N5 Graphic Communication
3.0(4)
3.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
extrude
allows you to take a simple 2d shape and pull it out into a 3d object
2
New cards
revolve
Allows to revolve half of a profile/shape around a central axis, making it into a cylindrical feature.
3
New cards
shell
Hollows out a solid 3D model to create a shell.
4
New cards
dimension
adds sizes to a drawing
5
New cards
chamfer
used to angle corners
6
New cards
fillet
used to round corners
7
New cards
workplanes
set planes where you can draw 2d sketches that allow you to build your model from the ground up, side to side, or front to back.
8
New cards
true shapes
this is used to show the actual shape a surface, when it is difficult to see because of the angle of the surface or position of the surface on an orthographic drawing.
9
New cards
sectional drawings
Sectional views are used on drawings to show the inside details of an object more clearly than hidden detail can. They are also used on sectional assemblies to show clearly, how component parts of a product fit together.
hatching lines are always at 45°
hatching lines are always at 45°
10
New cards
exploded drawing
an exploded view shows the separate parts that make up an assembly. the parts are arranged in line to help identify how they would fit together.
shows how the parts should be assembled and in what order.
shows how the parts should be assembled and in what order.
11
New cards
input devices that create digital files
scanner
handheld scanner
graphics tablet
keyboard
mouse
handheld scanner
graphics tablet
keyboard
mouse
12
New cards
benefits of digital sketches
easier to modify
can be used for illustrative purposes
can be easily used for testing and/or simulation
speed of production
can be electronically shared
saves on materials
allows for remote working
can be used for illustrative purposes
can be easily used for testing and/or simulation
speed of production
can be electronically shared
saves on materials
allows for remote working
13
New cards
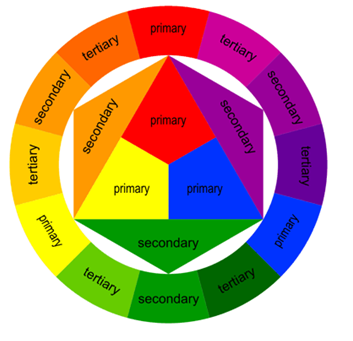
contrasting colours (colour wheel)
contrasting colours occur when colours at the opposite side of the colour wheel are used together. contrasting colours are bold and create an exciting mood/feeling.
ex. red & green
ex. red & green
14
New cards
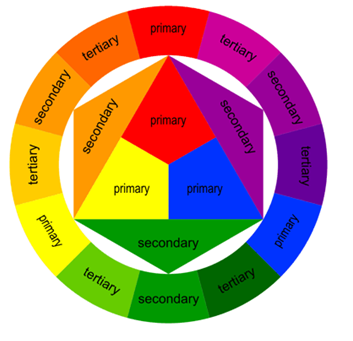
harmonising colours
harmony is created when colours close to each other on the colour wheel are used together. harmony is easy on the eye and creates a feeling of peace.
ex. yellow and orange together create a warm relaxing image.
ex. yellow and orange together create a warm relaxing image.
15
New cards
tints/shades of colour
tints and shades create greater colour options by adding white and black to colours.
• ex. adding WHITE to blue gives TINT of blue
• ex. adding BLACK to blue gives a SHADE of blue
• ex. adding WHITE to blue gives TINT of blue
• ex. adding BLACK to blue gives a SHADE of blue
16
New cards
preliminary graphics (stage 1)
• initial stages of graphic design, rough and introductory work. thumbnail sketches which are small rough sketches.
• dont take long and give an immediate representation of your work.
• allows you to develop a whole range of ideas quickly and which allows you to build on and expand your designs.
• dont take long and give an immediate representation of your work.
• allows you to develop a whole range of ideas quickly and which allows you to build on and expand your designs.
17
New cards
production graphics (stage 2)
• has to convey certain pieces of information which would be of use to someone like a technologist, engineer, architect, etc.
information provided:
• dimensions, moving parts, cross section, weight, material selection, etc.
forms:
• orthographic drawings, sectional views, exploded views, assembly views, perspective, isometric, sections, stepped sections & cut aways.
• drawings are usually produced on AutoCAD or other cad packages
information provided:
• dimensions, moving parts, cross section, weight, material selection, etc.
forms:
• orthographic drawings, sectional views, exploded views, assembly views, perspective, isometric, sections, stepped sections & cut aways.
