Semester 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
NUMBERS AND SETS
NUMBERS AND SETS
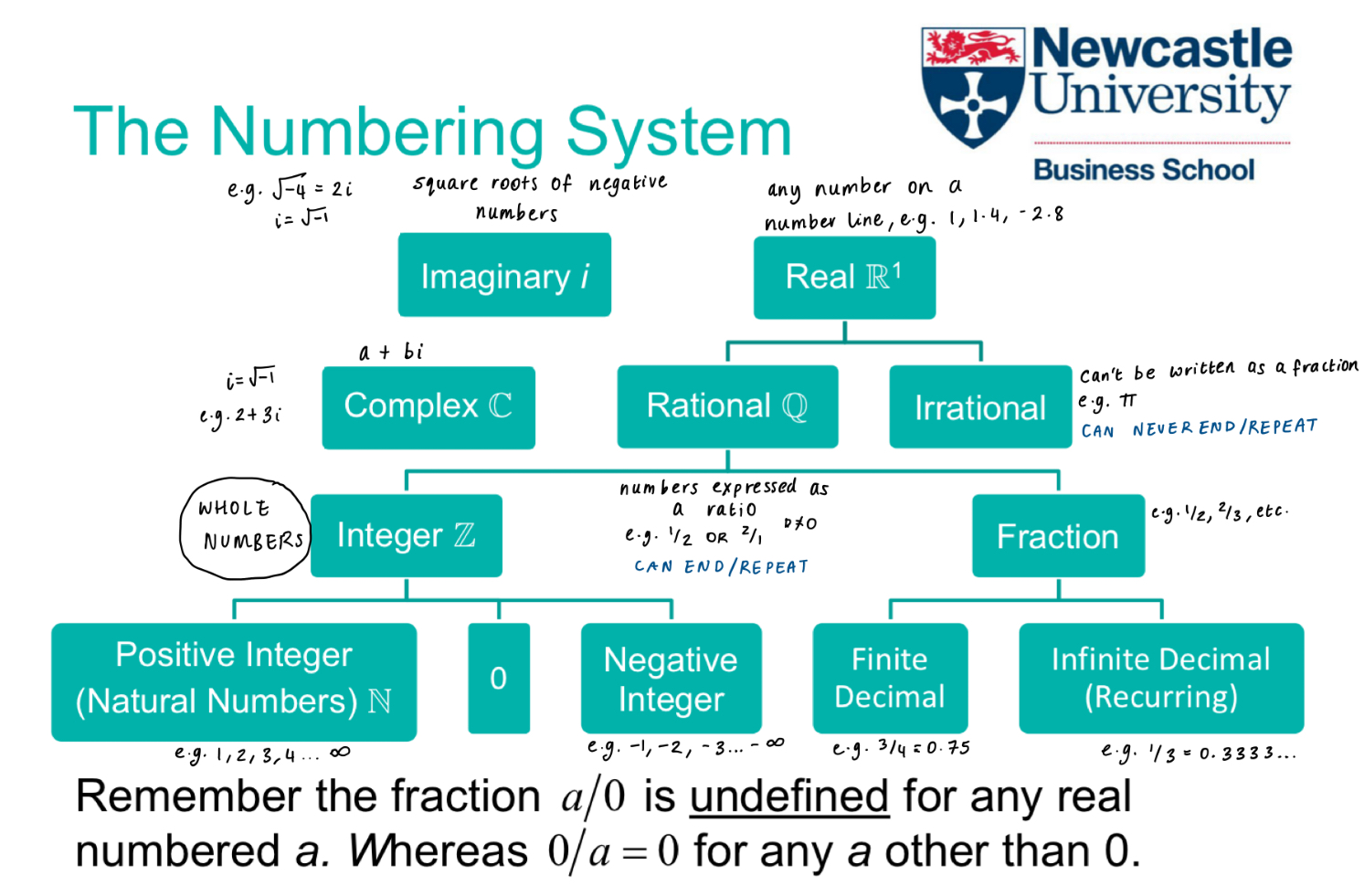
Name the different types of numbers in the numbering system.
∈
An element (of a set)
*a set is a collection of elements*
e.g. 2 ∈ Z (an integer)
How do we write:
a is a subset of A
Being in a implies I must be in set A
What condition is this in economics?
a ⊂ A
(the subset a is contained in set A)
OR
a ⇒ A
(a implies I must be in set A)
Sufficient condition - being in a is sufficient for being in A
How could we alternatively write this:
A contains a
Can’t be in a without first being in A
What condition is this in economics?
A ⊃ a
(set A contains subset a)
OR
A ⇐ a
(can’t be in subset a without being in set A first)
Necessary condition - being in A is a necessary condition for being in a
What would you write if:
a and A contain equivalent elements
How would this be implied?
What is this condition called?
a ⊂ A and A ⊂ e
OR
a ⇔ A
This is a sufficient and necessary condition
What are intervals?
need to write this
What are examples of different inequalities?
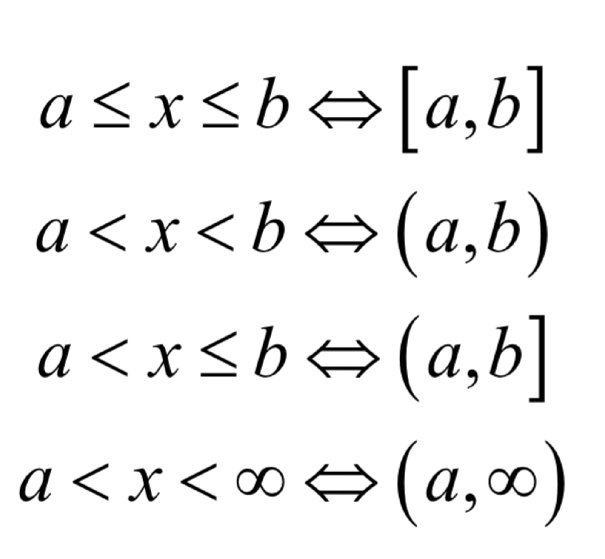
What does this look like on a Venn diagram:
Intersection (and) = n
Union (or) = u
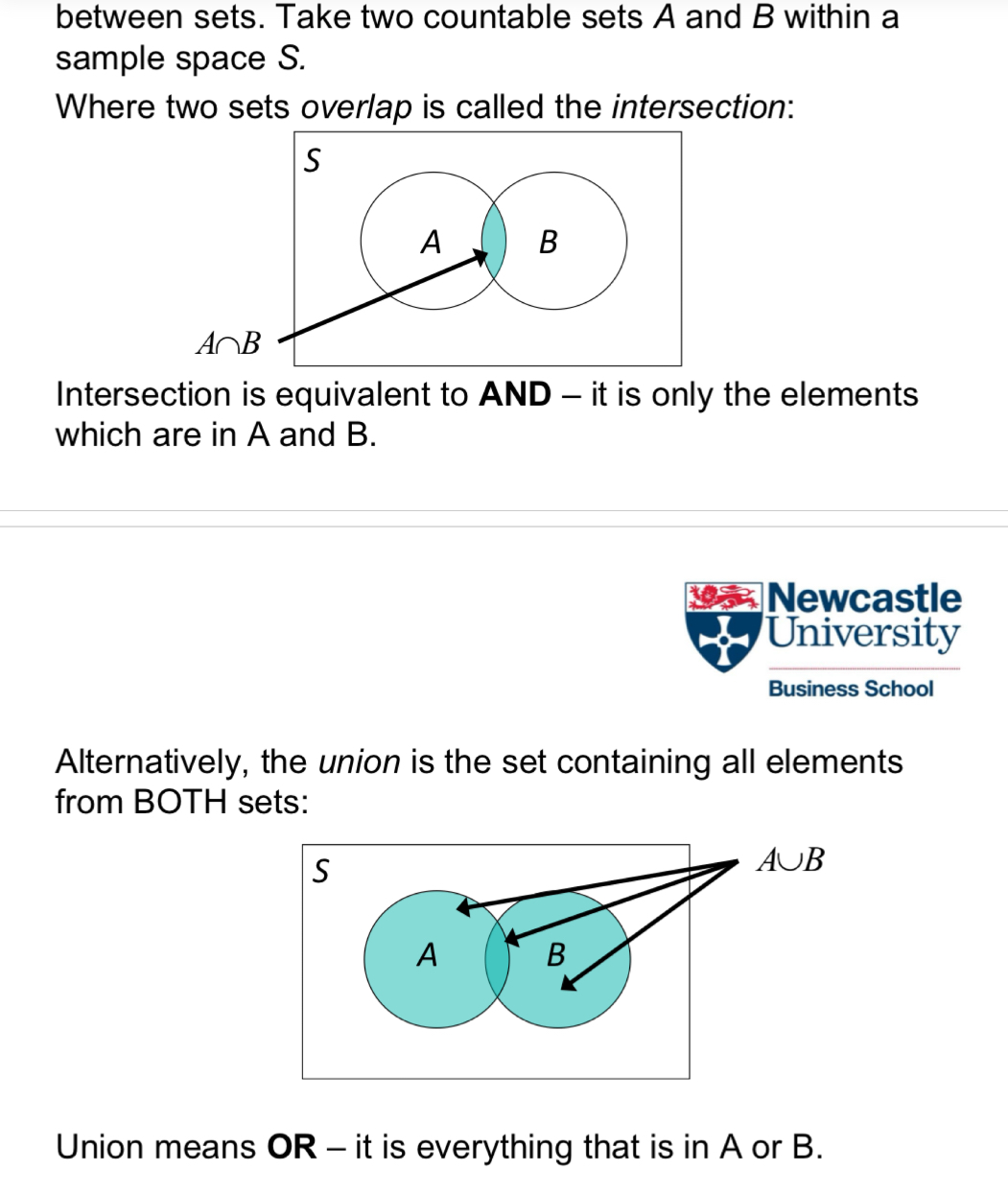
What does this look like on a Venn diagram:
A compliment of a set
A special set (null set)

LINEAR FUNCTIONS
LINEAR FUNCTIONS
NON-LINEAR FUNCTIONS
NON-LINEAR FUNCTIONS
What is the formula for compound interest?
