Apes Unit 4: Module 19-23 Test
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
core
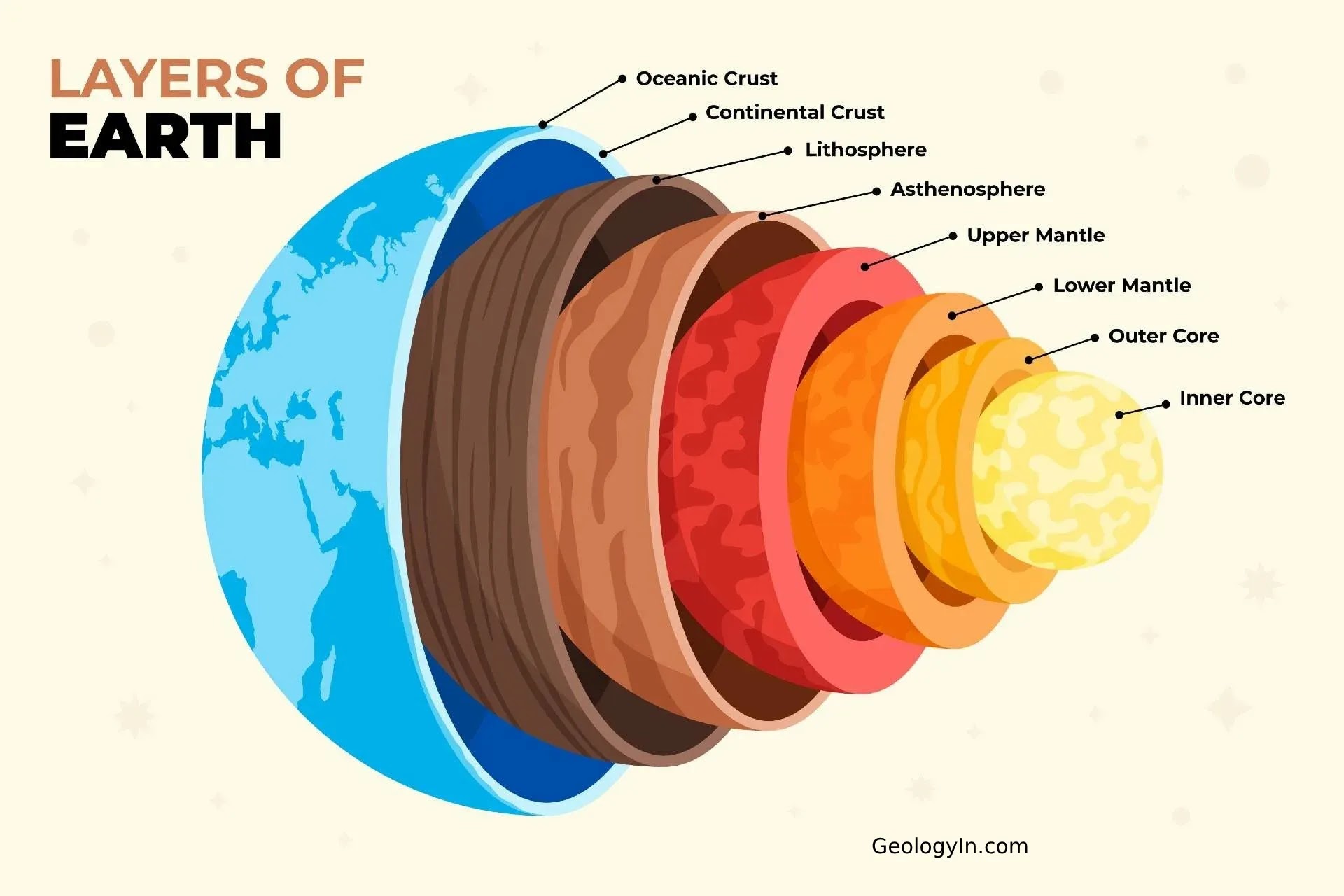
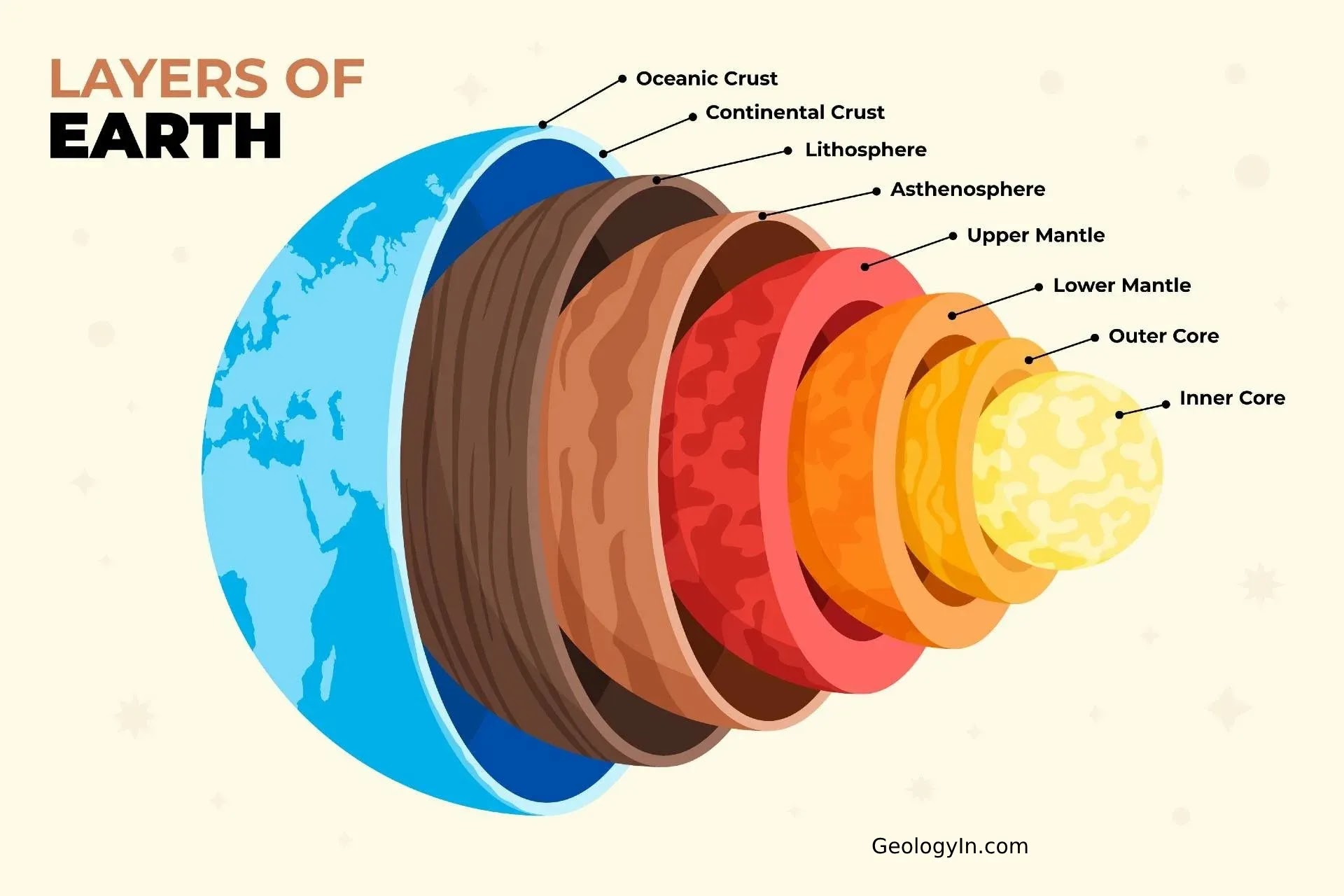
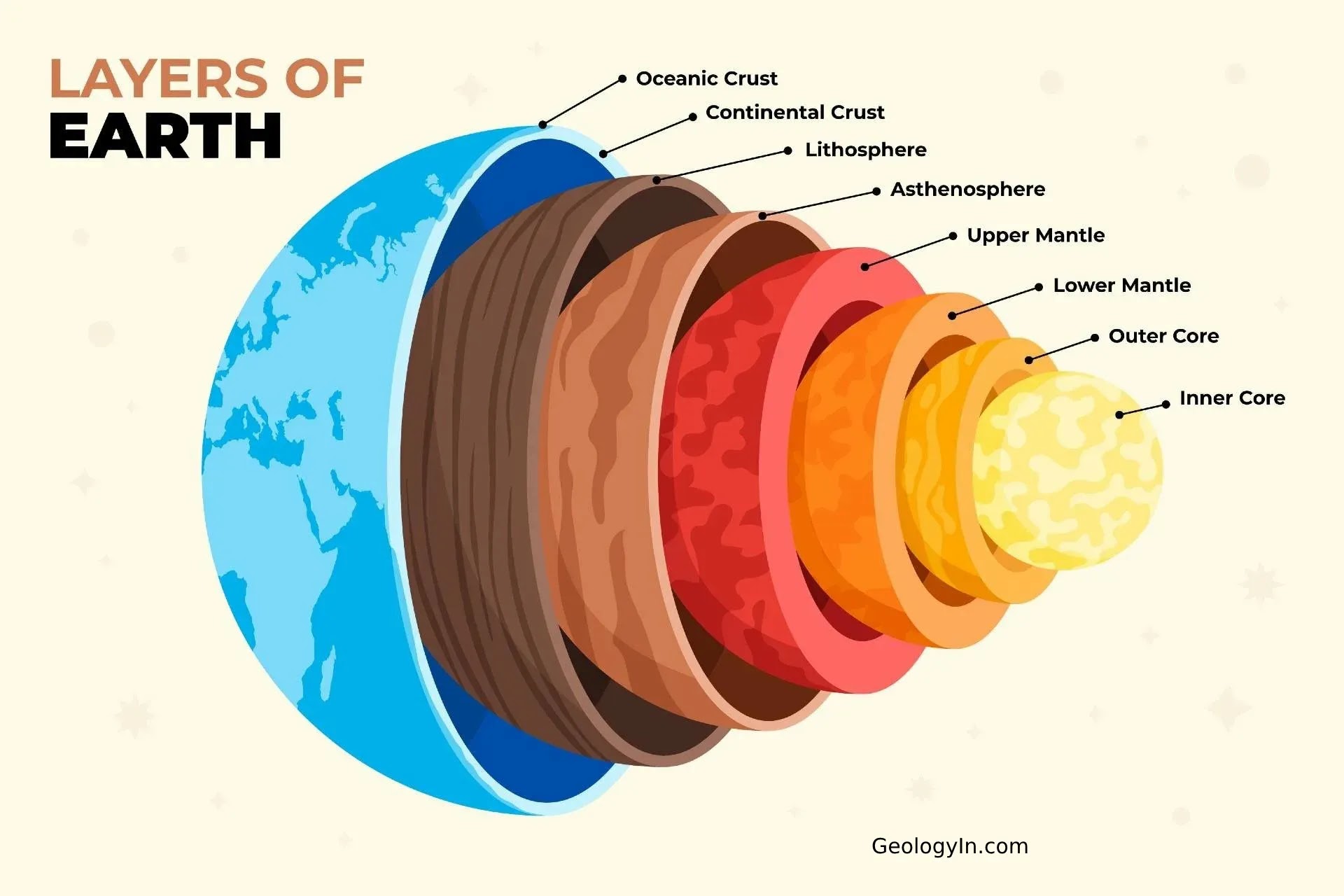
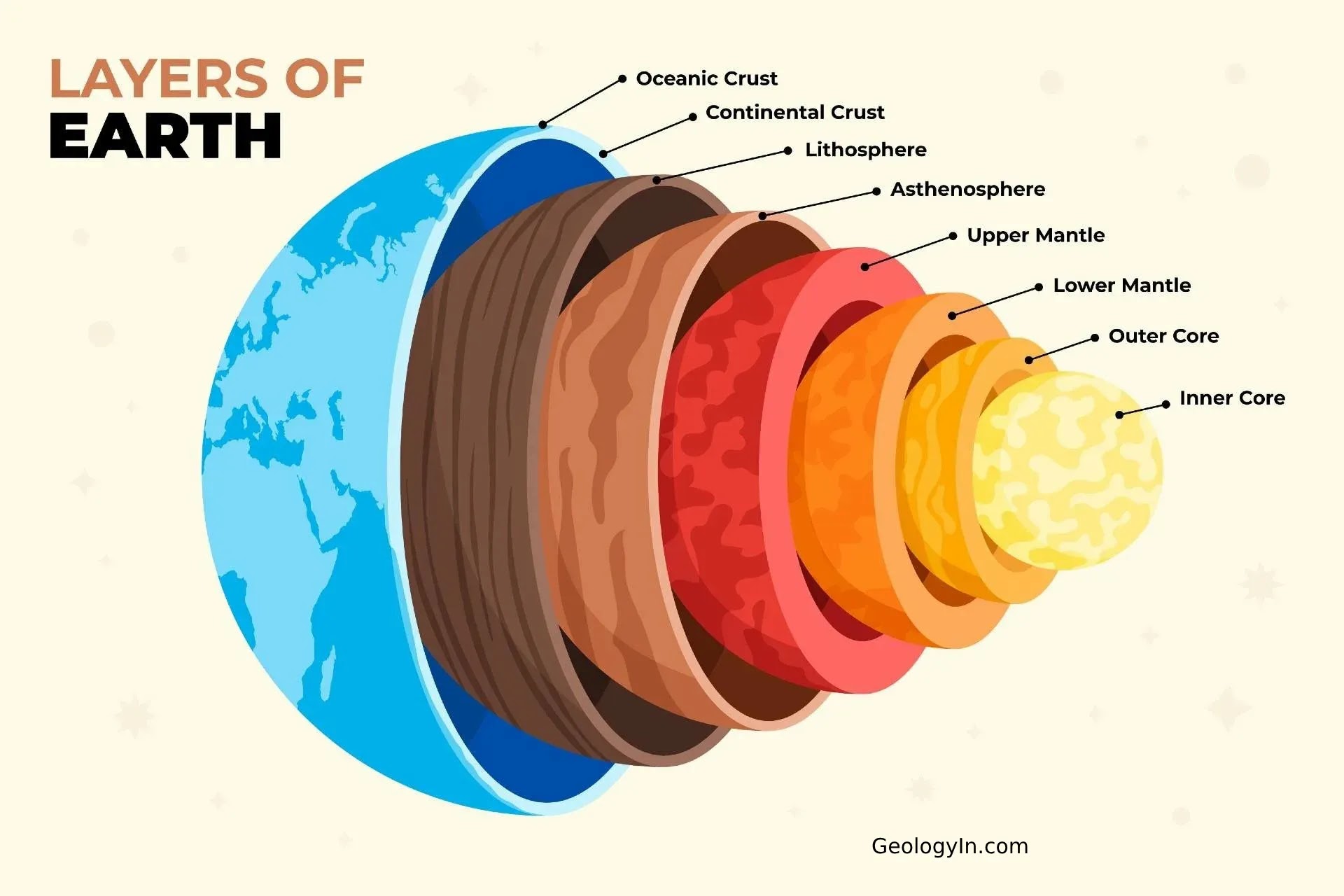
the innermost zone of earth’s interior, composed mostly of iron and nickel. It includes a liquid outer layer and a solid inner layer and releases mass amounts of heat
mantle
the layer of earth above the core, containing magma, the asthenosphere, and solid upper mantle
magma
molten rock
asthenosphere
the layer of earth located in the outer part of the mantle, composed of semi-molten rock (beneath the lithosphere)
lithosphere
the outermost layer of earth, including the solid upper mantle and crust
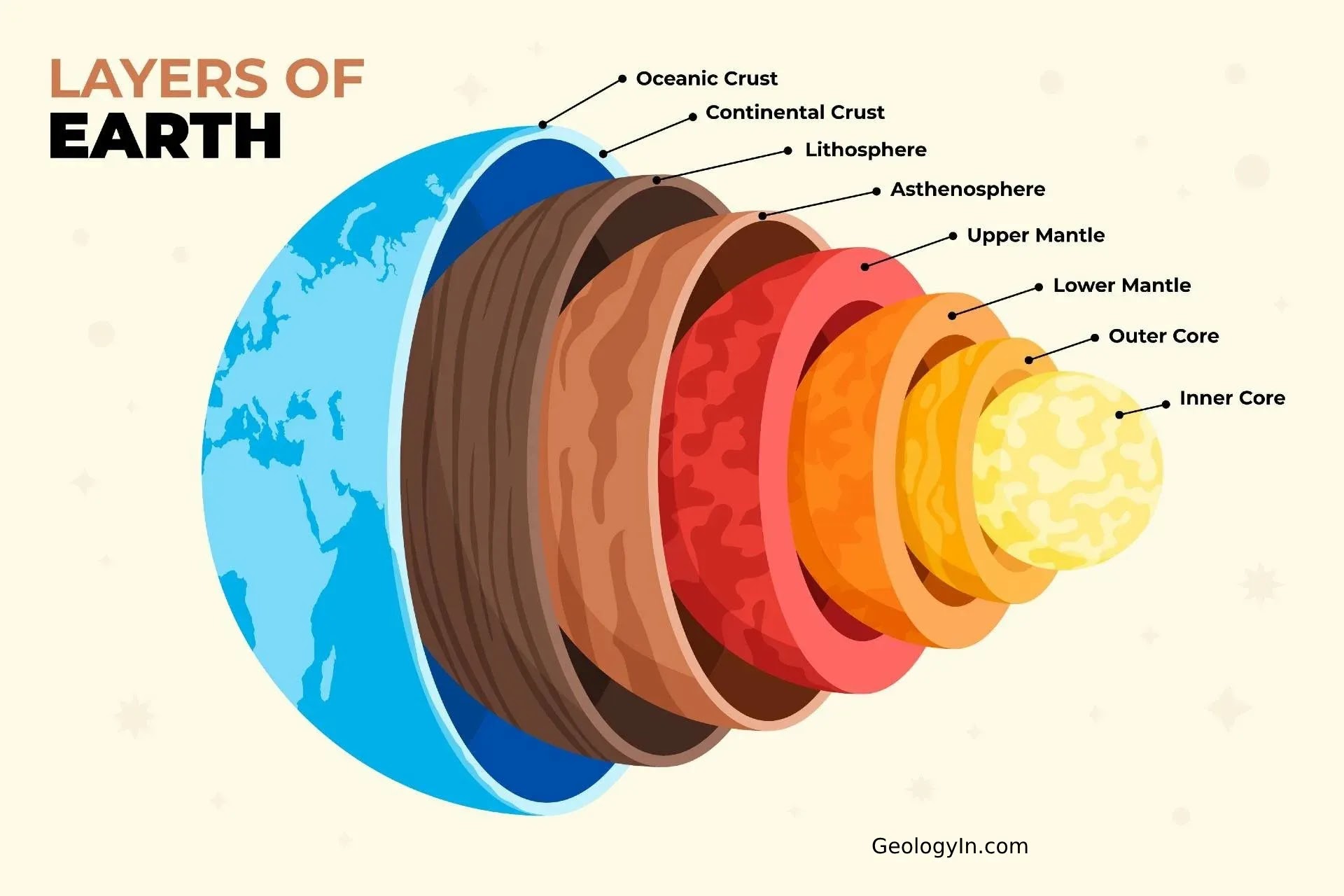
plate tectonics
the theory that the lithosphere of earth is divided into plates, most of which are in constant motion
earthquake
a sudden movement of earth’s crust caused by a release of potential energy from the movement of tectonic plates
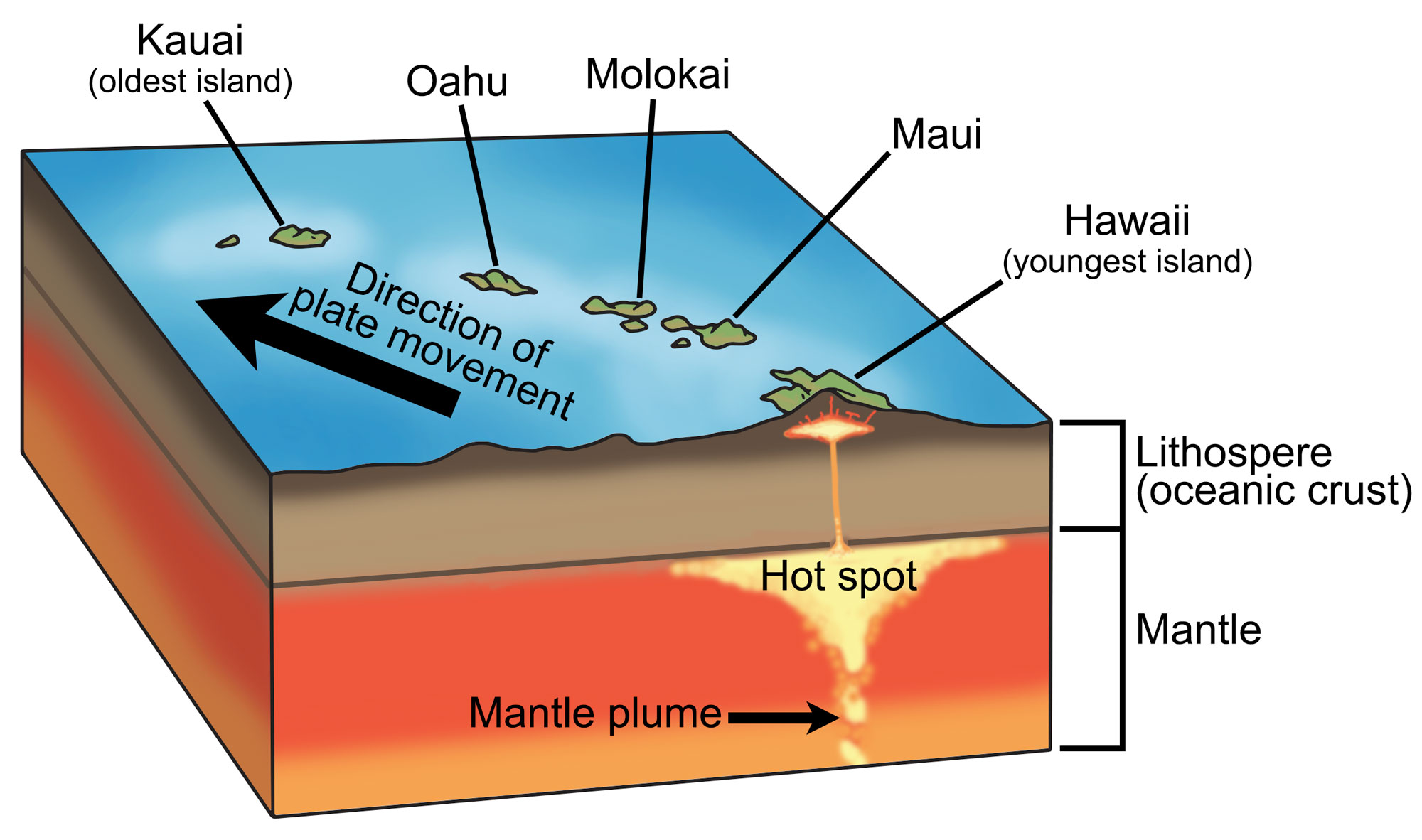
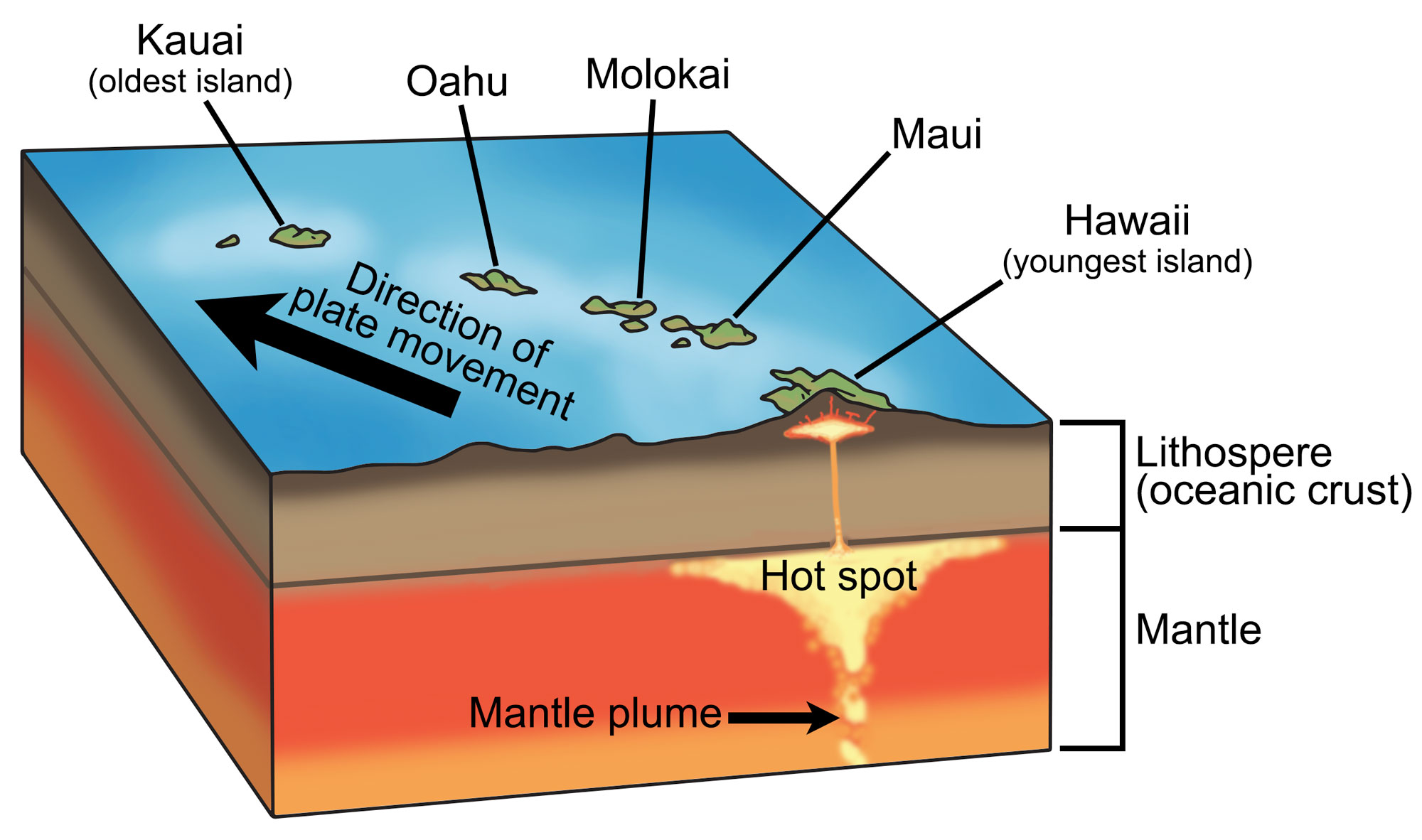
hot spot
in geology, a place where molten material from earths mantle reaches the lithosphere
volcano
a vent in the surface of earth that emits ash, gases, or molten lava
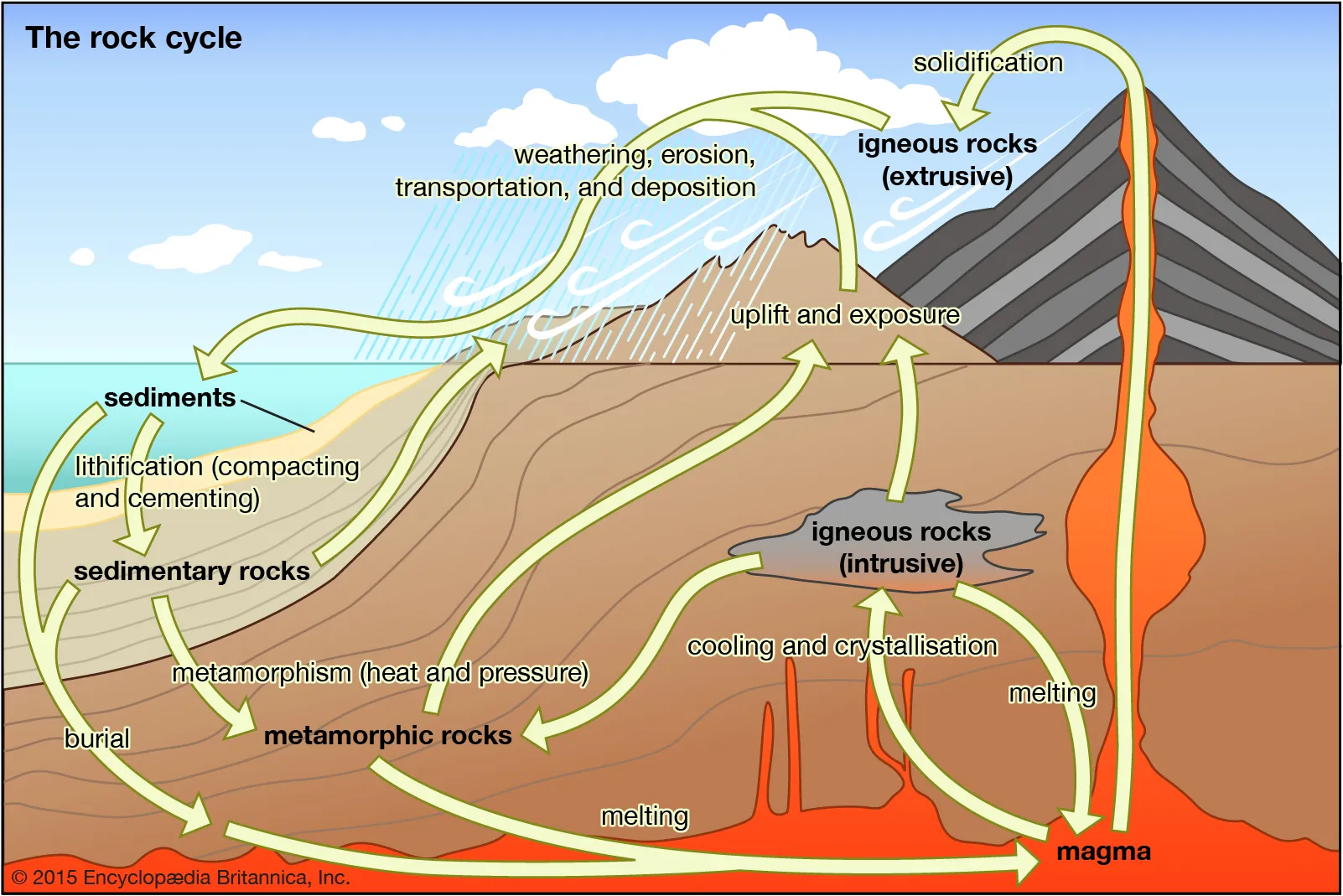
tsunami
