ABD and Preg
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
vitals w/ pulse ox, O2, IV, NPO; maybe fluids, EKG, NG tube
Shotgun orders for abdominal complaints
Last meal/drink/bowel movement/micturition, previous abd surgeries, similar episodes, sexual hx (LMP)
Pertinent hx for abdominal pain needs to include
rectal exam with stool guaiac and GU (pelvic or testicular)
All abdominal exams require a ___________________ (unless it’s like a slam dunk)
Acute abdomen
45 y/o patient presents to the ED for sudden onset 10/10 abdominal pain. They said that they were doing nothing when it started. On physical exam you note severe diffuse tenderness with involuntary guarding and rigidity. Peritoneal signs are positive. This is a red flag for what condition?
hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, hepatomegaly, PUD, pancreatitis, retrocecal appendicitis, cardiac pain, pneumonia, PE, pancreatitis
DDX for RUQ pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
Gastritis, PUD, pancreatitis, cardiac, pneumonia, PE
DDX for LUQ pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
Gastritis, PUD, pancreatitis, gastroparesis, cardiac, pneumonia, PE, AAA
DDX for MEQ pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
Appendicitis, IBD, PUD, mittelschmerz, ovarian cyst/torsion, TOA, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, ectopic preg, orchitis, testicular torsion, prostatitis, ureterolithiasis, mesenteric adenitis, hernia
DDX for RLQ pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
Diverticulitis, IBD, PUD, mittelschmerz, ovarian cyst/torsion, TOA, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, ectopic preg, orchitis, testicular torsion, prostatitis, ureterolithiasis, mesenteric adenitis, hernia
DDX for LLQ pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
Cystitis, hernia, PID, preg, prostatitis, ovarian cyst/torsion, testicular torsion
DDX for Suprapubic pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
ureterolithiasis, pyelonephritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, AAA, M/S pain
DDX for back/flank pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
AAA, cardiac, pancreatitis, DKA, bowel obstruction, hollow organ perf, intra-abdominal hemorrhage, IBS, gastroenteritis, sickle cell crisis, mesenteric ischemia, IBD, marijuana hyperemesis, cyclical vomiting syndrome
DDX for diffuse or any quadrant pain - think anatomically, physiologically, and by process
CBC, CMP, Lipase, Preg, UA; Maybe blood cultures, lactic, Cardiac, coags, fingerstick, ABG/VBG, STD testing, type and cross, EtOH, urine tox, urine culture and sensitivity
What labs you want for abdominal stuff?
acute abdominal series, bedside (me)/formal (U/S tech and radiologist read) U/S, CT with contrast, MRI
Imaging for abdominal pain
FAST exam
A bedside U/S that is used to identify free fluid - used for blunt/penetrating chest trauma, trauma in preg, pediatric trauma, undifferentiated hypotension, undifferentiated abd pain
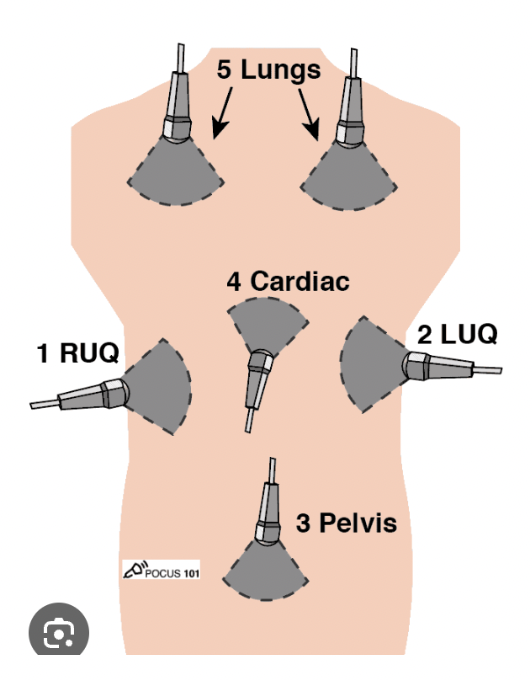
heart, RUQ, LUQ, pelvis, chest and lung viscera
What areas does the eFAST exam look at?
hematemesis or blood per the NG = Upper
How do you determine if a GI bleed is upper or lower?
