Chapter 18: Smaller Ecdysozoans
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
How many species are in Phylum Nematoda?
25,000 species
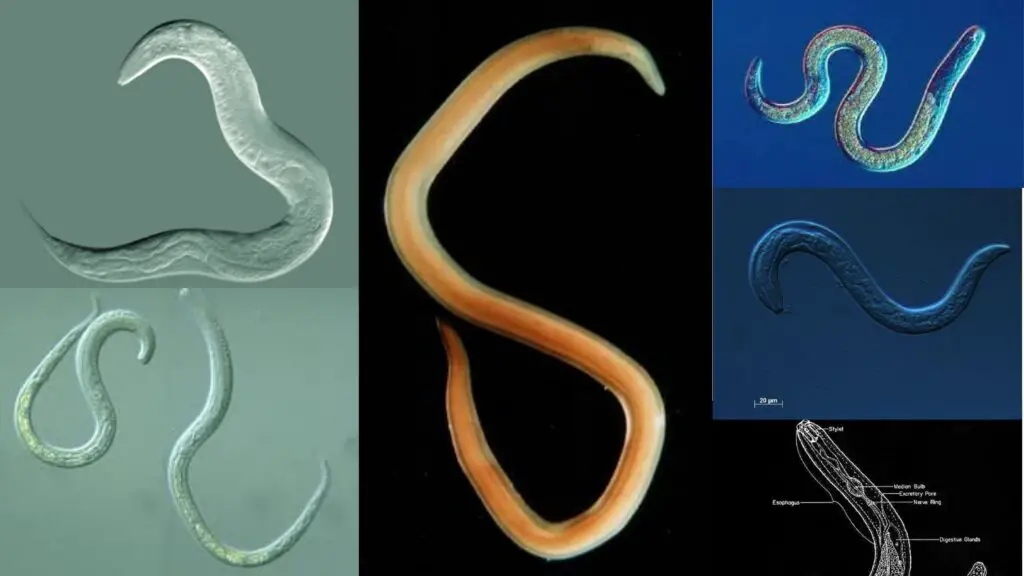
Where can organisms in Phylum Nematoda be found?
They live everywhere, especially abundant in topsoil.
What is a characteristic of many species in Phylum Nematoda?
Many are parasitic on nearly everything.
What is a model organism in developmental biology from Phylum Nematoda?
Caenorhabditis elegans.
Every cell in its body has been traced from its origin to its final state.
Why is Phylum Nematoda economically important?
It is hugely important to agriculture and medicine.
What is eutely in Phylum Nematoda?
to a fixed number of somatic cells.
What shape do organisms in Phylum Nematoda have?
Cylindrical shape
Flexible, nonliving cuticle
How is the excretory system of Phylum Nematoda structured?
It lacks protonephridia and is made of glands that empty into a pore.
What kind of pharynx do organisms in Phylum Nematoda have?
A muscular pharynx.
What is the typical size range of organisms in Phylum Nematoda?
Most are less than 5 cm, but a few can exceed 1 meter.
What type of cuticle do organisms in Phylum Nematoda have?
A thick, noncellular cuticle secreted by a hypodermis.\
Collagen
What role does the cuticle play in Phylum Nematoda organisms?
It contains the hydrostatic pressure and protects the worm from desiccation.
What type of muscles do organisms in Phylum Nematoda have?
Only longitudinal muscles, no circular muscles.
What are the components of each muscle in Phylum Nematoda?
Each muscle has a contractile fibrillar portion and a noncontractile sarcoplasmic portion.
How do muscles in Phylum Nematoda connect to the nervous system?
Each muscle cell body has a muscle arm that extends to the ventral or dorsal nerve.
What type of body cavity do organisms in Phylum Nematoda have?
A fluid-filled pseudocoelom.
What are the main parts of the digestive system in Phylum Nematoda?
Mouth, muscular pharynx, long nonmuscular intestine, rectum, and anus.
