psychology grrr agggggrg
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:20 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
sensation
receiving physical energy from the environment and encoding it into neural signals.
2
New cards
perception
organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
3
New cards
gestalt principals
we do not focus on small components, we perceive the bigger picture
-similarity
-pragnanz/good figure/simplicity
-proximity
-continuity
-closure
-common region/grouping
-figure ground
-symmetry
-common fate
-similarity
-pragnanz/good figure/simplicity
-proximity
-continuity
-closure
-common region/grouping
-figure ground
-symmetry
-common fate
4
New cards
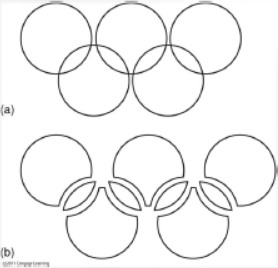
similarity gestalt principle
Similar things tend to appear grouped together

5
New cards
pragnanz/good figure/simplicity gestalt principle
Objects in the environment are seen in a way that makes them appear as similar as possible
6
New cards
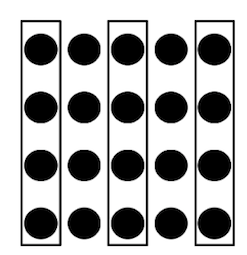
proximity gestalt principle
Things that are near each other seem to be grouped together

7
New cards
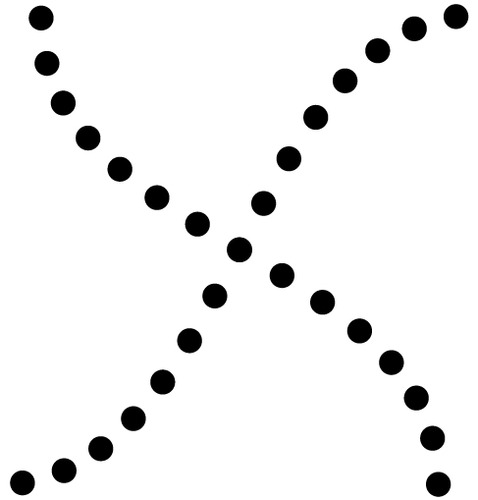
continuity gestalt principle
Points that are connected by straight or curving lines are seen in a way that follows the smoothest path
8
New cards
closure gestalt principle
We fill in gaps to create a complete, whole object

9
New cards
common region/grouping gestalt principle
A visual field with into objects/figures that stand out from their surroundings/ground
10
New cards
figure ground gestalt principle
the tendency to perceive objects, or figures, as existing on a background

11
New cards
symmetry gestalt principle
we perceive objects that are symmetrically arranged as wholes more often than those that aren't

12
New cards
common fate gestalt principle
things moving in the same direction are grouped together

13
New cards
depth perception
ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that strike the retina are two-dimensional; allows us to judge distance
14
New cards
Visual clif
checkered table experiment with the 6-14 month olds conducted by Elanor Gibson and Richard Walk
>81% refused to walk
>81% refused to walk
15
New cards
color deficient vision
a defective cornea or retina of the ye
-monochrome: no cones work
-dichromatic: one cone kinda works
-monochrome: no cones work
-dichromatic: one cone kinda works
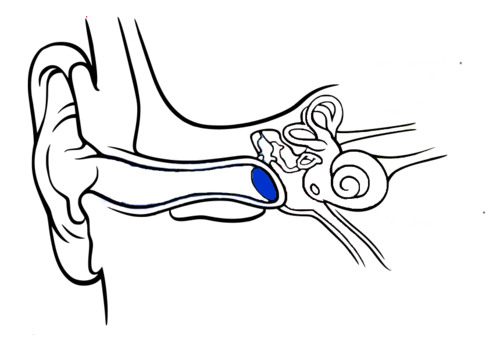
16
New cards
Binocular cues
use two eyes to see depth
-retinal disparity/binocular disparity
-convergence
-afterimages
-retinal disparity/binocular disparity
-convergence
-afterimages
17
New cards
retinal disparity/binocular disparity
eyes 6cm apart so two separate images are taken in but only one is processed
18
New cards
convergence
cross eye object thing
19
New cards
afterimages
sensations that linger after the stimulus is removed >reversed colors.
20
New cards
Monocular cues
Use only 1 eye to see depth
-accommodation/mucsel cue
-arial atmosphere/relative clarity
-linear perspective
-interposition
-relative size
-negative height
-light and shadow
-texture gradient
>pictorial and motion parallax
-accommodation/mucsel cue
-arial atmosphere/relative clarity
-linear perspective
-interposition
-relative size
-negative height
-light and shadow
-texture gradient
>pictorial and motion parallax
21
New cards
motion parallax
closer objects appear to move faster than objects that are farther

