FRST 100 - Sustainble Forestry
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
Global Forests (facts)
- Trees = largest living organism
- Oldest single non-clonal tree is more than 5,000+ yrs
- Rainforests can be found outside tropics
- Forests = most biodiverse biome
Most forest loss is NOT caused by big logging companies
Clonal vs. Non-Clonal
Clonal tree = copies itself (many trees from one root)
Non-clonal tree = two parents; independent tree
BIG challenge
Increasing wood & food production w/o cutting down / affecting forests
Taxonomy
Science of naming & grouping living things
- Classifying organisms
Taxa (taxon)
Groups used to classify living things
(kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species)
Species
Groups of individuals that look similar & interbreed freely (naturally), producing fertile offspring
Look, mate, babies, repoduce
Breeding vs. Interbreeding
Breeding = 2 dogs of same breed have puppies
Interbreeding = lion & tiger mate to produce liger
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Rules:
- Always italics
- Genus capitalized, species not
- Avoid adding author
e.g., Canis lupus familiaris
Tropic Hierarchy
Organism position in food chain (heterotropis, autotrophs, etc)
Conservation
Protecting & taking care of nature/natural resources
Autotroph
Makes own food (e.g., plants)
Producer
Organism that makes food (same as autotrophs)
Heterotroph
Eats other organisms for food
Primary Consumer
Eat producers
Secondary Consumer
Eats primary consumers
Tertiary Consumer
Eats secondary consumers
Decomposer
Breaks down dead matter (bacteria)
Ecological Hierarchy
How living things are organized in nature
5 Levels:
- Population = all individuals of a (single) species in an area
- Community = Groups of populations in an area
- Ecosystem = all living + non-living parts in an area
- Biome = large area with similar climate & plants
- Biosphere = whole planet interconnected
Population
All indivdiuals of a species in an area
Community
Groups of populations in an area
Ecosystem
All living & non-living parts in an area
Biome
Large area with similar climate & plants
Biosphere
Whole planet interconnected
Genus
Group of similar species
Species
Group of similar organisms that can reproduce
Subspecies
Variation of a species
Hybrid
Offspring from 2 different species
A Player
Top 10% high-preforming professional
Motivation
Energy & drive to learn & reach goals
Engagement
Interest & involvement in learning (how students appear to be)
Expectancy
How achieveable the goal feels
Support
Quality of learning environment
Value
How beneficial the goal seems
How many species exist today? Terrestrial plants & trees?
Species today: 1.7 million
Terrestrial plants: 330,000 species
Trees: 60,000 species
Trees: 3%, Terrestrial plants: 14%
Defintion of Tree’
Tree = woody plant, usually single stem ≥2 m tall; if multi-stemmed, at least 1 vertical stem ≥5 cm DBH
diameter at breast height
(planted forests = forests)
Botanist Definition of A Tree
Woody plant with secondary growth
Ecologist Definition of A Tree
Big woody plant providing habitat, microclimate, ecological functions
Forester Definition of A Tree
Plant producing timber ($$$)
Is Bamboo Considered a Tree? Why/Why not?
Not a tree (no secondary growth)
Is A Palm Tree A Tree?
Fits general/ecologist view, but no secondary growth or timber
Angiosperm
Seeds enclosed in a fruit
- Broadleaves = broad, flat leaves (deciduous or evergreen)
- Hardwood = wood w/ short fibers
e.g., Oak, Maple
Broadleaves
Broad, flat leaves (deciduous or evergreen); usually angiosperms
Hardwood
Wood with short fibers (angiosperms)
Gymnosperms
Naked seeds (usually in cones)
- Conifers = needle- or scale-like leaves, mostly evergreen
- Softwood = wood w/ llong fibers
e.g., Pine, Spruce
Conifers
Needle- or scale-like leaves, mostly evergreen
(gymnosperms)
Softwood
Wood with long fibers (gymnosperms)
Gingko (Maiden Tree), exception
- Gymnosperm (naked seeds)
- Only 1 living species
- Exists for 270 mil yrs
- Native to China
- Broad, deciduous leaves (unlike conifers)
- Seeds are fruit-like ovules (smelly!)
- Male or female
Gymnosperm BUT has broad leaves (angiosperms)
European Larch (Larix Decidua)
- Gynosperm / Conifer with deciduous needles (unusual for conifers)
- Genus Larix = 10 species
- One of the dominant species in boreal forests
“Australian pine” tree (Casuarina equisetifolia), exception
- Angiosperm that looks like a Gyno (conifer)
- Evergreen
- Mostly used as an ornamental plant
How Many Common Tree Species Are In BC?
