Chordates
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Symplesiomorphies of Phylum Chordata
Key characteristics: pharynx, notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, segmented post anal tail, endostyle (homologous to the thyroid).
Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicates)
All are marine filter feeders. Larvae look like tadpoles and all are free swimming. Most adults are sedentary.
Subphylum Cephalochordata (Amphioxus/lancelets)
All are marine filter feeders that typically burrow in mud. Adults have chordate traits but differ from vertebrates in using gill slits for filtering (not respiration).
Subphylum Vertebrata Characteristics
vertebral column, cranium, dorsal hollow nerve chord, pharyngeal gill slits
Superclass Cyclostomi
Classes Myxini and Petromyzontida
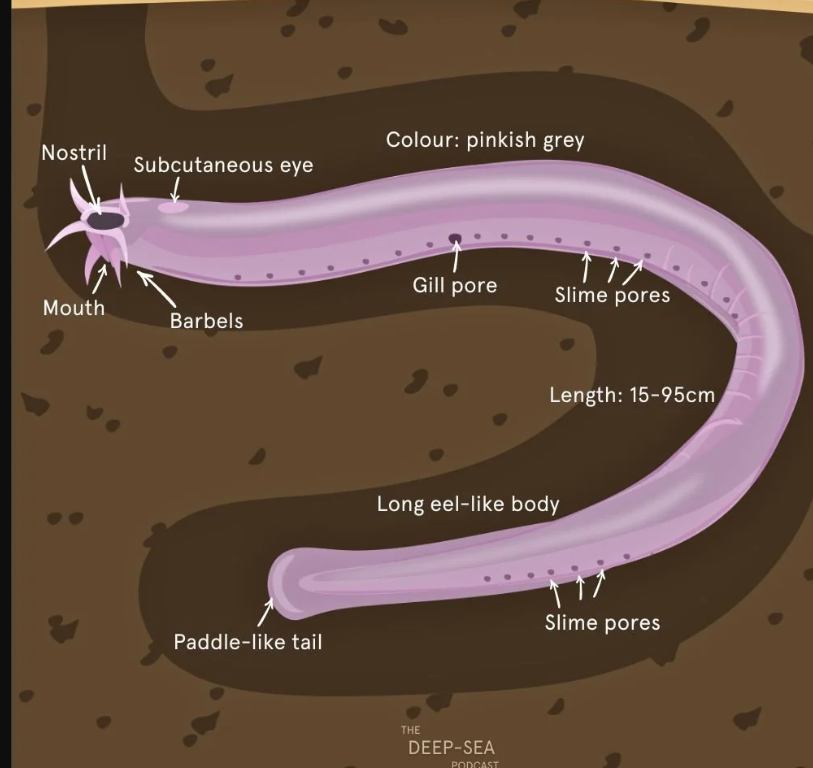
Order Myxiniformes
Hagfish, elongate, scaleless with reduced eyes and no vertebrae
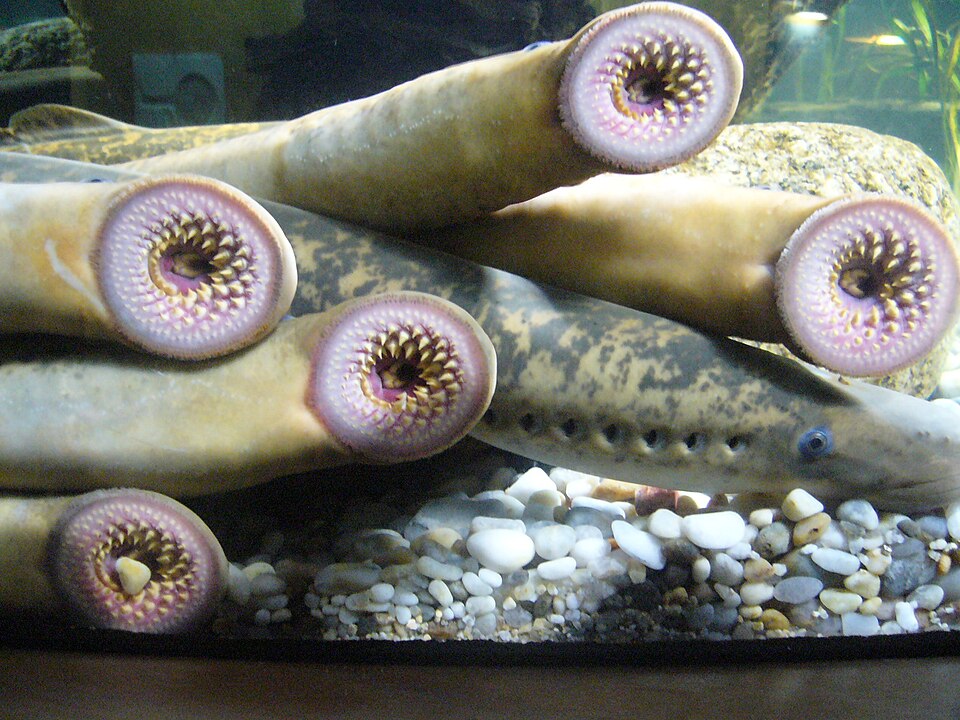

petromyzontiformes
Lamprey
Class Chondrichthyes
sharks, rays, and skates (Elasmobranchii) chimaeras (Holocephali). Non-calcified to semi-calcified endoskeletons; placoid scales (dermal denticles = tooth like);