y = A (1 + r)n
(A = initial balance, r = rate, n = periods)
LIMITS AND INEQUALITIES
LIMITS AND INEQUALITIES
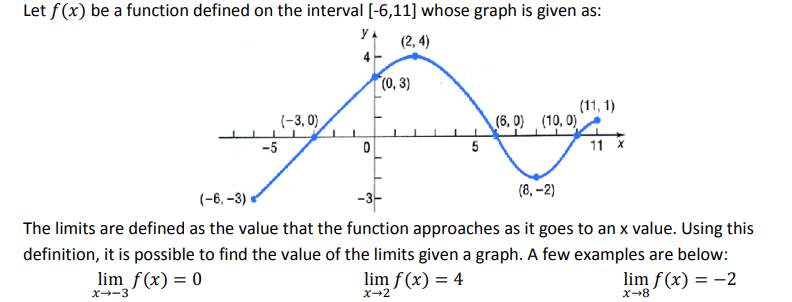
What are limits?
The value that the function approaches as it goes to an x value
e.g. shown on picture
How do you write out and calculate:
approaching from the left
approaching from the right
E.g. if limit was 4 use a table and do:
Approaching from the left (below):
3.9, 3.99, 3.999 > input that into the function & see what number it is closest to
Approaching from the right (above):
4.1, 4.01, 4.001 > input that into the function & see what number it is closest to
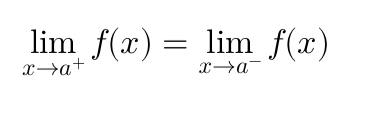
How do you work out the value of the function?
Should say: e.g. ‘2 if x=2’ so f(2) = 2 - DONT PUT INTO EQUATION
If just has the equation, then put the value into equation to find the limit

What are the 3 features that are required for a function to be continuous at a specific point (a limit)?
(continuity = drawing a graph at that point without lifting up your pen)
The value of the function approaching from the left (below) = value of function approaching from right (above) - so basically if limit exists > if not limit doesn’t exist
You can plug x = a into a function and get a REAL NUMBER
The limit = the function value at point a > if not there is a ‘jump’ or mismatch

What happens if any one of those features fails?
A function is discontinuous at point a
*REMEMBER*
Behaviour of y = value of the function
e.g. if function increasing, value of y increasing
*REMEMBER*
Behaviour of y = value of the function
e.g. if function increasing, value of y increasing
What types of inequalities are these:
x > y
x > y
A < z < B
x > y = strict inequality (x strictly greater than y)
x > y = weak inequality (x is greater than or equal to y)
A < z < B = double inequality (z is in the right half open interval) [A, B) - includes A but not B so the right half is ‘open’
AC > BC A = 2, B = 1
In terms of the direction of an inequality, what happens if you times with a:
positive number
negative number
Positive = preserves direction of inequality
e.g. C = 3, AC > BC bc 6 > 3
Negative = reverses direction of inequality
e.g. if C = -3, AC < BC bc -6 < -3
What is the formula for a rectangular hyperbola?
y = (C / x + B) + A
CALCULUS (DIFFERENTIATION)
CALCULUS (DIFFERENTIATION)
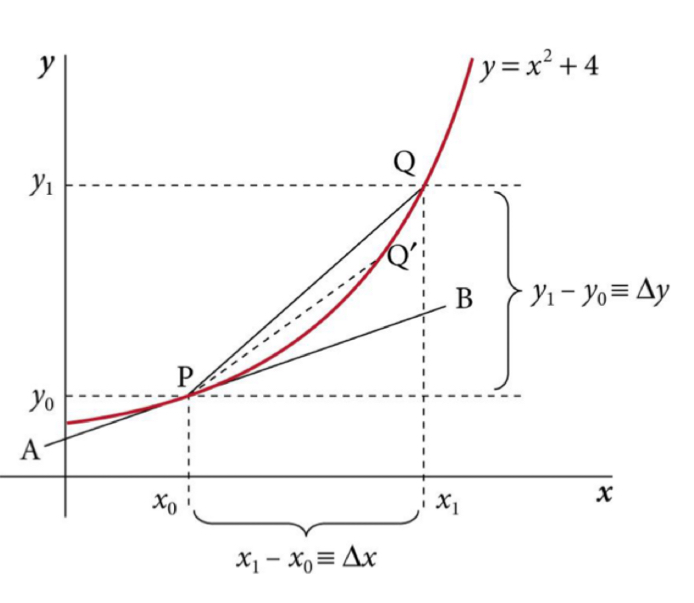
What is a line joining 2 points on a curve called?
A chord
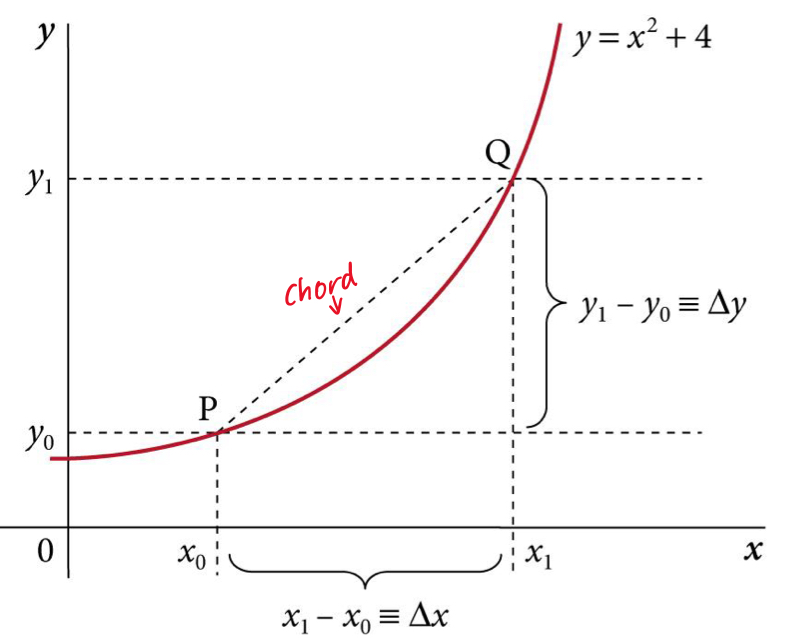
What is the slope of a straight line (chord) defined as?