a series of waves in the ocean caused by seismic activity or an undersea volcano that causes a massive displacement of water
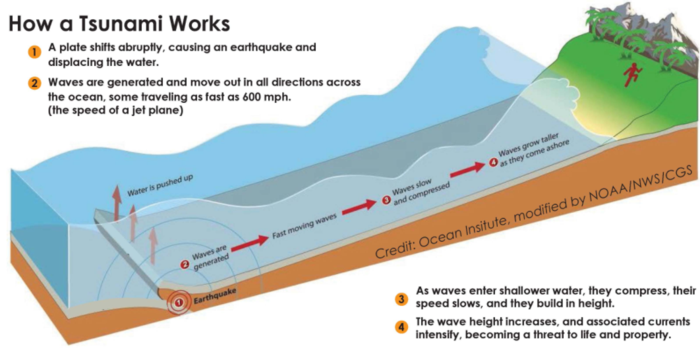
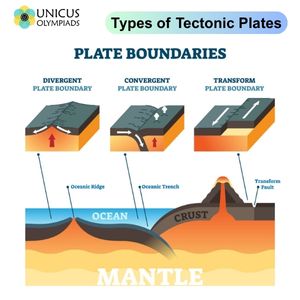
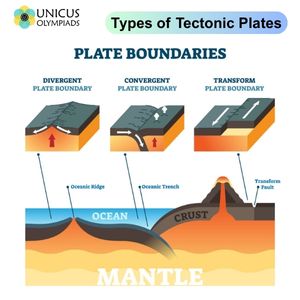
divergent boundary
an area below the ocean where tectonic plates move away from each other, a rising magma plume, forms ocean mountains, volcanoes, seafloor spreading, and rift valleys
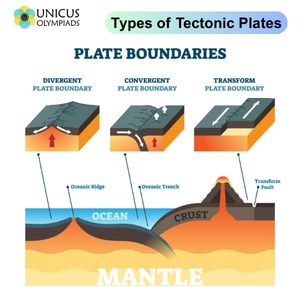
convergent boundary
an area where one plate moves into another plate and collides, forms mountains, island arcs, earthquakes, and volcanoes (subduction zone)
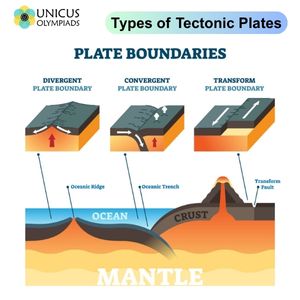
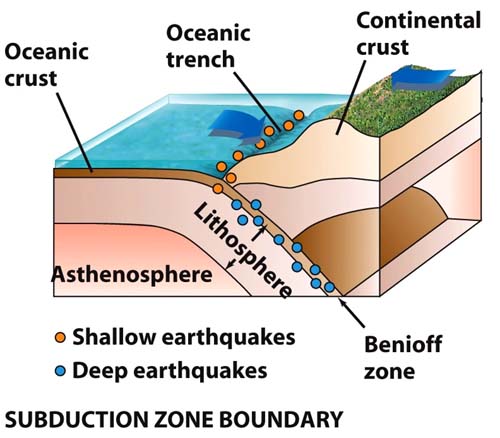
subduction
the process in which the edge of an oceanic plate moves downward beneath the continential plate and is pushed toward the center of the earth
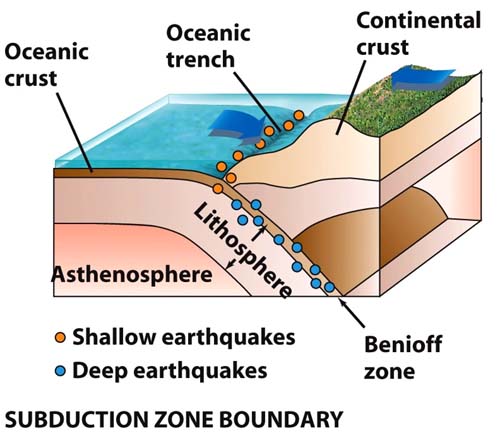
seafloor spreading
caused by a divergent boundary in which rising magma forms new oceanic crust on the seafloor at the boundaries between those plates
island arch
a chain of islands formed by volcanoes as a result of two tectonic plates coming together and experiencing subduction
collision zone
an area where two continental plates are pushed together and the colliding forces push up the crust to form a mountain range
transform boundary
an area where tectonic plates move sideways past each other (forms earthquakes)