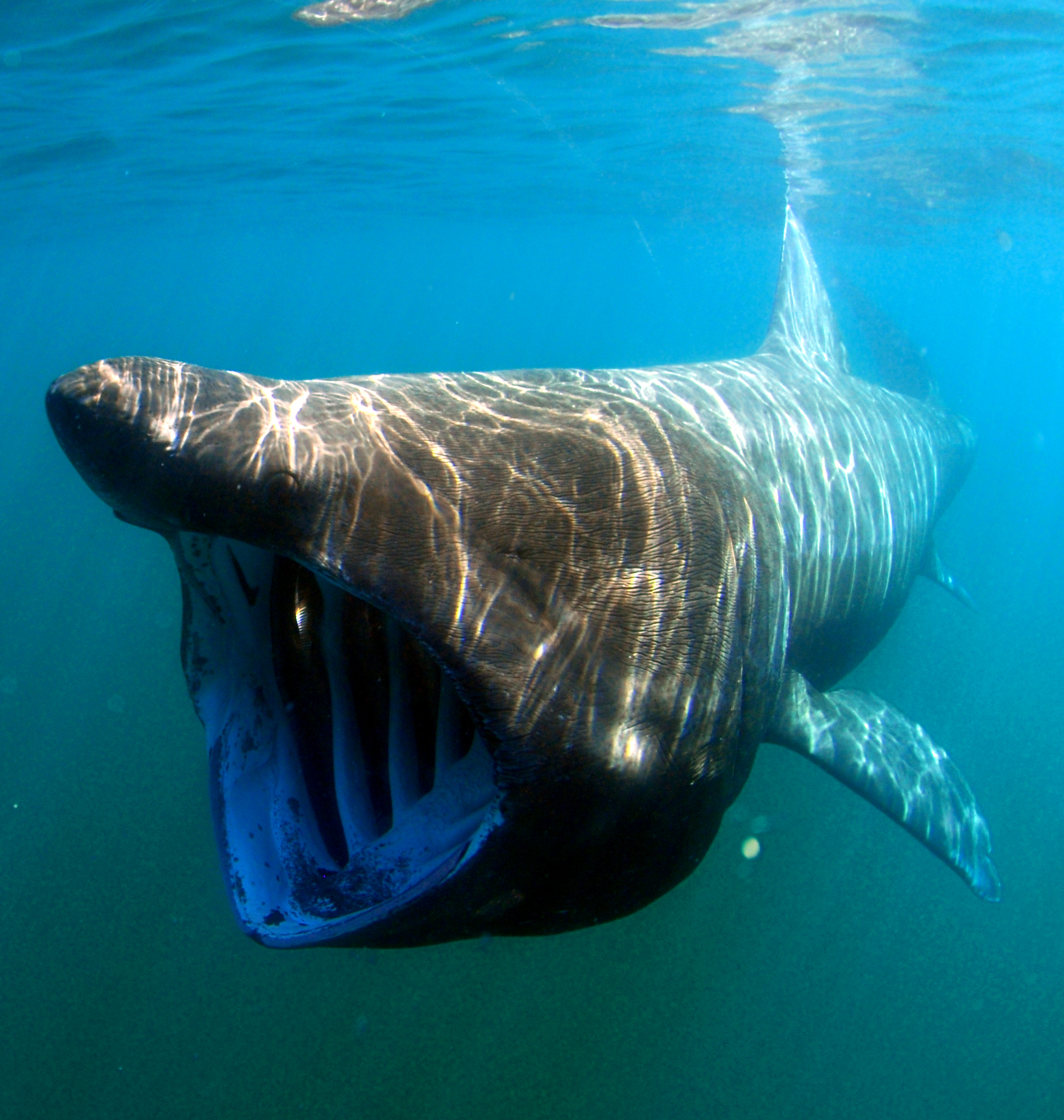

Order Lamniformes
Two dorsal fins, an anal fin, five gill slits, eyes without a nictitating membrane,mouth extends behind the eyes.
Superclass Osteichthyes
largest vertebrate group, comprising over 28,000 species. All have a bony endoskeleton with a two chambered heart.
class sarcopterygii
lobe finned fishes (lungfish and coelocanths)
Class Anctinopterygii
ray finned fishes, 50% of all vertebrae
Order Salmoniformes
are migratory, spawning in freshwater.
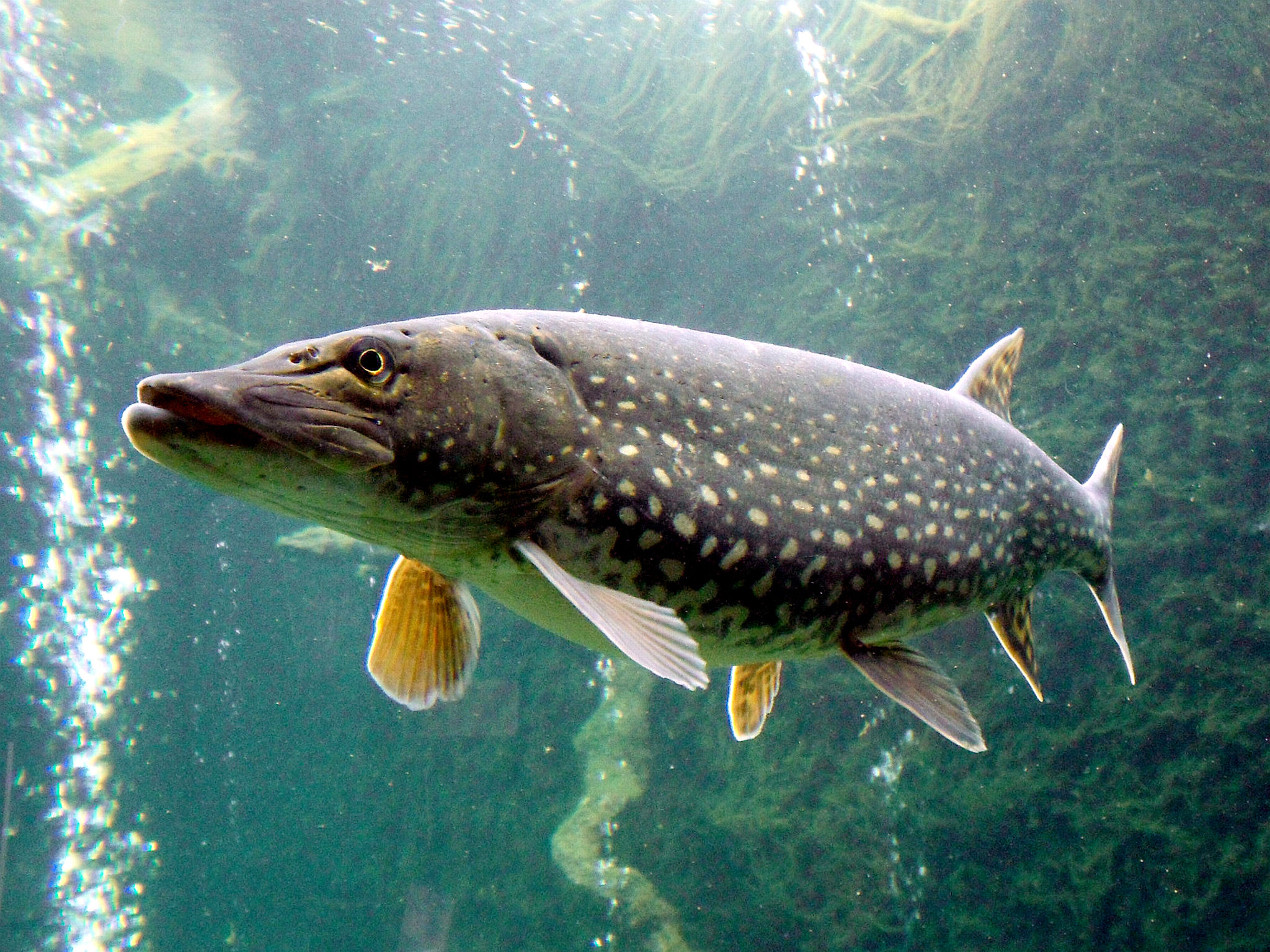

Order Esociformes