22
New cards
pictorial depth cues
clues about distance that can be given in a flat picture
23
New cards
visual accommodation/muscle cue
the lense of the eye changing thickness to see depth
24
New cards
arial atmosphere/relative clarity
things far away in the air seem fuzzy because of pollution and distance

25
New cards
linear perspective
parallel lines appear to converge at a vanishing point on the horizon. The closer the lines are, the greater the distance
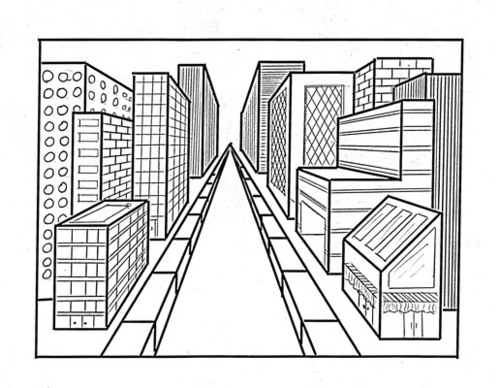
26
New cards
interposition
partial blocking of one object by another object. You think that the blocking object is closer
27
New cards
relative size
if two objects are roughly the same size, the object that looks the largest will be judged as being the closes

28
New cards
relative height
clear objects appear closer than blurry or fuzzy objects
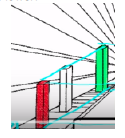
29
New cards
light and shadow
if there are two identical objects, the dimmer one seems farther away

30
New cards
texture gradient
texture becomes less and less apparent the farther it goes into the distance
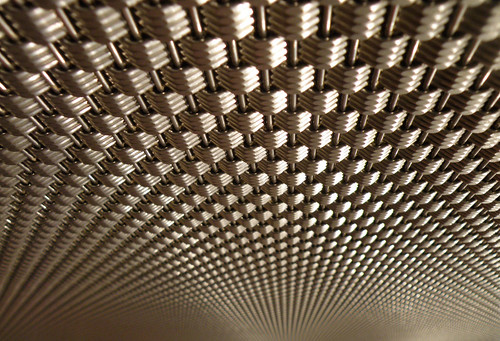
31
New cards
phi phenomenon
the illusion of movement created by presenting visual stimuli in rapid succession

32
New cards
stroboscopic effect
flip book thing

33
New cards
autokinetic effect
The tendency to perceive a stationary point of light in a dark room as moving
-candle in dark room thing
-candle in dark room thing
34
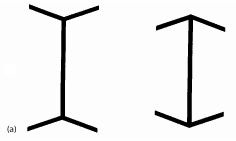
New cards
Muller Lyer Illusion
different line length thing
35
New cards
relative motion
while we move, things close to us appear to move fast in the opposite direction; things farther away appear to move very slowly or not at all