fault
a fracture in rock caused by movement of earth’s crust
crust
outer layer of the lithosphere, earths surface
O horizon
core
the innermost zone of earth’s interior, composed mostly of iron and nickel. It includes a liquid outer layer and a solid inner layer and releases mass amounts of heat
mantle
the layer of earth above the core, containing magma, the asthenosphere, and solid upper mantle
magma
molten rock
asthenosphere
the layer of earth located in the outer part of the mantle, composed of semi-molten rock (beneath the lithosphere)
lithosphere
the outermost layer of earth, including the solid upper mantle and crust
plate tectonics
the theory that the lithosphere of earth is divided into plates, most of which are in constant motion
earthquake
a sudden movement of earth’s crust caused by a release of potential energy from the movement of tectonic plates
hot spot
in geology, a place where molten material from earths mantle reaches the lithosphere
volcano
a vent in the surface of earth that emits ash, gases, or molten lava
tsunami
a series of waves in the ocean caused by seismic activity or an undersea volcano that causes a massive displacement of water
divergent boundary
an area below the ocean where tectonic plates move away from each other, a rising magma plume, forms ocean mountains, volcanoes, seafloor spreading, and rift valleys
convergent boundary
an area where one plate moves into another plate and collides, forms mountains, island arcs, earthquakes, and volcanoes (subduction zone)
subduction
the process in which the edge of an oceanic plate moves downward beneath the continential plate and is pushed toward the center of the earth
seafloor spreading
caused by a divergent boundary in which rising magma forms new oceanic crust on the seafloor at the boundaries between those plates
island arch*
a chain of islands formed by volcanoes as a result of two tectonic plates coming together and experiencing subduction
collision zone
an area where two continental plates are pushed together and the colliding forces push up the crust to form a mountain range
transform boundary
an area where tectonic plates move sideways past each other (forms earthquakes)
fault
a fracture in rock caused by movement of earth’s crust
crust
outer layer of the lithosphere, earths surface
O horizon
the uppermost horizon of soil. It is primarily composed of organic materials, such as leaves, needles, twigs, and moss, in various stages of decomposition. Also known as the organic layer.
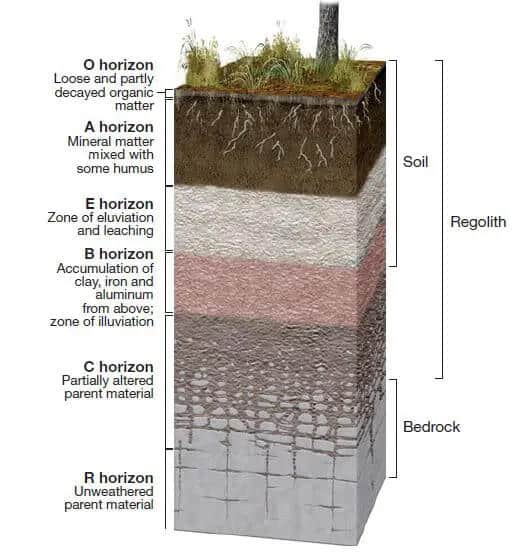
A horizon
(topsoil) zone of overlying organic material mixed with underlying mineral material
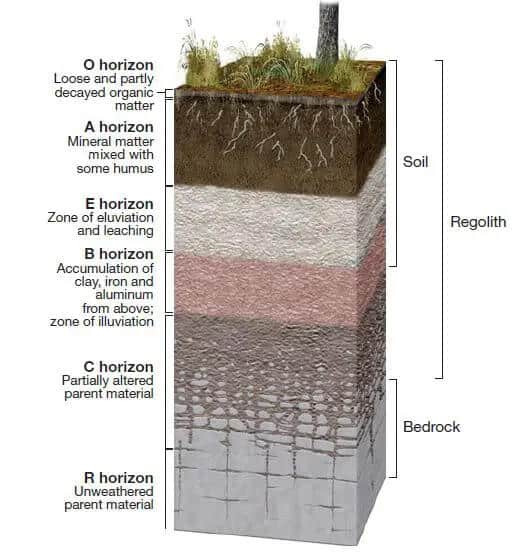
E horizon
