Vaginal
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
vaginal drug delivery
utilizes the vaginal cavity for drug absorption and effect at the site of application (local) or for systemic effect
Describe the anatomical and physiological challenges posed by the vaginal routes of admin
IUD requires doctor visit
Route used to treat hormones or to treat infections
Target region: vaginal cavity
Anatomic/ Physiologic Factor | Important considerations |
Length and width | 8-10 cm and 2 cm |
Volume of fluids | 2-3 mL |
Vascularization | High |
Surface area | Increases by presence of rugae and microridges |
Thickness of epithelium | Varies cyclically in response to changes in hormones; effects drug dissolution and permeability |
pH | Menstruating women: 3.5-4.5 (buffering capacity higher than non-menstrating women) Non-menustrating women: 6-7 |
Enzymatic activity | Low |
Drug transport | Passive transcellular transport of UI molecules
|
Analyze the physicochemical characteristics needed for vaginal drug delivery
MW | Log Ko/w | pKa |
< 1000 Da | 1-3 | Determines the number of UI species
Women in reproductive years vs. non-reproductive |
Analyze the formulation characteristics needed for vaginal drug delivery
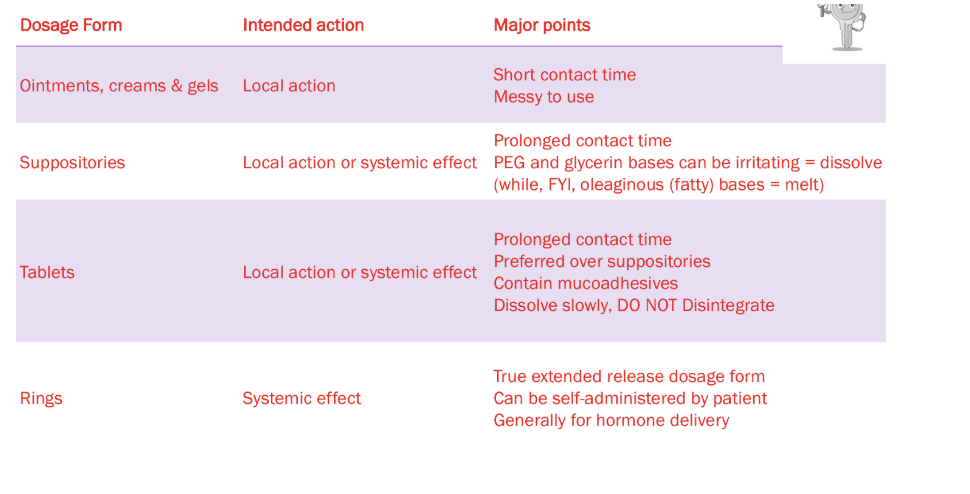
Formulations
Suppositories
Local action/ systemic effect
Tablets
Local action/systemic effect
Dissolve slowly
Don’t leak
Rings
True extended release dosage form
Generally hormone therapy
Ointments and creams
Local action
Messy to use
Characteristics
Volume of administration is low or about 1 suppositor
Leakage issues are common
Solubility and Dissolution Rate
Dissolution rate depends on the time of the month for menstruating women
Need to dissolve slowly and diffuse down the concentration gradient
Fats dissolution more likely to lead to leakage
Excipient
Mucoadhesives to increase viscosity and contact time
Surfactants and co-solvants to maintain necessary solubility for duration of activity
pH
Menstruating women - acidic
Non-menustrating women - neutral
PEG bases: can be irritating for suppositories
Select the best formulation for a patient based on your understanding of vaginal drug delivery and patient specific factors
Patient needs med with long contact time → patient should take Rings
Tablets have more compliance that suppositories because they dissolve slower and suppositories have leakage issues
For traveling- tablets are better because suppositories could melt
Local minor infections: creams, ointment, liquid
Adv/dis

local action
aimed at treating vaginal infections with antibiotic or antifungal or for relief of menopausal symptoms
systemic action
limited to relief of menopausal symptoms through the admin of hormones