6.2)
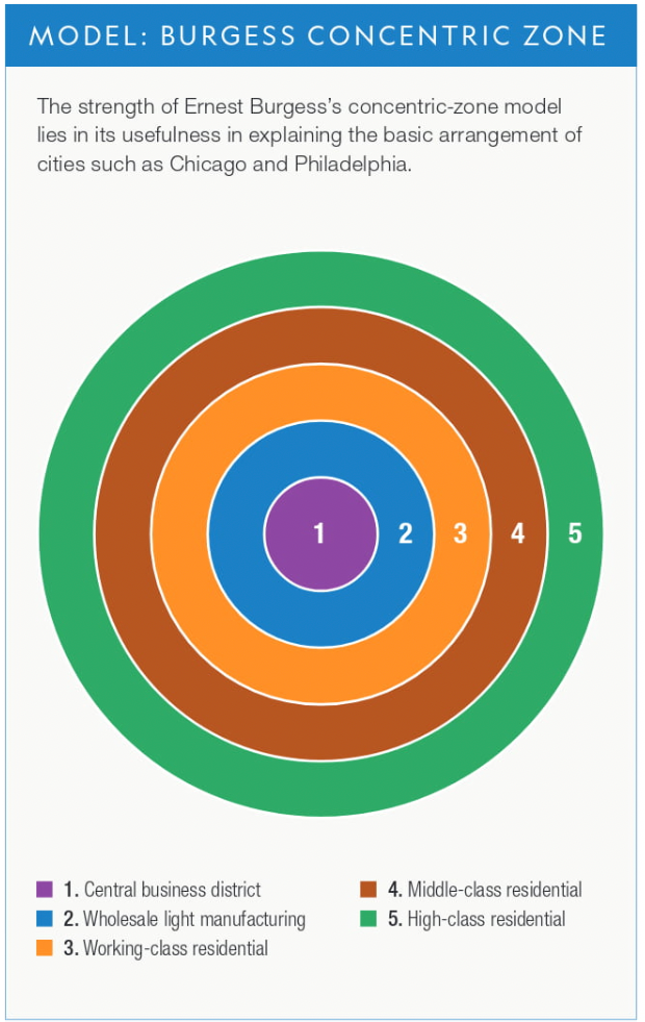
35
New cards
Galactic City Urban Model
(6.2)
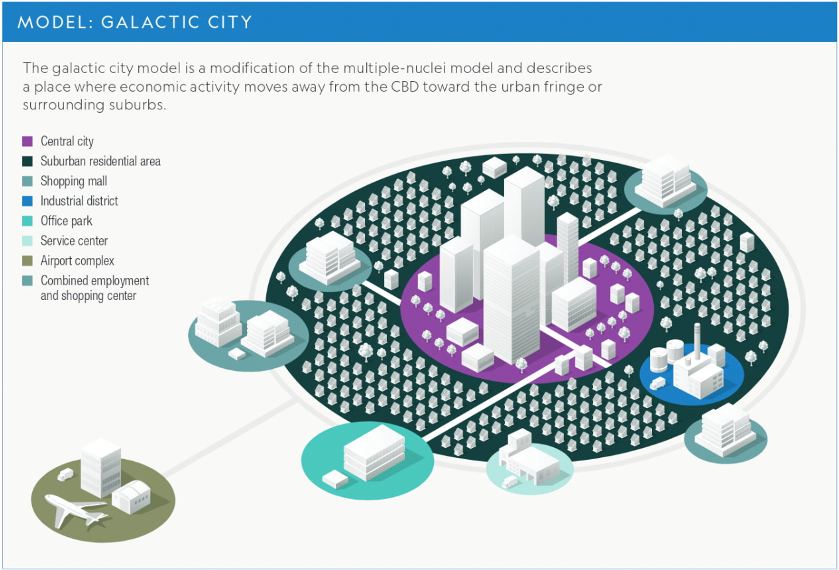
36
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Urban Model
(6.2)
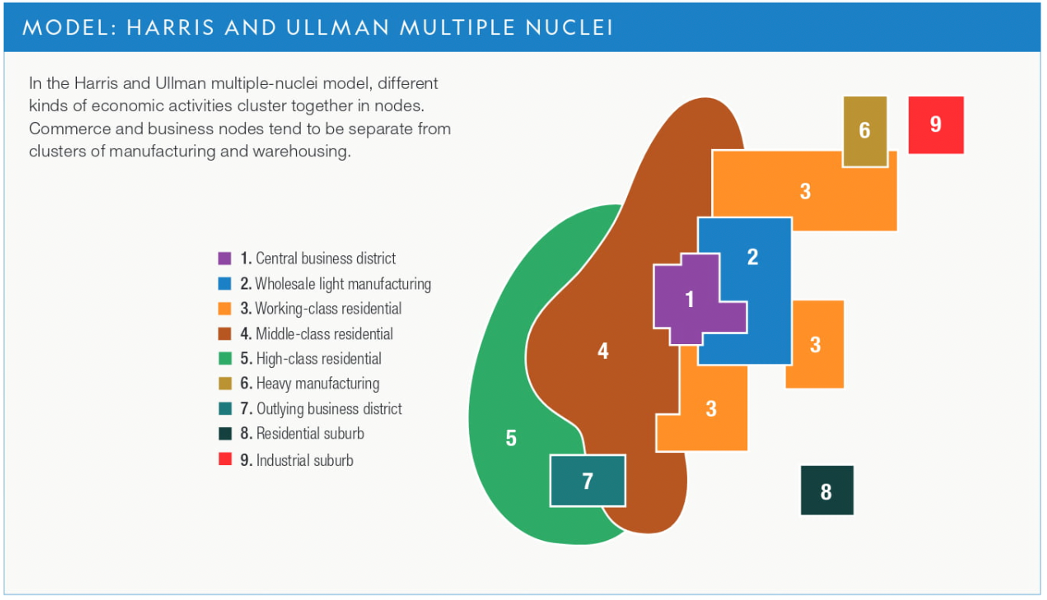
37
New cards
Hoyt Sector Urban Model
(6.2)
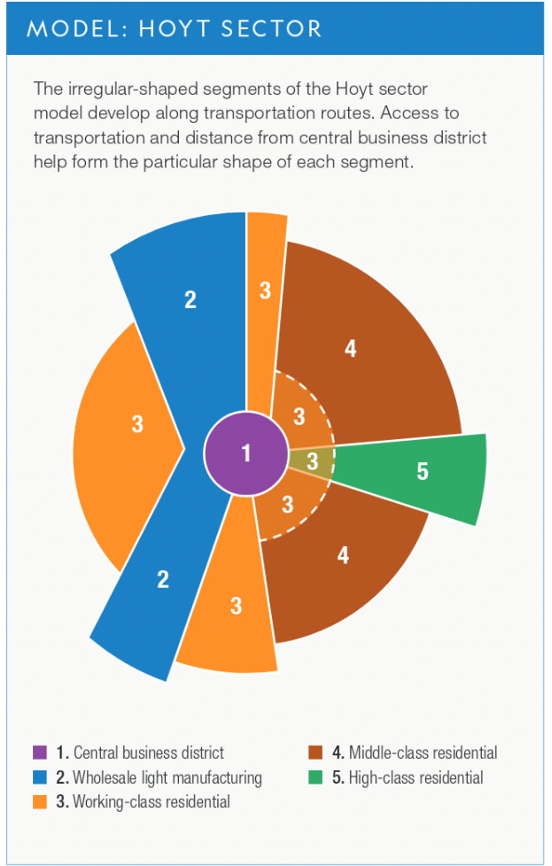
38
New cards
Filtering
when houses pass from one social group to another; usually occurs when the wealthiest move to new homes and people with less wealth move into the home they leave, or when a single family house is subdivided for use by two or more families (6.3)
39
New cards
Gated Communities
neighborhoods that are planned in order to control access and aesthetics within the community, for residents that are seeking safety, quiet, and homogeneity
EX: Loch Lloyd in photo (6.3)
EX: Loch Lloyd in photo (6.3)
40
New cards
Edge City
a node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area (6.3)
41
New cards
Boomburb
a suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city on its own with more than 100,000 residents (6.3)
