Anatomy and Physiology Final Exam Review
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All quiz/test questions (except midterm and quiz/exam 4)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
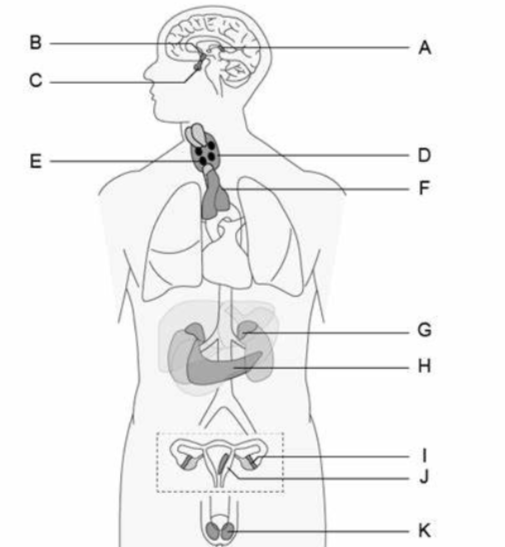
Which gland secretes estrogen?
I
Which test is utilized initially to screen for cervical cancer?
Pap smear
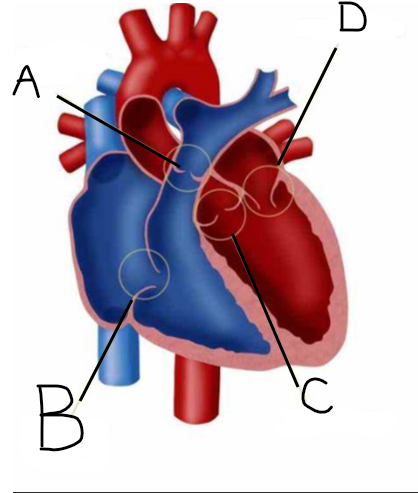
Which structure represents the pulmonic valve?
A
Which structure represents the tricuspid valve?
B
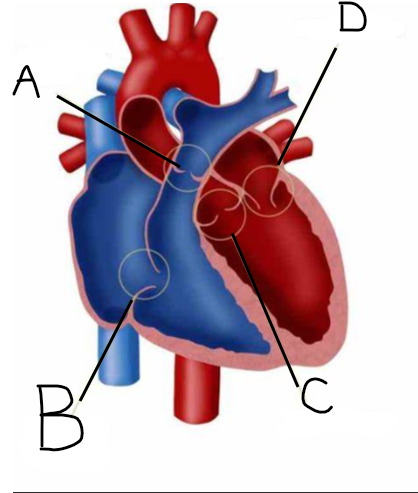
Which site represents the pulmonary vein?
E
________ is also known as the venous return or the end diastolic volume (EDV).
Preload
Which condition is caused by abnormal closing of the mitral valve?
Heart murmur
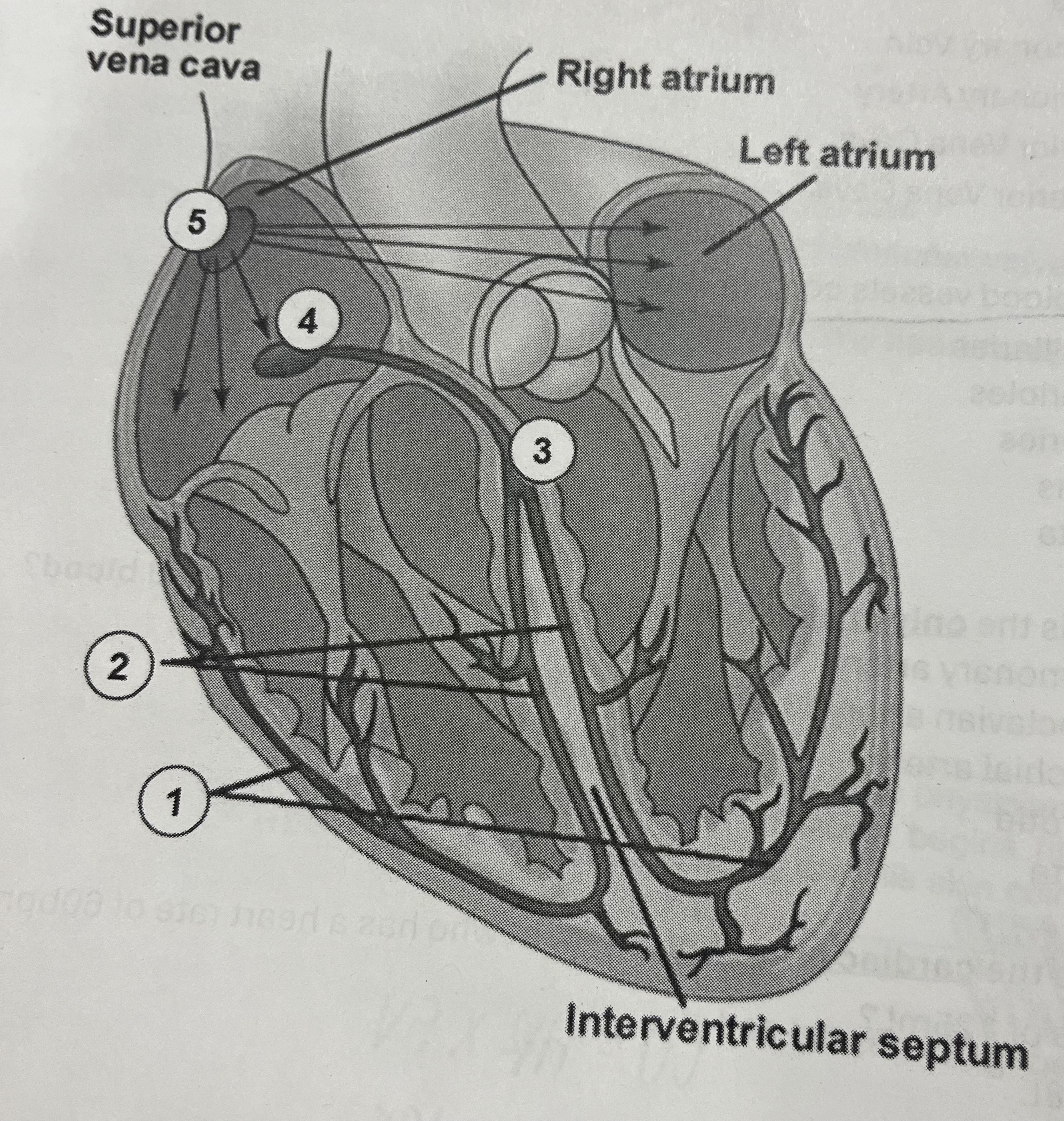
Which site acts as the pacemaker of the heart?
5
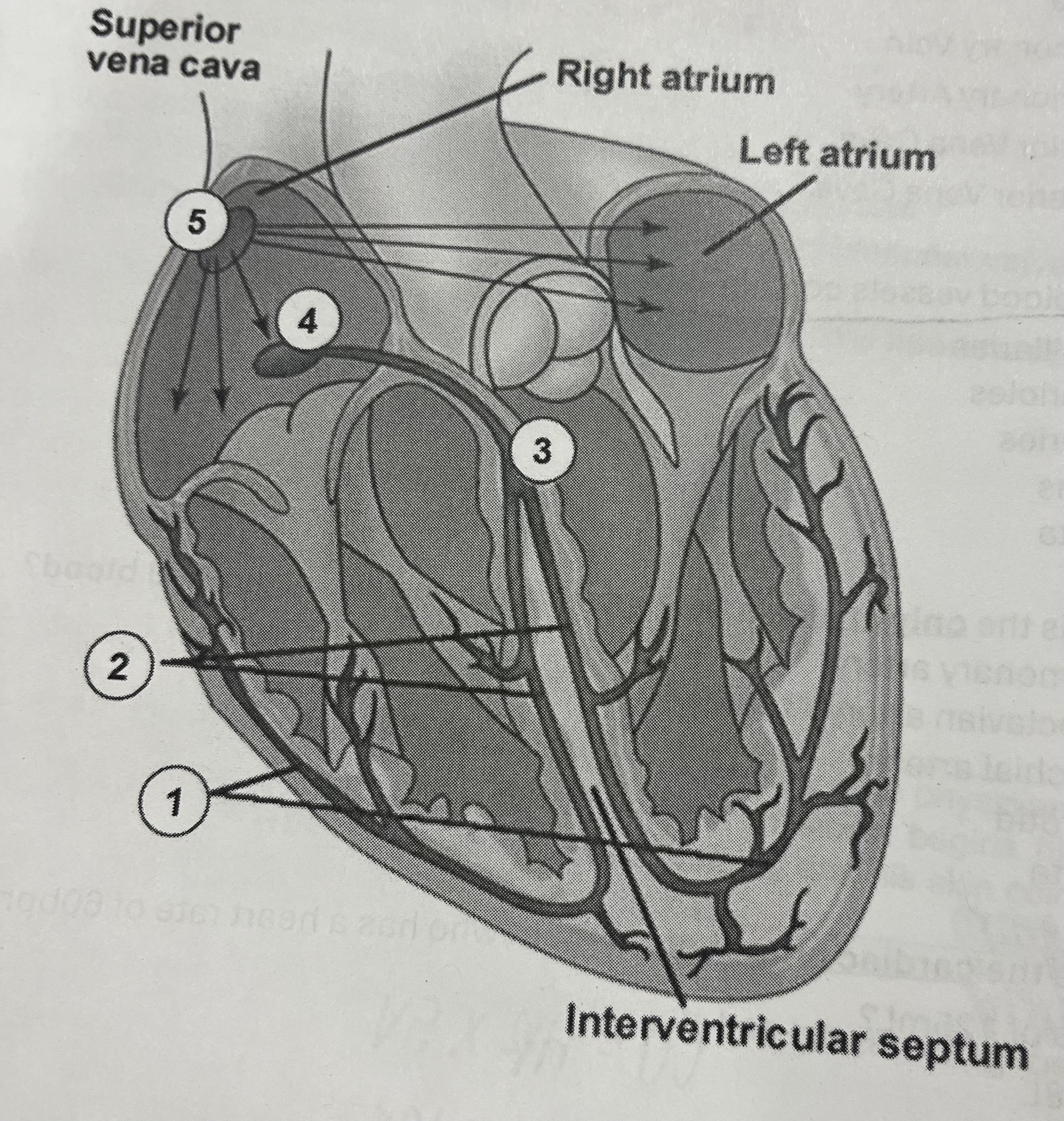
Which site represents the Purkinje Fibers?
1
The left ventricle delivers blood to the _________.
Aorta
Which blood vessels contain valves?
Veins
Which is the only artery in the body that carries deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary artery
What is the cardiac output of a patient who has a heart rate of 60 bpm and a stroke volume of 125 mL?
7.5 L
In the baroreceptor reflex, which of the actions will not occur when blood pressure falls?
Vasodilation
What is the definition of end diastolic volume?
Amount of blood in the ventricles after filling?
Stimulation of which cardiac receptor directly increases the heart rate?
Beta-1 adrenergic receptors
CW is a 77 yo male who reports to his PCP with chief complaints of cough, confusion, and a racing heartbeat. The physician begins his physical assessment and observes that CW has extreme difficulty breathing and his skin color appears blue. The physician is waiting for a full lab assessment but has initially diagnosed CW as most likely having ________.
Left heart failure
Which of the following mechanism steps does not produce blood vessel smooth muscle contraction?