• drawings are usually produced on AutoCAD or other cad packages
18
New cards
promotional graphics (stage 3)
• used by sales and marketing departments of companies. product or design is displayed and advertised.
forms:
• posters, leaflets, flyers, displays.
effectiveness:
• must attract consumers attention and make them want to look at it.
links:
• linked with features elements and principles of desk top publishing
forms:
• posters, leaflets, flyers, displays.
effectiveness:
• must attract consumers attention and make them want to look at it.
links:
• linked with features elements and principles of desk top publishing
19
New cards
line
used to divide up a layout or connect other elements. varies in thickness and in colour.
20
New cards
shape
creative use of shape can grab a reader's attention. shape can help organise a layout. shape be organic, or abstract.
21
New cards
texture
physical refers to the roughness or feel of the paper being used.
visual refers to textures such as wet/water, metal, stone, etc from an image.
visual refers to textures such as wet/water, metal, stone, etc from an image.
22
New cards
size
the relationship of items can be emphasised by size. the most important features are often the biggest creating dominance.
23
New cards
colour
the most effective element on the page. colour creates moods and excitement to engage the reader.
24
New cards
value
value deals with colour tones. darker colours have more value and therefore stand out more ot the reader.
25
New cards
mass
all items on a page have mass. a bold heading has more mass than a small heading. mass can catch the reader's attention and allow the design to ensure key features of images stand out.
26
New cards
balance
symmetrical/asymmetrical layout of a page. symmetry creates a formal page whereas asymmetry can create an exciting informal and unusual page.
27
New cards
contrast
contrasting colour and shapes can be used to make items stand out to create excitement.
28
New cards
dominance
items with greater emphasis stand out catching the readers eye and dominating the publication.
29
New cards
unity
careful positioning of items and good use of colour can make items on a page feel unified. this makes the page easier to follow and makes the whole page work as one item.
30
New cards
alignment
allows you to align text/graphics to the left, centre and right of a page ensuring that pages dont seem random.
31
New cards
whitespace
leaving areas of a layout free from text or graphics draws the reader eyes to the areas containing text and graphics. it allows the readers eyes to rest in busy layouts.
32
New cards
rhythm
allows a reader's eye to flow through page from beginning to end easily. this can be achieved through good use of shape layout balance alignment and colors.
33
New cards
typefaces
serifs: format fonts that create an elegant formal design for a publication
sanserifs: texts without flicks that are informal and normally used in modern publications or web page design.
sanserifs: texts without flicks that are informal and normally used in modern publications or web page design.

34
New cards
bold fonts
bold fonts are used to create emphasis. bold fonts usually feature in the headline of the article/document/page.
35
New cards
scale
enlarges or reduces the original size of an object
36
New cards
copy
copies and positions objects without having to redraw them each time.
37
New cards
break
removes a section from the middle of a line.
38
New cards
trim
cut or remove part of line
39
New cards
extend
makes a line longer
40
New cards
text
add writing to a drawing
41
New cards
ellipse
draw an ellipse (oval shape)
42
New cards
flush
forces the face of one object to be aligned with the face of another object
43
New cards
offset
used in co-ordination with other constraints, the offset too allows you to create a special distance between the components you are trying to assemble
44
New cards
orientate
this allows you to constrain components at angles to one another. the face or edge of a component can be angled to the face or angle of another component.
45
New cards
mate
the mate command joins two faces together
46
New cards
tangent
locks the round face of a cylinder to the round face of another cylinder of a flat face of prism
47
New cards
surface developments
similar to a net shape. focuses on a set surface of the prism as opposed to its entire shape.
48
New cards
1 point perspective
form of pictorial view. commonly used for views of room interiors, all surfaces converge on the same vanishing point.
49
New cards
2 point perspective
used to illustrate buildings and objects realistically. vanishing points can be positioned to give the impression of height as if viewed from above.
50
New cards
disadvantages of perspective views
has the effect of shortening the depths of the project. lengths breadths and heights reduce in size as you get closer to the vanishing points.
51
New cards
line graphs
used to show how values change over a period of time
52
New cards
pie charts
used to show how values compare to some whole numbers (used for percentages)
53
New cards
bar charts
used to show how values compare directly against other values