36
New cards
perpetual constancy
color constancy
size constancy
shape constancy
light constancy
size constancy
shape constancy
light constancy
37
New cards
color constancy
color of an object remains the same even if lighting conditions change
38
New cards
size constancy
e objects as the same apparent size regardless of their distance
39
New cards
shape constancy
angle changes or an object rotates and we still perceive the object as staying the same
40
New cards
light/brightness constancy
whiteness, blackness, and grayness of objects remains constant no matter how much the illumination
41
New cards
top down processing
general to more specific
looking at a whole
trying to find patterns
already know this stuff
looking at a whole
trying to find patterns
already know this stuff
42
New cards
bottom up processing
more specific to general
don't know info
don't know info
43
New cards
transduction
turning sensory info into neural impulses
44
New cards
difference threshold/just noticeable difference
min difference between stimuli 50% of the time
45
New cards
absolute threshold
min stimuli the body needs to consciously notice 50% of the time
46
New cards
weber's law
to compare objects they mush differ by the same constant percentages
47
New cards
subliminal perception
stimuli the conscious does not notice
48
New cards
signal detection theory
when you detect stimuli its intensity and your mental/physical state can change your perception
49
New cards
sensory adpatation
you get used to constant stimuli
50
New cards
psychophysics
study relationship between stimuli and response
51
New cards
Gustav Fecher (1801-1887)
german guy
made psychophysics
modern experimental psychology
black and white flashing lights produced color
studied synesthesia
made psychophysics
modern experimental psychology
black and white flashing lights produced color
studied synesthesia
52
New cards
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
harvard research dudes
noble prize dudes
analyzes brain impulses of cats and donkeys
special cells respond to visual features of enviroment
noble prize dudes
analyzes brain impulses of cats and donkeys
special cells respond to visual features of enviroment
53
New cards
Ernest Weber
just noticeable difference
