Generation and Transport of Electrical energy week 4 Transformers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the definition of a transformer.
static piece of apparatus
must have 2 or more windings
uses electromagnetic induction to transform alternating voltage and current into another system of voltage and current.
the transformed values are usually at different values and the same frequency
for the purpose of transmitting electrical power
what is the general operating frequency in the UK for the power network and general appliances
50hz
what is the primary function of a transformer
to change voltage level by “stepping it up or down” when required in the various stages of power transmission
what is the purpose of high voltage bushings on a transformer
In electric power, a bushing is a hollow electrical insulator that allows an electrical conductor to pass safely through a conducting barrier ( in this case the conducting barrier is the case of the transformer), without having an electrical contact with the conducting barrier
what are the electrical bushings in a high voltage transformer usually made of
porcelain
why is the oil conservator in a transformer usually not full
the volume of transformer oil can change with ambient temperature and loading conditions, therefore headroom is needed for it to be safe/prevent explosion.
it is usually half or a third full
if loading conditions are higher than more volts flow through oil resulting in oil heating and expanding.
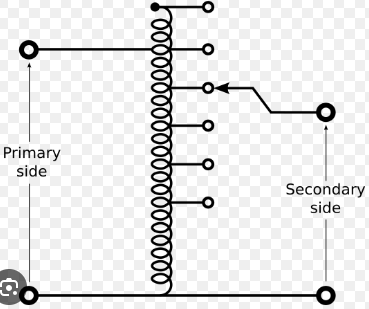
what is an autotransformer
it is a transformer where portions of the same winding act as both the primary and the secondary side of the transformer as shown in the image.
the windings of the transformer are electrically connected unlike a “normal” transformer

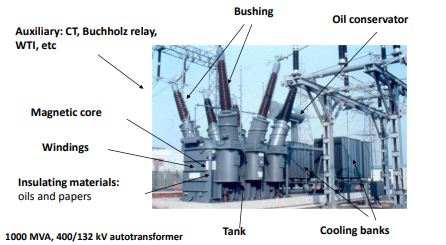
what are the 8 main parts of this high voltage transformer shown in the image
note: ignore the name of the transformer in the bottom right of the image
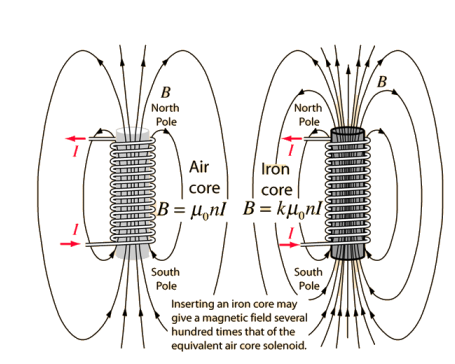
why are ferromagnetic cores used instead of some other material of core in a transformer for high power applications
they are used as they can provide tight magnetic coupling and they have high flux densities
what is the name given to a transformer with a ferromagnetic core
iron core transformer
when are air core transformer’s used
they are typically used in low power circuits as they are cheaper to manufacture and sometimes in low power high magnetic coupling and flux densities are not needed.
what are the pros/cons of using a iron core transformer vs a air core transformer
iron core pros:
tight magnetic coupling, high flux density, a magnetic field several hundred times stronger than an air core
iron core cons:
expensive to manufacture
air core pros:
cheap to manufacture
air core cons:
poor magnetic coupling, low flux density, a magnetic field several hundred times weaker than an iron core
why when manufacturing iron cores are a solid core not used and what is used instead.
stacks/sheets of electrical steel laminations ( made from iron or silicon alloys) are used which are made in a way to enhance magnetic properties.
if iron core is used then there will be a higher eddy current loss.
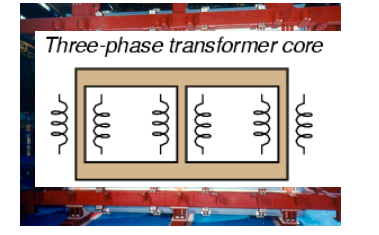
draw the simplified diagram of a three phase transformer core
what is the function of a tap changer
it is a mechanism in a transformer which…
allows variable turn ratios for the primary and secondary windings to be selected in steps.
the transformer obtains this variable ratio by connecting to different access points/taps.
there are taps along both the primary and secondary winding.
what is the use of a tap selector vs a tap diverter
the selector’s access the actual taps however they may not be switched during load as temporary open circuit between switching of taps may cause flashover.
this is where the diverter is used to switch between the tap banks and they can do this under load.
why do diverter’s need repairing more often than selector switches.
and how often does each need repairing
they typically go through more arcing event’s than selector’s as they act under load.
diverts need repairing/maintenance every 2-3 years whereas selectors need this every 5-7 years
in most high power transformers what is used as insulation around the copper windings ?
they are wrapped in laminated paper to provide electrical insulation. papers are typically immersed in oil to provide further insulation
what are the two main 3 phase connection types for transformers
delta and star
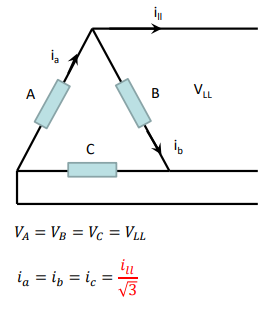
when are delta connections used in transformers? and explain the workings/ derivations which prove this.
delta connections are more economical for high current low voltage windings.
line to line current is sqrt3 multipled by ia/ib/ic
whereas the phase voltage/line to line voltage is the same as Va=Vb=Vc
why are delta and star connections used together in transformers
it reduces the zero sequence impedance current in the windings.
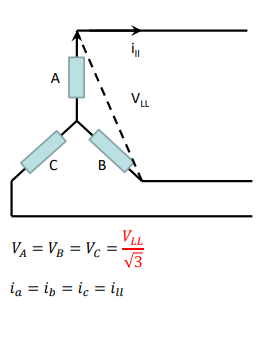
when are star connections used in transformers? and explain the workings/ derivations which prove this.
star connections are more economical for high voltage low current windings.
because of the inherent shape there is a single neutral pint available in the middle of the star for earthing, allows the taps and tap changer to be located near neutral.
line to line voltage is sqrt3 multipled by Va/Vb/Vc
whereas the phase current/line to line current is the same as ia=ib=ic
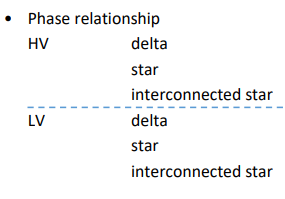
for Phase relationship annotation what are all of the acronyms for HV and LV phase relationship

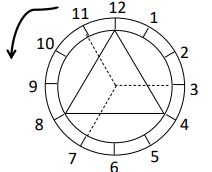
on this phase relationship clock what does each number represent in degrees and which direction do you count the clock in
you count the clock anticlockwise.
the clock shows the phase shift angle of the phase shift.
so:
12 = 0 degrees
11 = 30 degrees
10 = 60 degrees
6 = 180 degrees …. etc
what does the phase relationship YNyn6 mean
HV = star
LV = star
phase shift = 180 degrees
the n’s are always added after the y connections to show the neutrals but not any of the other types of connections