zone of leaching of metals and nutrients; occurs in some soils beneath either the O horizon or the A horizon
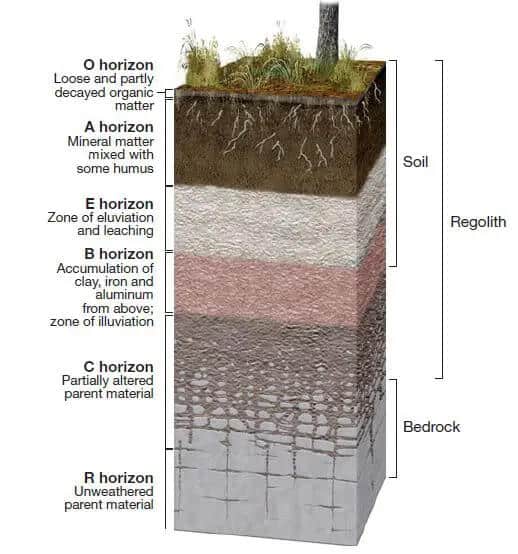
B horizon
zone of accumulation of metals and nutrients
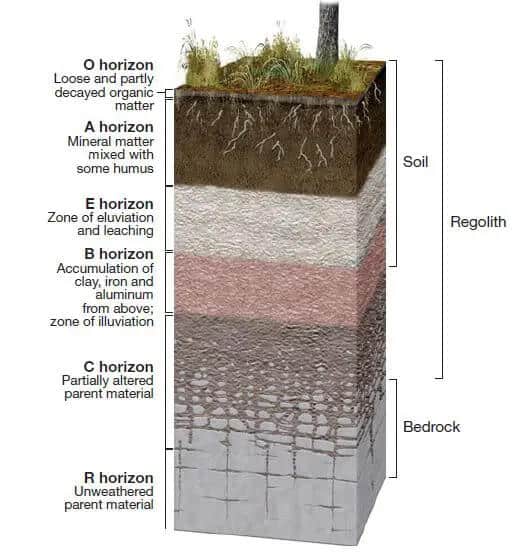
C horizon
least weathered portion of the soil profile similar to parent material
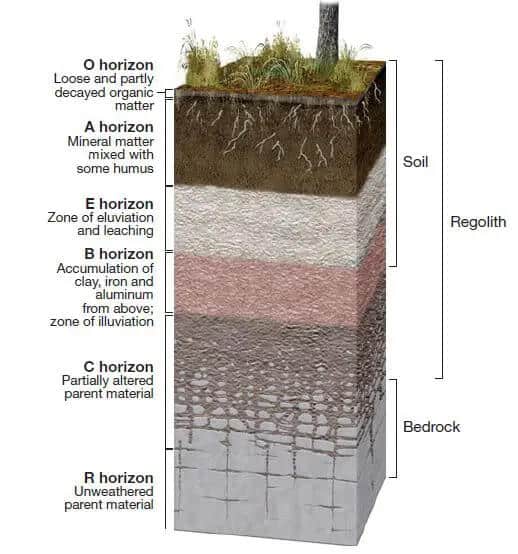
R horizon
bedrock
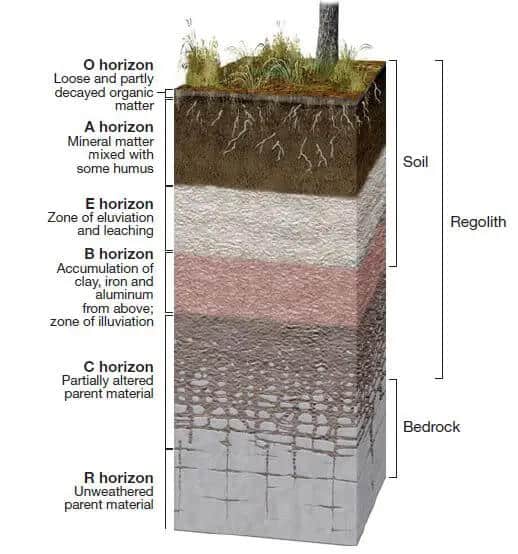
soil formation
parent material is slowly broken down by biological, chemical and physical weathering
loam
soil containing 20% clay, 40% sand, and 40% silt, good for growing most crops
time=distance/rate
time=distance/rate
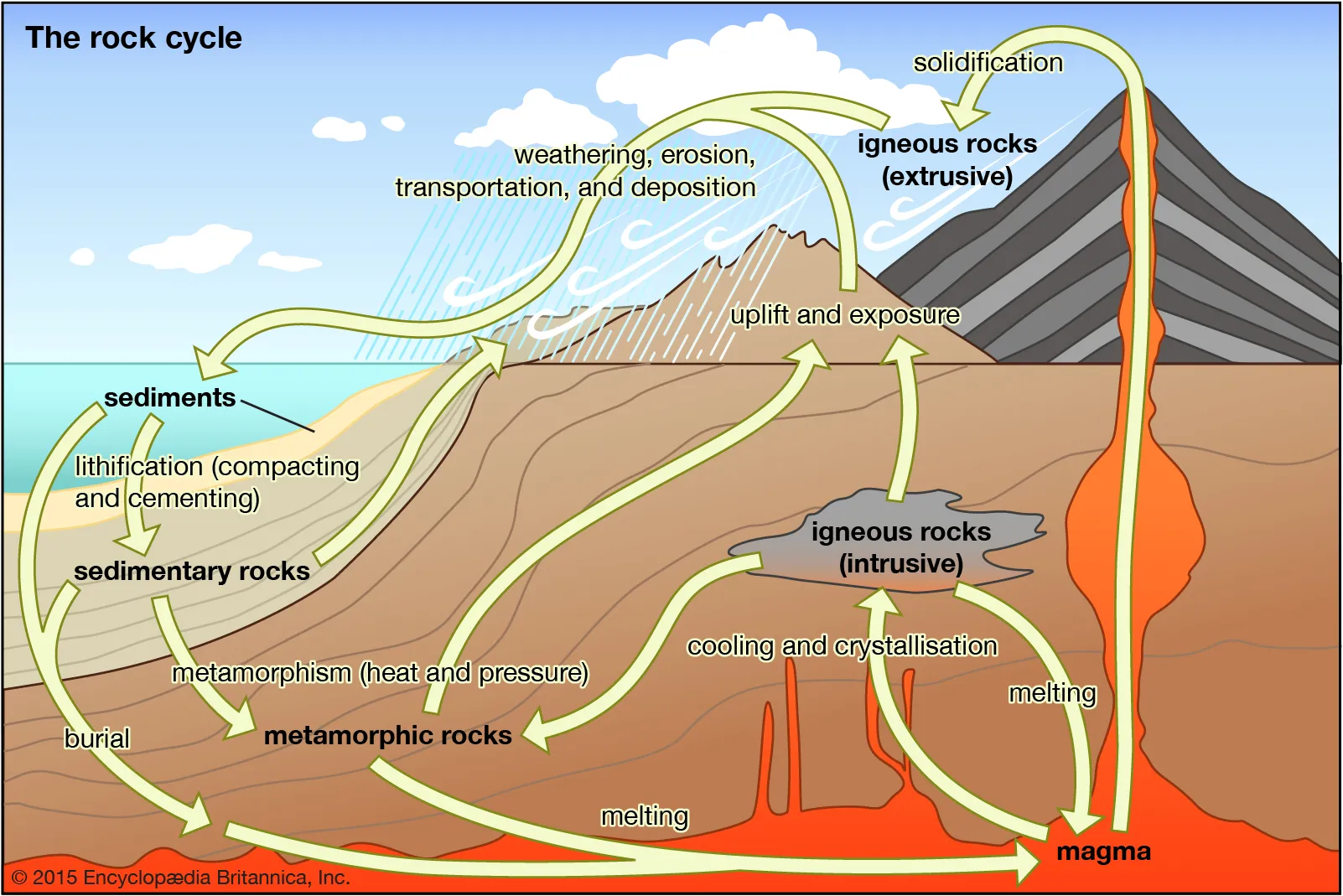
igenous rock
rock formed directly from magma
sedimentary rock
rock that froms when sediments such as muds, sands, or gravels are compressed by overlying sediments
metamorphic rock
rock that forms when a sedimentary rock, igneous rock, or other metamorphic rock is subjected to high temperature and pressure
rock cycle
the geological cycle governing the constant formation, alteration, and destruction of rock material that results from tectonics, weathering, and erosion among other processes
watershed
all the land in an area that drains into a particular stream, river, lake, or wetland
hubbard brook watershed
