CH 25: Evolutionary Biology: From Origin of Life to Mass Extinctions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the difference between punctuated equilibrium and gradualism in speciation?
Punctuated equilibrium suggests rapid speciation followed by stasis, while gradualism proposes that speciation occurs gradually over time.
What are the major evolutionary events that characterize macroevolution?
Macroevolution involves broad patterns of evolution above the species level, dramatic changes over long time spans, and the cumulative effects of many speciation and extinction events.
What was the estimated age of the Earth and the earliest fossils?
The Earth is estimated to be 5 billion years old, with the earliest fossils of bacteria dating back 3.5 billion years.
What conditions characterized the early Earth environment?
The early Earth had no oxygen, a hot atmosphere with escaping gases, a solidifying crust, and was bombarded by meteors.
What is the composition of the modern atmosphere?
The modern atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% argon, with small amounts of carbon dioxide and water vapor.
What did Stanley Miller's experiment demonstrate?
Miller's experiment showed that organic compounds, including amino acids, could form under conditions similar to those of early Earth.
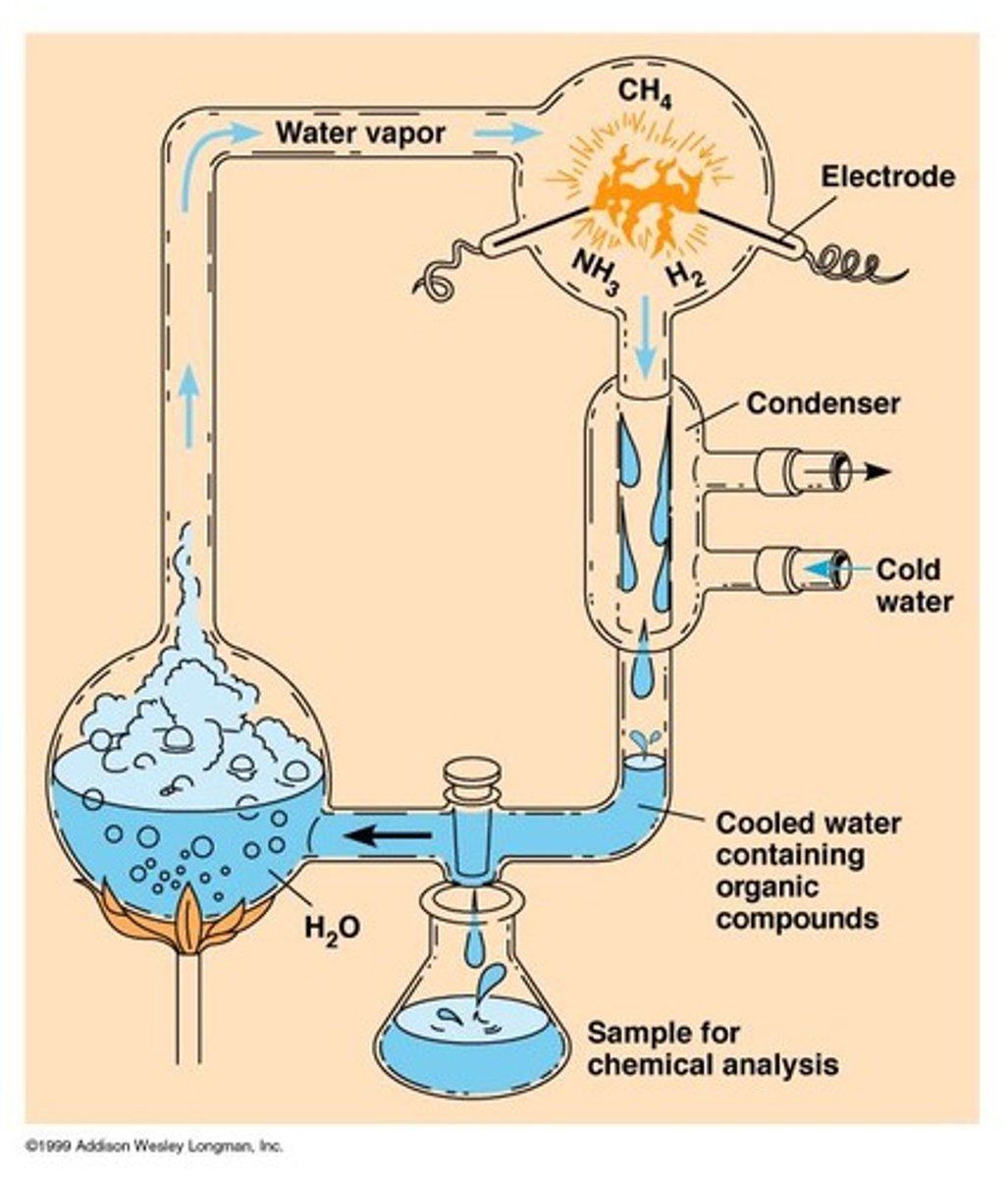
What role do hot volcanic vents play in the origin of life?
