[MT 6315] Unit 5: Chromosome Aberrations
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:18 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
1
New cards
Chromosomal Mutations
Also known as **chromosomal** **aberrations** which refer to the **changes** in **chromosomal** **structure or number** which can lead to **chromosomal abnormalities** (deletion, duplication, rearrangement, and inversion of genes)
\
\
2
New cards
Chromosomal Mutations
They are **relatively large** compared to gene mutations
3
New cards
Chromosomal Mutations
What is rare in live births but it is a common cause for **spontaneous abortions**?
\
\
4
New cards
Chromosome Mutations
Refers to **variations from the** **wild-type condition** in either chromosome structure or chromosome number.
5
New cards
**…mutation in one or more of the** __**genes**__ on the chromosome
A person can have a normal chromosome in number and structure but **still have the disease** or condition caused by a mutation in one or more of the **____** on the chromosome
6
New cards
False. They **arise spontaneously or are induced by chemical or radiation mutagens.**
(True or False): Chromosome mutations do not arise spontaneously or are induced by chemical or radiation mutagens.
7
New cards
Wild type
Refers to what is **normally possessed** by the population at large and the **normal version** of your chromosome
8
New cards
**Gene**: Nucleotide sequence
**Chromosome**: Structure or number
**Chromosome**: Structure or number
### Gene vs Chromosome Mutation:
Alteration
1) Nucleotide sequence
2) Structure or number
Alteration
1) Nucleotide sequence
2) Structure or number
9
New cards
**Gene**: DNA replication and mutagens
**Chromosome**: Crossing over during meiosis
**Chromosome**: Crossing over during meiosis
### Gene vs Chromosome Mutation:
Errors
1) Crossing over during meiosis
2) DNA replication and mutagens
Errors
1) Crossing over during meiosis
2) DNA replication and mutagens
10
New cards
**Gene**: Nucleotide sequence
**Chromosome**: Segment
**Chromosome**: Segment
### Gene vs Chromosome Mutation:
Alteration Location
1) Segment
2) Nucleotide sequence
Alteration Location
1) Segment
2) Nucleotide sequence
11
New cards
**Gene**: Single
**Chromosome**: Several
**Chromosome**: Several
### Gene vs Chromosome Mutation:
Genes affected
1) Single
2) Several
Genes affected
1) Single
2) Several
12
New cards
**Gene**: Low
**Chromosome**: Lethal potential
**Chromosome**: Lethal potential
### Gene vs Chromosome Mutation:
Influence
1) Low
2) Lethal potential
Influence
1) Low
2) Lethal potential
13
New cards
Deletion (del) / Deficiency
### Variation in Structure:
A **particular** or **portion** of a chromosome is **missing**; thus, it involves the **loss of a segment** of a chromosome
A **particular** or **portion** of a chromosome is **missing**; thus, it involves the **loss of a segment** of a chromosome
14
New cards
Duplication
### Variation in Structure:
**Extra copy** of chromosome or the **doubling of a segment of a chromosome**
**Extra copy** of chromosome or the **doubling of a segment of a chromosome**
15
New cards
Inversion
### Variation in Structure:
**Rotation** of sequence or **change in the orientation or sequence** of the chromosome
**Rotation** of sequence or **change in the orientation or sequence** of the chromosome
16
New cards
Translocation
### Variation in Structure:
**Transfer** of a portion of a chromosome to another
**Transfer** of a portion of a chromosome to another
17
New cards
Monosomics
### Variation in Number:
**One** copy instead of a diploid chromosome
**One** copy instead of a diploid chromosome
18
New cards
Nullisomics
### Variation in Number:
**A lack of both** **the normal chromosomes** or a pair of species
**A lack of both** **the normal chromosomes** or a pair of species
19
New cards
Aneuploidy
### Variation in Number:
Presence of the **abnormal number of chromosome** in a cell
Presence of the **abnormal number of chromosome** in a cell
20
New cards
Euploidy
### Variation in Number:
* Number of **complete** **set** of chromosome
* Organism or cell has one or exact multiple of complete set(s) of chromosomes
* A **somatic cell** with the normal number of chromosomes for that species
* Number of **complete** **set** of chromosome
* Organism or cell has one or exact multiple of complete set(s) of chromosomes
* A **somatic cell** with the normal number of chromosomes for that species
21
New cards
Polyploidy
### Variation in Number:
* **More than 2 complete sets** of chromosomes
* Common among plants
* **More than 2 complete sets** of chromosomes
* Common among plants
22
New cards
Deletion
* The segment may be **located anywhere along the chromosome**.