the Hubbard Brook deforestation experiment resulted in increased water runoff and a dramatic rise in streamwater nitrate concentrations in the deforested area. It also showed a significant loss of other minerals, like calcium, from the soil, and demonstrated that forests play a crucial role in retaining nutrients within an ecosystem.
chesapeake bay watershed
researchers clear-cut one watershed to determine the importance of trees in retaining soil nutrients. they compared nutrient run-off in the clear-cut watershed with that in a control watershed that was not clear-cut
insolation
incoming solar radiation which is the main source of energy on earth
albedo
the percentage of incoming sunlight reflected from a surface; snow and light colors have high albedo; areas with lower albedo absorb more heat dark
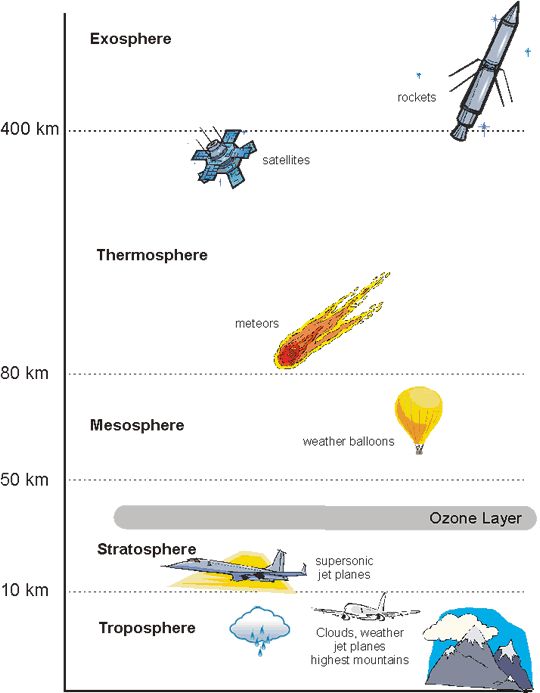
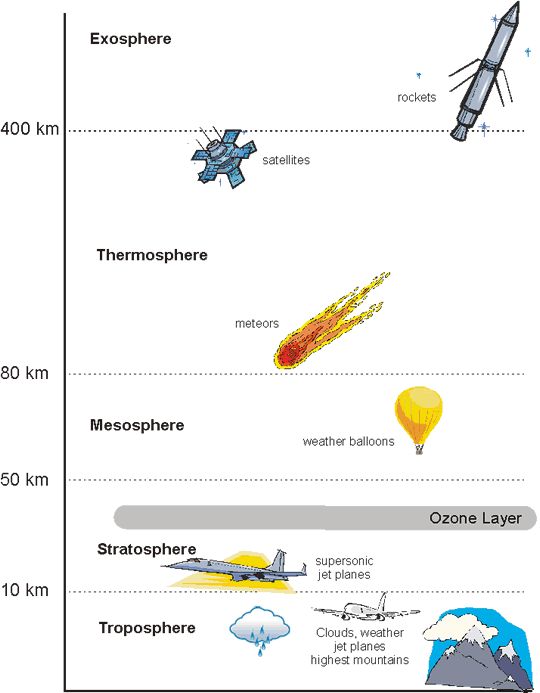
troposphere
a layer of the atmosphere closest to the surface of earth, extending 10km (where weather occurs)
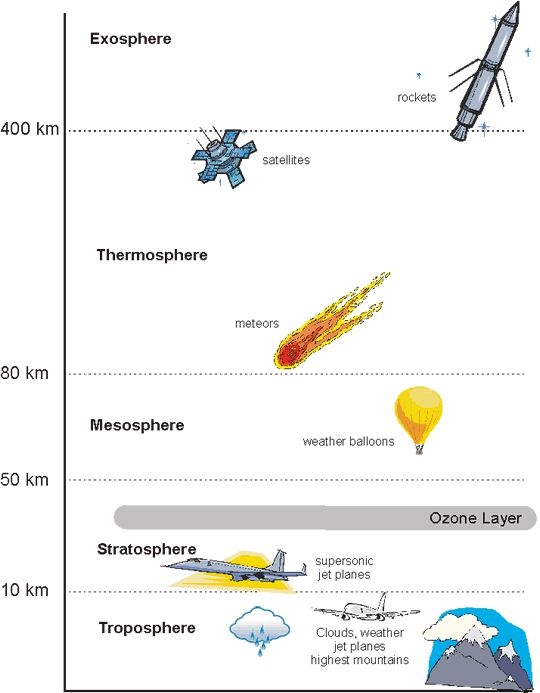
stratosphere
the layer of the atmosphere above the troposphere, extending 50-85 km above the surface of the earth
ozone
a plae blue gas composed of molecules made up of three oxygen atoms
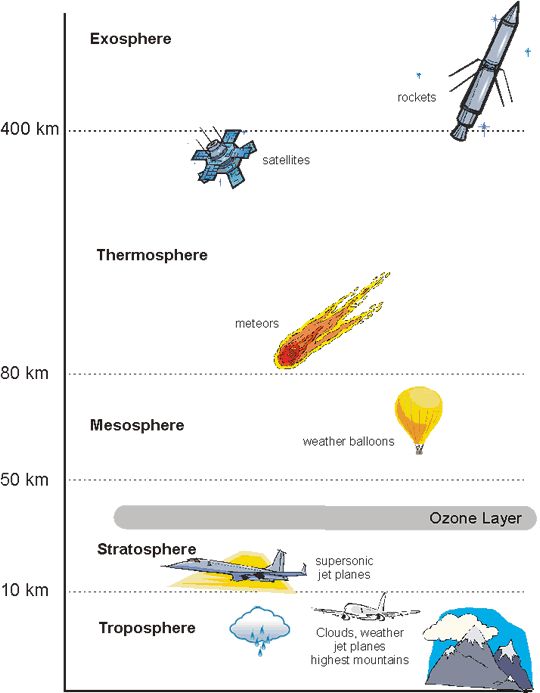
mesosphere
the layer of the atmosphere above the stratosphere, extending 50-85km above the surface of the earth
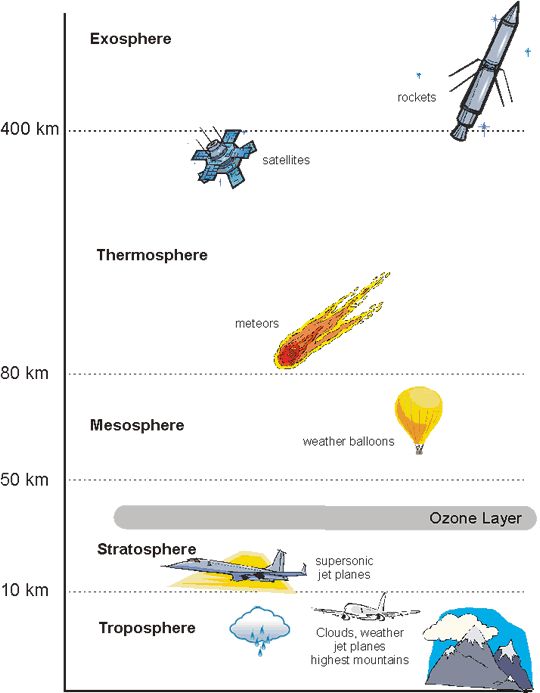
thermosphere