you can only compare objects by the same constant percentage
you can only compare objects by the same constant percentage
54
New cards
perpetual set
your eyes will see what they want to see
-expectation, emotion, and motivation can interfere
-expectation, emotion, and motivation can interfere
55
New cards
schemas
filling system in the brain
-object schemas
-person schemas
-social schemas
-self schemas
-event schemas: social etiquette
-object schemas
-person schemas
-social schemas
-self schemas
-event schemas: social etiquette
56
New cards
context effects
how marketing, the location you find the stimulus in, and cultural differences can change your perception
57
New cards
divided attention
multitasking is really switching fast
58
New cards
selective attention
only paying attention to specific things
-cocktail party effect
-stroop effect
inattentional blindness
-cocktail party effect
-stroop effect
inattentional blindness
59
New cards
cocktail party effect
ability to attend to only one voice among many
60
New cards
stroop effect
you recognize the color of the word first
61
New cards
intentional blindness
when you don't see things because you are hyperfocused
62
New cards
wavelenghts
wave's width
distance from the peak of one light or sound wave to the next peak
equal to hue, pitch, and frequency
short wavelength = high frequency
long wavelenght = low frequency
distance from the peak of one light or sound wave to the next peak
equal to hue, pitch, and frequency
short wavelength = high frequency
long wavelenght = low frequency
63
New cards
amplitude vision
wave's height
peak of the wave to the trough of the wave
equals intensity and brightness and volume
tall amplitude = bright colors
short amplitude = dull colors
peak of the wave to the trough of the wave
equals intensity and brightness and volume
tall amplitude = bright colors
short amplitude = dull colors
64
New cards
wavelength spectrum
little light chart thing
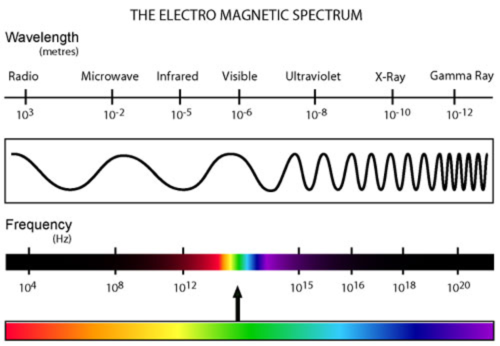
65
New cards
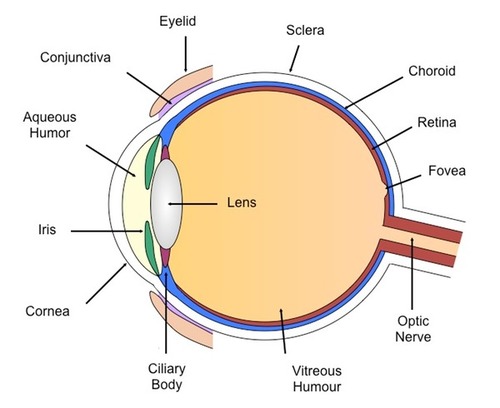
process of vision
cornea > pupil > iris > lens > vitreous humor > retina > optic nerve > visual cortex
66
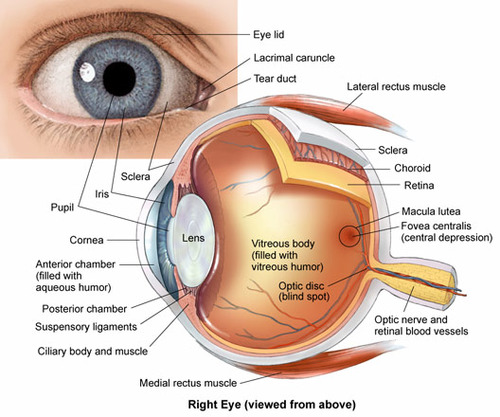
New cards
pupil
adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enter
67
New cards