* Starts **in breaks of chromosomes**
* Caused by **agents or by errors in recombination**
* Starts **in breaks of chromosomes**
* Caused by **agents or by errors in recombination**
23
New cards
The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN)
It is an **international standard for human chromosome nomenclature**, which includes **band names**, **symbols** and **abbreviated terms** used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities.
24
New cards
Minus sign (-)
What sign indicates the presence of deletion?
25
New cards
del
Abbreviation for deletions of parts
26
New cards
Terminal deletion
Type of deletion that occurs towards the **end** of a chromosome
27
New cards
Intercalary/interstitial deletion
Type of deletion that occurs from the **interior** of a chromosome
28
New cards
Microdeletion
Type of deletion that refers to a relatively **small amount** (up to **5Mb** that could include a dozen genes) of deletion. It is also found in **children** with physical abnormalities.
29
New cards
Cri-du-chat Syndrome
### Deletion
* **Chromosome:** 5p-
* **Phenotype**: Cat-like cry, facial anomalies (round small head and flattened bridge of the nose; eyes are spaced wide apart)
* Discovered by Jerome Lejeune (1963)
* **Chromosome:** 5p-
* **Phenotype**: Cat-like cry, facial anomalies (round small head and flattened bridge of the nose; eyes are spaced wide apart)
* Discovered by Jerome Lejeune (1963)
30
New cards
Wilm’s tumor
### Deletion
* **Chromosome:** 11q- \[Chromosome 11 (WT1)\]
* **Phenotype**: Kidney tumors, genital and urinary tract abnormalities
* **Chromosome:** 11q- \[Chromosome 11 (WT1)\]
* **Phenotype**: Kidney tumors, genital and urinary tract abnormalities
31
New cards
Retinoblastoma
### Deletion
* **Chromosome:** 13q-
* **Phenotype**: Cancer of the eye
* **Chromosome:** 13q-
* **Phenotype**: Cancer of the eye
32
New cards
Prader-Willi syndrome
### Deletion
* **Chromosome:** 15q- \[Chromosome 15q11-q13 (UPD)\]
* **Phenotype**: Weak slow growth (infant), obesity, compulsive eating (children and adults); poor sucking reflexes
* **Chromosome:** 15q- \[Chromosome 15q11-q13 (UPD)\]
* **Phenotype**: Weak slow growth (infant), obesity, compulsive eating (children and adults); poor sucking reflexes
33
New cards
Error in chromosome
## Deletion
### Cri-du-chat syndrome
Rare genetic disorder that is __not the result of anything that the parents had done__ but rather an ___
### Cri-du-chat syndrome
Rare genetic disorder that is __not the result of anything that the parents had done__ but rather an ___
34
New cards
Pathognomonic cry of the cat
## Deletion
### Cri du chat syndrome
The abnormal anatomy of the throat
### Cri du chat syndrome
The abnormal anatomy of the throat
35
New cards
q11 and q13
## Deletion
### Prader-Willi syndrome
Bands included
### Prader-Willi syndrome
Bands included
36
New cards
Angelman syndrome
### Deletion
* Often smile and laugh frequently, and have happy, excitable personalities
* Tend to live close to a normal life span, but the disorder can't be cured
* Often smile and laugh frequently, and have happy, excitable personalities
* Tend to live close to a normal life span, but the disorder can't be cured
37
New cards
6 and 12 months of age
## Deletion
### Angelman syndrome
Developmental delays begin between about _____ and are considered to be the **first signs**
### Angelman syndrome
Developmental delays begin between about _____ and are considered to be the **first signs**
38
New cards
2 and 3 years old
## Deletion
### Angelman syndrome
Seizures begin between about __ and __ years old
### Angelman syndrome
Seizures begin between about __ and __ years old
39
New cards
OCA2
## Deletion
### Angelman syndrome
Which lost gene that is located on the segment of chromosome 15 is associated with light-colored hair and fair skin?