Ca2+ binds to active myosin cross bridges which slide along actin to create muscle tension
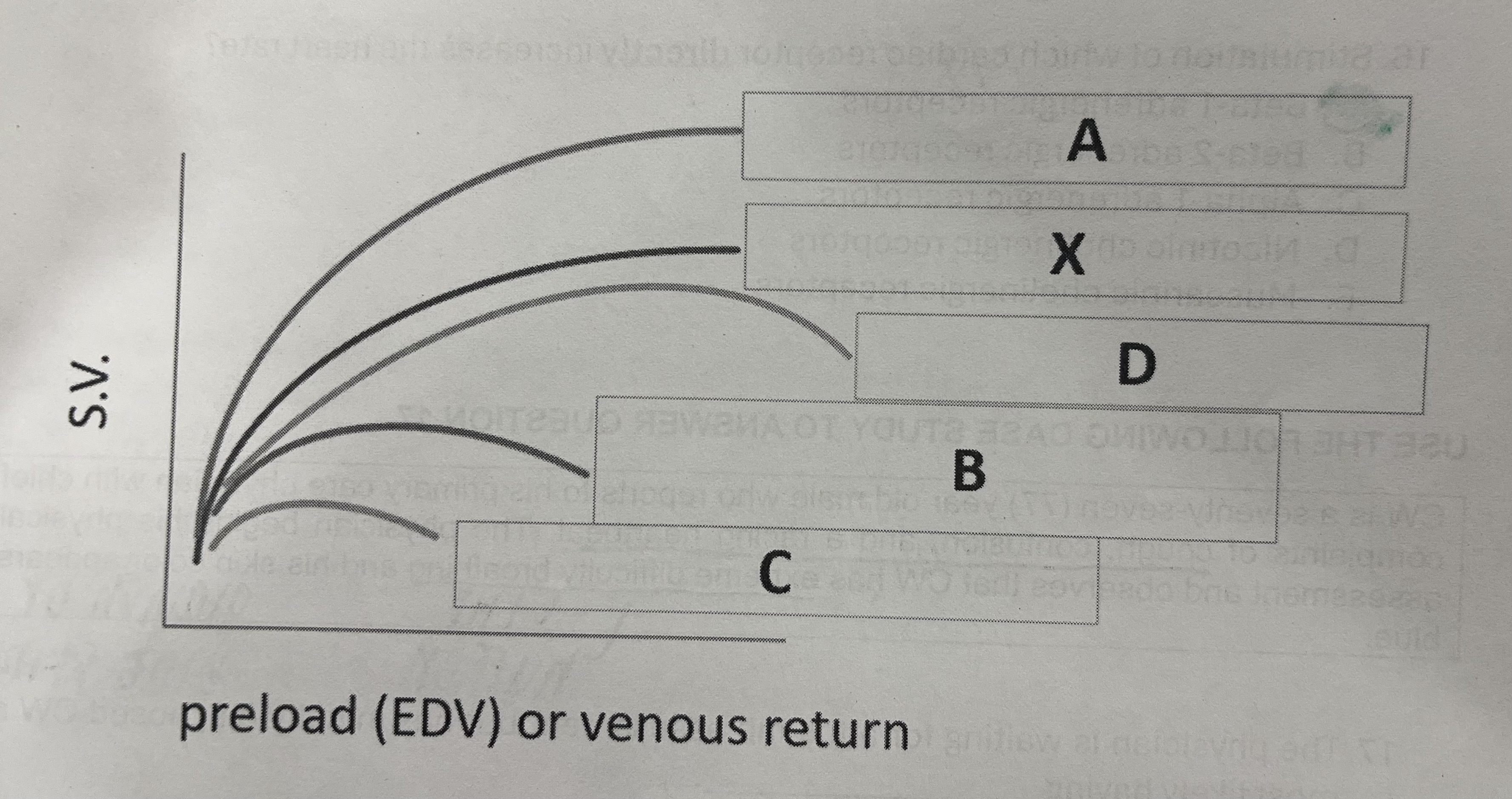
If curve X represents a normal heart, which curve would represent the normal heart that is exercising?
A
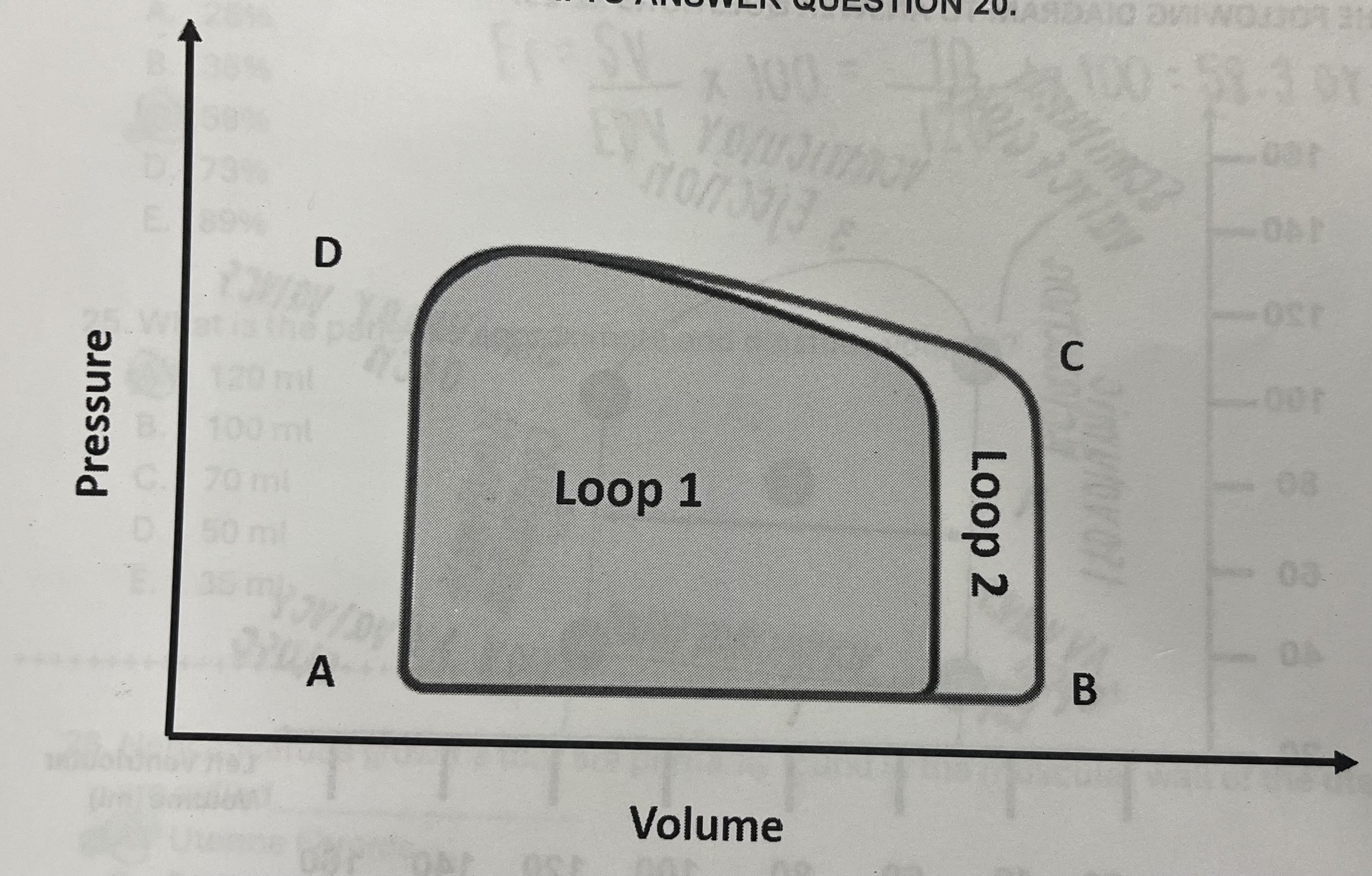
What caused the change in shape from loop 2 (original pressure volume loop) to loop 1?
Decreased EDV
Which of the following vessels is responsible for carrying oxygenated blood to the left side of the heart?
Pulmonary vein
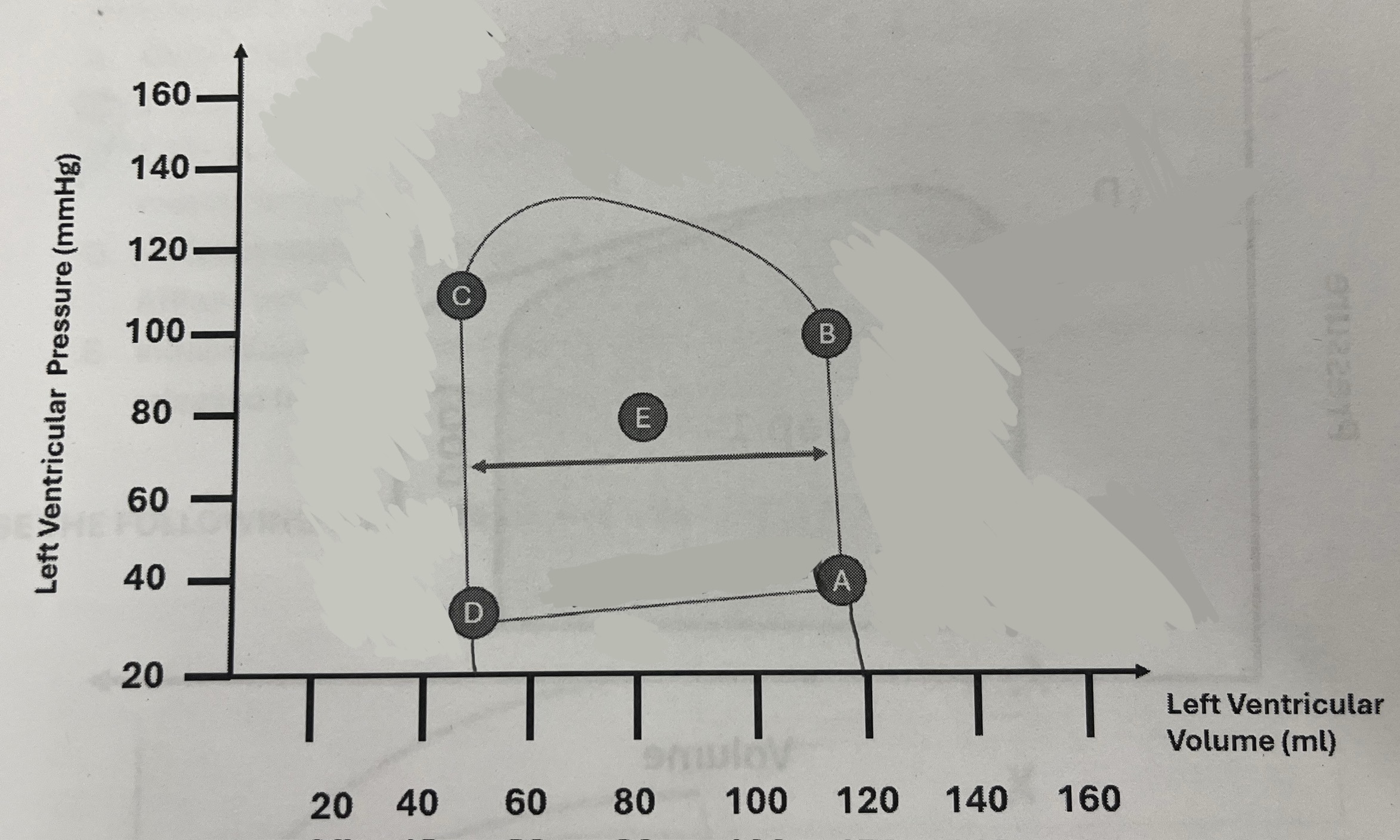
What is the approximate stroke volume of the patient?