40 (90% conifers - gyno)
Primary Growth
Growth in length (happens both at same time in shoot and roots)
Gravitropism
Growth from gravity
Heliotropism
Growth from light
Secondary Growth
Growth in width (radical)
Growth from cambium (cell divison & expansion)
Cambium (secondary growth)
Undifferentiated tissue → makes xylem inside, phloem outside
Xylem
Moves water & nutrients
Phloem
More sap
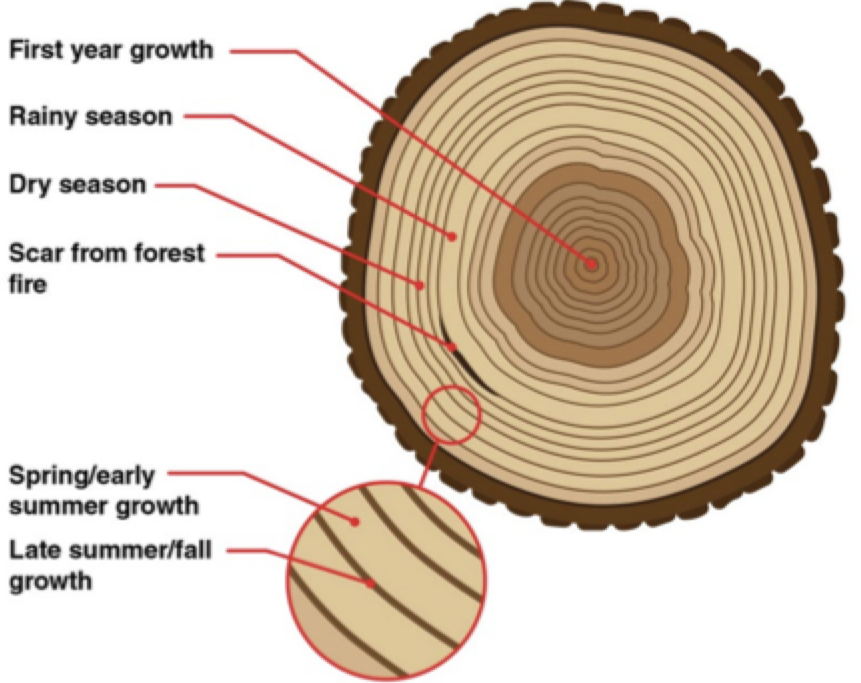
Tree Rings
Show tree growth
- Inter-annual variation = year-to-year
- Intra-annual = seasonal variations
- 1 ring = early wood + late wood
Early wood = fast growth, large vessels, light wood
Late wood = slow growth, small vessels, dark & dense wood
Mycorrhizae
Fungi that help plants absorb nutrients
What is the photosynthesis equation that trees need to live?
Water (H2O)+ Carbon Dioxide (CO2) + LIght (solar energy)
= Carbohydrate (CxH2yOy) + Oxygen (O2)
What is the respiration equation that trees need to live?
Carbohydrate (CxH2yOy) + Oxygen (O2) + Respiration
= Water (H2O) + Carbon Dioxide (CO2) + Heat Energy
-
Carbon Dioxide = plant food
Respiration
Uses carbohydrates for energy
Carbohydrate
Sugar made in photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Makes carbohydrates from light, CO2, water
Gross Photosynthesis
Total carbohydrates made (producing)
Net Photosynthesis
Gross photosynthesis – respiration (carbohydrates left after energy use)
Respiration - consuming
Net - total amount
Theory of Tolerance
Species can live & reproduce only within certain limits of an environmental factor
(water, light, wind, pH level)
Ecological Niche
Set of environmental conditions where a species can grow & reproduce (temp., percipitation)
E.g., - tree species that have ecological niche:
Black spruce, Western Hemlock, Douglas Fir, Lodgepole Pine
Forests
Large area covered mainly with trees and undergrowth
>0.5 ha, trees >5 m tall, >10% canopy cover; excludes mostly agricultural or urban land
Primary/natural Forest
naturally grown native trees, no clear human damage, ecological processes continue
Planted Forest/plantation
Trees mostly planted/seeded
Forest Estate
All land containing forests
Forest Stand
Continuous area of similar (homogeneous) forest
Forest Plot
Small measured area for data collection (forest metrics)
Afforestation
Planting trees where there were none before (planting/seeding) = forest
Reforestation
Re-growing a forest on land that was already forest (planting/seeding)
Deforestation
Clearing forests
Turning forest into another land use (usage) / permanently reducing canopy cover below 10% (degradation)
What are the variables affecting climate and microclimate?