long & streamlined. Pike, Mudminnows and pickerel.

Order Perciformes
fin spines on dorsal, anal and pelvic fins. 4 gill arches.
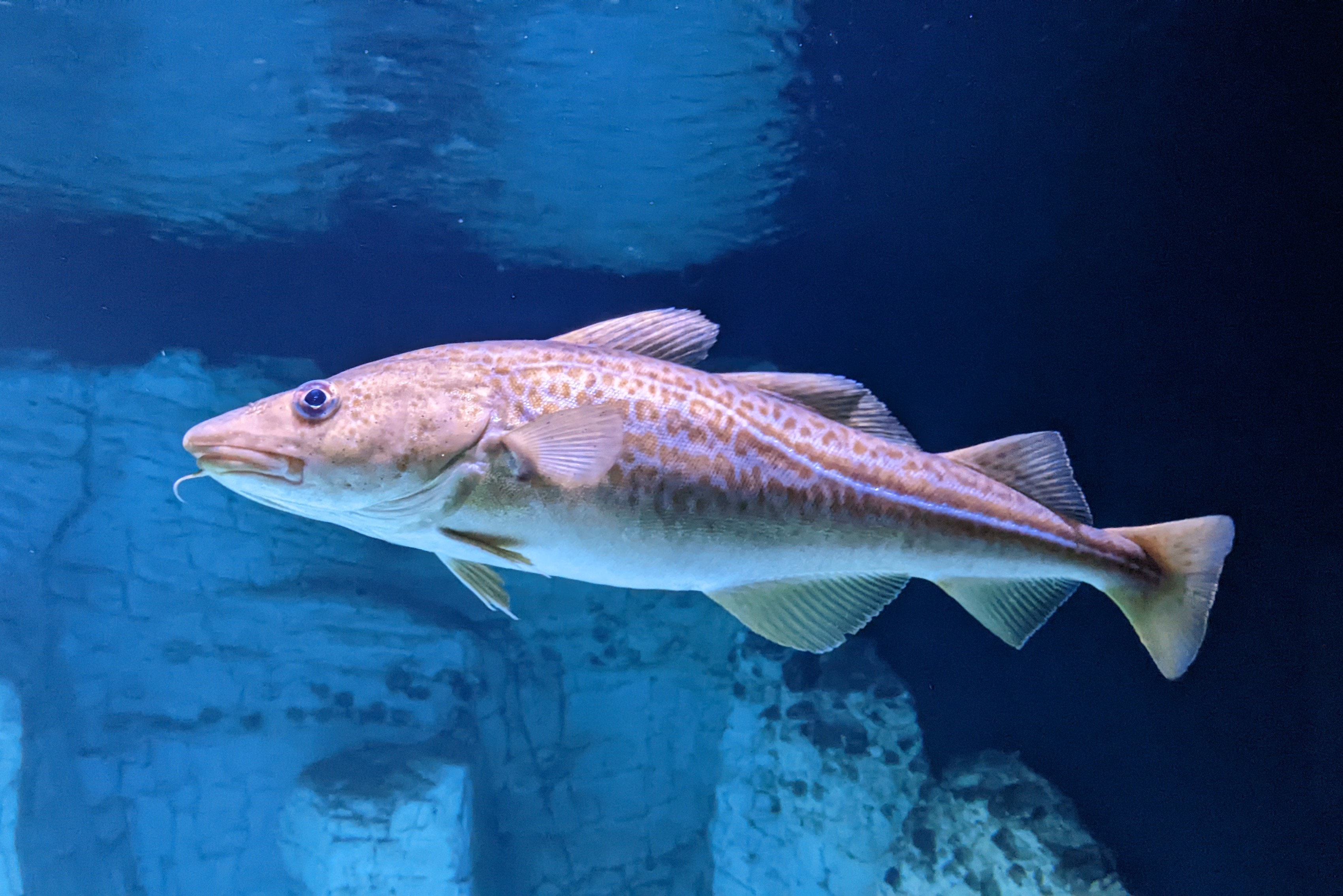

Order Gadiformes
cod, hakes, pollack, haddock. fins are spineless
Order pleuronectiformes
flatfish, flounder, halibut, sole
Order Anguilliformes
Eels. Elongated fish, lack pelvic fins and some lack pectoral fins. Dorsal and Anal fins are flushed with caudal.
order lophiiformes
angler fish
Synapomorphies of Vertebrata
vertebral column, cranium, cartilaginous/bony endoskeleton, tripartite brain, muscularized pharynx
Class Amphibia
