Managing Diversity in a Multicultural Workplace
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
Diversity
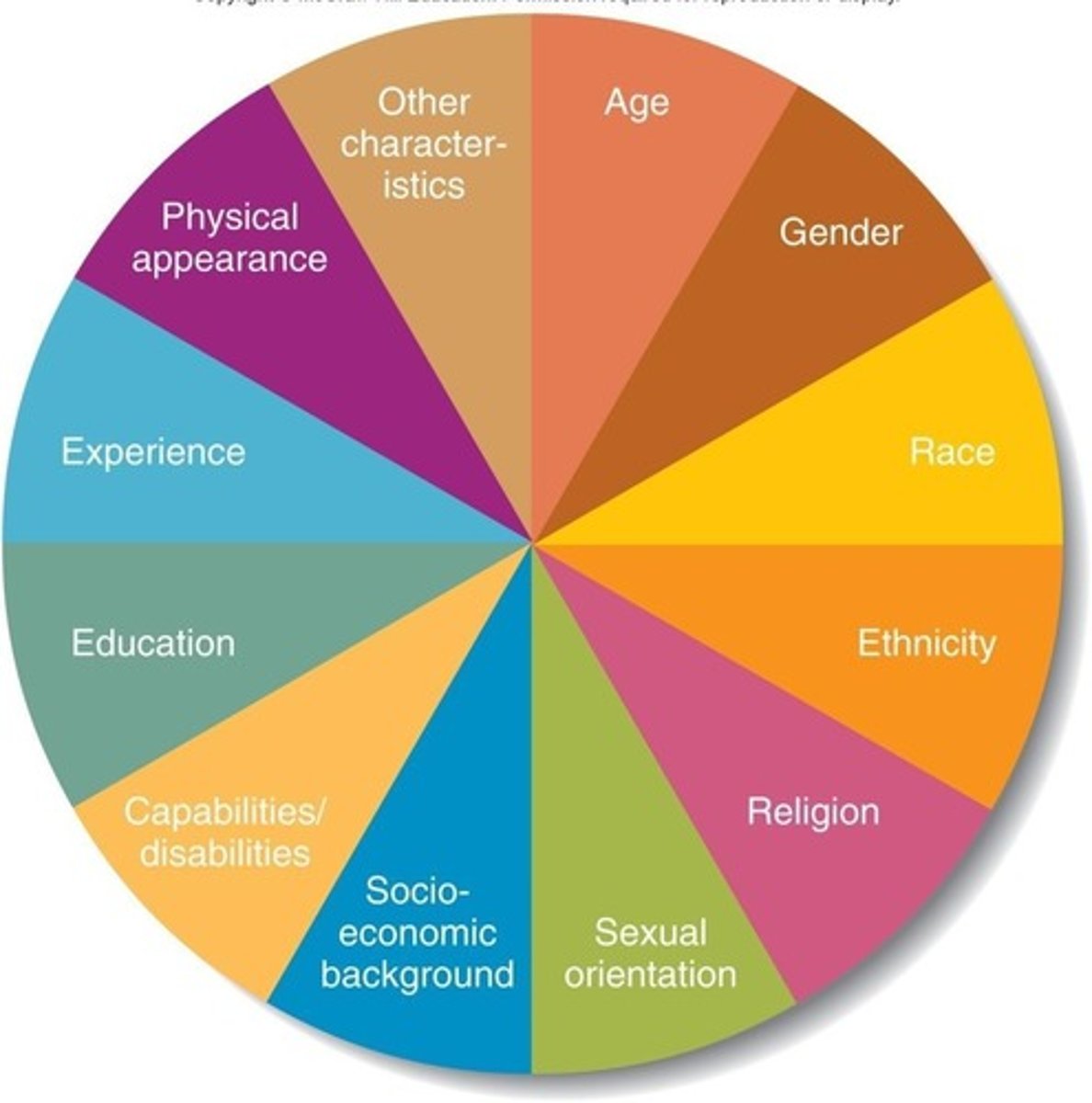
Dissimilarities or differences among people due to age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, socioeconomic background, education, experience, physical appearance, capabilities/disabilities, and any other characteristic that is used to distinguish between people.
Effective management of diversity
Both an ethical and a business imperative.
Sources of Diversity in the Workplace
Includes age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, socioeconomic background, education, experience, physical appearance, capabilities/disabilities.
Benefits of a Diverse Workforce
A variety of points of view and approaches to problems and opportunities can improve managerial decision making.