How thick is the intestine of organisms in Phylum Nematoda?
The intestine is only one cell layer thick.
How does defecation occur in Phylum Nematoda?
Muscles pull the anus open, and high hydrostatic pressure forces the waste out.
What type of metabolism do many nematodes have?
Many have anaerobic metabolism, lacking the Krebs and/or cytochrome cycle.
Do all nematodes have anaerobic metabolism?
No, some are obligate aerobes and have the corresponding cellular machinery.
What is the structure of the nervous system in Phylum Nematoda?
A ring of nerve tissue around the pharynx gives rise to both a dorsal and ventral nerve cord.
Where are sensory papillae located in Phylum Nematoda?
are clustered around the head.
What are amphids in Phylum Nematoda?
are a pair of better sense organs that open on each side of the head.
In parasitic forms, they are called phasmids.
What is the structure of the amphids in Phylum Nematoda?
They are deep cellular pits with cilia.
What is the reproductive system like in Phylum Nematoda?
Most nematodes are dioecious, with males having a pair of copulatory spicules.
Fertilization is internal, and eggs are stored in the uterus until deposition.
How many juvenile stages do Nematodes have, and what happens between each stage?
have four juvenile stages, each separated by a cuticle molt.
What type of organism is Ascaris lumbricoides?
It is highly parasitic on humans.
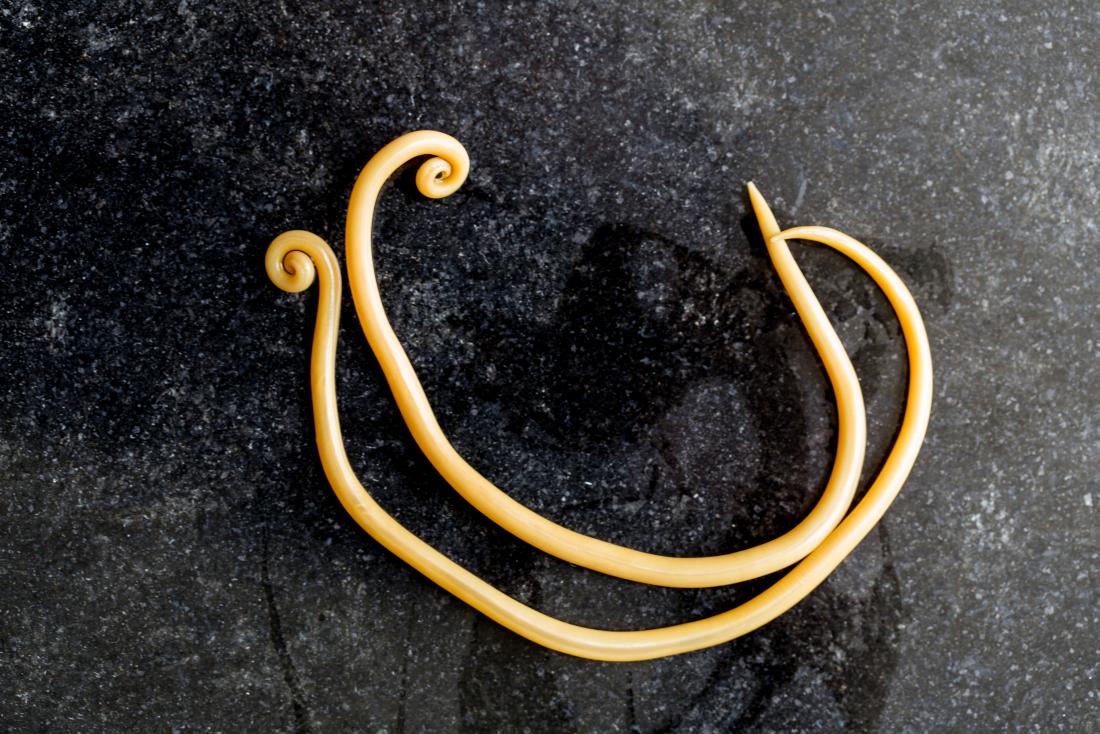

What is the infection rate of Ascaris lumbricoides in some counties in the southeastern US?