Blood products if SBP under 100/HR over 100, 2 giant IVs, correct coagulopathies, 1 g ceftriaxone, PPI bolus, Octreotide bolus then drip (varices), punt to ICU
Treatment plan for GI bleeds

trauma (results in massive bleeding)
Solid organ rupture is caused by
excessive dilation, infection, acid/base erosion, trauma (bleeding → infection → sepsis)
Hollow organ rupture is caused by (often the end result of acutely evolving situation)
Hollow organ rupture
If a patient presents with progressing severe abdominal pain that suddenly improves only to worsen with a fever, this is a red flag for
IV fluids, Abx, vasopressors if in shock, pain management, surgery; maybe NG or catheter
Treatment plan for hollow organ rupture - ideally we avoid this
Ischemic bowel disease (AKA the reason we might get a lactic)
An acute/chronic ischemia of the intestines that is caused by an acute embolism, vascular disease, or decreased cardiac output
pain is outta proportion to exam
Red flag for Ischemic bowel disease
surgical re-vascularization/necrotic debriedment
Treatment plan for Ischemic bowel disease
pregnant
Say it with me now, All females of childbearing age with abdominal pain are _______________ until proven otherwise
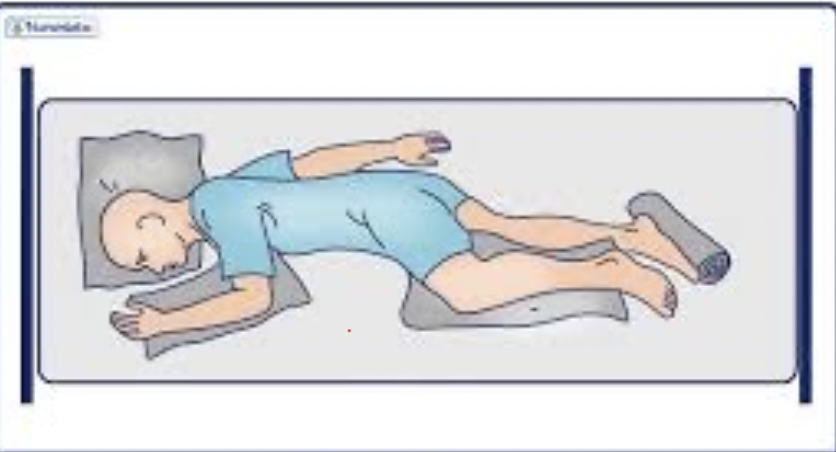
Semi-left lateral decubitus (AKA SIMs)
What position can be used to minimize vena cava compression in a pregnant patient?
the increase in plasma and blood volume (up resuscitation by 50%)
When giving pregnant patients fluids, what do we need to account for?
R/o spontaneous abortion, FAST exam (check for blood outside the uterus), vaginal U/S (fetal activity and HR), hcg QUANT, CBC, type and screen, antibody screen, UA, RhoGAM (if Rh neg), D/c with close OB followup
23 y/o female presents to the ED for vaginal bleeding, she is 18 weeks pregnant. What do we need to do?
FAST exam, hcg QUANT, CBC, type and screen, antibody screen, UA, RhoGAM (if Rh neg), Vaginal U/S (determines if we can do a pelvic safely), ADMIT
23 y/o female presents to the ED for vaginal bleeding, she is 24 weeks pregnant. What do we need to do?
abruptio placentae, placenta previa, vasa previa
When doing a vaginal U/s in a 20+ week pregnant patient with vaginal bleeding, what are we hoping to r/o?
Bedside fast, vaginal U/S, sterile pelvic AFTER vaginal u/s to identify injury, bleeding, or amniotic fluid leakage, RhoGAM (if Rh neg), admit
28 y/o pregnant female presents to the ED after being involved in an MVC. She is 26 weeks. What are we doing team?