Creative Ideas from Diverse Employees
Diverse employees can provide a wider range of creative ideas.
Attunement to Diverse Customers
Diverse employees are more attuned to the needs of diverse customers.
Retention of Organizational Members
Diversity can increase the retention of valued organizational members.
Diversity Expectations
Diversity is expected/required by other firms.
Throughput in Diverse Teams
The extent to which team members understand one another and seamlessly build upon each other's contributions.
Positive Return on Investment
Refers to the financial benefits gained from effective diversity management.
Legal and Ethical Aspects of Diversity
Both legal and ethical considerations are important in managing diversity.
Inclusion in Diverse Teams
Truly diverse and inclusive teams welcome, preserve and leverage differences.
Assimilation of Minority Perspectives
Ensuring that those with minority perspectives do not assimilate to the dominant group's norms over time.
Managerial Decision Making
Improved by a variety of points of view from a diverse workforce.
Steps for Managing Diversity
List of actions managers can take to effectively manage diversity.
Sexual Harassment Forms
Identification of the two major forms of sexual harassment and methods for elimination.
Schemas and Perception
Can result in unfair treatment in the workplace.
Diversity and Organizational Performance
Diverse teams often outperform homogeneous teams.
Welcome and Preserve Differences
Key actions for managing diversity effectively.
Solicit and Leverage Uniqueness
Encouraging unique contributions from all team members.
Title VII of the 1964 CRA
This law, as amended in 1972, states that an employer cannot discriminate on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
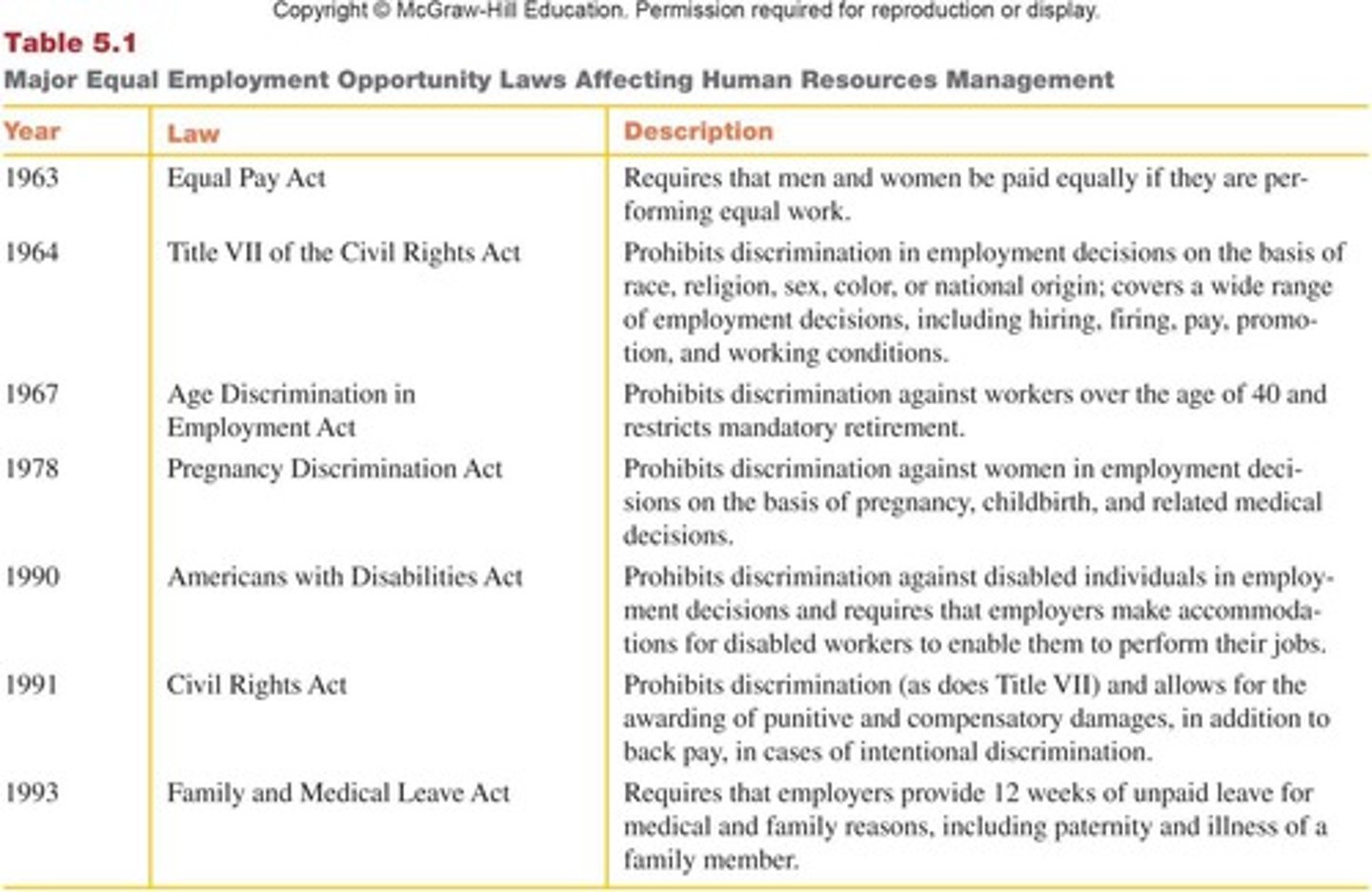
EEOC
Has the responsibility to administer and enforce the Civil Rights Law at work.