△y / △x
What is a tangent?
A line which touches a curve at one point
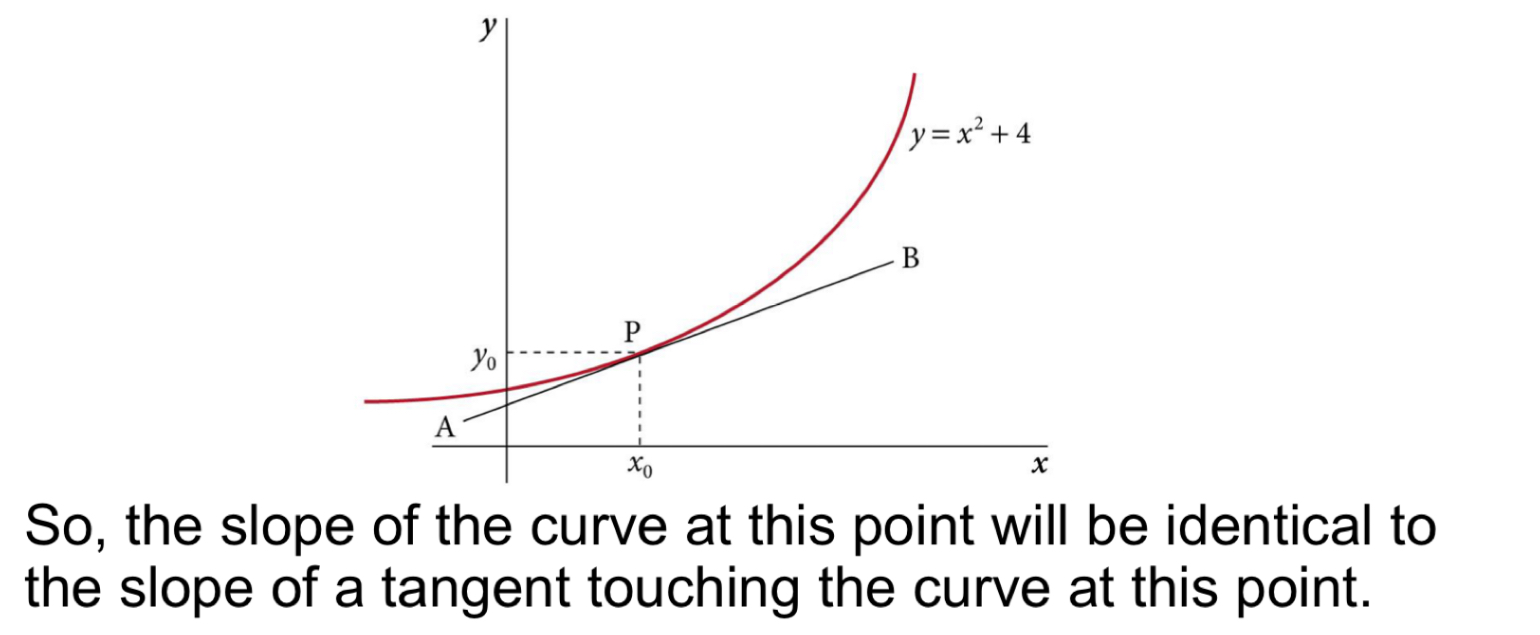
What is the slope of a tangent defined as?
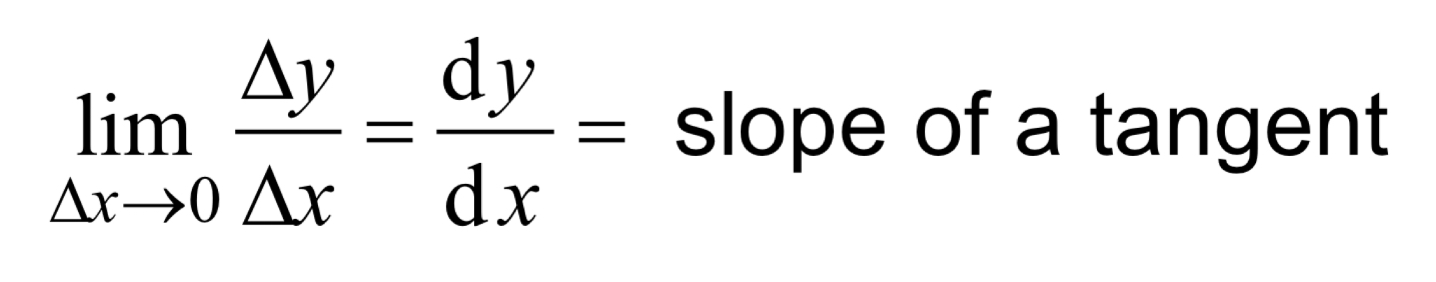
How can we find the slope of a tangent at any point along the curve (without graphing the function)?
E.g. if want the slope of a tangent at point P:
If we have a chord (PQ)
As we move point Q around the curve, nearer to point P
= slope of the chord will become a better approximation of the slope of a tangent at point P
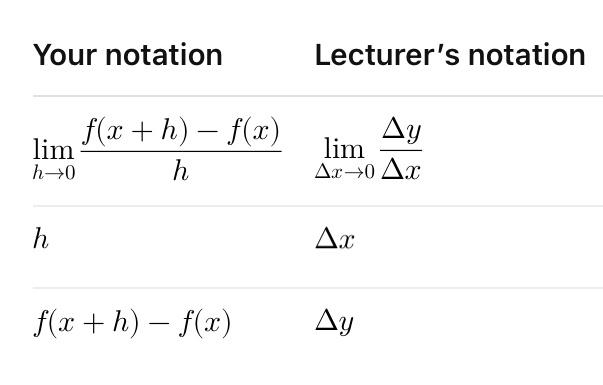
Find the meaning of this notation:
Find the notation for these meanings:

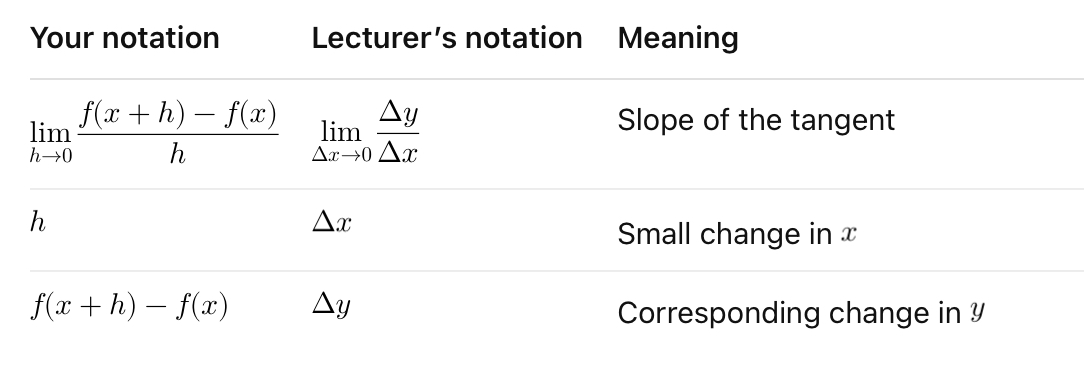
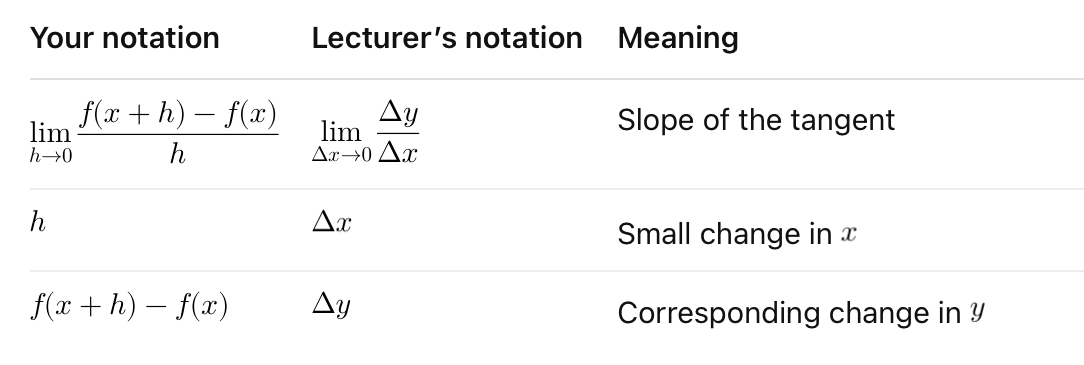
What does differentiating from first principles mean?