70 mL
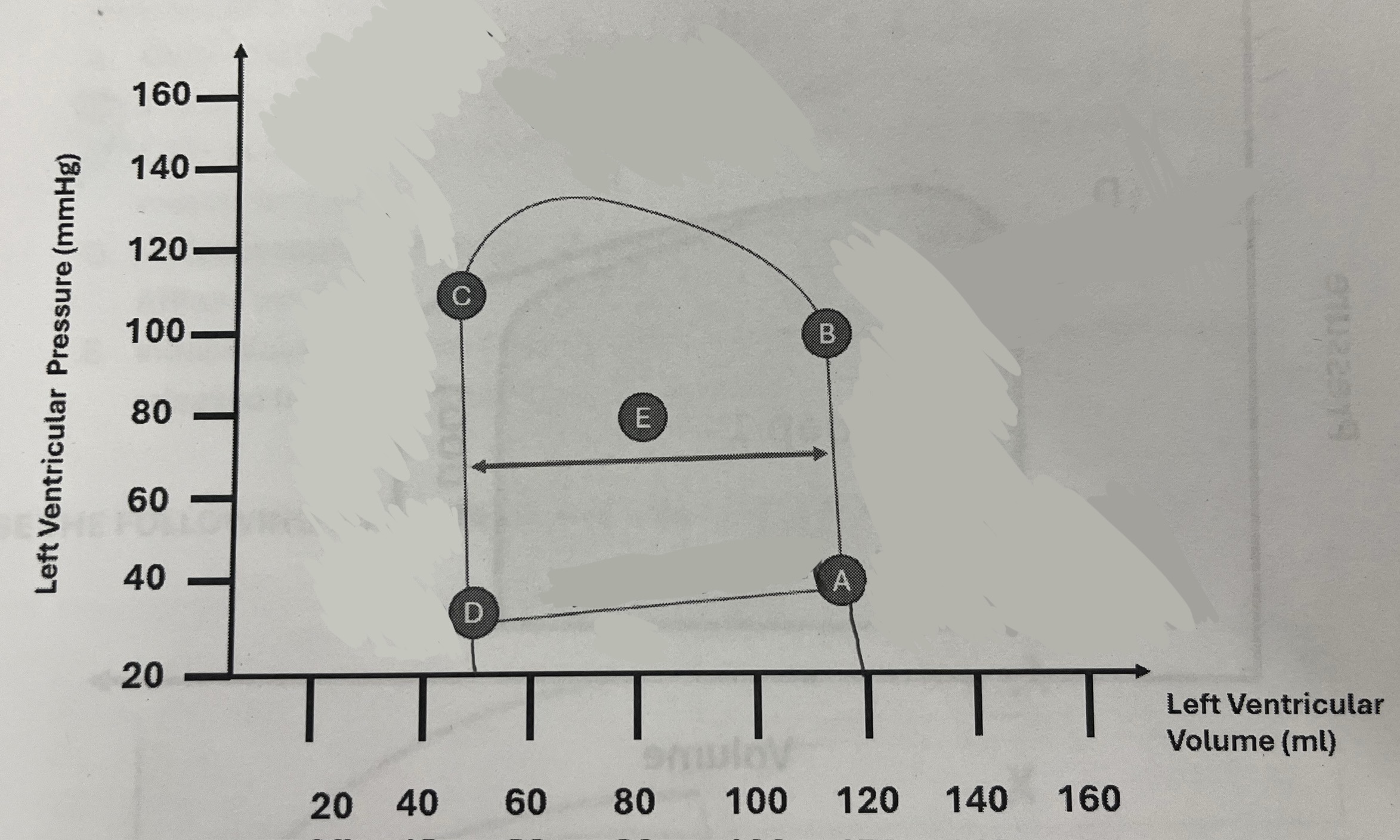
What event occurs at point B?
Semilunar valve opens
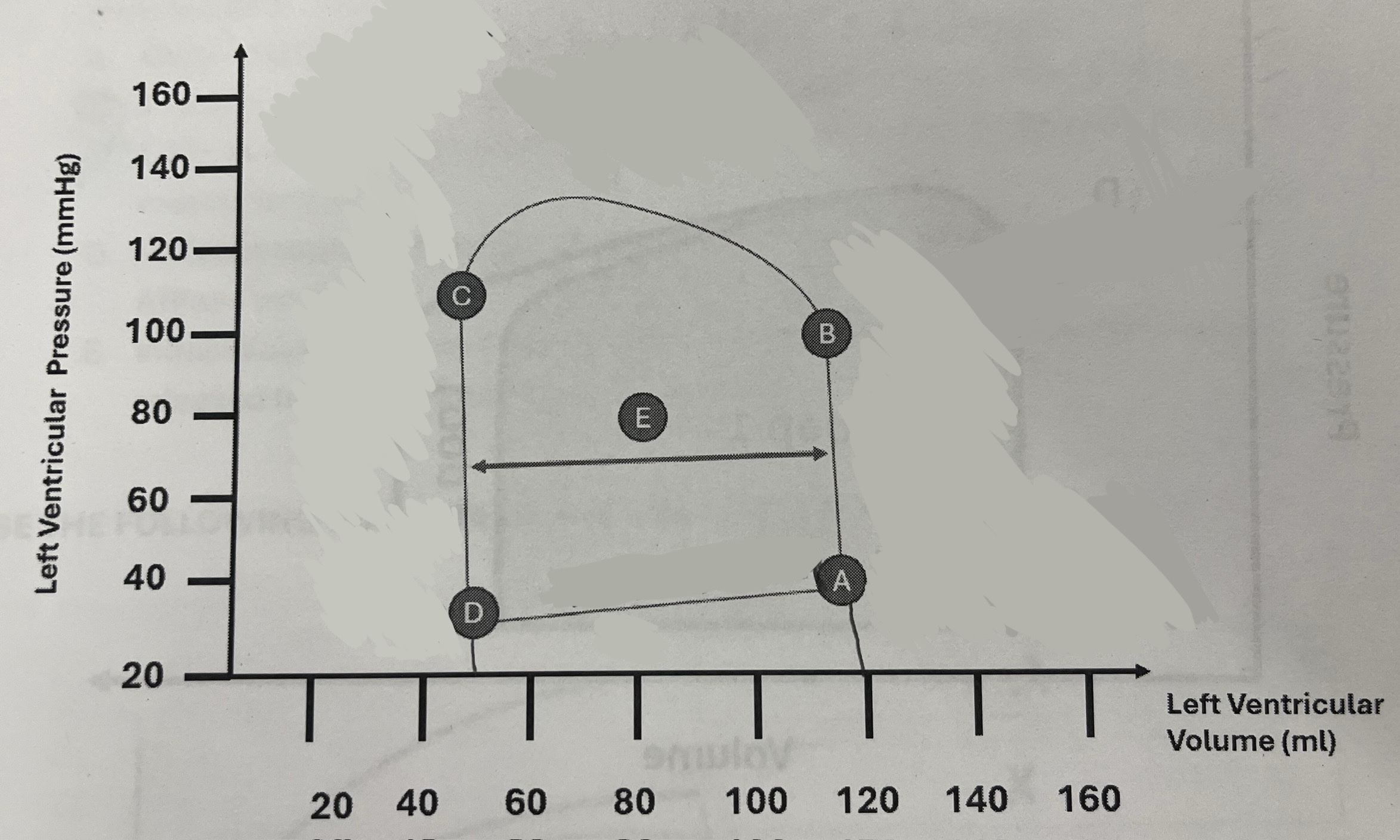
What is the patient’s approximate ejection fraction?
58%
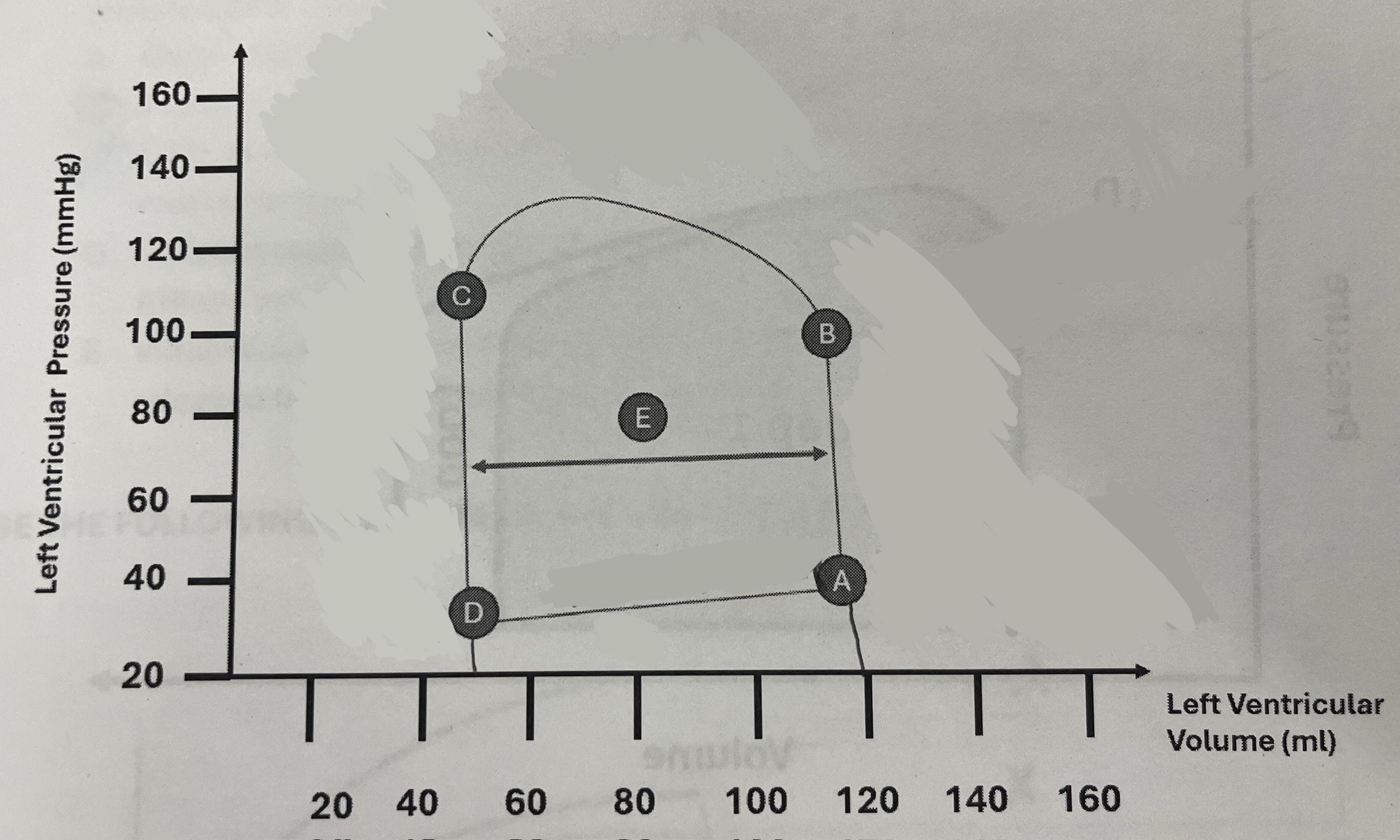
What is the patient’s approximate end diastolic volume?
120 mL
Noncancerous growths that are primary found in the muscular wall of the uterus are called ______.
Uterine fibroids
Which structure releases progesterone after ovulation?