EPA of 1963 (amended in 1972)
States that it is unlawful to discriminate in pay on the basis of sex when jobs involve equal work, require equivalent skills, effort, and responsibility, and are performed under similar working conditions.
ADEA of 1967
Made it unlawful to discriminate against employees or applicants over the age of 40.
ADA of 1990
Prohibits employers with 15 or more workers from discriminating against qualified individuals with disabilities.
PDA of 1978
Prohibits using pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions to discriminate in any term or condition of employment.
FMLA of 1993
Requires that employers provide 12 weeks of unpaid leave for medical and family reasons, including paternity and illness of a family member.
Sexual Harassment
Unwelcome sexual advances is an example of this.
Aging U.S. Population
Median age in the United States is 38.8 years; by 2060, 24% of the population will be over 65.
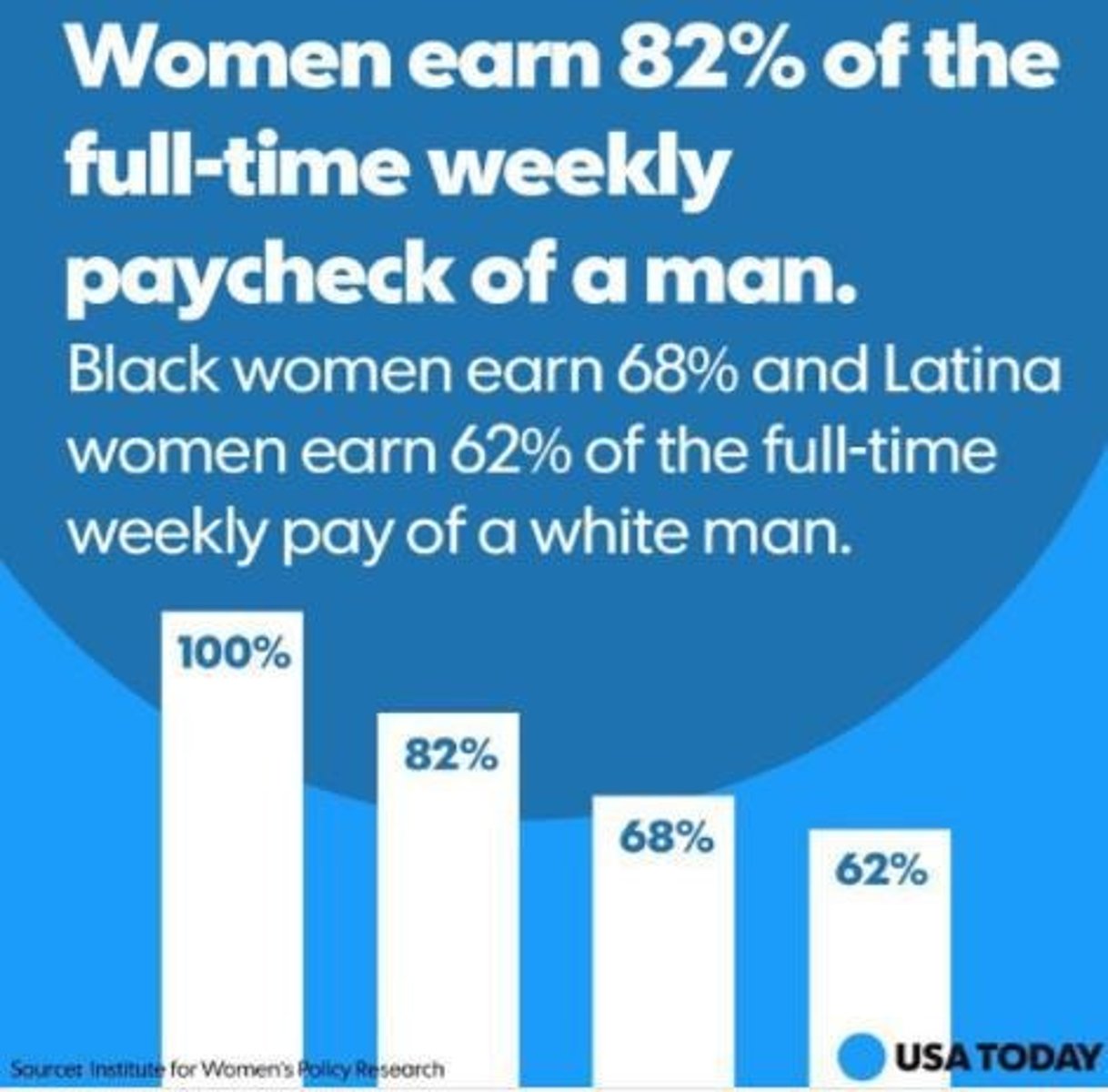
Women in the Workplace
U.S. workforce is 44.8% female; women's median weekly earnings are $843 compared to $1022 for men.
Corporate Officer Positions
Women hold only 26.5% of corporate officer positions in S&P 500 companies.
Top Earners in Companies
11% of top earners in these companies are women.
Glass Ceiling
A metaphor alluding to the invisible barriers that prevent minorities and women from being promoted to top corporate positions.
Census Bureau Races
American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian Indian, Black, African American, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, Other Asian, Native Hawaiian, Guamanian or Chamorro, Samoan, Other Pacific Islander, White, and other races.
U.S. Census Bureau Ethnicity
Treats ethnicity in terms of whether a person is Hispanic, Latino, or of Spanish origin or not.
Hispanic Identification Preference
Most Hispanics prefer to be identified by their country of origin.
Accommodation for Religious Beliefs
Includes scheduling of critical meetings, providing flexible time off for religious observances, and posting holy days for different religions on the company calendar.
Disability Issues
Involves providing reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities, promoting a nondiscriminatory workplace environment, and educating the organization about disabilities and AIDS.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Legislation enacted in 1990 aimed at preventing discrimination against individuals with disabilities.