Hot volcanic vents mix hydrogen and sulfide, providing energy for the formation of organic compounds, independent of light.
What evidence suggests that ribosomes and transfer RNA have a common ancestor?
All ribosomal RNAs show similar anatomy, and transfer RNAs also exhibit similarities, indicating a common evolutionary origin.
What are the characteristics of the first living cells?
The first living cells had a boundary to separate from the environment, enzymes for energy extraction, RNA for controlling enzyme activity, and a genetic code.
How did early life forms affect the environment?
Early heterotrophic cells did not use oxygen for respiration and obtained energy through glycolysis or fermentation, while autotrophs evolved to use light energy.
What was the impact of photosynthesis on Earth's atmosphere?
Photosynthesis produced oxygen as a waste product, which allowed the evolution of aerobic organisms and changed the food chain.
What is the endosymbiotic theory regarding mitochondria and chloroplasts?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought to be free-living prokaryotes that became symbiotic with eukaryotic cells, evidenced by their unique DNA.
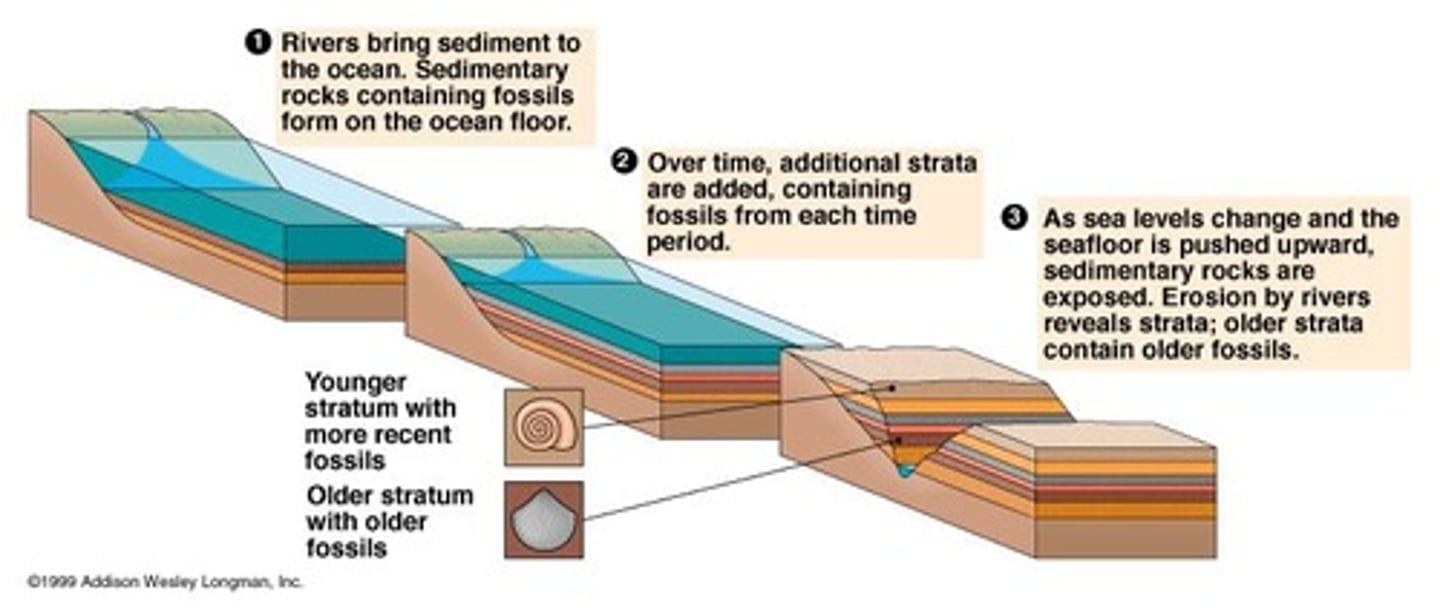
What are fossils and how do they form?
Fossils are remains or imprints of past life preserved in sediments, forming through processes like weathering of rock.