### Angelman syndrome
Which lost gene that is located on the segment of chromosome 15 is associated with light-colored hair and fair skin?
40
New cards
**Prader-Willi:** q-arm, paternal deletion
**Angelman:** maternal origin
**Angelman:** maternal origin
## Deletion
### Prader-Willi vs Angelman syndrome
What is missing in Chromosome # 15?
### Prader-Willi vs Angelman syndrome
What is missing in Chromosome # 15?
41
New cards
Duplication
Results in the **doubling of a segment** of a chromosome
42
New cards
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A
### Duplication
dup(17p12) or “duplication involving P-arm chromosome #17 with band-1 and subband-2”
dup(17p12) or “duplication involving P-arm chromosome #17 with band-1 and subband-2”
43
New cards
Tandem
### Duplication
* Duplicated but the sequence is maintained
* Duplicated but the sequence is maintained
44
New cards
Reverse
### Duplication
* Backwards duplication
* Backwards duplication
45
New cards
Terminal
### Duplication
* Terminal site or towards the end of the chromosome
* Terminal site or towards the end of the chromosome
46
New cards
Normal
### Duplication: *Gene Dose*
* Wild Type, Female
* B+B+
* Wild Type, Female
* B+B+
47
New cards
Duplicated once
### Duplication: *Gene Dose*
* Heterozygous Bar Female
* B+B
* Heterozygous Bar Female
* B+B
48
New cards
Both strands are duplicated
### Duplication: *Gene Dose*
* Homozygous Bar
* BB
* Homozygous Bar
* BB
49
New cards
Double duplication in pair
### Duplication: *Gene Dose*
* Heterozygous Double Bar
* B+B0
* Heterozygous Double Bar
* B+B0
50
New cards
Paracentric
### Inversion
The inverted segment **does not include the centromere**
The inverted segment **does not include the centromere**
51
New cards
Pericentric
### Inversion
The inverted segment **includes the centromere**
The inverted segment **includes the centromere**
52
New cards
Translocation
Change in position of chromosome segments and the gene sequences they contai
53
New cards
Intrachromosomal
### Translocation
Change in position of a chromosome segment **within the same chromosome**
Change in position of a chromosome segment **within the same chromosome**
54
New cards
Interchromosomal
### Translocation
Transfer of a chromosome segment **from one chromosome into a non-homologous chromosome**
Transfer of a chromosome segment **from one chromosome into a non-homologous chromosome**
55
New cards
Reciprocal
### Translocation: Interchromosomal
Exchange of segments **between two chromosomes**
Exchange of segments **between two chromosomes**
56
New cards
Non-reciprocal
### Translocation: Interchromosomal
* **Transfer** of segment in one direction from **one chromosome to another**
* One-way translocation
* **Transfer** of segment in one direction from **one chromosome to another**
* One-way translocation
57
New cards
Isochromes
### Translocation
* Short arms and/or the long arms of the same chromosome **join at the centromere**
* Two copies of a **large genetic region**
* **Mirror image** appearance of banding patterns extending in both directions from the centromere
* Short arms and/or the long arms of the same chromosome **join at the centromere**
* Two copies of a **large genetic region**