Socioeconomic Background
Refers to a combination of social class and income-related factors.
Socioeconomic Diversity
Requires that managers be sensitive and responsive to the needs and concerns of individuals who might not be as well off as others.
Sexual Orientation Issues
Includes employment and workplace discrimination and provision of same-sex partner benefits.
Protections Against Employment Discrimination
Legislation aimed at preventing discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity.
Physical Sources of Diversity
Refers to whether individuals are attractive or unattractive, thin or overweight, which often has no bearing on job performance.
Influence of Physical Diversity
Sometimes physical sources of diversity end up influencing advancement rates and salaries.
Critical Managerial Roles
Managers can take steps to become sensitive to the effects of diversity, leverage contributions from diverse employees, and prevent unfair treatment.
Procedural Justice
A moral principle calling for the use of fair procedures to determine how to distribute outcomes to organizational members.
Distributive Justice
A moral principle calling for fair distribution of pay, promotions, and other organizational resources based on meaningful contributions that individuals have made and not personal characteristics over which they have no control.
Perception
The process through which people select, organize, and interpret what they see, hear, touch, smell, and taste to give meaning and order to the world around them.
Schema
An abstract knowledge structure stored in memory that allows people to organize and interpret information about a person, event, or situation.
Gender Schema
Preconceived beliefs or ideas about the nature of men and women, their traits, attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
Ethnocentrism
The moral principles and beliefs held by a society or group.
Stereotype
A fixed general image of a particular person or group; the belief that everyone in that group has the same characteristics.
Values
May be positive or negative but an overgeneralization.
Prejudice
May be a result of stereotyping, and is a deeply felt negative feelings associated with a group.
Scripts
A sequence of events that help us act within a culture.
Discrimination
An expression of racism, consisting of acts or behavior against people of another group.