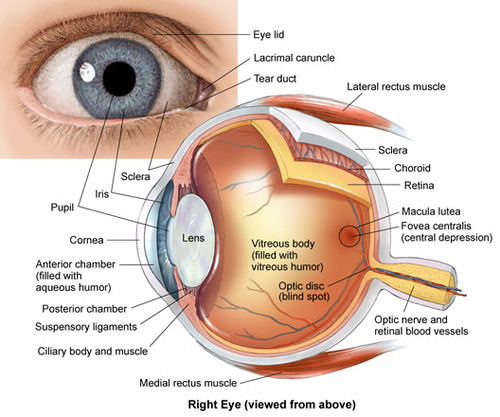
iris
muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye and that controls the size of the pupil
in between cornea and the lens
in between cornea and the lens
68
New cards
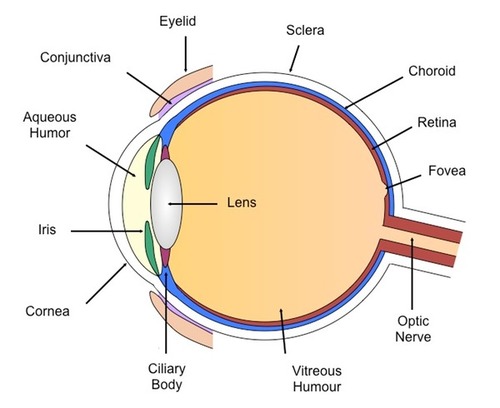
lens
structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus light rays on the retina
behind the pupil
>accommodation: lens changing size
behind the pupil
>accommodation: lens changing size
69
New cards
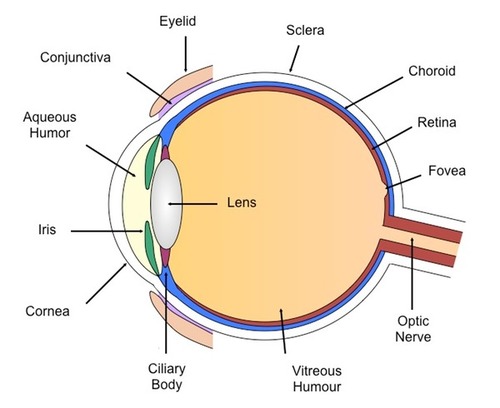
retina
contains the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of transduction
connects brain to optic nerve
gets images from the back of the eye
connects brain to optic nerve
gets images from the back of the eye
70
New cards
rods
type of retinal receptors
detect black, white, and shades of gray
peripheral and twilight vision
120 million rods
detect black, white, and shades of gray
peripheral and twilight vision
120 million rods
71
New cards
cones
type of retinal receptors
detect color
daylight
6 million cones
detect color
daylight
6 million cones
72
New cards
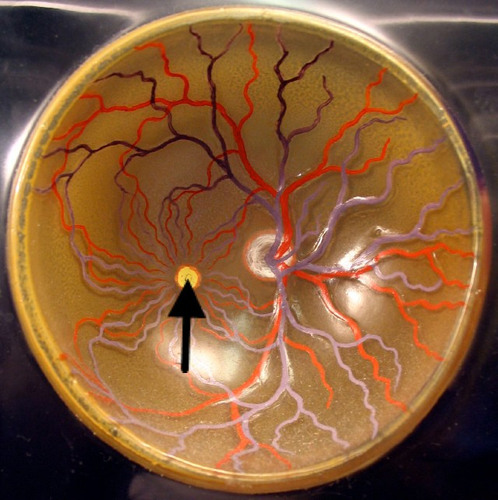
fovea
central focal point in the retina
cones home
deals with acuity
cones home
deals with acuity
73
New cards
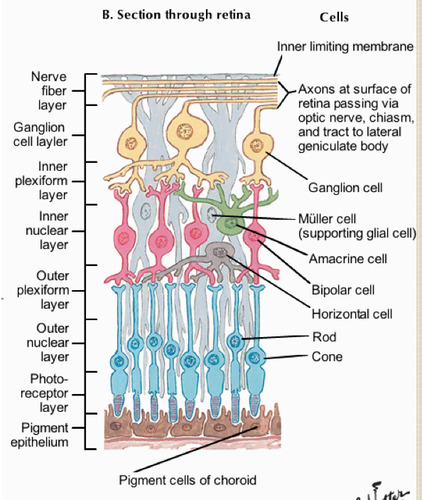
bipolar cells
neurons that connect the rods and cones w/the ganglion cells
74
New cards
ganglion cells
neurons that connect to the bipolar cells
a bunch of axons make the optic nerve
a bunch of axons make the optic nerve
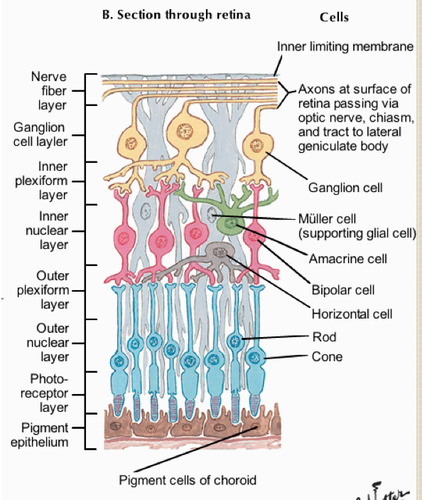
75
New cards
optic nerve
nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
76
New cards
blind spots
optic nerve leaves the eye
no receptor cells
no receptor cells
77
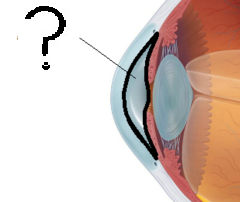
New cards
aqueous humorous
clear fluid that gives the cornea it's rounded shape
78
New cards
cornea
covers the iris and the pupil
focuses light that enters the eye
focuses light that enters the eye
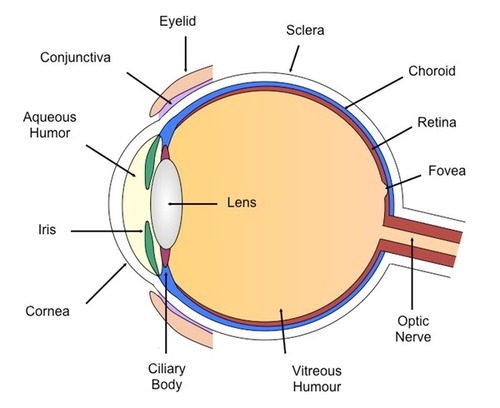
79
New cards
dark adaptation
from light to dark
80
New cards
light adaptation
from dark to light
81
New cards
the transduction process
1) photochemical reactions happen in rods and cones
2) bipolar cells are activated
3) ganglion cells are activated and axons converge making the optic nerve