Finding the slope of a tangent (by looking at the slope between 2 points that get infinitely close together)
= derivative of a function
What is the formula for finding the slope of a tangent?
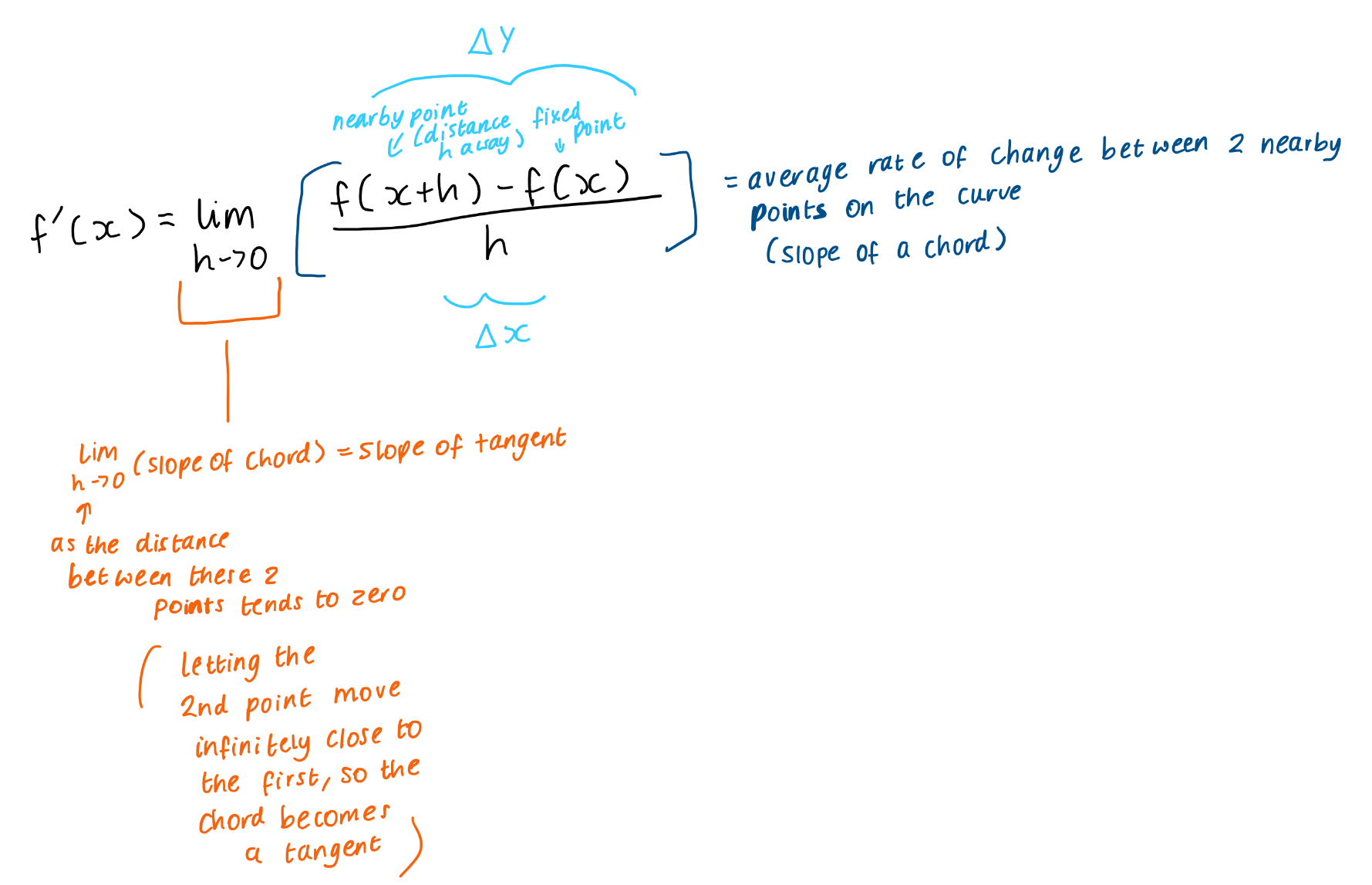
Differentiating from first principles:
Describe the 7 steps
For each step, explain what is going on
Get your formula and & work out your answer shorthand already (extra)
Write out the formula for f’(x)
Work out f(x+h)
Substitute f(x+h) and f(x) into formula
Get rid of brackets + cancel out common terms
Factor + simplify (divide by h)
Take the limit (h=0) to get final answer & check answer the same as step 1

What are the 7 rules of differentiation?
(SPAMPF Q)
Sums of functions rule
Power rule
Additive constant rule
Multiplicative constant rule
(more complicated rules)
Product rule
Function of a function rule (chain rule)
Quotient rule
(5+6 are the same thing just 5 is 2 brackets with different things and 6 is same thing in both brackets)
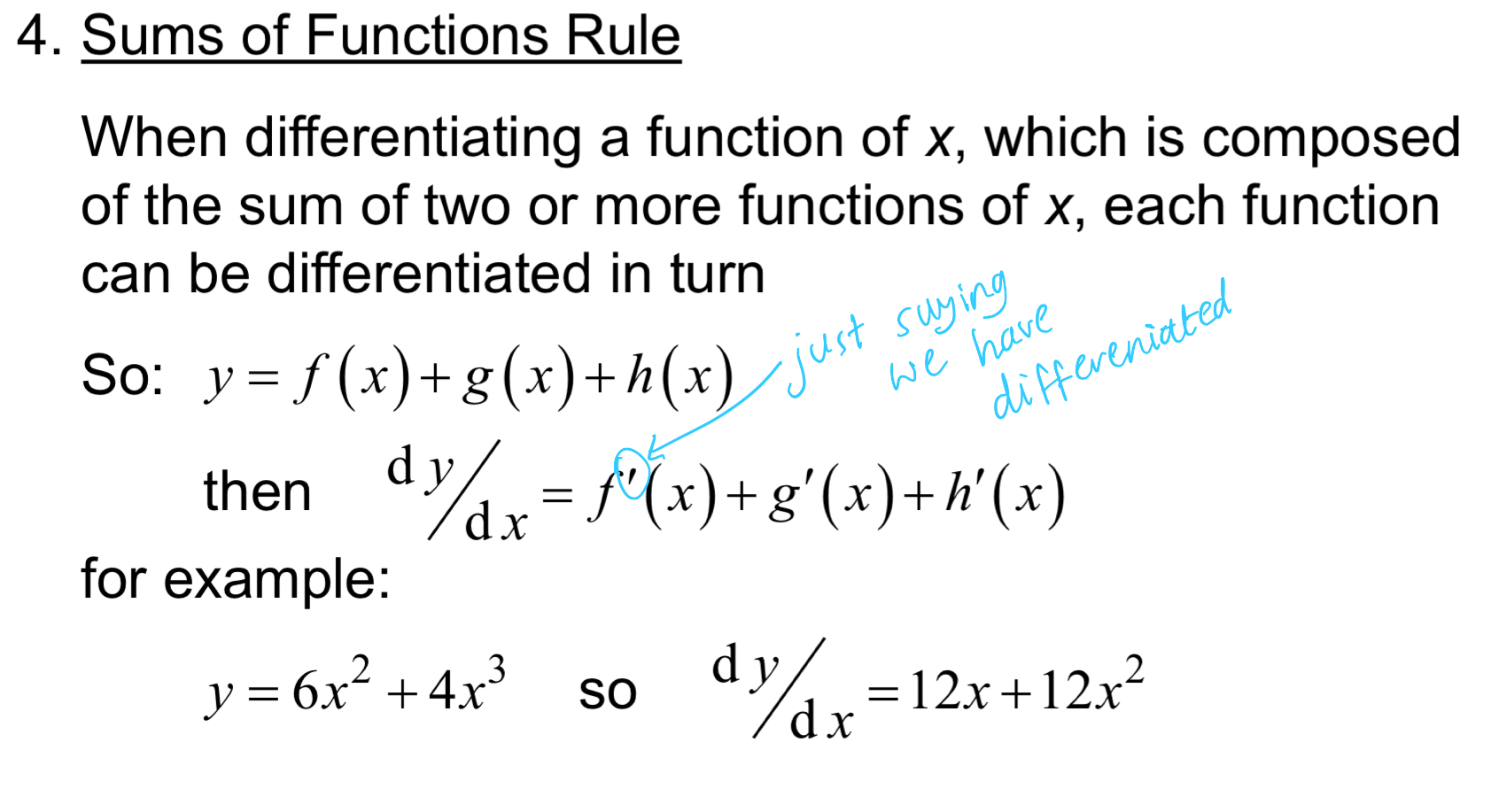
Sums of functions rule
if f(x) contains different functions within it
e.g. f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