Racism
A belief in the inherent superiority of one race due to genetics or biology.
Etiquette
A set of rules, manners, and customs for polite behavior in a society or group.
Overt Discrimination
Knowingly and willingly denying diverse individuals access to opportunities and outcomes in an organization.
Forms of Sexual Harassment
Harassment on the basis of sex when such conduct substantially interferes with a person's work performance or creates an intimidating, hostile, or offensive work environment.
Quid pro quo
Unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature. Asking for or forcing an employee to perform sexual favors in exchange for receiving some reward or avoiding negative consequences.
Hostile work environment
A work setting where intimidation, insults, and ridicule are sufficiently severe and repetitive to alter working conditions.
Sexually oriented remarks
Comments about someone's personal appearance that are sexual in nature, contributing to an unpleasant work environment.
Lewd jokes
Inappropriate humor of a sexual nature that contributes to a hostile work environment.
Displaying pornography
Showing sexually explicit material in the workplace, which can create a hostile work environment.
Management approaches to address sexual harassment
Strategies including instructional/educational methods, raising awareness, training, and legal procedures.
Corrective action
Steps taken to address and rectify incidents of sexual harassment once they have been confirmed.
Sexual harassment policy
A formal statement developed and communicated by management to prevent and address sexual harassment.
Fair complaint procedure
An equitable process for investigating charges of sexual harassment.
Sexual harassment education and training
Programs provided to all organizational members to inform them about sexual harassment and prevention strategies.
Communication of policy
The act of informing new employees about the sexual harassment policy and periodically reviewing it with current employees.
Alternative reporting methods
Options provided to employees for reporting incidents of sexual harassment without fear of retaliation.
Protection of reporting employees
Ensuring that employees who report sexual harassment have their rights safeguarded.
Confidentiality of allegations
The principle that allegations of sexual harassment should be kept private.
Timely investigations
The necessity for investigations of harassment charges to proceed without unnecessary delays.
Protection from third-party harassment
Managers' responsibility to safeguard employees from sexual harassment by non-employees.
Employees as victims
Individuals who may be affected by unwanted sexual attention in the workplace.
Delayed complaints
The phenomenon where employees wait before filing complaints regarding sexual harassment.
Familiarity with policy
The requirement for suppliers and customers to be aware of a firm's sexual harassment policy.
Documentation/Reporting guidelines
Instructions and standards outlining how incidents of sexual harassment should be documented and reported.
Legal Procedures
The formal processes involved in addressing sexual harassment claims, including punitive measures and grievance processes.
Management recommendations
Suggestions made by management to improve the handling of sexual harassment and diversity in the workplace.
Programs/Projects/Initiatives
Organizational efforts aimed at addressing sexual harassment and promoting diversity.
Secure top management commitment
A step in managing diversity effectively that involves obtaining the support and involvement of senior leadership.
Increase the accuracy of perceptions
A step in managing diversity that focuses on improving how individuals perceive each other within the organization.
Increase diversity awareness
A step aimed at enhancing understanding and recognition of diversity within the workplace.
Increase diversity skills
A step that involves developing the skills necessary to work effectively in a diverse environment.
Encourage flexibility
A step that promotes adaptability among organizational members to accommodate diverse perspectives.
Pay close attention to how organizational members are evaluated
A step that emphasizes the importance of fair evaluation processes in managing diversity.
Consider the numbers
A step that involves analyzing demographic data to inform diversity management strategies.
Empower employees to challenge discriminatory behaviors
A step that encourages staff to confront and address discrimination in the workplace.
Reward employees for effectively managing diversity
A step that recognizes and incentivizes individuals who contribute positively to diversity efforts.
Provide training utilizing a multi-pronged, ongoing approach
A step that involves continuous and varied training methods to enhance diversity management skills.
Encourage mentoring of diverse employees
A step that promotes the guidance of diverse individuals by more experienced members of the organization.
Diversity Awareness Programs
Programs designed to educate members about diversity and promote understanding of different perspectives.
Uncover personal biases and stereotypes
An objective of diversity awareness programs aimed at revealing individual prejudices.
Assess personal beliefs, attitudes, and values
A process involved in diversity awareness programs to evaluate one's own perspectives.
Develop an atmosphere in which people feel free to share their differing perspectives
An objective of diversity programs that fosters open communication among members.
Improve understanding of others who are different
A goal of diversity awareness initiatives that seeks to enhance empathy and knowledge of diverse groups.