4)then info gets sent too the thalamus
2) bipolar cells are activated
3) ganglion cells are activated and axons converge making the optic nerve
4)then info gets sent too the thalamus
82
New cards
feature detectors
nerve cells that only respond to certain traits
83
New cards
parallel processing
multitask
84
New cards
trichromatic theory
the retina has red, green, and blue and when they combine they make a single perceivable color
>white
>white
85
New cards
opponent processing theory
opposing retinal processes enable after images
86
New cards
acuity
the sharpness of vision
87
New cards
nearsided/myopia
close is good but far is bad because rays converge in front of the retina
88
New cards
farsided/hyperopia
far is good but close is bad because rays converge in front of the retina
89
New cards
prosopagnosia
basically face blindneess
90
New cards
cataracts
when the lens gets cloudy
91
New cards
agnosopia/blind sight
primal visual cortex is damaged but vision stem still works so sometimes you get to see
92
New cards
frequency
number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
equals pitch
equals pitch
93
New cards
pitch
tone's highness or lowness.
shorter waves = higher pitch
longer waves = lower pitch
shorter waves = higher pitch
longer waves = lower pitch
94
New cards
amplitude sound
wave's height
peak of the wave to the trough of the wave
equals intensity and brightness and volume
tall amplitude = loud sounds
short amplitude = dull sounds
peak of the wave to the trough of the wave
equals intensity and brightness and volume
tall amplitude = loud sounds
short amplitude = dull sounds
95
New cards
timbre
quality of sound
96
New cards
process of hearing
pinna > ear canal > eardrum > ossicles (hammer, anvil, stirrup) > oval window > cochlea > cochlear fluid > cilia > organ of Corti
97
New cards
outer ear
traps sound waves and channels them through the auditory canal to the eardrum
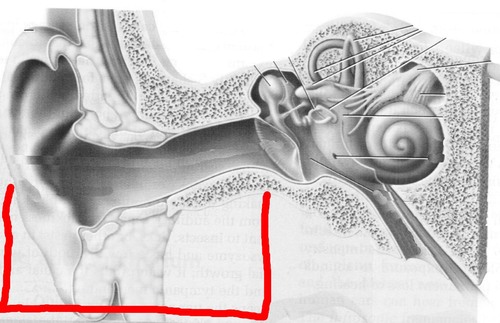
98
New cards
pinna
skin part of ear
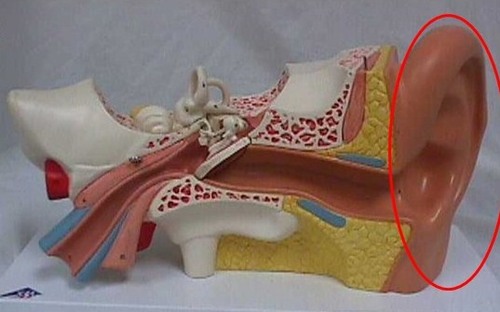
99
New cards
auditory canal
canal in which sound waves travel
eardrum is at the end
eardrum is at the end
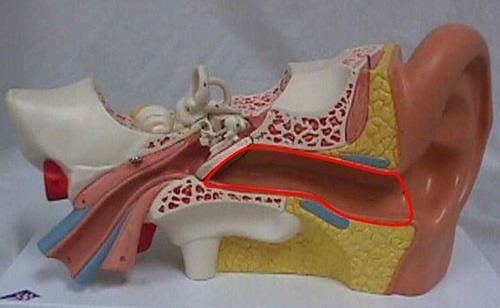
100
New cards
ear drum
tight membrane that vibrates when sound waves hit i