then each function within the function needs to be differentiated
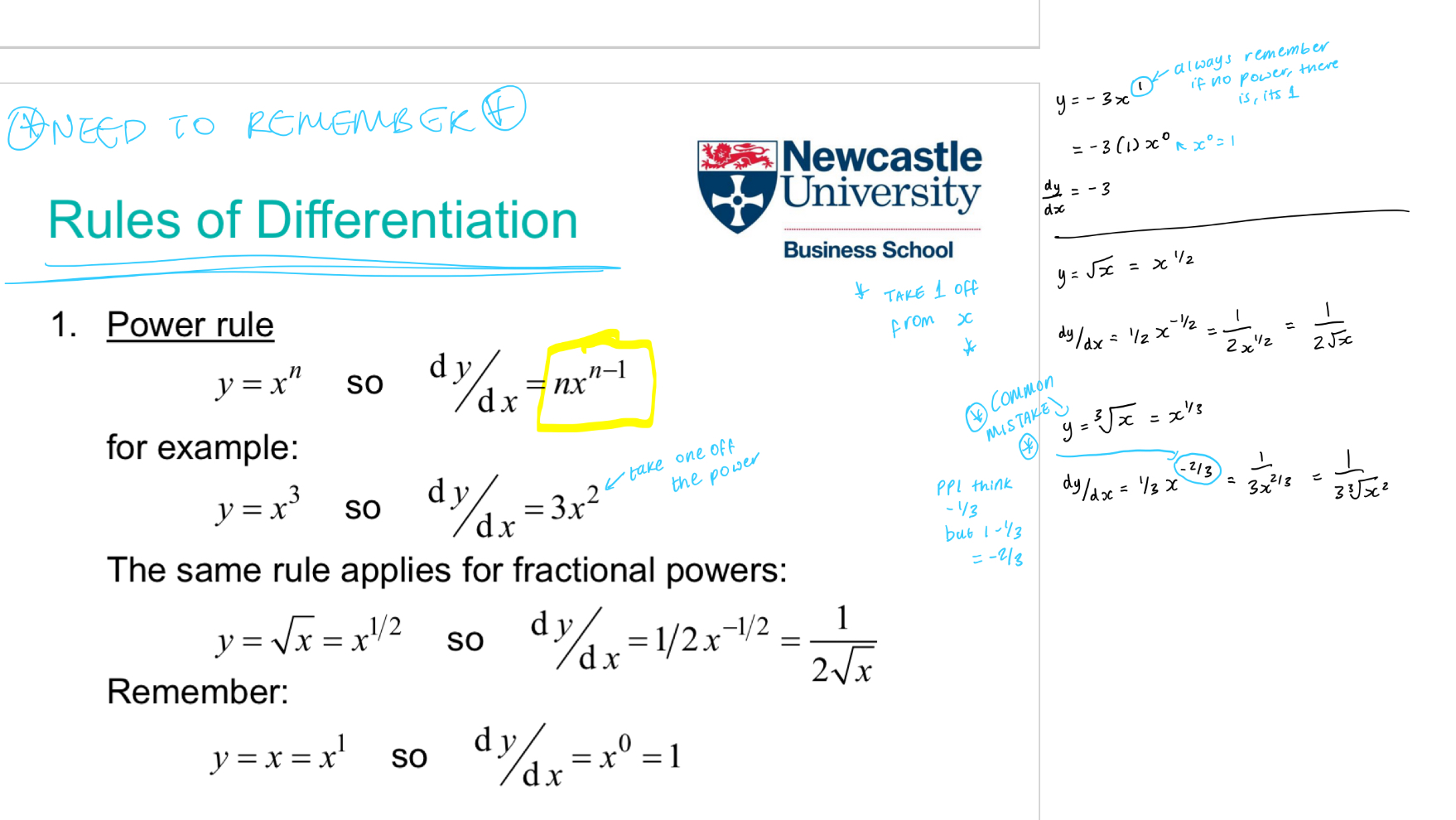
Power rule
for the power, you always minus 1
and whatever the power is, you times it by the constant
square root = fraction > √x = x1/2 OR 3√x = x1/3
*1 minus the fraction*
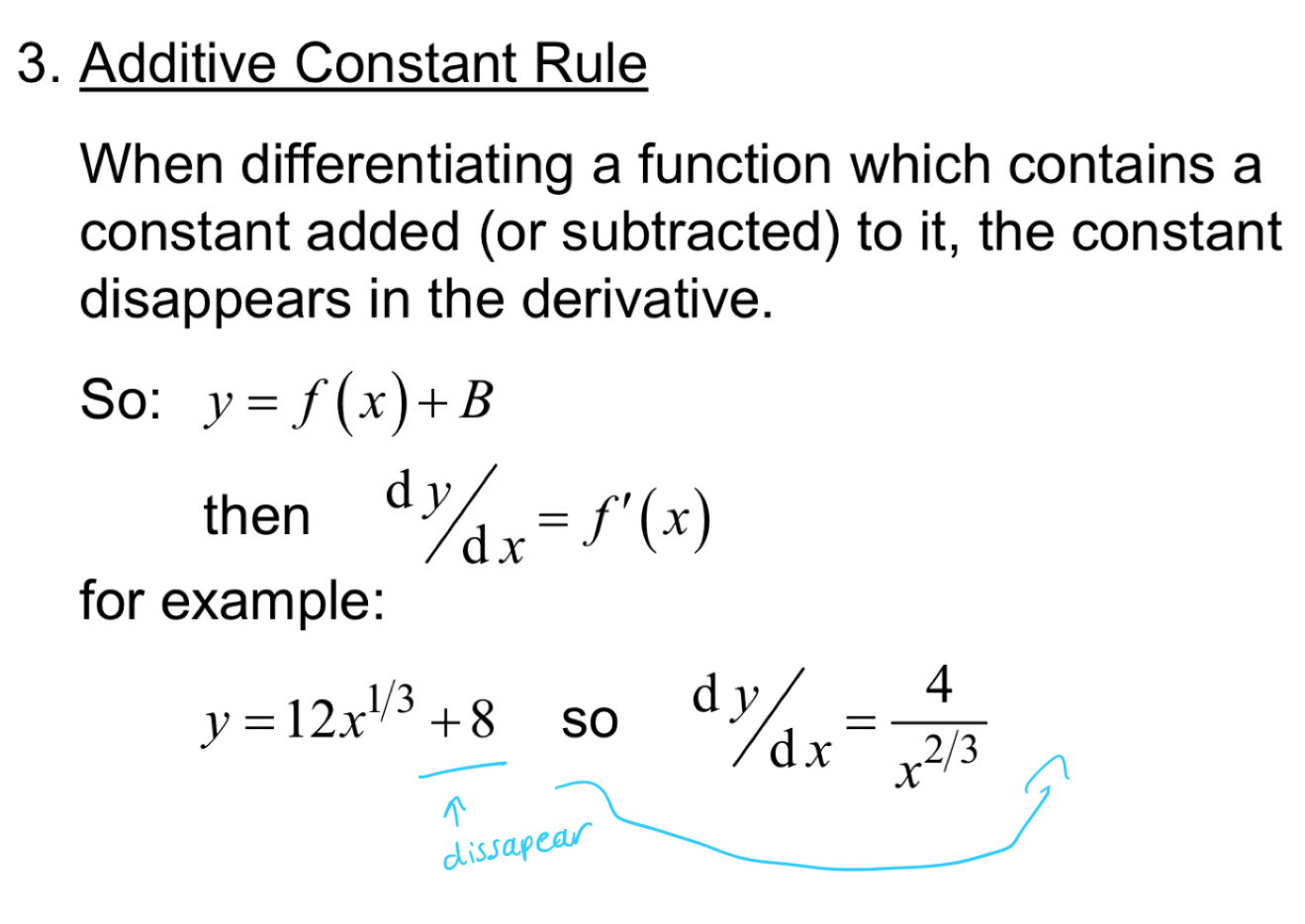
Additive constant rule
constant disappears in the derivative
Multiplicative constant rule
any constant that multiplies an x term remains unchanged when differentiated (just times by power)

Product rule
different things in each bracket
dy/dx = v(du/dx) + u (dv/dx)
U WITH A V, V WITH A U
because of things in front = cross multiplication

Function of a function rule (chain rule)
same thing in each bracket
dy/dx = dy/du x du/dx
over u = main one outside of brackets
over x = equation inside brackets
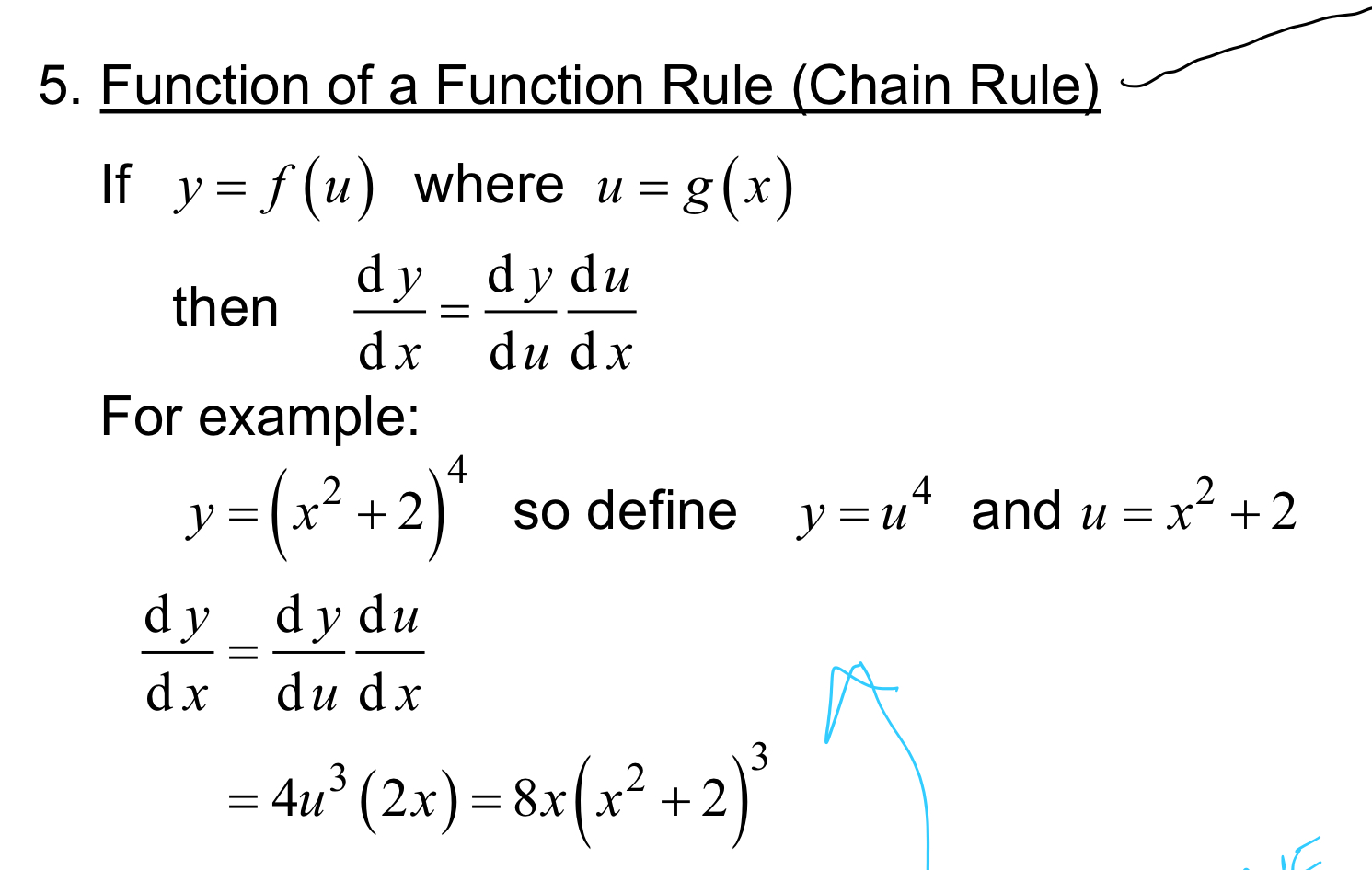
Quotient rule
OPTIMISATION
OPTIMISATION
Is x or y:
independent
dependent
x = independent (changes)
y = dependent (measure)
When a function of x/y is differentiated - what does this give us?
The derivative of the function = gradient function for a line/curve
This means you can calculate the gradient of the tangent (to the curve) at any point along its length
What is a stationary point?
What is the necessary condition for a stationary point?
Necessary condition = dy/dx = 0
A point on the graph of the function where the function's derivative is zero/slope is 0
This means the function (dependent variable, usually price) has stopped increasing/decreasing (it is flat)
What are 3 different types of stationary points?
Turning points = maximums (turns from positive to negative) - OPTIMA of the function
Turning points = minimums (turns from negative to positive) - OPTIMA of the function
Points of inflection
FOR A QUADRATIC FUNCTION:
If we want to find the coordinates of a stationary points what are the steps to finding it?
Differentiate the function (dy/dx or f’(x))
FOC dy/dx = 0
Work out formula to get x value/values (quadratic or cubic formula)
Put x coordinate back into original formula to get your y coordinate
= e.g. (1.5, -0.75) = OPTIMA
FOR A CUBIC FUNCTION:
If we want to find the coordinates of a stationary points what are the steps to finding it?