42
New cards
Gentrification
the process of wealthier residents moving into a neighborhood and making significant improvements to the buildings and infrastructure (6.3)

43
New cards
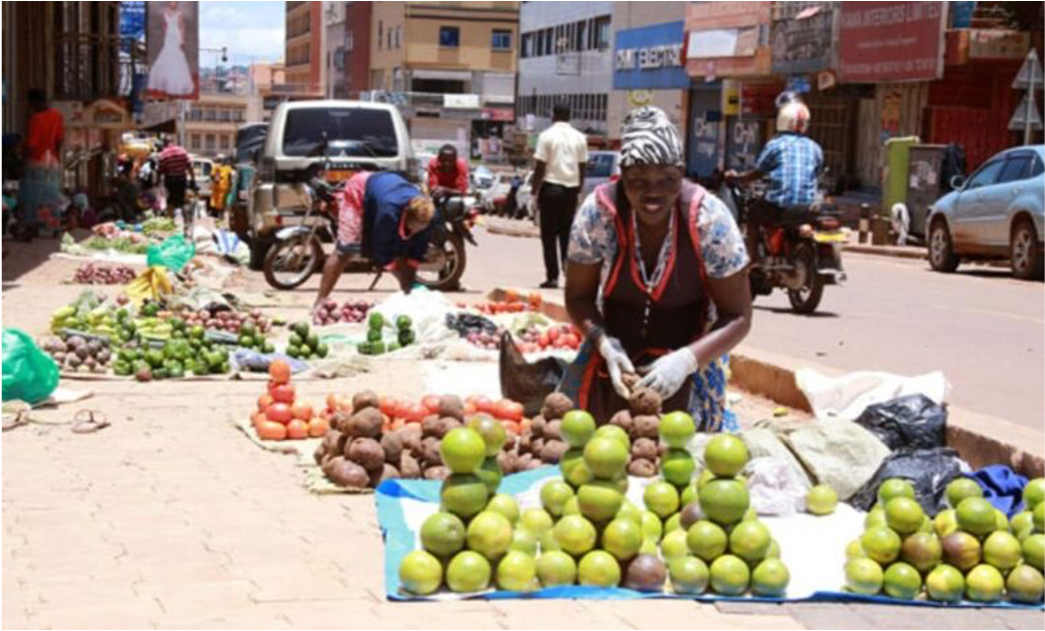
Informal Economy
the portion of the economy that is not taxed, regulated, or managed by the government; important, effective, and vibrant in slums and squatter settlements; prevalent in areas where the government has been ineffective at promoting the growth of businesses
informal economy in a more developed state can be called the **shadow** economy as well (6.3)
informal economy in a more developed state can be called the **shadow** economy as well (6.3)

44
New cards
Smart Growth
policies that preserve farmland and undeveloped spaces near a city (6.3)
45
New cards
Urban Infill
the process of building up underused lands in the city, like brownfields, unused airports, and closed military bases; the opposite of leapfrog development and urban sprawl (6.3)
46
New cards
Slow Growth