Corpus Luteum
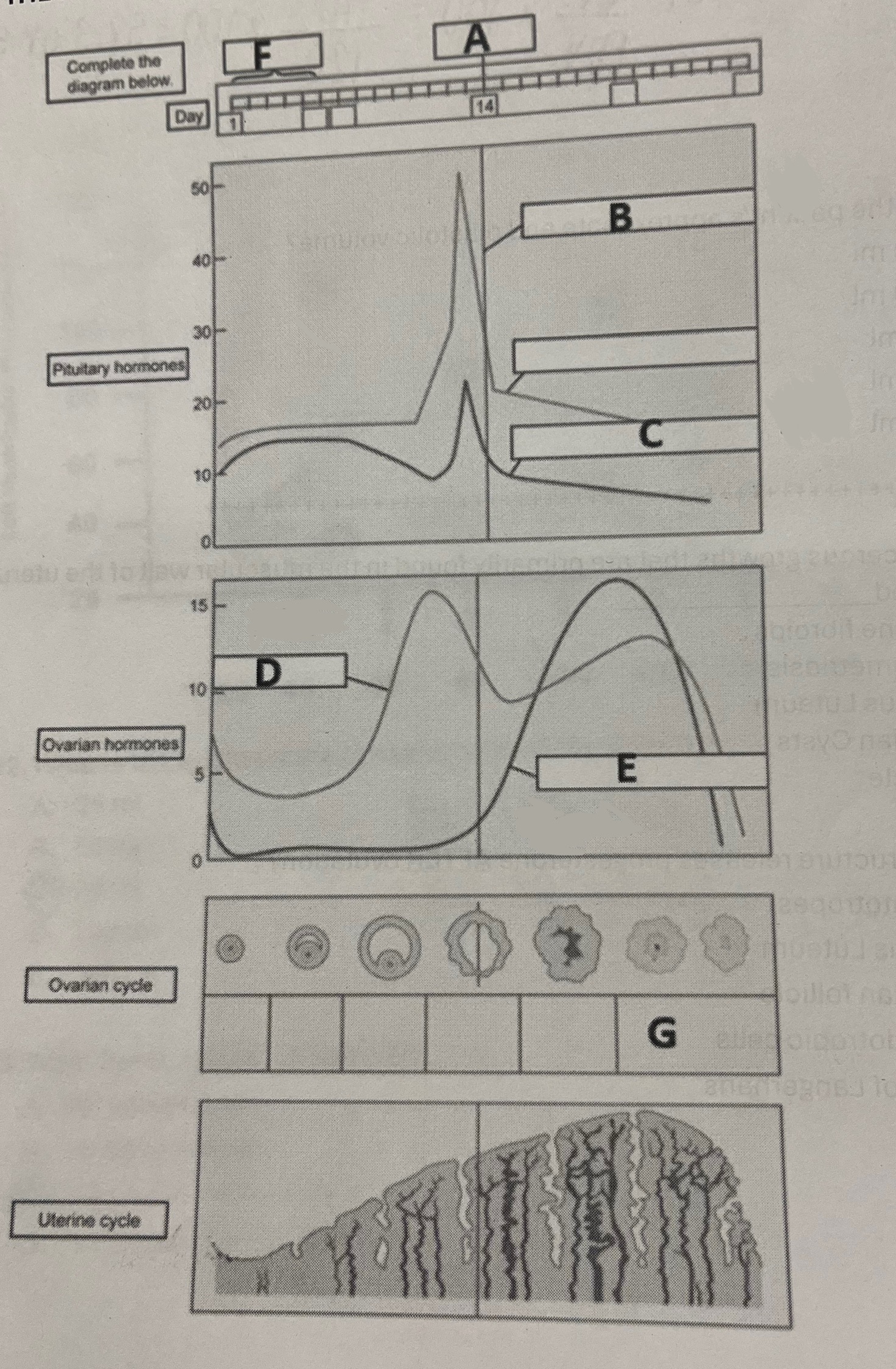
Hormone E most likely represents
Progesterone
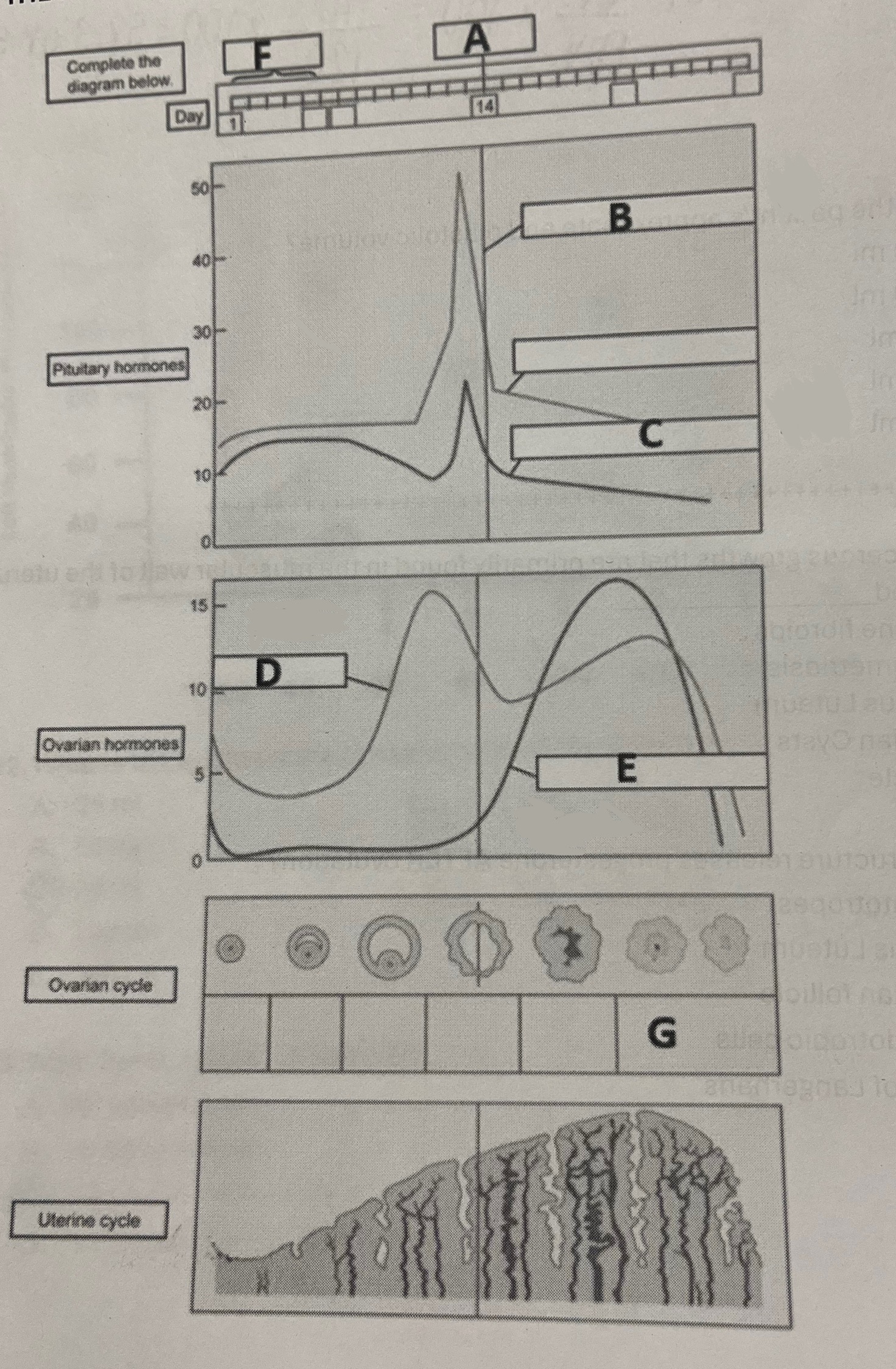
Hormone B most likely represents
Luteinizing hormone
Site A represents
Aldosterone
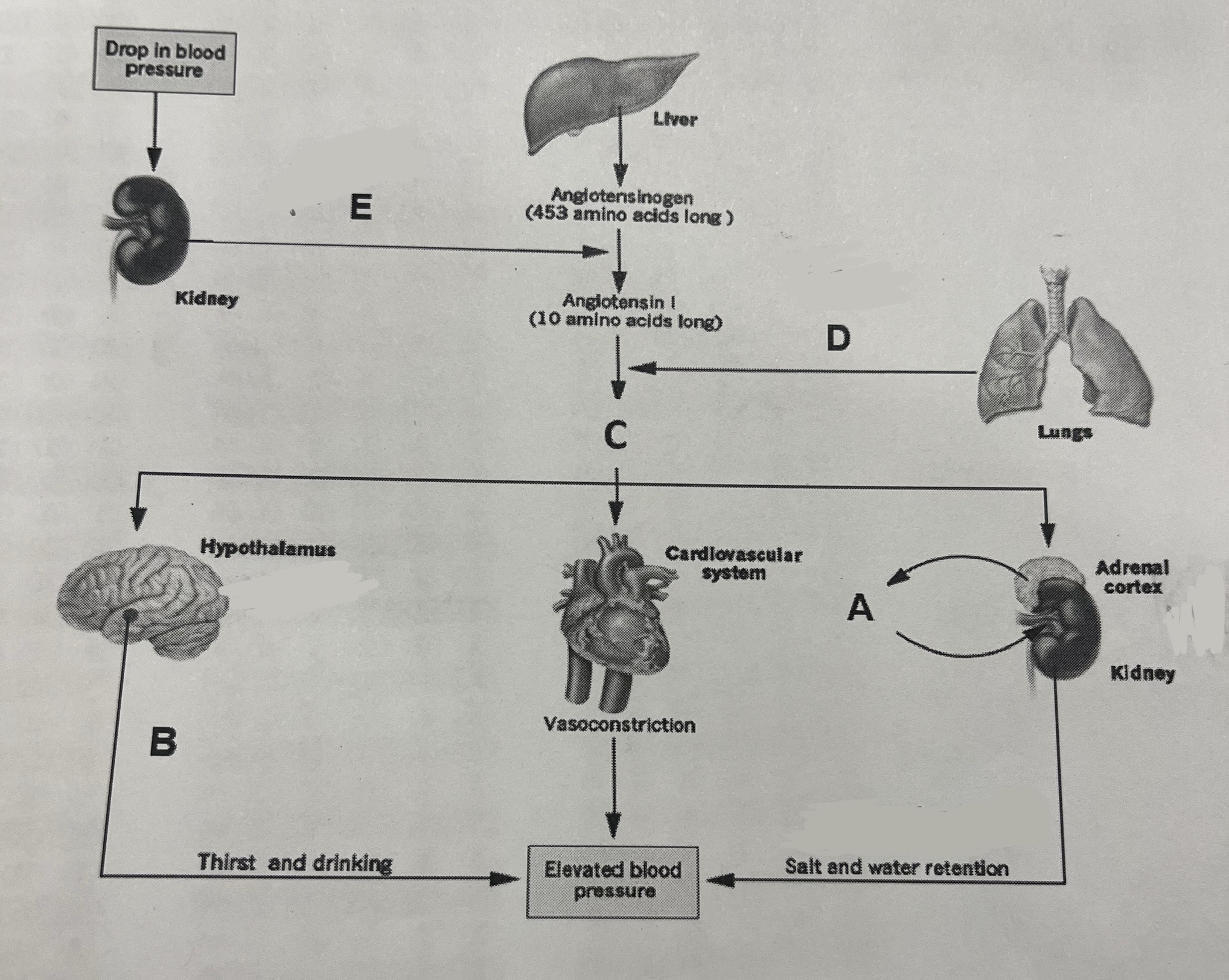
TR is a 63 yo woman who presents to her PCP with complaints of increasing darkening of the skin, dizziness, and eas fatigability. She claims that she cannot stand on account of severe postural dizziness.
PE: pulse of 106 bpm, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg suping and 70/40 sitting
Labs: fasting blood glucose 66 mg/dL (70-100 mg/dL), Na 136 mEq/L (165-145), K 5.0 mEq/L (3.0-5.5) aldosterone 1 ng/dL (2-9 ng/dL), 8 am plasma cortisol 1.2 μgm/dL (6-23 μgm/dL)
What is the function of aldosterone?
Promote salt and water retention
TR is a 63 yo woman who presents to her PCP with complaints of increasing darkening of the skin, dizziness, and eas fatigability. She claims that she cannot stand on account of severe postural dizziness.
PE: pulse of 106 bpm, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg suping and 70/40 sitting
Labs: fasting blood glucose 66 mg/dL (70-100 mg/dL), Na 136 mEq/L (165-145), K 5.0 mEq/L (3.0-5.5) aldosterone 1 ng/dL (2-9 ng/dL), 8 am plasma cortisol 1.2 μgm/dL (6-23 μgm/dL)
What effect does cortisol have on the body?
Stimulates glucose synthesis
TR is a 63 yo woman who presents to her PCP with complaints of increasing darkening of the skin, dizziness, and eas fatigability. She claims that she cannot stand on account of severe postural dizziness.
PE: pulse of 106 bpm, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg suping and 70/40 sitting
Labs: fasting blood glucose 66 mg/dL (70-100 mg/dL), Na 136 mEq/L (165-145), K 5.0 mEq/L (3.0-5.5) aldosterone 1 ng/dL (2-9 ng/dL), 8 am plasma cortisol 1.2 μgm/dL (6-23 μgm/dL)
Which hormone causes the darkening of the skin?
GnRH
TR is a 63 yo woman who presents to her PCP with complaints of increasing darkening of the skin, dizziness, and eas fatigability. She claims that she cannot stand on account of severe postural dizziness.
PE: pulse of 106 bpm, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg suping and 70/40 sitting
Labs: fasting blood glucose 66 mg/dL (70-100 mg/dL), Na 136 mEq/L (165-145), K 5.0 mEq/L (3.0-5.5) aldosterone 1 ng/dL (2-9 ng/dL), 8 am plasma cortisol 1.2 μgm/dL (6-23 μgm/dL)
What is the most probable diagnosis?
Addison’s disease (Adrenal insufficiency)

What is the most likely diagnosis?