mucosal glands in skin, water permeable
Order Urodela
Salamanders, body segmented with costal grooves, simplified skull, no middle ear cavity
Order Anura
Frogs and Toads, skulls have reduced bones, tails short or absent, vary by lifestage, hind limbs elongated, caudal vertebrae are fused into urostyle
Order Gymnophonia
Caecilians, limbless, serpentine bodies. Tail reduced, eyes reduced, dense, ossified skulls.
Amphibia families that occur in Maine
Ambystomatidae, Plethodontidae, Proteidae, Salamandridae, Bufonidae, Hylidae, Ranidae

Ambystomatidae
mole salamanders, no nasolabial grooves, have lungs, ambystoma laterale
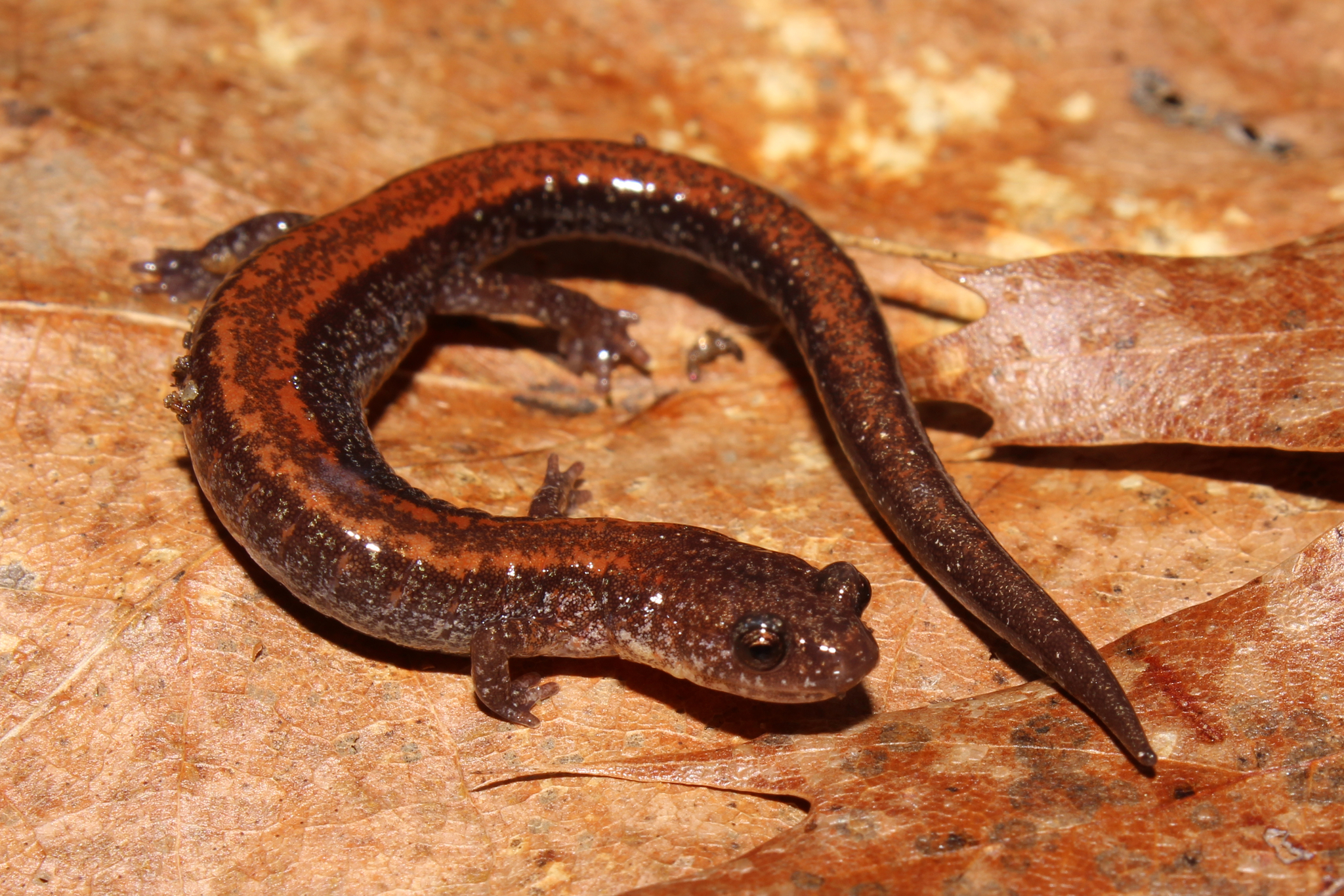

Plethodontidae
lungless salamanders, have nasolabial grooves. plethodon cinereus
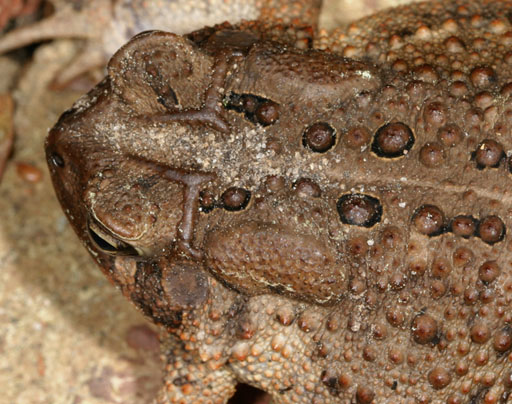

Bufonidae
true toads, teeth absent in upper and lower jaws, skin ossified to skull, shortened limbs, parotoid glands. Bufo americanus
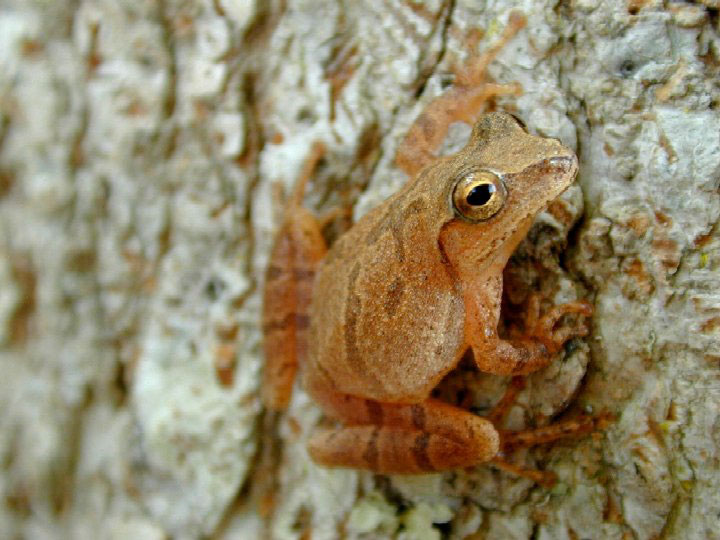

Hylidae
Tree frogs, horizontal pupils, enlarged finger pads, hyla versicolor and pseudacris crucifer
Class Reptilia
all sauropsids, orders: Squamata, Testudines, Crocodilia
Order Squamata