slowing the growth of a city as a way to limit the problems associated with growth and improve sustainability (6.3)
47
New cards
New Urbanism
urban planning movement that emerged in the 1990s which uses many of the ideas of smart growth (increasing walkability, affordable housing, vibrance, growth, etc) (6.3)
48
New cards
Greenbelt
a ring of parkland, agricultural land, or other type of open space maintained around an urban area to limit sprawl and pollution
EX cities with greenbelts: Chicago, San Francisco, Ontario (pictured), London (6.3)
EX cities with greenbelts: Chicago, San Francisco, Ontario (pictured), London (6.3)
49
New cards
Exurbanism
the flow of residents leaving the cities to a farther extent than suburbs, typically for affordable, quiet life; also called counter-urbanism or deurbanization (6.3)
50
New cards
Brownfields
areas filled with abandoned factories, dilapidated buildings, and contaminated soil; expensive to repair/remove and devalue neighboring properties (6.4)
51
New cards
Redlining
the process by which banks refuse loans to those who want to purchase and improve properties in certain urban areas (6.4)
52
New cards
Blockbusting
when one ethnic group, usually middle-class white people, would be frightened into selling their homes at low prices when they hear that another ethnic group is moving into an neighborhood, typically done by real estate agents and investors for profit; cause of white flight (6.4)
53
New cards
Eminent Domain
laws that allow governments to seize land for public use after paying market value for the property, typically to build new roads or schools, or sell the land to private businesses who will build hotels, hospitals, or other developments (6.4)
54
New cards
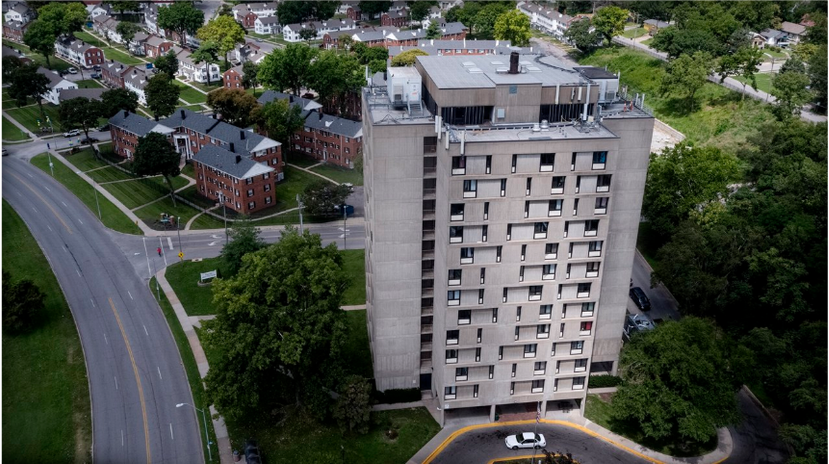
Housing Projects
public housing developments that were built in areas of the inner city where housing was unavailable; often associated with crime, drugs, and poor maintenance (6.4)

55
New cards
NIMBY Movement
“not in my backyard;” movement against programs and infrastructure that help the impoverished out of fear of reduced property values and crime (6.4)
56
New cards