Bladder infection
Which of the following is released by the thyroid gland?
Calcitonin
Which thyroid hormone is the most physiologically active?
T3
What is the function of 5 alpha-dihidrotestosterone (DHT) in males?
Produces the secondary male characteristics

What disorder triggered the effect on the eye?
Graves’ Disease

Which gland is most likely dysfunctional?
Thyroid Gland

The eye disorder associated with the above disease is called
Exophthalmos
Which hormone produces labor contraction during childbirth?
Oxytocin
Which hormones are stored and/or released by the posterior pituitary gland?
Oxytocin and ADH
Which hormone is primarily responsible for lowering blood glucose levels?
Insulin
Which statement best describes Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus?
T1DM is caused by the absence of insulin.
Which substance is released by the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine
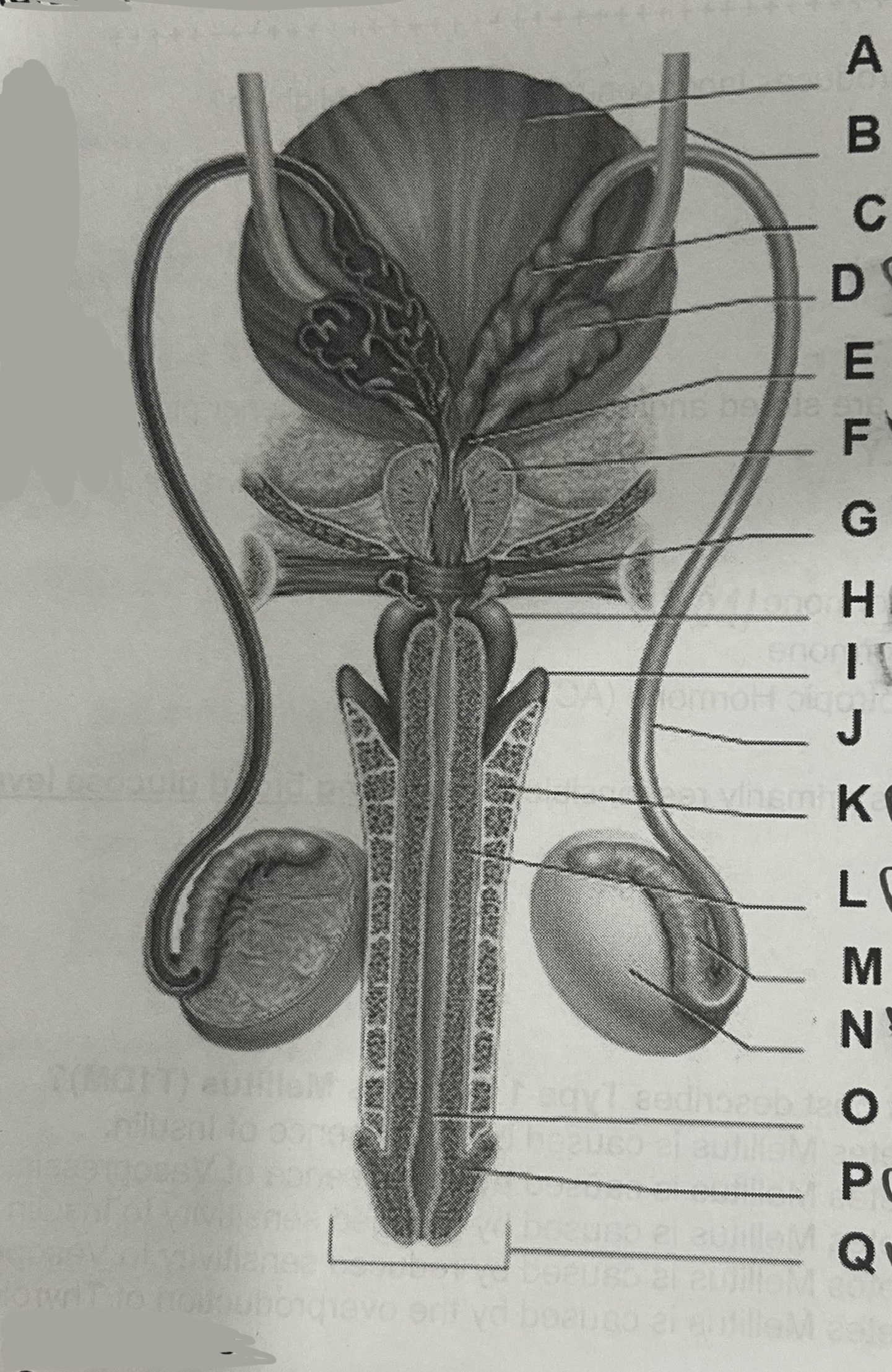
Letter K represents the
Corpus cavernosum
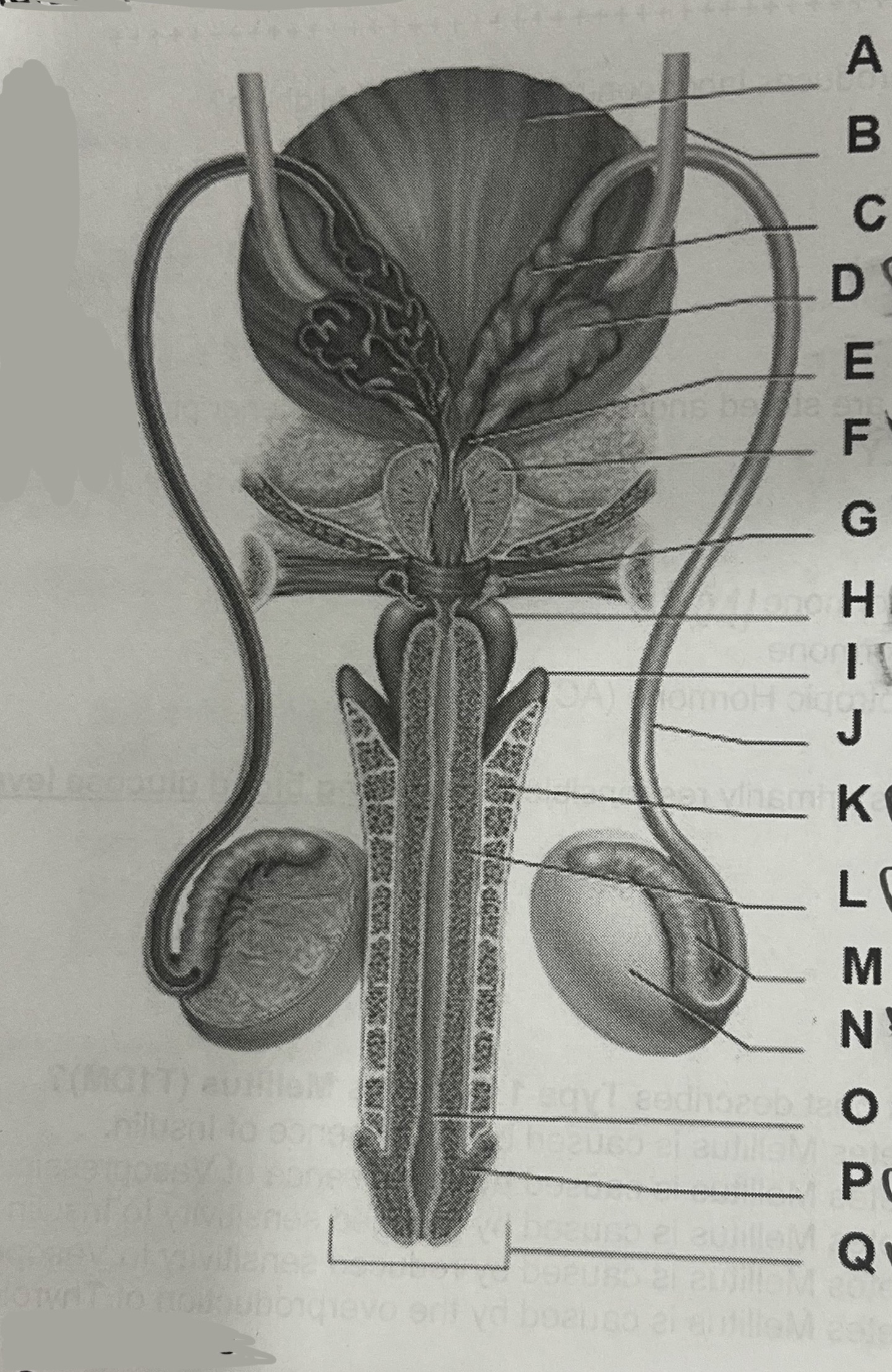
Letter F represents the
Prostate gland
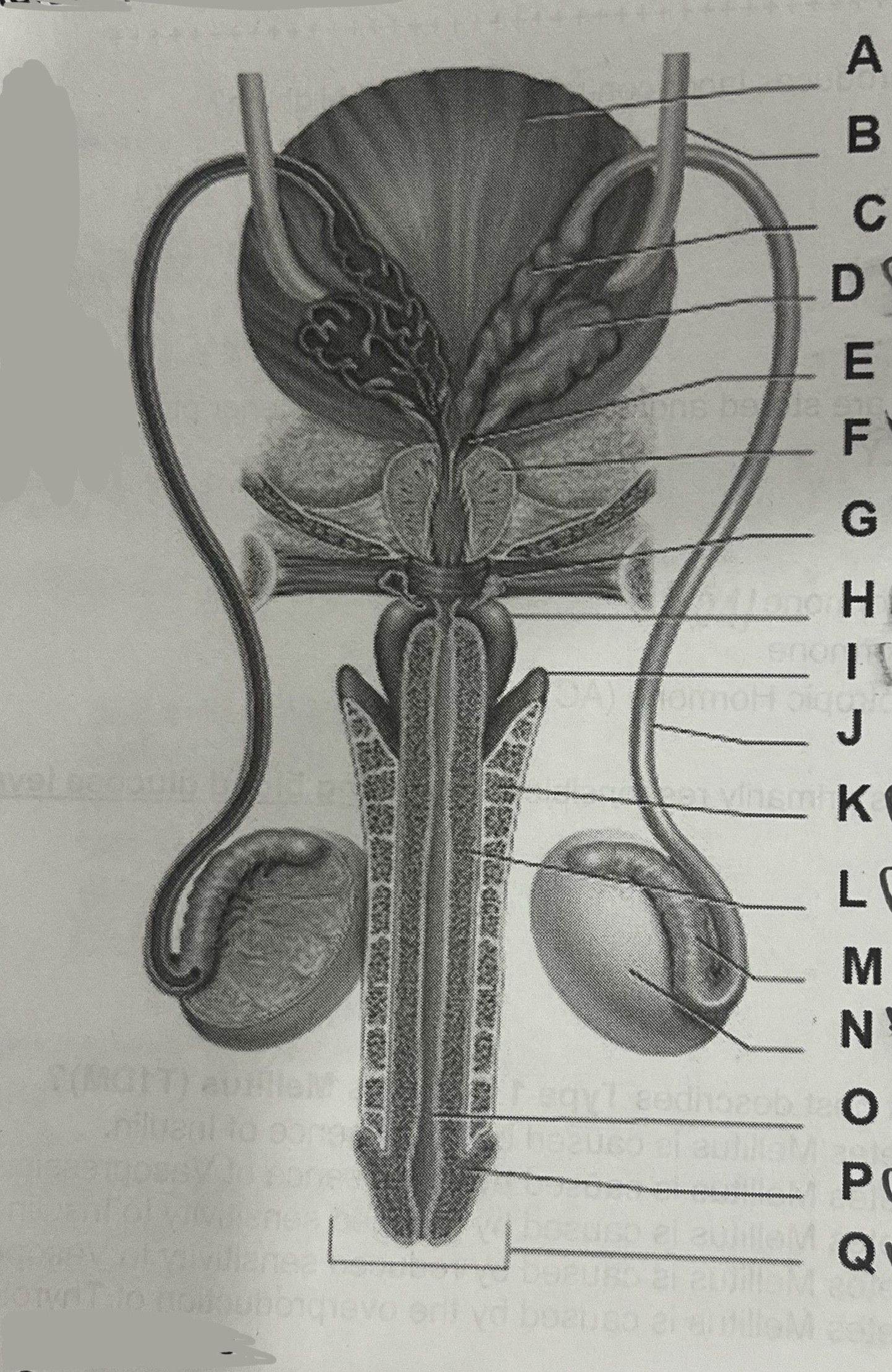
Letter D represents the
Seminal vesicle
A 51 yo male has begun experiencing muscle weakness, fatigue, minimal body hair, and female type distribution of body fat. It is determined that his hypothalamus hormone is elevated and that he has low levels of circulating testosterone, FSH, and LH.
