divisions of nervous system, endocrine system, neurons
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the two branches of the nervous system
CNS central nervous system and PNS peripheral nervous system
What are the branches of the CNS
spinal cord and brain
what are the branches of the PNS
somatic (SNS) and autonomic (ANS)
What are the branches of the ANS
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
what is the somatic subdivision
sensory and motor voluntary movement
what does the sympathetic subdivision do
increases heart rate and breathing rate, pupils dilate, inhibits digestion and saliva production - fight or flight system fueled by adrenaline
what does the parasympathetic subdivision do
decreases heart rate and breathing rate, pupils constrict, stimulates digestion and saliva digestion - rest and digest
what are the 3 types of neurons
sensory, motor, relay
function and structure of sensory neuron
stimulates electrical impulse from receptors to the relay neuron in CNS - cell body in the middle of axon, shorter axon and longer dendrites
function and structure of motor neuron
carries electrical impulse from CNS/relay neuron to effector organ causing a response - long axon and shorter dendrites + myelin sheath
function and structure of relay neuron
carries electrical impulse from sensory neuron to motor neuron across synapses - shorter dendrites and longer axon
what is the endocrine system
system of glands which produce hormones that are released into the bloodstream - helps regulate the activity of cells and organs in the body, communicates chemical messages to the organs of the body
pituitary gland
produces hormones in the brain which stimulate other glands to produce their hormones - regulatory function
what is the sympathomedullary pathway (SAM response)
threat processed by hypothalamus
activation of sympathetic branch of ANS
nerve message to adrenal gland
adrenaline released into bloodstream
fight or flight response
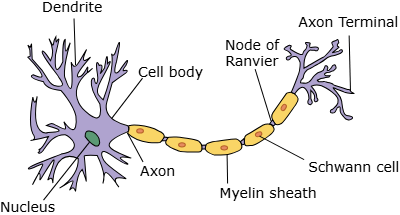
motor neurone
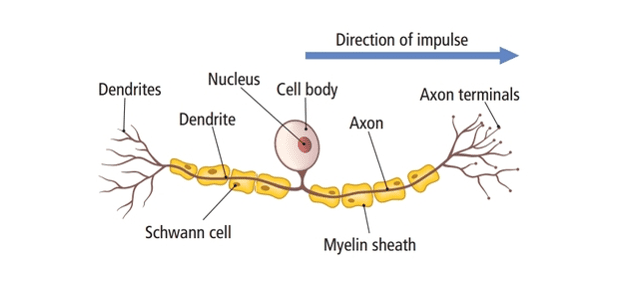
sensory neurone
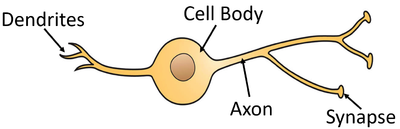
relay neurone