Food Desert
an area where residents have limited or no access to fresh, healthy food because of inadequate transportation; a common issue in both urban and rural communities due to grocery stores’ favor for suburban locations with wealthier residents, cheaper property, and ability to pave vast parking lots (6.4)
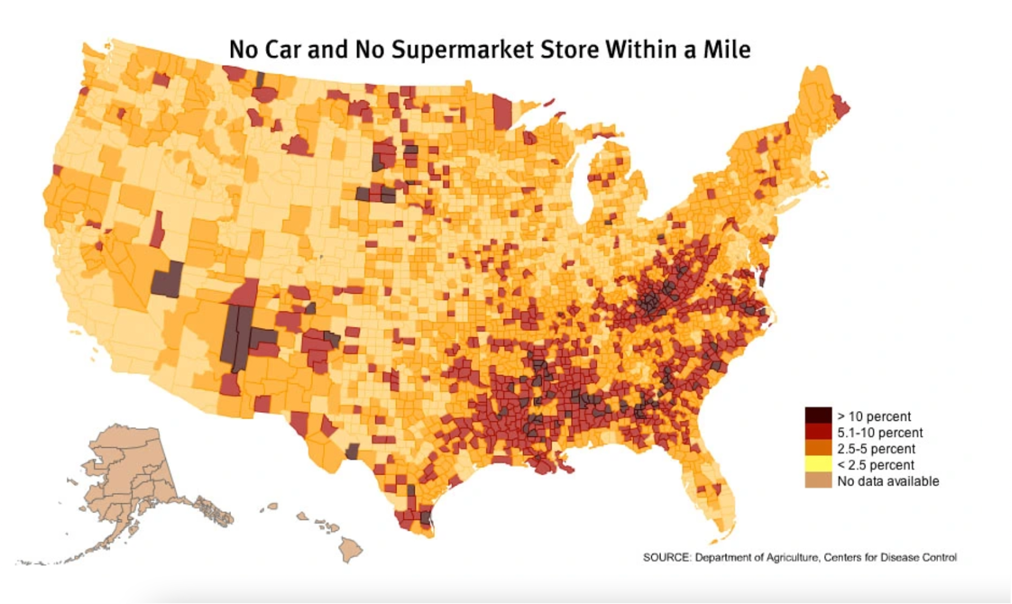
57
New cards
Urban Sprawl
when cities expand horizontally (more land mass) due to availability of automobiles, highways, and inexpensive land outside the urban area (6.4)
58
New cards
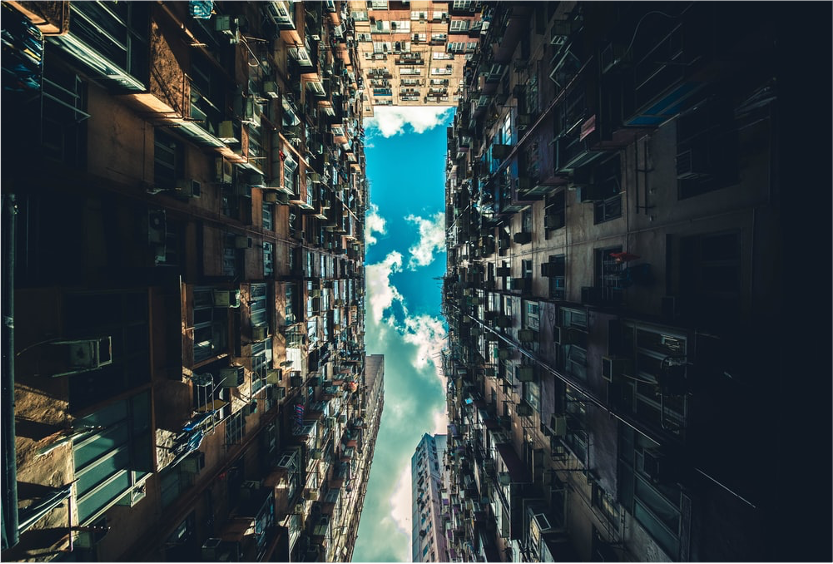
Urban Canyons
streets lined with tall buildings can channel and intensify winds, as well as prevent sunlight from reaching the ground (6.4)

59
New cards
Impermeability
buildings, streets, and parking lots do not allow water to soak into the ground, which can cause flooding; the ground is impermeable due to concrete (6.4)
60
New cards
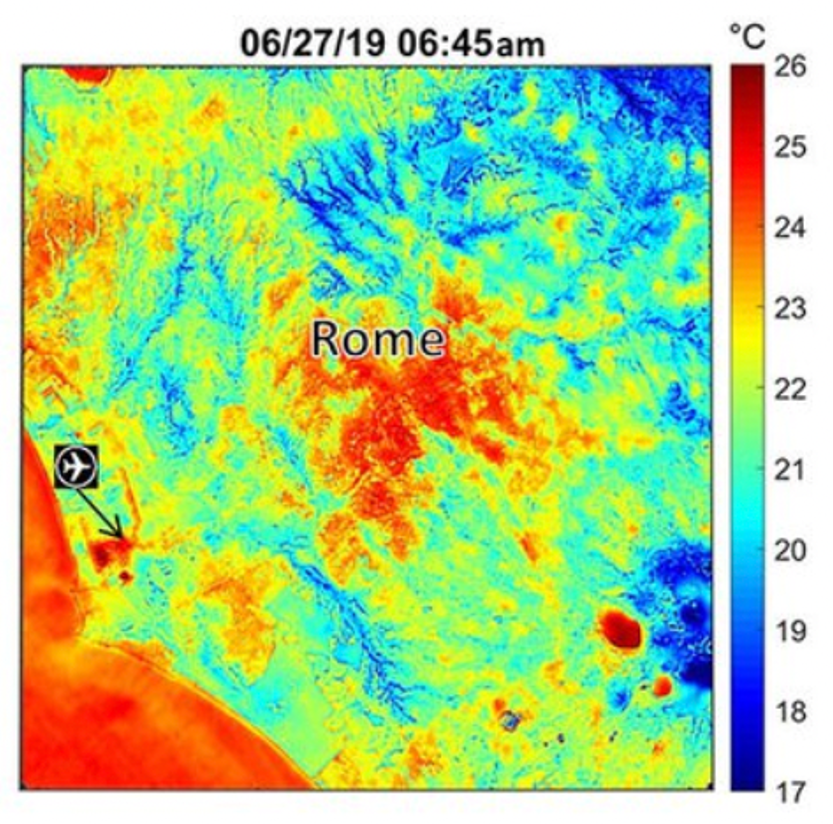
Urban Heat Islands
the concentration of buildings can raise the temperature in the core of a city (6.4)