Differentiate the function (dy/dx or f’(x))
FOC dy/dx = 0
Factorise or use quadratic formula to get 2 roots
Put 2 x coordinates back into original formula to get your y coordinates
How do we classify the stationary point for both:
quadratic function
cubic function
Find the second derivative (differentiate the differentiated function) - SLOPE OF THE SLOPE
d²y/dx² or f’’(x)
Put your x coordinate/coordinates into f’’(x)
For quadratic - should get 1 output
For cubic - should get 2 (same number - one min, one max, e.g. 24 and -24)
Can classify it by:
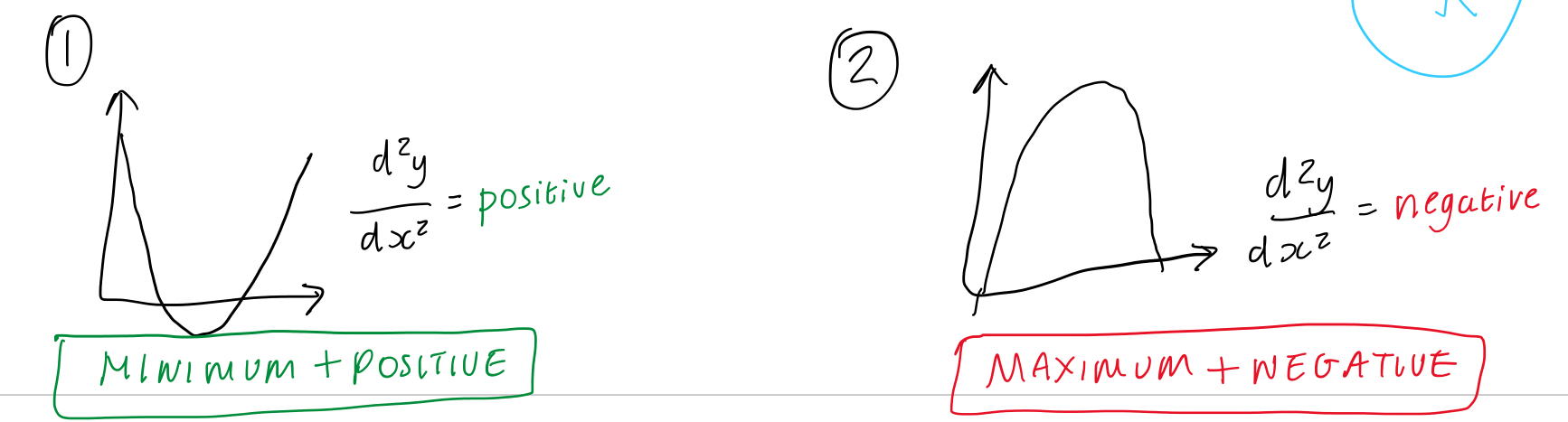
If dy/dx = 0 and d²y/dx² < 0 then the point is a maximum for y (negative number)
If dy/dx = 0 and d²y/dx² > 0 then the point is a minimum for y (positive number)
e.g. if we graphed (5,25), the 2nd derivative (-2) confirms this point is a (local and global) maximum of the function
When are turning points described as:
local
global
Local turning points (cubic function)
local maximum or minimum
when there are other points on the curve which have higher/lower values of y
Global turning points (quadratic function)
global AND local maximum or minimum
no other higher/lower points on curve

What are points of inflection?
POI is where d²y/dx² = 0 (2nd derivative = 0)
Where curve changes curvature
If d²y/dx² = 0 at a particular point, then this implies the slope of the original function is nor increasing or decreasing at that point > so the slope of the original function meets a (local) max or min value
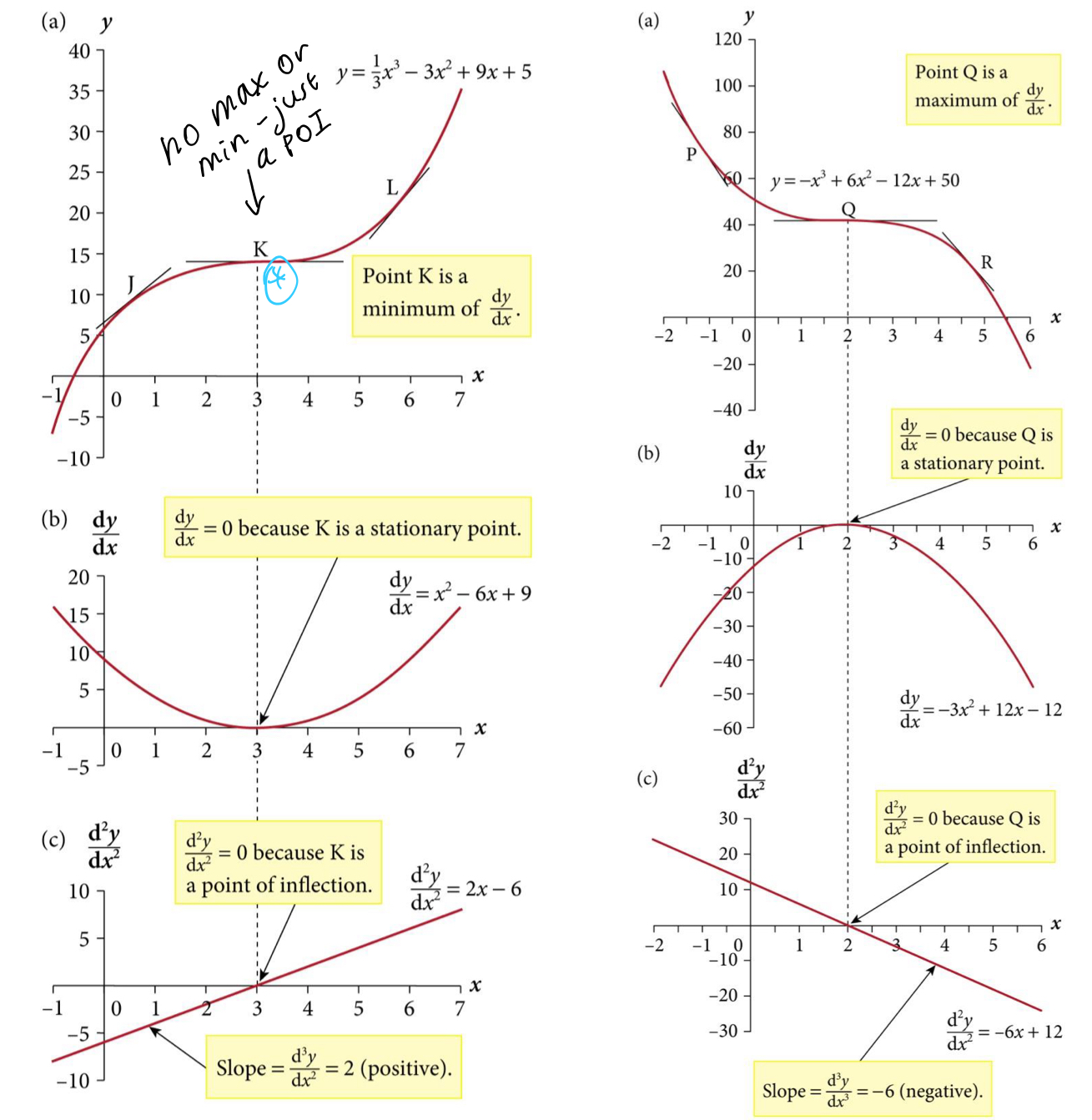
How can you classify points of inflection?
When dy/dx = 0 and d²y/dx² = 0
If d³y/dx³ > 0 = upward flowing around stationary point
If d³y/dx³ < 0 = downward flowing around stationary point

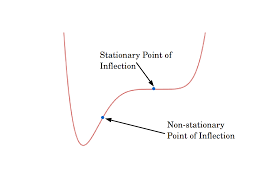
What is the difference between the 2 types of POI:
stationary
non stationary
Stationary = concave > convex (gradient decreasing then increasing)
f’(x) = 0 AND f’’(x) = 0
Non-stationary = convex > concave (gradient increasing then decreasing)
f’(x) = a number and f’’(x) = 0
What does it mean if f’’’(x), so the 3rd derivative = 0
You’ve got something wrong - go check it again
d³y/dx³ should always equal a positive or negative number for a point of inflection
Econ Applications
Econ Applications
What are features of total costs (q)?
Positive fixed costs = graph starts above zero (when p = 0) > TC has positive intercept
TC increase with output (TR’(q) > 0 bc MC increase after making 1 output)
quadratic TC > steepness of curve increases with output (TC’’(q) > 0) as productivity decreases with output rising (curve convex from below)
What is the formula for TC (q)
TC (q) = TVC (q) + TFC
What is the formula for TR (q)
What does TR always have to be a function of?