Some counties have a 25% infection rate.
How many eggs does Ascaris lumbricoides produce per day?
It produces 200,000 eggs a day.
How are Ascaris lumbricoides eggs typically ingested?
Eggs are ingested through uncooked vegetables or by putting unwashed hands in the mouth.
What is the first step in the life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides?
The host swallows the eggs.
After hatching, where do the larvae of Ascaris lumbricoides burrow?
through the intestinal wall into veins or lymph vessels.
How do Ascaris lumbricoides larvae migrate after entering the veins or lymph vessels?
migrate to the lungs through the circulatory system.
What happens after the larvae reach the lungs?
They break out of the lungs, crawl up the trachea, and are swallowed.
After being swallowed again, where do the larvae of Ascaris lumbricoides go?
go through the stomach and mature in the intestine.
How long does it take for Ascaris lumbricoides to mature in the intestine after hatching?
About two months after hatching
How does the anterior end of a hookworm appear?
curves dorsally.
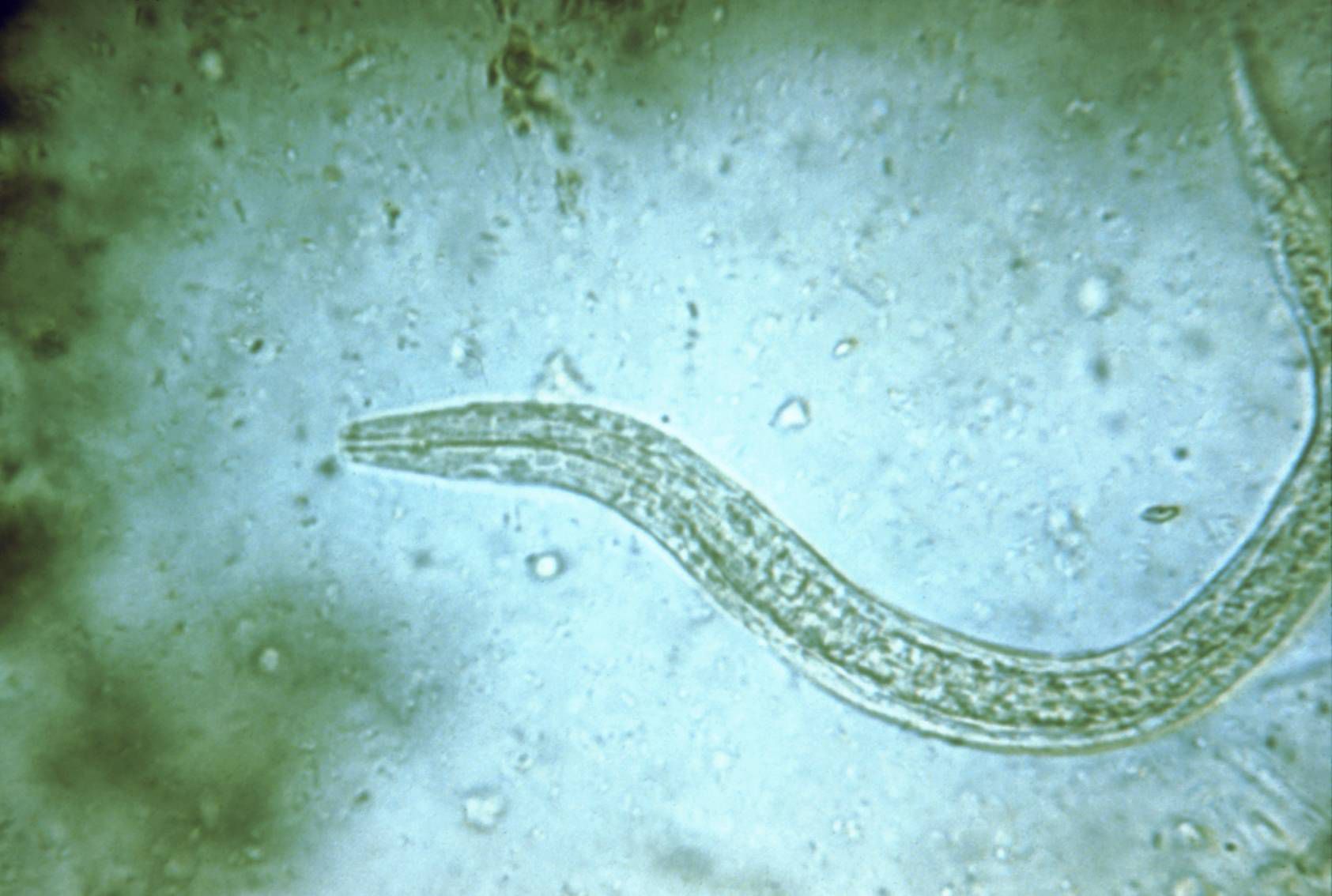
What is found in the mouth of hookworms?
Large plates that cut into the intestinal wall.
What do hookworms do once they attach to the intestinal wall?
They suck blood and pump it through the intestine.
How do hookworm eggs spread?
Eggs pass in feces, juveniles hatch in soil, live on bacteria, juveniles leave and burrow into skin when contact is made, go through lungs, into digestive tract
What can extreme hookworm infections cause?
Growth problems.
Where do adult Trichina worms burrow?
in the lining of the intestine.
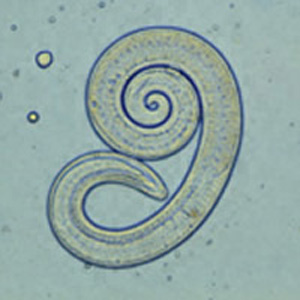
What happens after adult Trichina worms release living young?
The juveniles penetrate the blood, get everywhere, and encyst intracellularly.