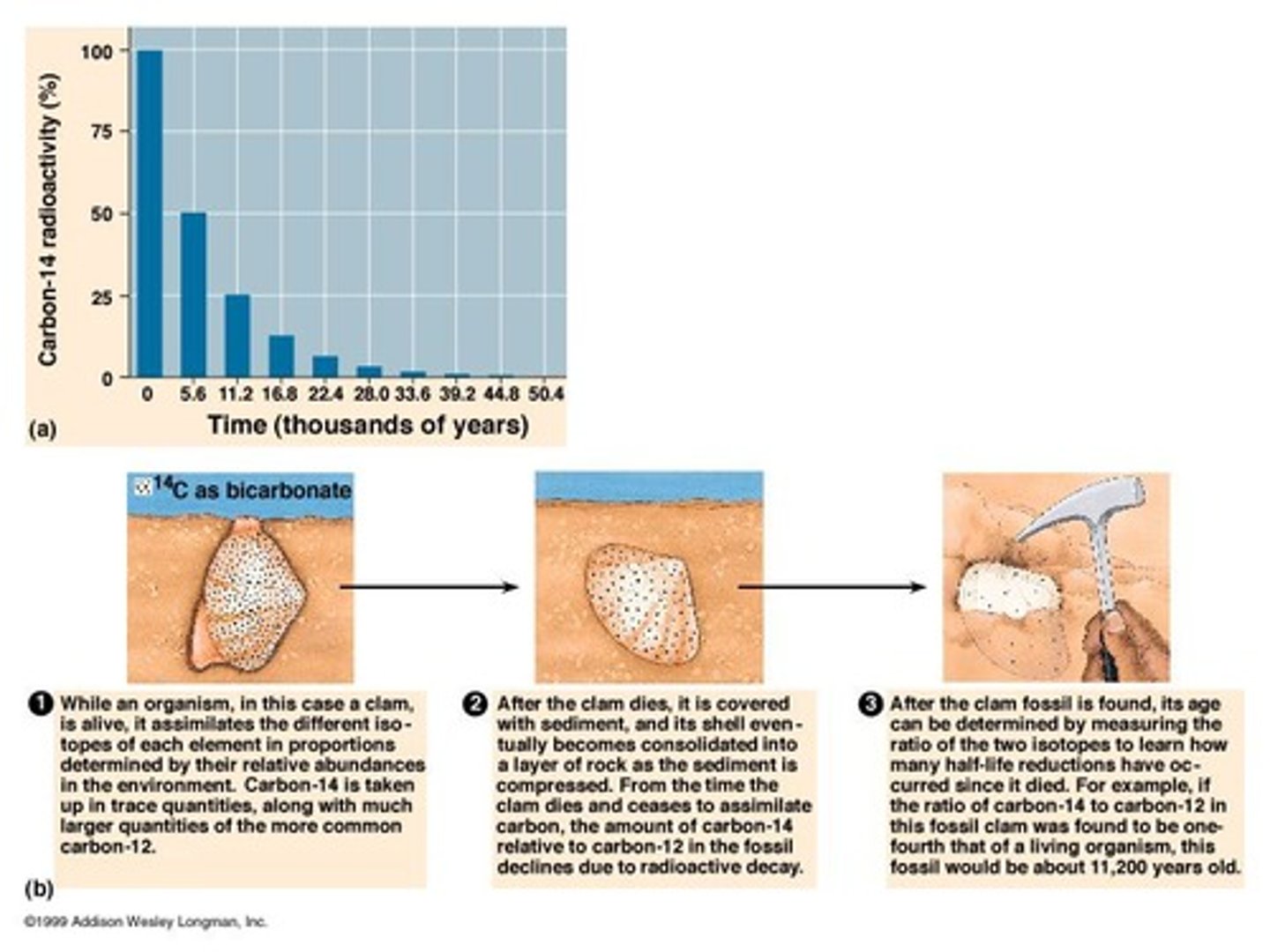
What does radiocarbon dating measure?
Radiocarbon dating measures the age of fossils based on the decay of carbon-14 isotopes.
What is the significance of the fossil record in understanding evolution?
The fossil record shows the order of appearance of organisms, with more complex forms appearing after simpler ones, and indicates extinction events.