- Air temperature: average and variation
- Precipitation: sum and variation
Climate Graphs
Chart showing temp. & perciptation (rainfall)
Precipitation = shown as bars; vertical columns
Height of bar = amount of rainfall/snowfall
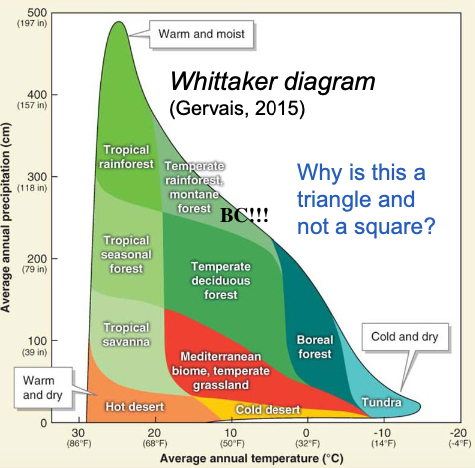
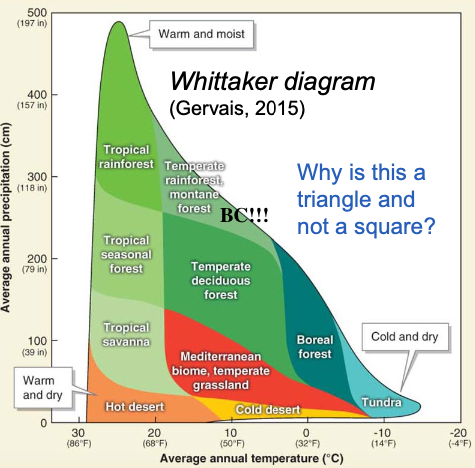
Whittaker Diagram
Graph showing how biomes are distributed (based on temperature & precipitation)
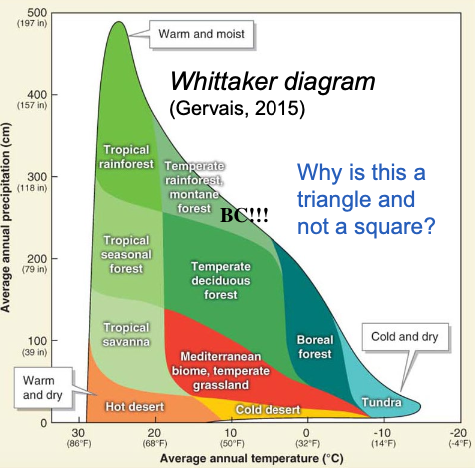
World Biomes
Vegetation (plants) in an area depends on climate
(temperature & precipitation, averages & seasons)
Biome
Very large area w/ similar climate & vegetation
Formation
Community w/ specific vegetation structure
(e.g., cold desert, temperate deciduous forest - sheds leaves)
- Biome subdivision
Growth Form
Type of plant: trees, shrubs, herbs, epiphytes (grow on other plants), lianas (woody vines), bryophytes (mosses & lichens)
Factors that affect forests
Human = Degration & deforestation
Natural = Abiotic & Biotic
Tropical Rainforest (natural) - tropical wet
Vegetation = All types (plants)
Adaptations = Compete for light, shade, layers, wet soil
Features = High biodiverse & biomass; 2nd most abundant after boreal forest
Human Impact = Logging, burning, cattle ranching, agriculture
rainy, warm, humid, sunny - hot, wet forest
Tropical Seasonal Forest - tropical monsoon
Vegetation = broadleaf deciduous trees (angio) & shrubs
Adaptations = Handles extreme humidity/wet, grows leafs anually, survive fire
Features = Monsoon (rain/wind) climate, biodiverse
Human Impact = Mostly clear for farming (agriculture)
wet & dry seasons (sometimes sunny)
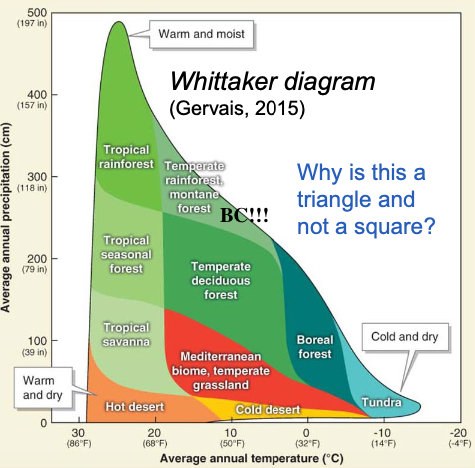
Temperate Deciduous Forest - humid subtropical/continental
Vegetation = Broadleaf deciduous trees (angio)
Adaptations = Grow leafs annually, survive cold & heat
Features = Pretty fall colours
Human Impact = Mostly farms & cities
moderate climate forest, loses leaves in winter
(Less adaptive to fire than tropical seasonal because it sheds leaves often)
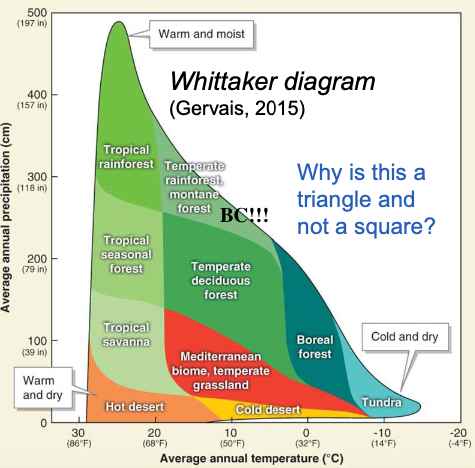
Temperate Rainforest - marine west coast
Vegetation = Needleleaf & broadleaf trees, epiphytes, bryophytes (moss), shrubs, ferns
Adaptations = Layers, long-living, shade tolerant, regrow in gaps
Features = Valuable wood, high biodiversity & biomass, rare, important to protect/conservation
Human Impact = Logging, turning forest to city
e.g., BC!!!