What is the function of FSH in the male?
Simulates the sertoli cells to initiate spermatogenesis.
A 51 yo male has begun experiencing muscle weakness, fatigue, minimal body hair, and female type distribution of body fat. It is determined that his hypothalamus hormone is elevated and that he has low levels of circulating testosterone, FSH, and LH.
Which organ releases LH?
Anterior pituitary gland
A 51 yo male has begun experiencing muscle weakness, fatigue, minimal body hair, and female type distribution of body fat. It is determined that his hypothalamus hormone is elevated and that he has low levels of circulating testosterone, FSH, and LH.
Which hormone is released by the hypothalamus to stimulate the pituitary and ultimately the reproductive organs (testes and ovaries)?
GnRH

Which of the following is the most probable cause of the patient’s signs and symptoms?
Cushing’s disease

The physician concludes that the patient has a tumor. The tumor is most likely located in the _______.
Anterior pituitary
Which cells are responsible for releasing insulin from the pancreas?
Beta cells
Which cells produce the hormone inhibin in males?
Sertoli cells
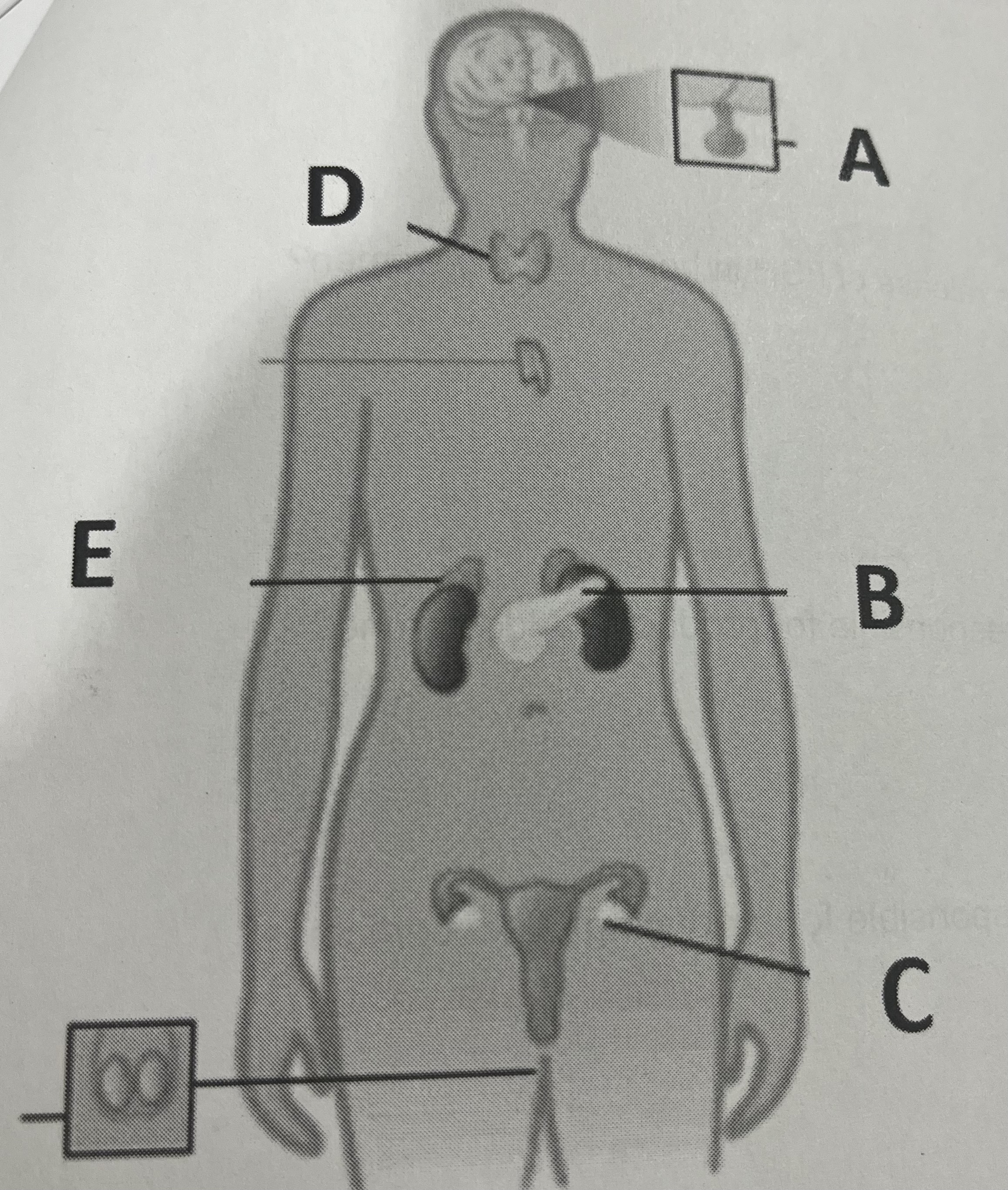
insulin is released form which gland?
B
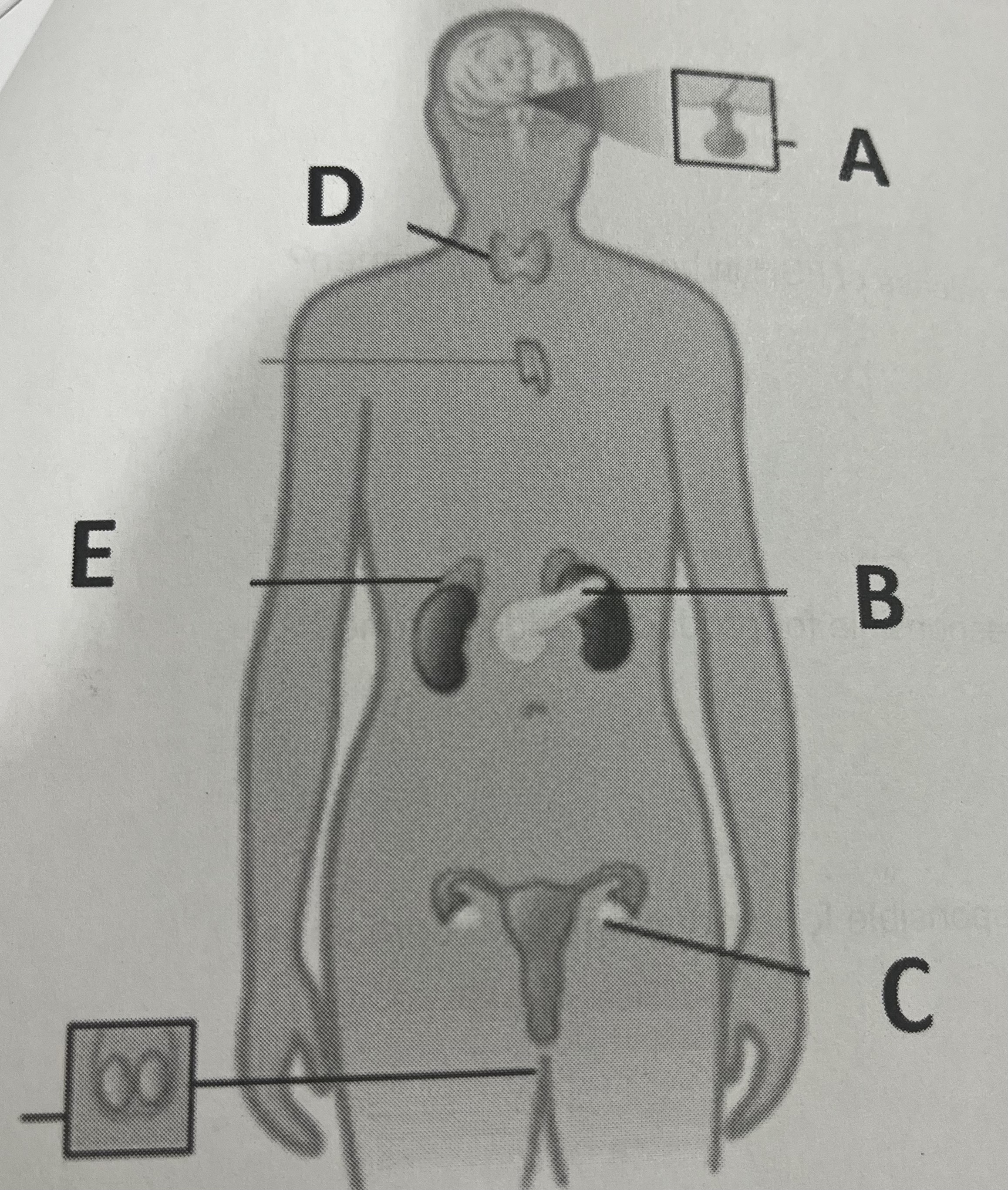
Which structure releases aldosterone?
E
Which cells produce testosterone in med?
Leydig
Which hormone prevents the release of FSH in both men and women?
Inhibin
Whichadrenal cortex layer is responsible for producing aldosterone?
Zona glomerulosa
Which adrenal cortex layer is responsible for producing glococorticoids?
Zona fasciculata
AH is a 28 yo female who has been recently diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (hypothyroidism) She also discovers she is six weeks pregnant. What is the most likely outcome if the hashimoto’s thyroiditis is not treated?
The fetus’ brain will be the under-developed.
Which hormone increases basal metabolic rate?
Thyroid hormone
Which hormone increases glucocorticoid production?
Adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
What is the neurotransmitter that is released by the preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
Relaxation of bronchi is caused by the
Sympathetic nervous system
Increased gastrointestinal motility is caused by the
Parasympathetic nervous system
Contraction of the ciliary muscles of the eye is caused by the
Sympathetic nervous system
Increased heart rate, increased force of contraction, and increased impulse conduction is controlled by the
Sympathetic nervous system
Increased salivation is caused by the
Parasympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic preganglionic nerves emanate from which regions of the spinal cord
Thoracic and lumbar
The nicotinic receptor is an example of a
Ligand gated ion channel

Based on the constellation of symptoms, Methamphetamine is most likely mimicking which neurotransmitter?
Norepinephrine

Activation of which receptor most likely caused the abnormal blood pressure?
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor

As an emergency attendant, you are charged with identifying hypothetical medications which could slow the patient’s heart rate. Which hypothetical medications below could be used to reduce the heart rate?
Metoprolol (beta-1 blocker)
The fight of flight response is caused primarily by the activation of which nervous system?
Sympathetic nervous system
Which adrenergic receptor is found on the presynaptic neuron and serves as an auto receptor that decreases neurotransmitter release?
Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors
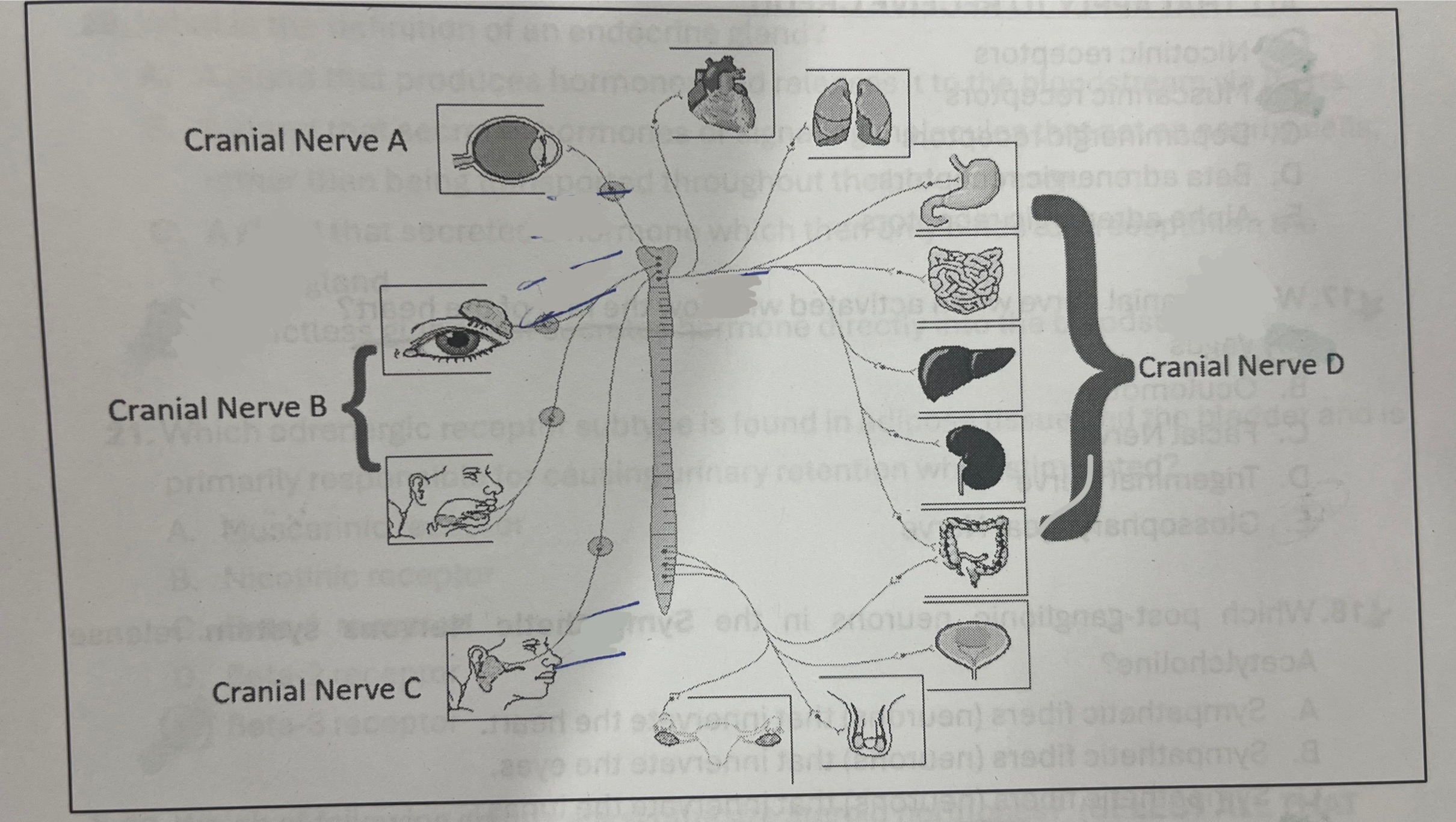
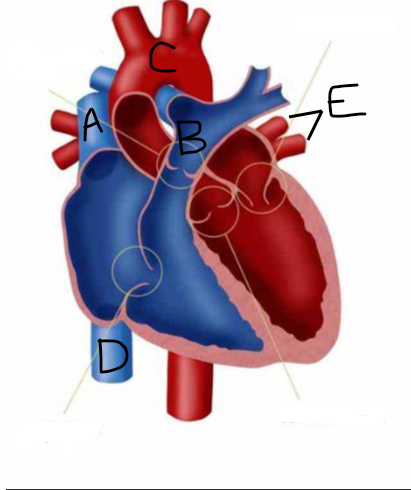
Which cranial nerve represents the vagus nerve?
D
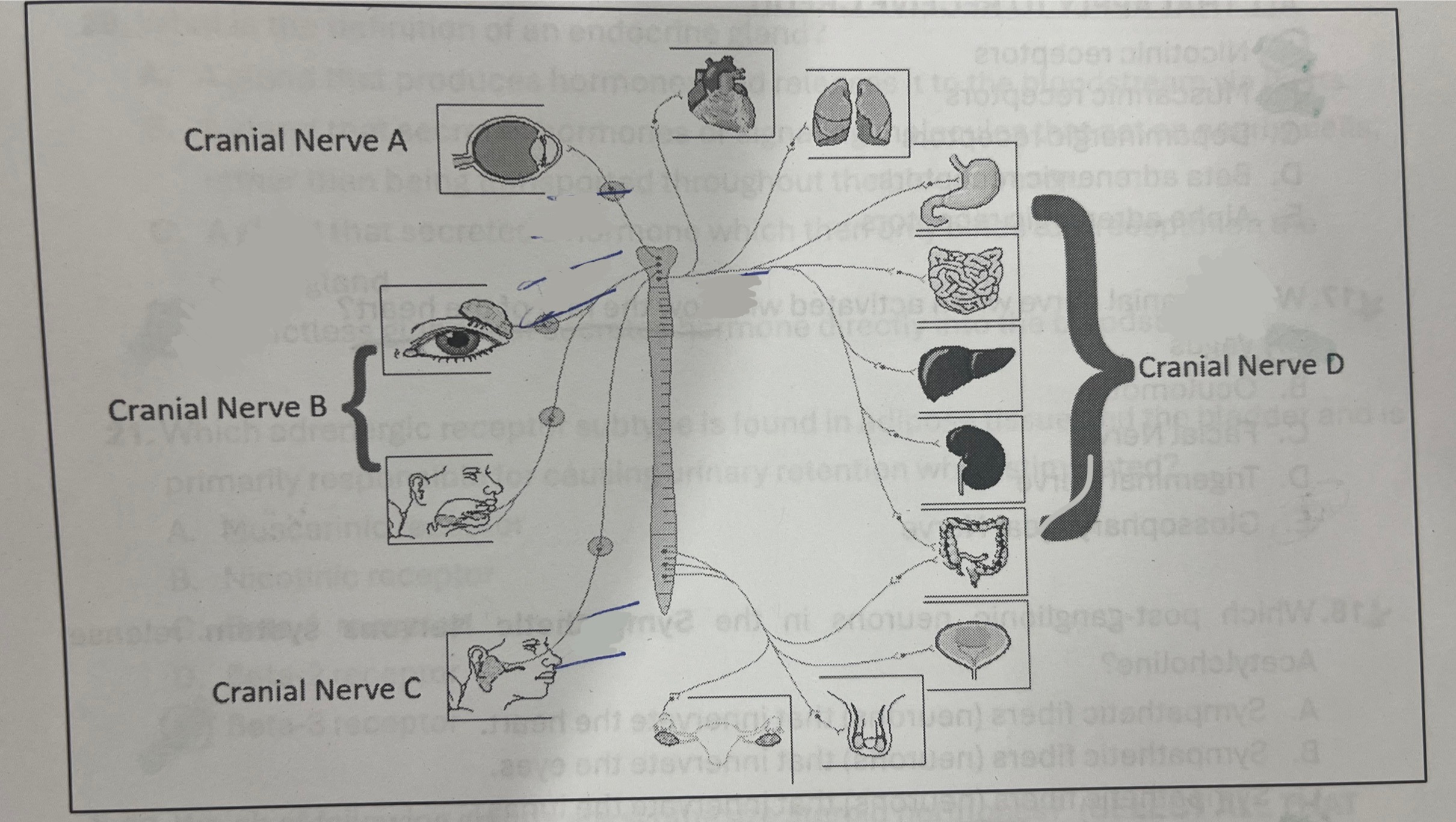
Which nerve represents the glossopharyngeal nerve?
C
Which receptors are stimulated by direct interaction with ACh?
Nicotinic and muscarinic
Which cranial nerve, when activated, will slow the rate of the heart?
Vagus
Which post-ganglionic neurons in the SNS release ACh?
Sympathetic fibers/neurons that innervate the sweat glands
Which protein is primarily responsible for terminating the actions of neurotransmitters released by sympathetic neurons?
Norepinephrine transporter
What is the definition of an endocrine gland?
A ductless gland that secretes hormone directly into the bloodstream
Which adrenergic receptor subtype is found in adipose tissue and the bladder and is primarily responsible for causing urinary retention when stimulated?
Beta-3 receptor
A drug or chemical that mimics the actions of an endogenous (natural) neurotransmitter or hormone is called
An agonist
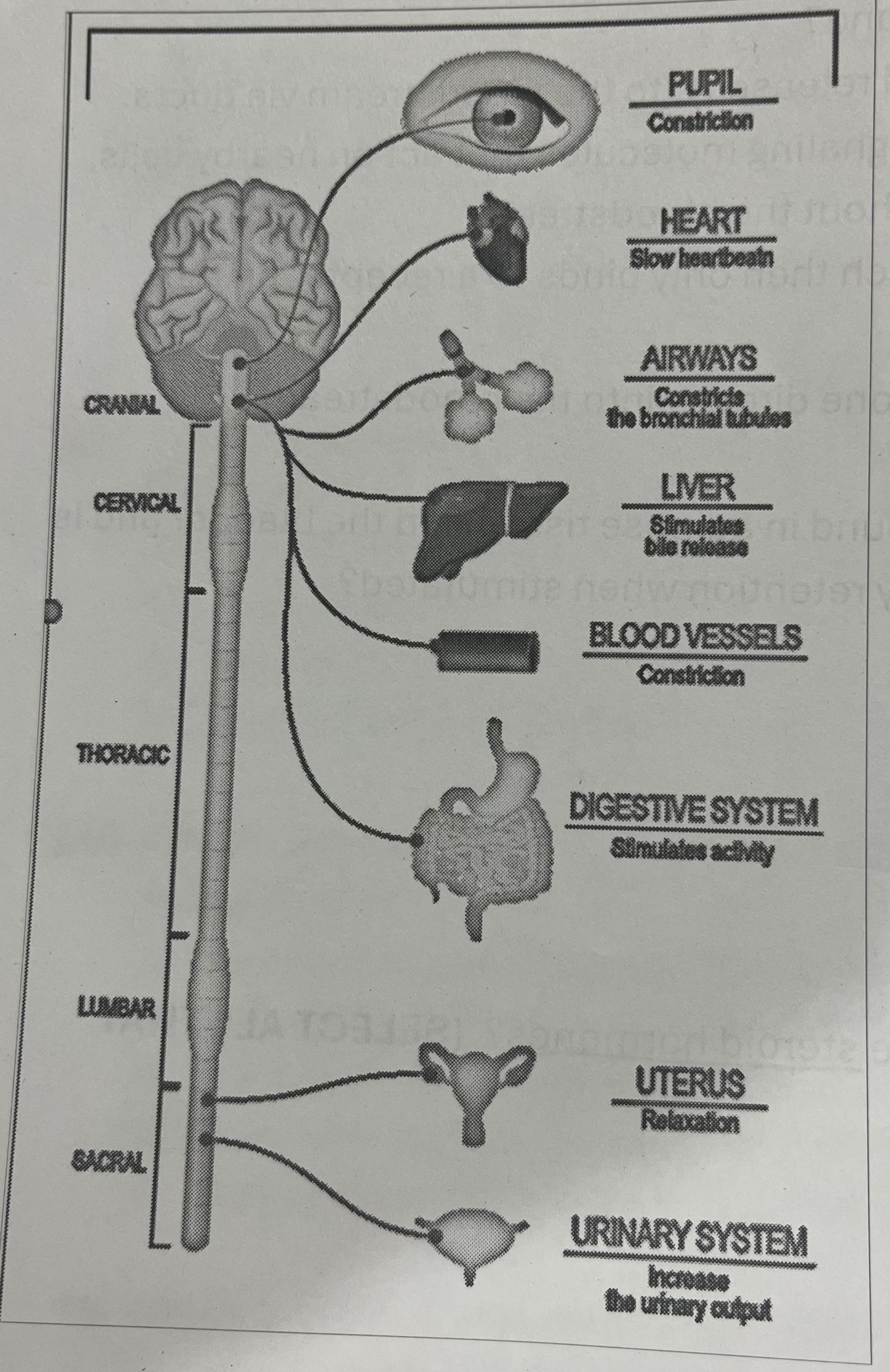
Which division of the autonomic nervous system is depicted in the diagram above?