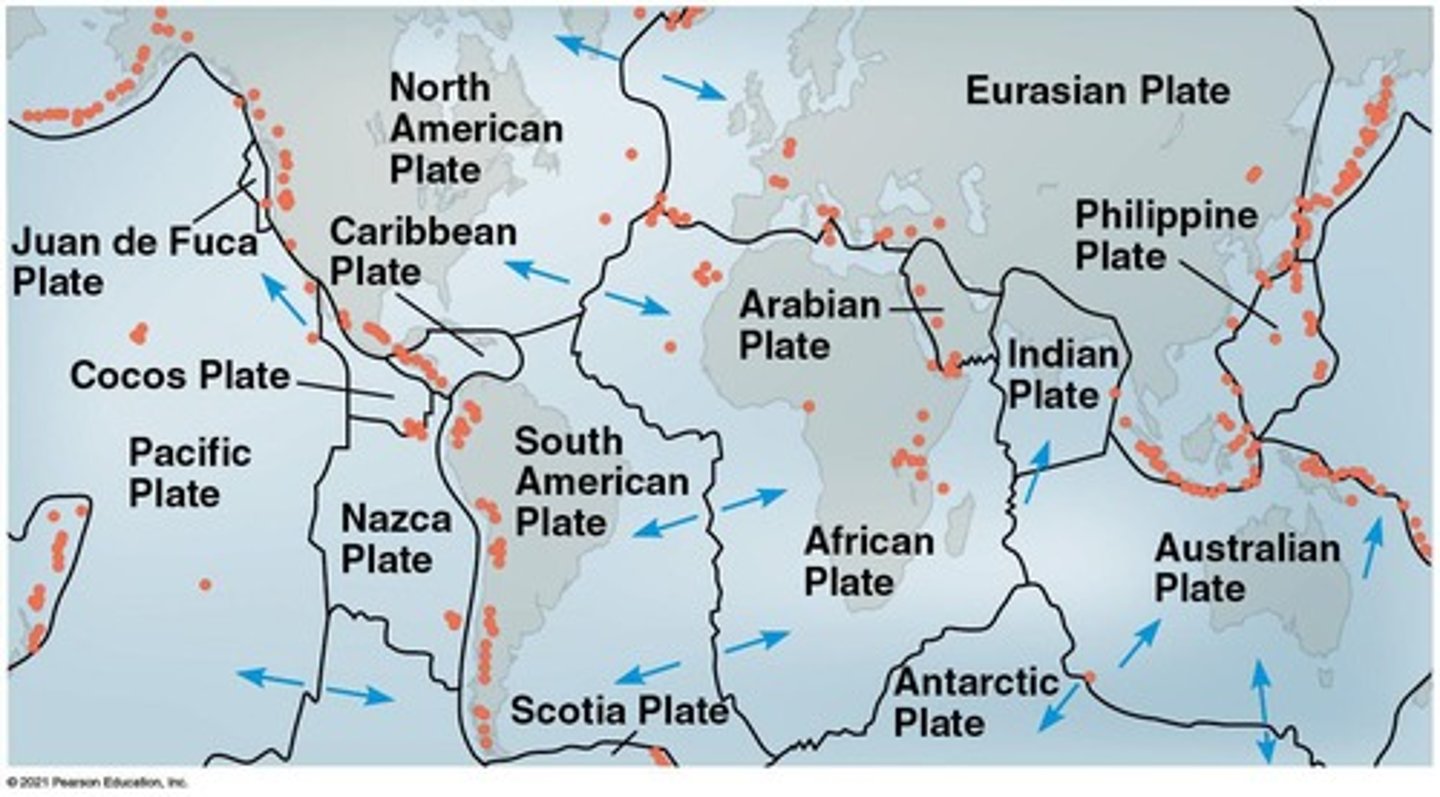
What is plate tectonics and how does it relate to the history of life?
Plate tectonics theorizes that Earth's crust is made of plates that drift, causing continental drift and influencing species distribution and evolution.
What are mass extinctions and their consequences?
Mass extinctions eliminate a large number of species, paving the way for adaptive radiations and the emergence of new groups of organisms.
What is adaptive radiation?
Adaptive radiation is a period of rapid evolutionary change where new species evolve to fill ecological niches.
How can adaptive radiation occur in response to environmental changes?
Adaptive radiation can occur through colonization of new regions with few competitors or the evolution of novel characteristics that exploit new resources.
What evidence supports the theory of evolution through natural selection?
Fossils show consistent distribution throughout strata, and the order of fossil appearance indicates evolutionary changes over time.
What is the significance of the Galapagos finches in studying evolution?
The Galapagos finches demonstrate adaptive radiation, with 14 species evolving from a common ancestor in a short time.
What are some hypotheses for the origin of life?
Hypotheses include the Miller-Urey experiment, hydrothermal vents, and meteorite origins of organic compounds.
What are the main differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes and specialized organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures.
What is the role of developmental genes in evolution?
Changes in the sequences and regulation of developmental genes can lead to significant evolutionary changes.
What is the impact of climate change on modern species?
Climate change poses threats to species survival, potentially leading to modern extinction events similar to historical mass extinctions.