* **Mirror image** appearance of banding patterns extending in both directions from the centromere
58
New cards
Robertsonian (rob)
### Translocation
* Most common form
* **Two chromosomes** make up the person's DNA, joined together in an abnormal way; joining at centromeres
* 1 in 1,000 people
* Tiny short arms
* Most common form
* **Two chromosomes** make up the person's DNA, joined together in an abnormal way; joining at centromeres
* 1 in 1,000 people
* Tiny short arms
59
New cards
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
### Translocation
* **Philadelphia** chromosome
* Reciprocal translocation between chromosome 22 and 9
* Transition of *C-ABL within the BCR*
* causes the *CML* to grow and reproduce out of control
* Uncontrolled replication of **myeloblasts**
* **Philadelphia** chromosome
* Reciprocal translocation between chromosome 22 and 9
* Transition of *C-ABL within the BCR*
* causes the *CML* to grow and reproduce out of control
* Uncontrolled replication of **myeloblasts**
60
New cards
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
### Translocation
* Africa
* Virus-induced tumor
* Malignant B cells secrete antibodies
* Reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 8 and 14
* Activation of *C-MYC*
* Highly aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
* Africa
* Virus-induced tumor
* Malignant B cells secrete antibodies
* Reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 8 and 14
* Activation of *C-MYC*
* Highly aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
61
New cards
Nondisjunction (non separation)
### Translocation
* **Irregular distribution** of sister chromatids during mitosis or of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
* Phenomenon of **unequal separation**
* **Irregular distribution** of sister chromatids during mitosis or of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
* Phenomenon of **unequal separation**
62
New cards
Nullisomy
**Aneuploidy**
* Loss of **one homologous pair**; 2N-2
* Loss of **one homologous pair**; 2N-2
63
New cards
Monosomy
### Aneuploidy
* It involves a loss of a **single chromosome**; 2N-1
* It involves a loss of a **single chromosome**; 2N-1
64
New cards
Trisomy
### Aneuploidy
* Involves a single extra chromosome; 2N+1
* Cell is still a diploid but with additional chromosome
* Involves a single extra chromosome; 2N+1
* Cell is still a diploid but with additional chromosome
65
New cards
Tetrasomy
### Aneuploidy
* Two extra chromosomes; 2N+2
* Four copies of a particular chromosome
* Two extra chromosomes; 2N+2
* Four copies of a particular chromosome
66
New cards
Down Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* Trisomy-21
* Mongolism
* Phenotypic features:
* Wide skull that is flat at the back
* Eyelids have an epicanthic fold
* Iris contains spots
* Tongue are furrowed & protruding
* Physical growth, behavior and mental development are retarded
* Some have congenital heart defects.
* Trisomy-21
* Mongolism
* Phenotypic features:
* Wide skull that is flat at the back
* Eyelids have an epicanthic fold
* Iris contains spots
* Tongue are furrowed & protruding
* Physical growth, behavior and mental development are retarded
* Some have congenital heart defects.