How is Trichina transmitted to humans?
It is contracted from eating undercooked meat.
How many Trichina infections occur annually in the US?
10-20 infections a year.
What are Filarial worms named for?
They are named because females release live young called microfilariae into the circulatory system.
What disease can some Filarial worms cause after long and repeated exposure?
Elephantiasis
after long and repeated exposure, others cause river blindness
What is the most commonly known Filarial worm in the US?
dog heartworm, spread by mosquitos
What is the origin of the name Nematomorpha?
thread; form
commonly called horsehair worms.
How many species of Nematomorpha are there?
About 320 species worldwide.
What is the lifestyle of Nematomorpha worms?
Free-living as adults and parasitic in arthropods during the juvenile stage.
How long can Nematomorpha worms grow?
They can grow up to 1 meter in length, though most are smaller.
What is the shape of the anterior and posterior ends of Nematomorpha worms?
is usually rounded, and the posterior end is rounded with two or three caudal lobes.
What systems are absent in Nematomorpha worms?
They lack circulatory, respiratory, and excretory systems.
What type of nerve system do Nematomorpha worms have?
A nerve ring around the pharynx and a midventral nerve cord.
How do Nematomorpha worms reproduce?
Dioecious, gonads empty into cloaca through gonoduct, eggs discharged into water in long strings
What is the origin of the name Kinorhyncha?
to move; beak
How many species of Kinorhyncha are there?
About 180 species, worldwide, intertidal to 8000 m

Where do most Kinorhyncha species live?
Most live in sediment.
How is the body of a Kinorhyncha worm divided?
It has head, neck, and trunk regions, with the trunk having 11 segments.