Fastest timber growth of all forest types
wet, moderate climate forest
rainy, mild, humid
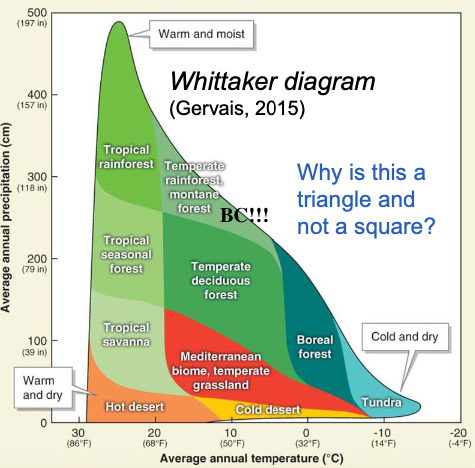
Boreal Forest - subarctic
Vegetation = Needleleaf evergreen (gymno)
Adaptations = Resist forest, grow in low light, recover after fire
Features = Most common forest, many summer insects, only in N. Hemisphere
Most abundant forest by area
Forest in cold N. regions, mainly conifers
cold, snowy/windy, less sunny (little rain; precipitation is snow)
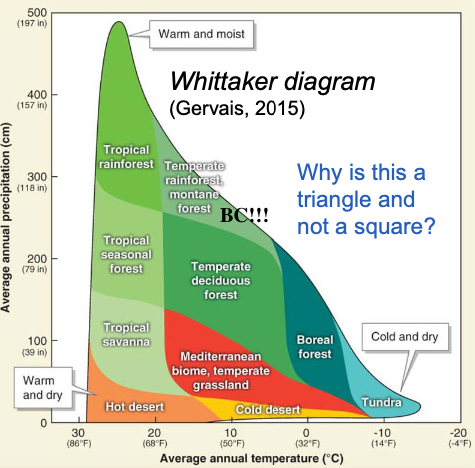
Montane Forest - cold mountain
Vegetation = Needleleaf (N. Hemisphere), broadleaf evergreen (S. Hemisphere) trees
Adaptations = Resist cold, fire, and drought
Features = Diverse, found at all latitudes
Human Impact = Logging, fire suppression
cold, sometimes snowy/windy, less sunny
Biogeoclimatic Zone (BC)
Area with similar climate & dominant
- Each zone can be split into subzones depending on how wet/dry and warm/cool it is
- Vladimir Krajina
e.g., IDFdk = Interior Douglas-fir, dry & cool)
By Timber Products
(how wood is used after trees are cut)
Pulp
Fiber & particle boards
Solid lumber
Veneer
Speciality Plantaions
Bamboo, Agroforestry
Not Forestry
Fruits, palm oil, cork
Globally, does more wood comes from natural forests or plantations?
Wood comes more from natural forests
Forest Classification Examples (plantaion → natural)
A. Fast-growing industrial plantation of exotic species (human-controlled)
B. Unmanaged natural forest of exotic species (unmanaged, exotic)
C. Natural forest but intensively managed (somewhat human-influenced)
D. Planted forest for restoration (looks natural but still planted)
E. Undisturbed natural forest (fully natural)
Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) - metrics
Tree width/diameter measured ~1.3 m above ground
Mean DBH = Average width of all trees in area
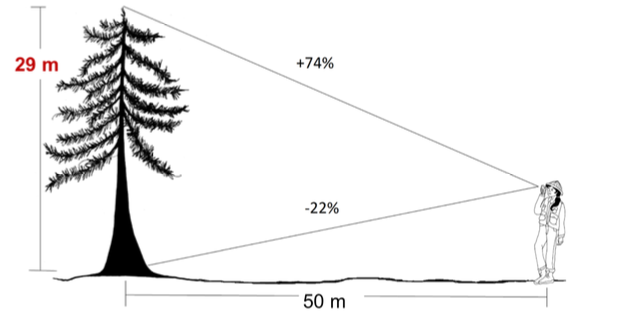
Height
Height = Tree height from ground to tip
At stand level, height can be =
Mean height = average height of all trees
Dominant height = average height of the tallest trees
Tree Density (stocked)
# of trees per area/ha