the layer of the atmosphere that extends from 85-600km above the surface of the earth (where you see northern lights)
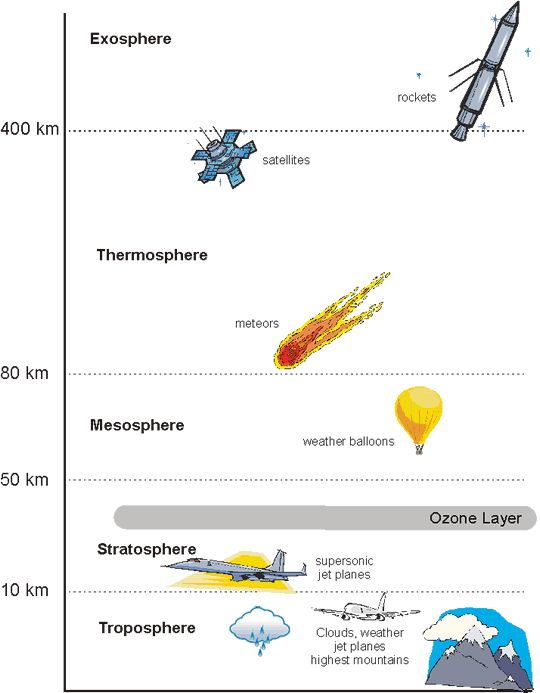
exosphere
the outermost layer of the atmosphere which extends from 600-10,000km above the surface of the earth
adiabatic cooling
the cooling effect of reduced pressure on air as it rises higher in the atmosphere and expands
latent heat release
the release of energy when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid water
atmospheric convection current
global patterns of air movement that are initialized by the unequal pressure heating of earth
intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)
the latitude that receives the most intense sunlight, which causes the ascending branches of the two hadley cells to converge
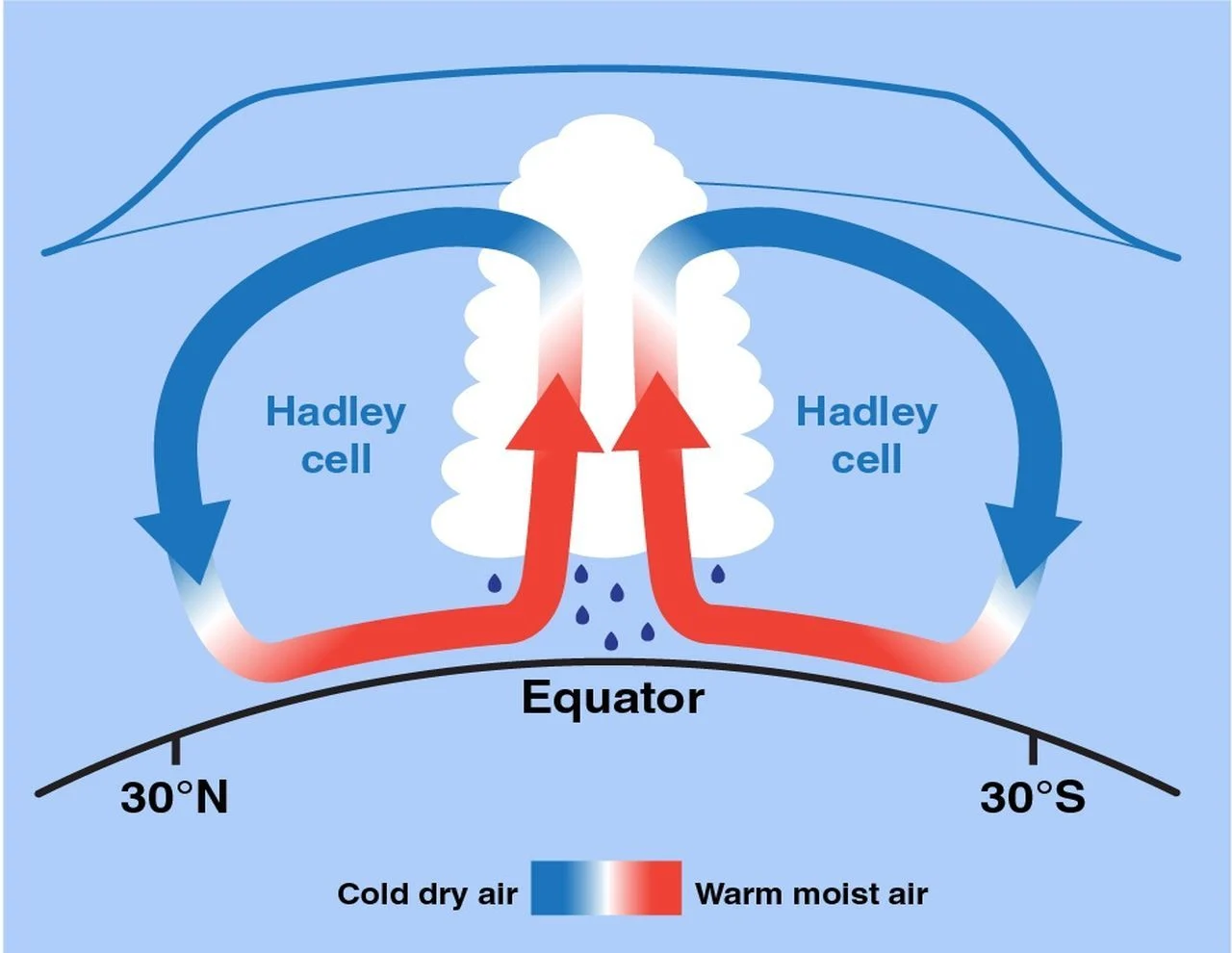
hadley cell
a convection current in the atmosphere that cycles between the equator and 30° N and 30° S; deserts form here due to lack of moisture
polar cell
a convection current in the atmosphere, formed by air that rises at 60° N and 60° S and sinks in the poles, 90° N and 90° S
ferrell cell
a convection current in the atmosphere that lies between hadley cells and polar cells
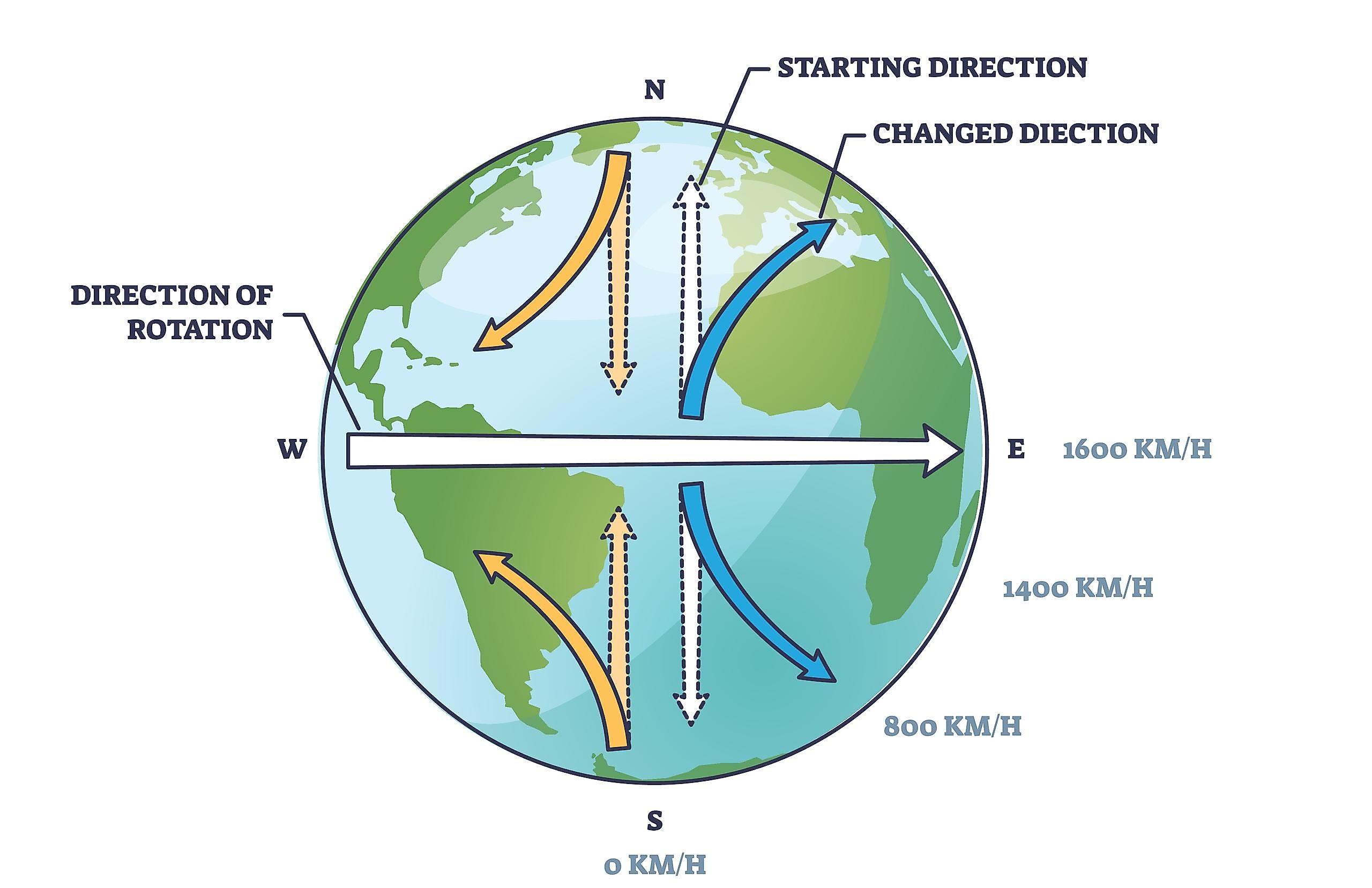
coriolis effect
the coriolis effect is the apparent deflection of moving objects due to the Earth's rotation, causing objects to curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere
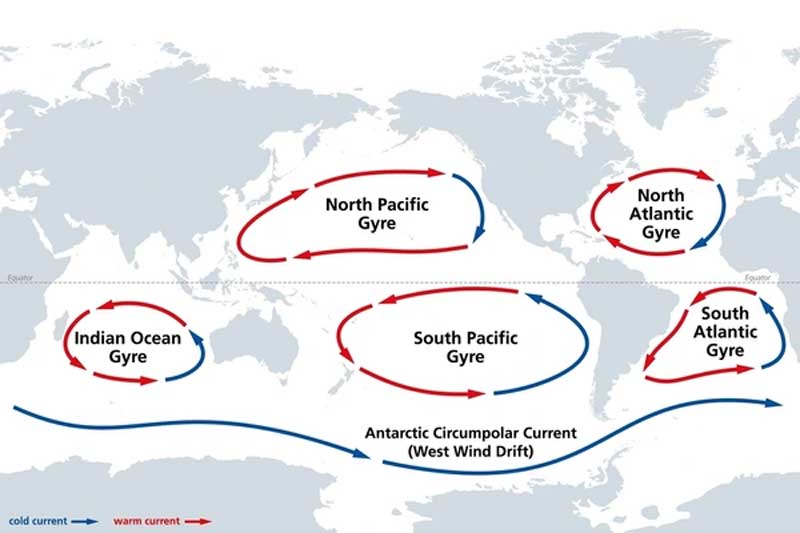
gyre
a large-scale pattern of water circulation that moves clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counter-clockwise in the southern hemisphere
upwelling
the upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents
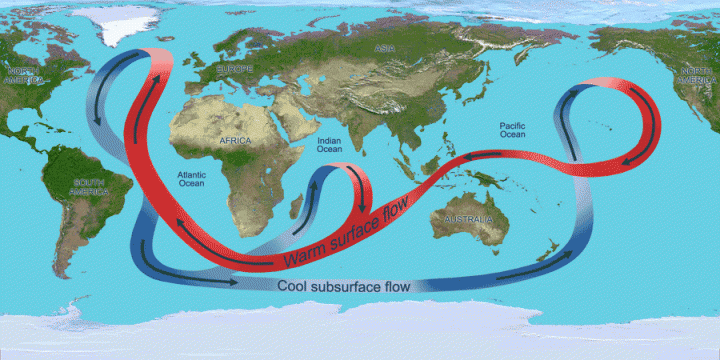
thermohaline circulation
an oceanic circulation pattern that drives the mixing of surface water and deep water; mixing salt, nutrients, and temperature throughout the ocean
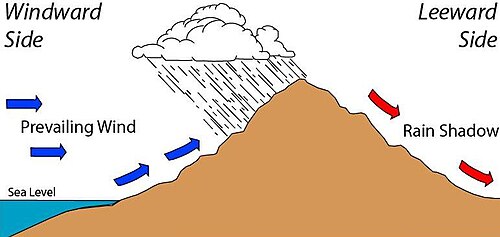
rain shadows
a region with dry conditions found on the leeward (the side sheltered from the wind, opposite the windward side) side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing percipitation on the windward (the side that faces the prevailing wind, forcing the air to rise, cool, and release moisture, leading to high precipitation) side
El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
A reversal of wind and water currents in the South Pacific; warm equator currents bring heat and precipitation to Americas; Suppressed upwellings off South American coast
La Niña
following an El Niño event, trade winds in the South Pacific reverse strongly, causing regions that were hot and dry to become cooler and wetter. Increased upwellings brings cooler-than-normal conditions trade winds move:
W ← ← ← E