What are scalids, and what is their function in Kinorhyncha?
are spines on the head that function in locomotion, chemoreception, and mechanoreception.
What is the body structure of Kinorhyncha like?
The body has a chitinous cuticle, cellular epidermis, and longitudinal epidermal cords.
Can Kinorhyncha swim?
No, they cannot swim. They burrow in mud and anchor with spines.
What type of digestive system do Kinorhyncha have?
They have a complete digestive system with a mouth that has a proboscis. They feed on diatoms or by digesting detritus.
What is the composition of the pseudocoel in Kinorhyncha?
is filled with amebocytes and organs, with little fluid space.
What is the excretory system of Kinorhyncha?
They have a pair of multinucleated soleonocyte protonephridia
How is the nervous system of Kinorhyncha organized?
is in contact with the epidermis, and it has a multilobed brain.
How do Kinorhyncha reproduce?
Sexes separate, paired gonads and gonoducts, six juvenile stages and a nonmolting adult
What is the origin of the name Priapulida?
phallus

Where do Priapulida species live?
They are marine and live in cold water, ranging from intertidal zones to very deep waters.
What is the size of Priapulida?
They have cylindrical bodies and can grow up to 40 cm in length.
What is the feeding behavior of Priapulida?
Most are burrowing and predaceous, feeding on soft-bodied invertebrates.
How is the body of a Priapulida structured?
has an introvert, a trunk, and one or two caudal appendages.
What features does the introvert of Priapulida have?
has papillae and curved spines (scalids) around the mouth.
Is the trunk of Priapulida metameric?
No, the trunk is not metameric but is divided into 30 to 100 rings, covered in tubercles and spines, which are probably sensory.
What is the structure of the digestive system in Priapulida?
It has a muscular pharynx, a straight intestine, and a rectum.
How is the nervous system of Priapulida organized?
They have a nerve ring around the pharynx and a midventral nerve cord.
What is found in the body cavity of Priapulida?
Amebocytes, which sometimes contain a respiratory pigment called hemerythrin.
How do Priapulida reproduce?
They are dioecious with external fertilization. One genus has direct development, and females brood the embryos.
What is the origin of the name Loricifera?
corset; bearing
When was Phylum Loricifera first described?
Described in 1983, less than 100 species
What is a characteristic feature of all Loricifera species?
Have a protective case called a lorica.
Where do Loricifera species live?
They live in spaces among marine gravel.
How is the body of Loricifera organized?
The body has five regions: mouth cone, head (or introvert), neck, thorax, and abdomen.
What does the introvert of Loricifera have?
Nine circlets of scalids that serve locomotor and sensory functions.
Can the forepart of a Loricifera body retract?
Yes, the entire forepart of the body can be retracted into the lorica.
What is the likely diet of Loricifera species?
They probably feed on bacteria.
Are Loricifera pseudocoelomate or aceolomate?
can be both
What is the reproductive system like in Loricifera?
They are dioecious, and the sexes are dimorphic.
What is the larval phase of Loricifera called?
Higgins larvae.
What is notable about the life cycle of Loricifera?
is variable, with both benthic and pelagic forms.
Which two allied taxa are part of Clade Panarthropoda?
Onychophora and Tardigrada
What happens to the coelom in Clade Panarthropoda?
The coelom is reduced, and a new cavity called a hemocoel develops.
Traditional coelom mixed with blastocoel
Lined by extracellular matrix, not mesoderm
Are there any true coelomic cavities in Panarthropoda?
Yes, sometimes there are pockets of true coelomic cavities surrounding certain organs.
What are the Greek roots of the name "Onychophora"?
claw and to bear
What are Onychophora commonly called?
Velvet worms or walking worms.
How many species of Onychophora are there?
About 70 species; Most are found in rainforests.
What is the diet of most Onychophora species?
They are predaceous on insects, gastropods, and annelids.
How long is the fossil history of Onychophora?
They have a 500 million-year fossil history with little change.