67
New cards
Patau Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* Trisomy 13
* Phenotypic features:
* Cleft lip and palate
* Small eyes; cyclopia (single median eye)
* Polydactyly (extra fingers and toes)
* Mental and developmental retardation
* Severe malformations of the brain and nervous system
* Proboscis (elongated appendage from head)
* Polycystic kidney
* Trisomy 13
* Phenotypic features:
* Cleft lip and palate
* Small eyes; cyclopia (single median eye)
* Polydactyly (extra fingers and toes)
* Mental and developmental retardation
* Severe malformations of the brain and nervous system
* Proboscis (elongated appendage from head)
* Polycystic kidney
68
New cards
Edward Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* Trisomy 18
* Most affected infants are female
* Average survival time is **2-4 months**
* Phenotypic features:
* Multiple congenital malformations
* Clenched fists
* Elongated skull
* Low-set malformed ears
* **Club foot** (talipes) - twisted foot that turns in and points down
* Trisomy 18
* Most affected infants are female
* Average survival time is **2-4 months**
* Phenotypic features:
* Multiple congenital malformations
* Clenched fists
* Elongated skull
* Low-set malformed ears
* **Club foot** (talipes) - twisted foot that turns in and points down
69
New cards
Turner Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* 45, X
* Monosomy for the **X chromosome**
* Only affects **females**
* Absence of Barr body
* Absence of X chromosome
* Phenotypic features:
* Short and wide-chested
* Extra folds of skin on the neck
* Underdeveloped breasts and rudimentary ovaries
* Color blindness
* Narrowing of aorta
* 45, X
* Monosomy for the **X chromosome**
* Only affects **females**
* Absence of Barr body
* Absence of X chromosome
* Phenotypic features:
* Short and wide-chested
* Extra folds of skin on the neck
* Underdeveloped breasts and rudimentary ovaries
* Color blindness
* Narrowing of aorta
70
New cards
Klinefelter Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* (47, XXY), (48, XXYY), (48, XXXY), and (49, XXXXY)
* Breast development because of the decrease in the production of testosterone
* Phenotypic features:
* Poor sexual development
* Very low fertility
* (47, XXY), (48, XXYY), (48, XXXY), and (49, XXXXY)
* Breast development because of the decrease in the production of testosterone
* Phenotypic features:
* Poor sexual development
* Very low fertility
71
New cards
Jacob Syndrome
### Aneuploidy
* (47, XYY)
* Criminal behavior with extra Y chromosome
* A more rare genetic condition compared to Klinefelter
* Phenotypic features:
* Above average height
* Suffered personality disorders
* Below normal intelligence
* (47, XYY)
* Criminal behavior with extra Y chromosome
* A more rare genetic condition compared to Klinefelter
* Phenotypic features:
* Above average height
* Suffered personality disorders
* Below normal intelligence
72
New cards
Triploidy
### Polyploidy
* Most common form
* Caused by fertilization of diploid gametes with haploid gametes
* 69 chromosomes
* 69, XXY (Klinefelter)
* 69, XXX
* 69, XYY (Jacob Syndrome)
* Most common form
* Caused by fertilization of diploid gametes with haploid gametes
* 69 chromosomes
* 69, XXY (Klinefelter)
* 69, XXX
* 69, XYY (Jacob Syndrome)
73
New cards
False. Structural defect = missing 1 arm in chromosome; Numerical aberrations = > or < the number of total chromosomes
(True or False): Structural defect refers to the more than or less than the number of total chromosomes, while numerical aberrations refers to the missing one arm in chromosome.
74
New cards
Inversion
It results when a **segment of a chromosome is excised** and then reintegrated in an orientation **180°** from the original orientation.
75
New cards
True
(True or False): In translocation, the same genes would be present despite the change in the position.
76
New cards
False, it should be **nullisomy**
(True or False): In monosomy, humans with this condition will **typically** **not survive**.
77
New cards
Cri-du-chat Syndrome
Which syndrome?
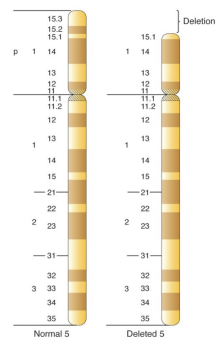
78
New cards
dup
Abbreviation for duplication
79
New cards
Reciprocal
### Translocation: Interchromosomal
Type of translocation that occurs when the chromosomal segments are exchanged **between two non-homologous chromosomes**
Type of translocation that occurs when the chromosomal segments are exchanged **between two non-homologous chromosomes**
80
New cards
False. Robertsonian forms a very **recognizable and long product** due to the merging happened in both **q arms**.
(True or False): In Robertsonian translocation, the product is short and unrecognizable due to the merging in both p arms.