TR (q) = P(q) x Q
Q - Should always be TR (q) = 2q² - 2q
*NO P’S*
What price, TR (q) and MR (q) do these both set:
Monopoly
Perfect competition
Monopoly - firm acts as a price setter, pricing in relation to market demand
e.g. q = 600 - 1/2p
so TR (q) = 1200q - 2q²
so MR (q) = TR’(q) = 1200 - 2q = CURVE
Perfect competition - firm acts as a price taker, adopting the fixed market defined price
e.g. £320
so TR (q) = 320q
so MR (q) = TR’(q) = 320 = LINEAR
monopoly = more equation
perf comp = less equation/singular number
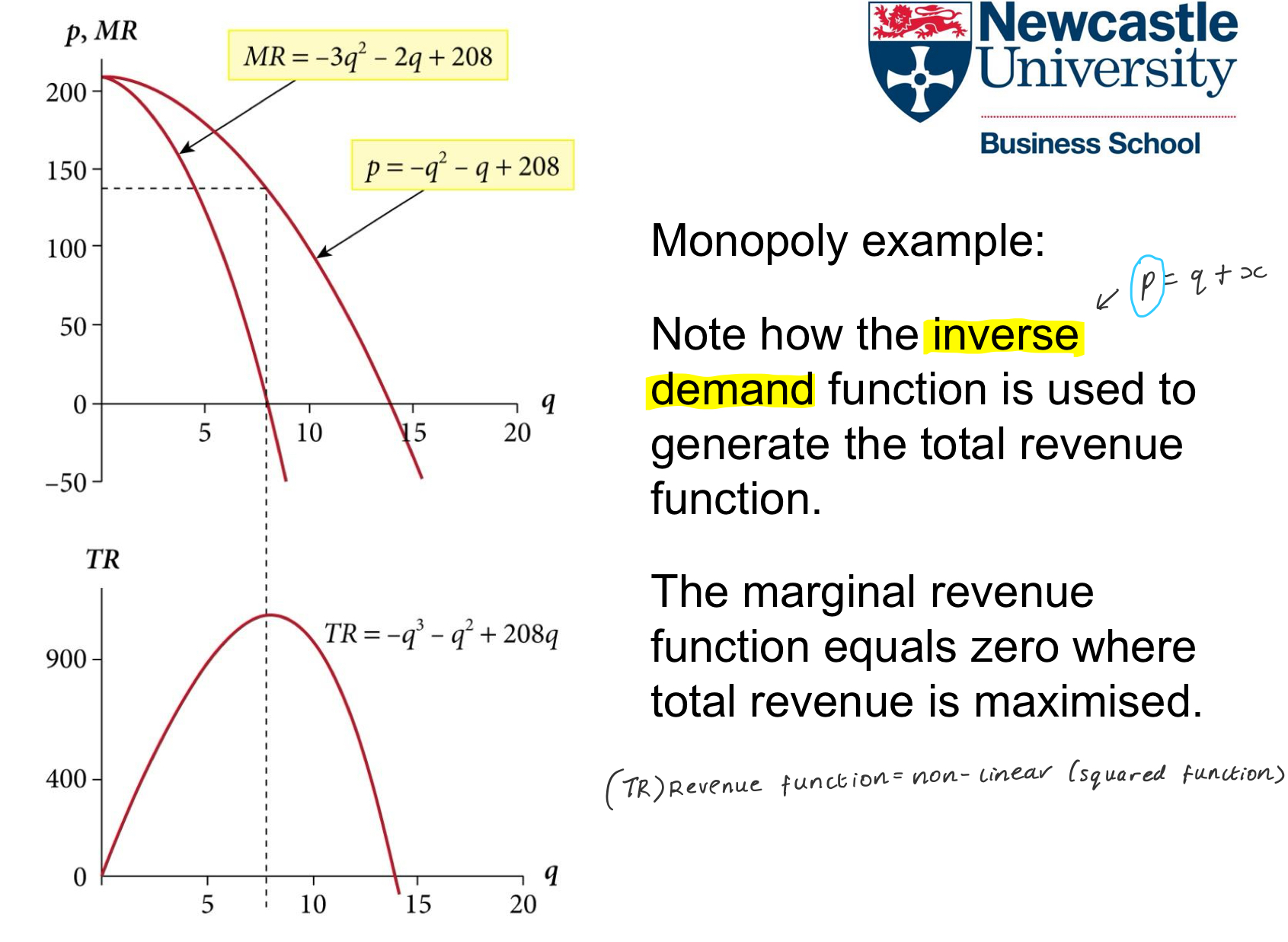
If, e.g. for a monopoly, you get given a demand function, e.g.
q = 600q - 1/2p
to work out TR (q) what do you need to do?
Convert into an inverse demand function (p = q)
e.g.
q = 600 - 1/2p > p = 1200 - q
TR (q) = (1200 - 2q) x q
TR (q) = 1200q - 2q²
What is the formula for π (q)
(total profit)
π (q) = TR (q) - TC (q)
What is the formula for MR (q)
MR (q) = TR’(q)
(slope of TR curve OR first derivative of TR)
What is the formula for MC (q)
MC = TC’(q)
(slope of TC curve OR first derivative of TC)
Are marginal costs independent of fixed costs?
YES
Marginal costs only change due to the change in quantity
Fixed costs do not change with quantity
Which is why in an equation of TVC + TFC, e.g.
AVC = 500q² + 5q and FC = 200
TC (q) = 500q² + 5q + 200
but MC (q) = 1000q + 5
(getting rid of the 200 - the TFC)
What is the formula for AC (q)
AC (q) = TC (q) / q
e.g. TC (q) = 5q² + 5q + 2000
then
AC (q) = 5q² + 5q + 2000 / q
= 5q + 5 + 2000q^-1
How do you find the point where AC are at its minimum?
AC (min) = MC
(the q where they both are)
REMEMBER:
q² / q = q (2-1)
q^0 / q = q^-1 (0-1)
REMEMBER:
q² / q = q (2-1)
q^0 / q = q^-1 (0-1)
REMEMBER:
1/2p = 600 - q
can be written as:
p = 2(600 - q)
OR
p = (600 - q) / ½ or 0.5
What are the steps to finding:
1) the profit maximising level of output
2) the maximum profit a firm can achieve
3) checking if MC = MR at profit maximising level of output
4) selling price which is charged at profit maximising level of output
1) Identify if its a monopoly or perfect competition
2) Write expressions for TR (q), TC (q) and π (q)
(remember put brackets around to reduce mistakes)
3) Order conditions:
FOC: π’(q) = 0 (slope of the function at the optimum point = 0)
quadratic > linear - can just solve = 0 (only 1 q)
cubic > quadratic - use quadratic formula (2 q’s)
quadratic formula = q=(-b±√(b²-4ac))/(2a)
SOC: π’’(q) < 0 for a max
linear - already get answer to compare to 0 (GLOBAL)
quadratic > linear - input quantity’s found into π’’(q) then compare to 0 (2 LOCALS)
What are the steps to finding:
1) the profit maximising level of output
2) the maximum profit a firm can achieve
3) checking if MC = MR at profit maximising level of output
4) selling price which is charged at profit maximising level of output
1) Get ORIGINAL π (q) function (from step 2)
2) Input MAX PROFIT quantity ONLY to find maximum profit
3) answer = £ to 2.d.p.
What are the steps to finding:
1) the profit maximising level of output
2) the maximum profit a firm can achieve
3) checking if MC = MR at profit maximising level of output
4) selling price which is charged at profit maximising level of output
1) Write expressions for MC (q) and MR (q)
2) Input profit max quantity into equations
3) Check MC = MR > IF DON’T YOU HAVE ANSWER WRONG GO BACK AND CHECK
What are the steps to finding:
1) the profit maximising level of output
2) the maximum profit a firm can achieve
3) checking if MC = MR at profit maximising level of output
4) *extra step if asked* - selling price which is charged at profit maximising level of output
1) Use price equation
2) Input profit max quantity
3) Answer with £ to 2.d.p