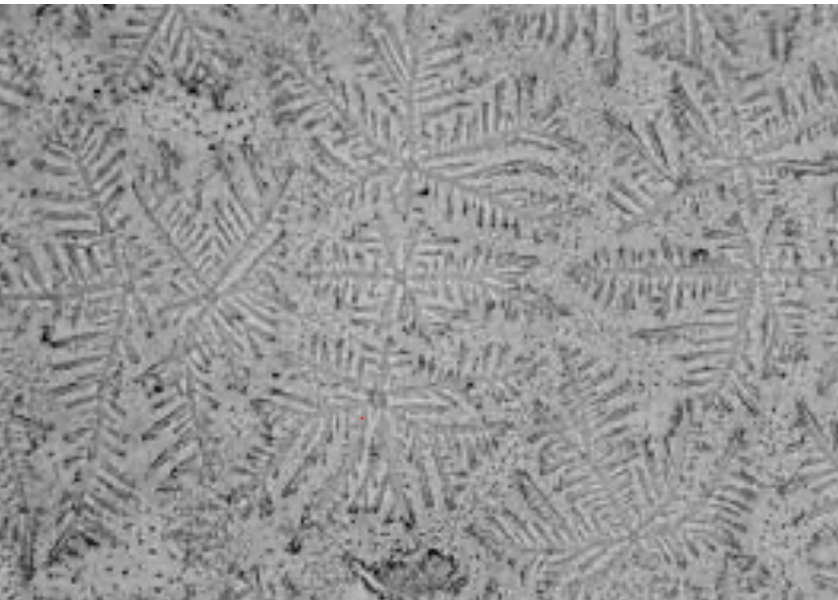
nitrazine paper pH strip, ferning
How can we tell the difference between blood and amniotic fluid?
Preeclampsia
Hypertension (over 140/80) when 20+ weeks gestation + new onset proteinuria or sudden increase OR development of HELLP syndrome
hemolysis, elevated LFTs, low platelets
HELLP syndrome includes
Punt to OB and discharge
Treatment plan for mild Preeclampsia

labetalol, hydralazine, nifedipine, IV mag, admit to a high risk pregnancy center
Treatment plan for severe Preeclampsia (SBP over 160)

delivery
Definitive treatment for Preeclampsia

Eclampsia
New onset seizures with preeclampsia in a women between 20 weeks gestation and 4 weeks postpartum
labetalol, hydralazine, nifedipine, IV mag, emergent delivery (consult OB)
Treatment plan for Eclampsia
get extra hands you have 2 patients, try to get patient to OB or call them to the ED, get mom and baby on the monitor, IV fluids expeditiously, prepare the perineum by cleaning with mild soap, water, and iodine swabs, displace shoulders inferiorly, keep the cord patent until OB arrives, keep baby even with mom
Pro tips for catching a baby in the ED
imminent delivery
Complete cervical effacement and the fetus is at the vaginal introitus (crowning)
multiple sexual partners, hx of STI/PID, hx of sexual abuse, IUD insertion within the previous month, frequent vaginal douching, , adolescence, Young adult, Lower SES, post-abortion
Risk factors for PID
Ectopic pregnancy (more likely), Tubal factor infertility is increased by 12-50%, increased risk of borderline ovarian tumors, Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (perihepatitis), Tubo-ovarian abscess (late complication)
Complications of PID
analgesics (NSAIDs), control emesis and fever, fluid replacement, Broad spectrum abx (Inpatient: cefotetan/Cefoxitin + doxy OR Clinda + gentamicin OR ampicillin/sulbactam + doxy; Outpatient: ceftriaxone/Cefoxitin and probenecid OR 3rd CPH + doxy with or w/o metro; Levofloxacin/ofloxacin with or w/o metro)
24 y/o female presents to the ED for crampy, dull abdominal pain. She notes that over the last couple of days she’s had some wack vaginal discharge sometimes with blood. Her boyfriend was recently treated for chlamydia but she “never had any symptoms so.” Vitals are stable with the exception of a fever. On physical exam you note lower abdominal tenderness (AKA uterine/adnexal tenderness) and cervical motion tenderness with mucopurulent secretions . What is your treatment plan?