scaly, snakes and lizards, cranial kinesis, paired hemipenes and pleurodont dentition
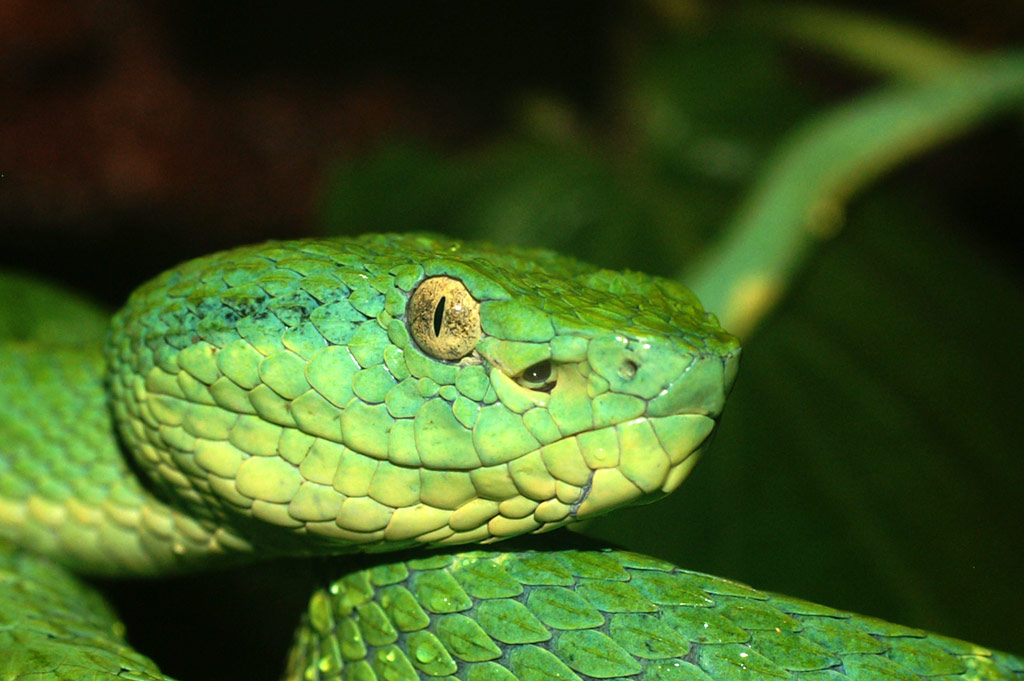

Family Viperidae
loreal pit, triangle shaped head and keeled scales
Family Colubridae
11 spp in Maine. liochlorophis vernalis
Order Testudines
turtles, terrapins and torises, modified ribs form the carapace, skull fused, beak with no teeth
Family Chelydridae
snapping turtles, limbs cannot be fully retracted into the shell, upper jaw hooked. Snapping turtle Chelydra serpentina
Family Emydidae
lack inframarginal scutes and have convex eighth cervical vertebrae, Clemmys guttata/insculpta