81
New cards
Acrocentrics
The term for having both tiny short arms or p-arms
82
New cards
Tyrosine kinase
A type of protein that promotes proliferation in chronic myelogenous leukemia
83
New cards
C-myc
Linked to cell proliferation that causes metastasis or rapid growth of cancer cells
84
New cards
Aneuploidy
Phenotypic effects range from minor physical symptoms to devastating and lethal deficiencies in major organ systems.
85
New cards
Aneuploidy
There is **variation** in the amount of specific chromosomes inside a set
86
New cards
False, it is the **maternal age** since the integrity of primary oocytes decreases as the woman ages and maternal selection becomes less effective.
(True or False): Paternal age is the leading risk factor for autosomal trisomy.
87
New cards
False, it should be **Y chromosome**
(True or False): Early studies associate violent criminal behavior with the presence of extra X chromosome
88
New cards
True
(True or False): Addition of extra copies of either sex chromosome interferes with normal development and causes both physical and mental problems
89
New cards
* Errors in meiosis during **gamete** formation
* Events in **fertilization**
* Errors in **mitosis** following fertilization
* Events in **fertilization**
* Errors in **mitosis** following fertilization
**VARIATION IN COMPLETE SETS OF CHROMOSOMES**
Abnormalities in the number of haploid chromosomal sets can arise in several ways:
* Errors in meiosis during _______ formation
* Events in _______
* Errors in _______ following fertilization
Abnormalities in the number of haploid chromosomal sets can arise in several ways:
* Errors in meiosis during _______ formation
* Events in _______
* Errors in _______ following fertilization
90
New cards
Tetraploidy
There is a **DNA duplication but no cell division** (endomitosis), which results in **4n**.
91
New cards
Triploidy
There is a diploid cell that was fertilized by your chromosome, or diploid sperm cell that fertilized an egg
92
New cards
Chromosome aberration/mutation
Chromosomal disorders form a category of human genetic diseases, that are manifested by developmental and reproductive abnormalities, as well as playing an important role in the pathogenesis of malignancy
93
New cards
Inversion (inv)
Functional impacts include:
* Inhibit recombination in heterokaryotes, chromosomes displaying different orientation are expected to evolve independently and lead to distinct gene-expression patterns
* Have a role as disease-causing mutations by both directly affecting gene structure or regulation in different ways, and by predisposing to other secondary arrangements in the offspring of inversion carriers.
* Inhibit recombination in heterokaryotes, chromosomes displaying different orientation are expected to evolve independently and lead to distinct gene-expression patterns
* Have a role as disease-causing mutations by both directly affecting gene structure or regulation in different ways, and by predisposing to other secondary arrangements in the offspring of inversion carriers.
94
New cards
95
New cards
Burkitt Lymphoma
* **Overexpression** of the **proto-oncogene** leads to the disease
* A cancer with tumor that **grows in the jaw**
* Can be detected through FISH
* A cancer with tumor that **grows in the jaw**
* Can be detected through FISH
96
New cards
97
New cards
Robertsonian Translocation (rob)
* Only occur in (Human) Chromosome 13, 14 15, 21 and 22
* The ends of their short arms have similar repetitive DNA sequences that predispose their fusion
* The ends of their short arms have similar repetitive DNA sequences that predispose their fusion
98
New cards
Philadelphia Chromosome
* Chromosome 9 (ABL) and 22 (BCR)
* Not found in any nonleukemic WBC
* Not found in any nonleukemic WBC
99
New cards
Deletion (del) / Deficiency
* Lethal on Homozygous
* Zero (0) copy of the genes
* Usually Lethal (Heterozygotes)
* Results in zygotic loss, still birth, or infant death
\
* Zero (0) copy of the genes
* Usually Lethal (Heterozygotes)
* Results in zygotic loss, still birth, or infant death
\
100
New cards
Deletion (del) / Deficiency
* Critical for tumor suppressor gene