Parasympathetic nervous system
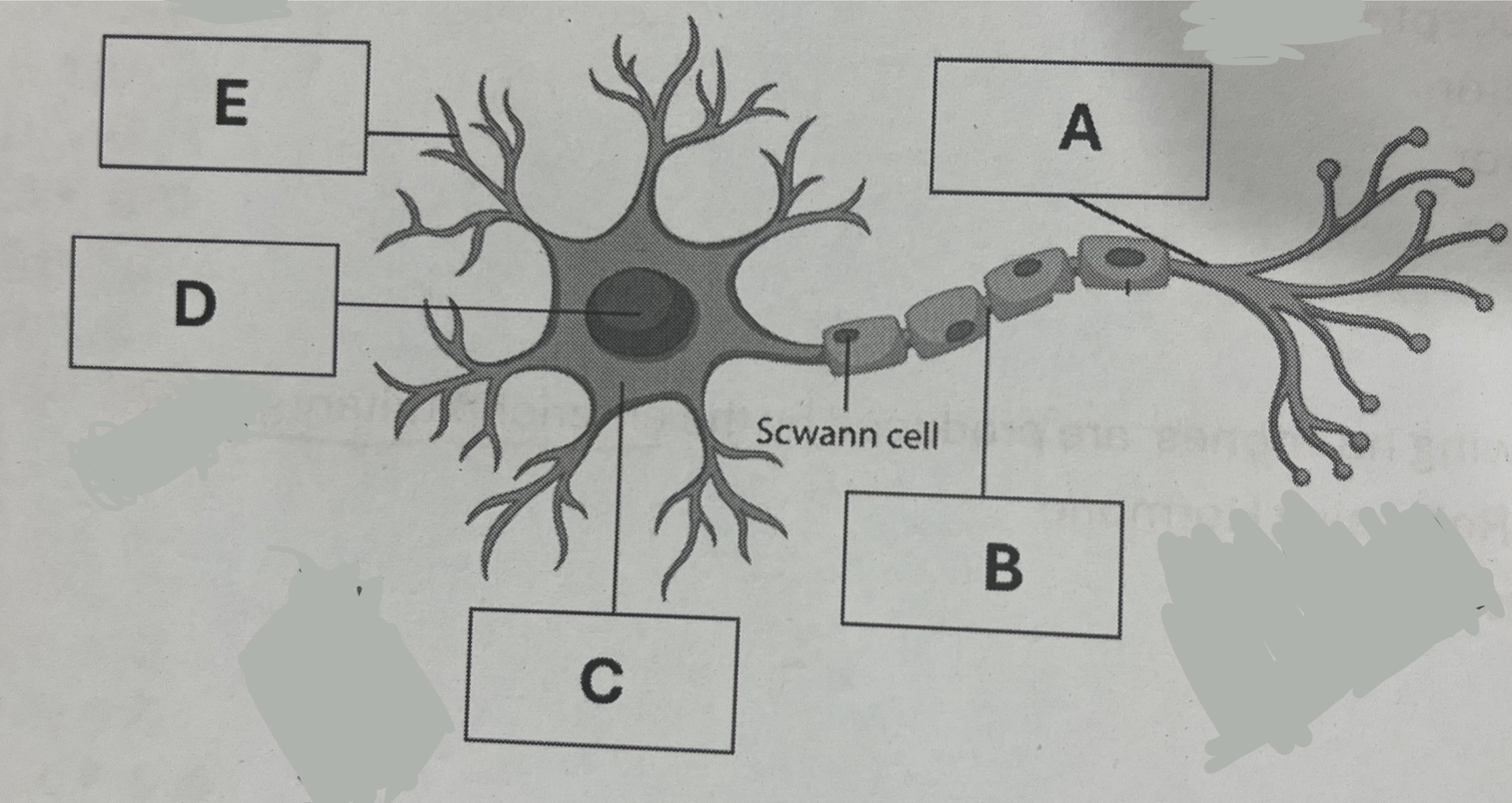
Point A represents which structure?
Axon
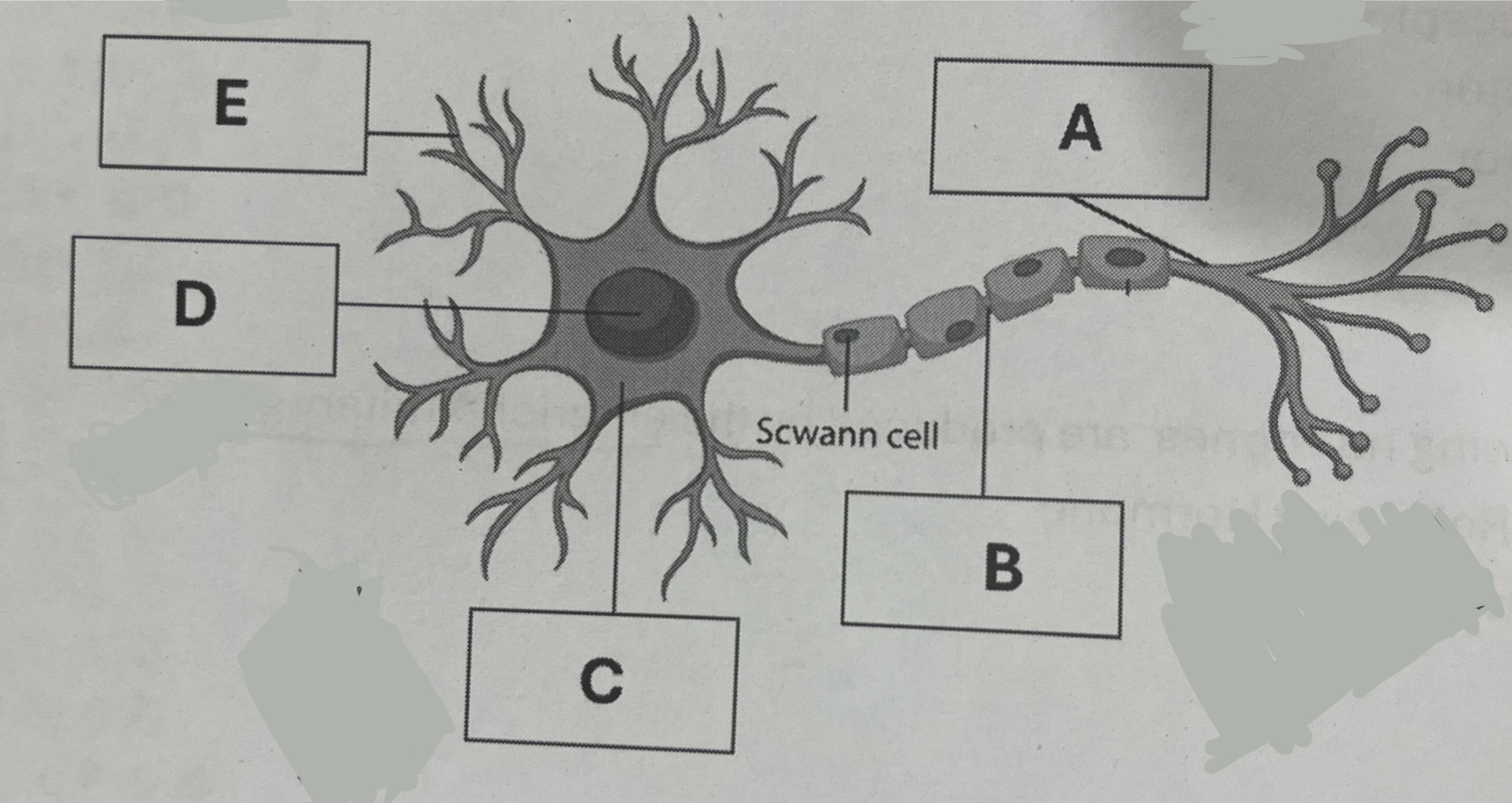
Point B represents which structure?
Node of ranvier
Which enzyme is responsible for synthesizing acetylcholine?
Choline Acetyltransferase
The SLUDGE effect is caused by the activation of
Muscarinic receptors
Which of the following hormones are produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Luteinizing hormone
Which of the following hormones is released by the hypothalamus?
Corticotropin releasing hormone
The stimulation of which receptor in the lungs and heart will cause bronchoconstriction and bradycardia?
Muscarinic cholinergic receptor
Which enzyme is responsible for degrading ACh
Acetylcholinesterase
Rest and digest is caused by the activation of which division of the autonomic nervous system?
Parasympathetic nervous system
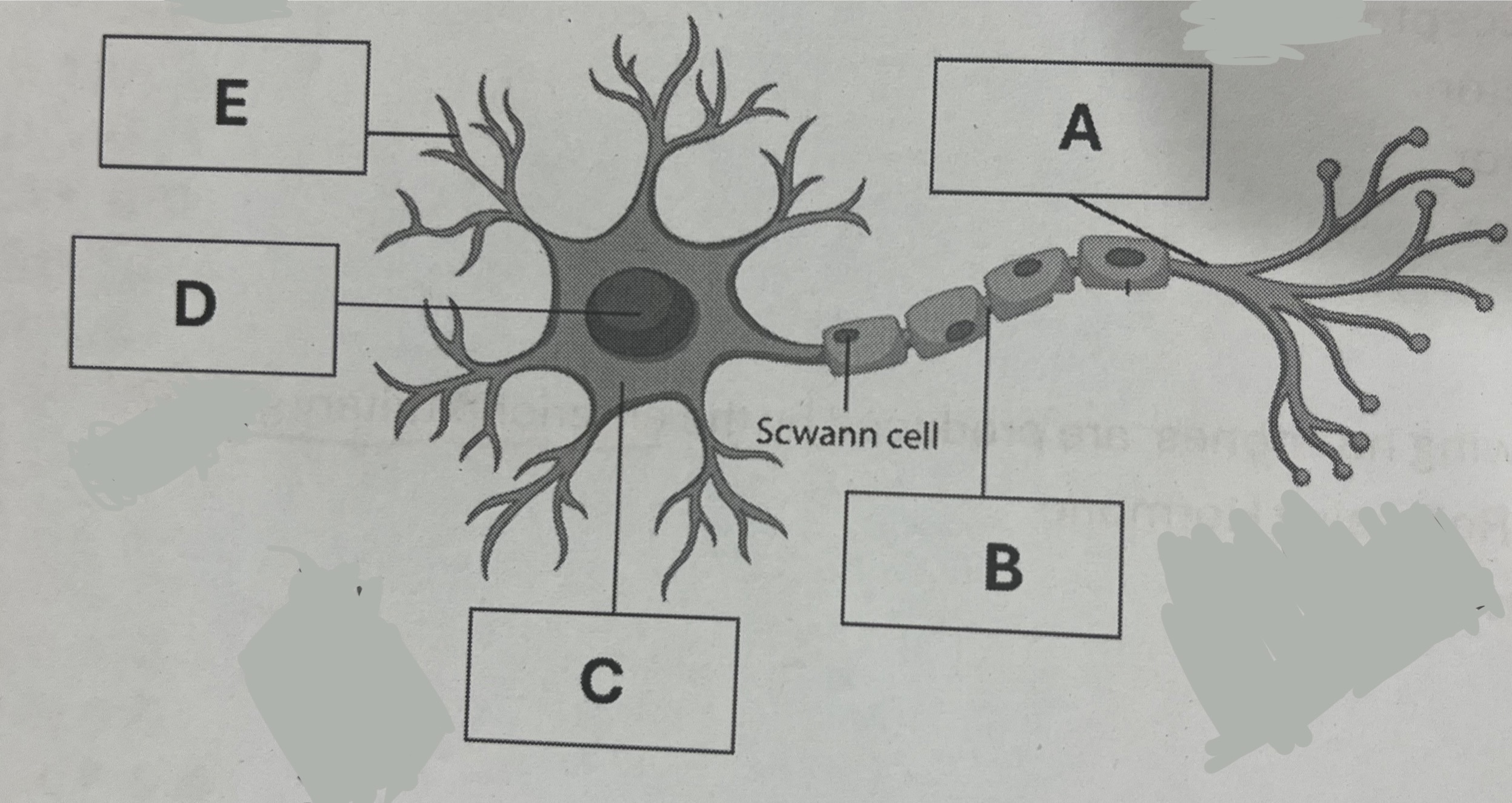
The neurotransmitter will be released from
A
Which layer of the adrenal gland releases epinephrine?
Adrenal Medulla
Which ANS receptor is found in the blood vessels and causes vasoconstriction and the rise in blood pressure when activated?
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors