Mycology Lab Practical
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Why is potassium hydroxide preparation done on a skin, hair or nail specimen?
It helps break down any organic material to visualize fungal elements more clearly under a microscope.
What is the purpose of using an India ink wet mount?
Used as a quick test for Cryptococcus sp, resulting in a halo under the microscope
Why is lactophenol blue (or red or colorless) stain used for a fungal wet mount?
Because it does 3 things:
1) Kill any living organism
2) Preserve them
3) Stain them to see the structure
What are some key words to describe the texture of mold?
Cottony, wooly, velvety, granular, folded, smooth, waxy, creamy
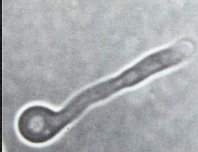
What is the result of this germ tube?
Positive
How do you know if a germ tube is positive or negative?
A positive germ tube means there is NO separation between the bulb and the stalk
A negative germ tube means there is separation between them :^]
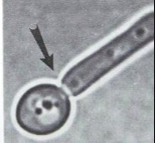
What is the results of this germ tube?
Negative
What is the pathogenicity of Coccidioides immitis??
Coccidiodomycosis —> Self-limiting lung infection
Pnuemonia
AKA valley fever
Dimorphic fungi
What is the colony morphology for Coccidioides immitis?
Grows moderately rapid
White, beige and wooly
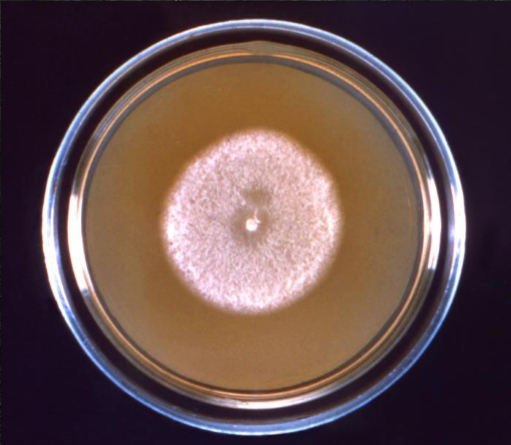
Which sp is this?
Coccidioides immitis (Colony)
What is the key microscopic feature of coccidioides immitis?
Arthroconidia —> Barrel shaped, alternating with empty cells
Conidiophores absent
Spherules that can be seen on direct specimen
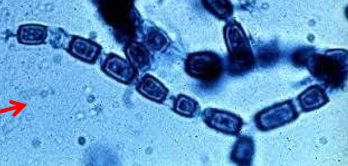
Which sp is this?
Coccidioides immitis (microscope)
What is the pathogenicity of Histoplasma capsulatum?
Histoplasmosis —> presenting in benign pulmonary form
Dimorphic fungi
What is the key geographic preference for Histoplasma capsulatum?
Bat caves w/ high nitrogen content
Ohio and Mississippi River Valley
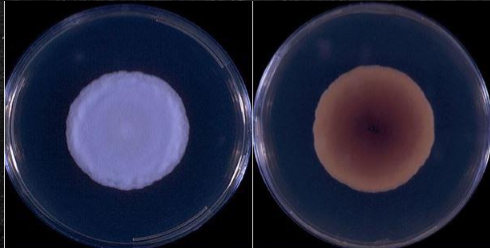
Which sp is this? What temperature is this at?
Histoplasma capsulatum; 25C (Colony)
Which sp is this? At which temperature?
Histoplasma capsulatum; 37C (Colony)
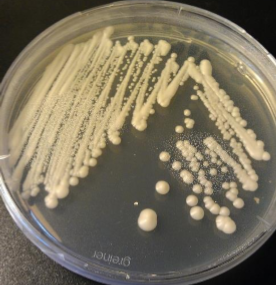
Which sp is this? At what temperature?
Histoplasma capsulatum; 25C (Micro)
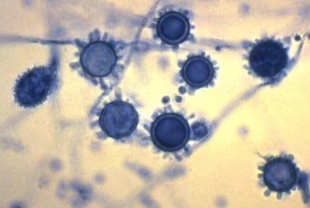
Which sp is this? At what temperature?
Histoplasma capsulatum; 37C (Micro)
What is the pathogenic of Blastomyces dermatitidis?
Flu-like but if it chronic then it can become pulmonary and results in ulcerative lesions of the skin and bone
Causes blastosmycosis
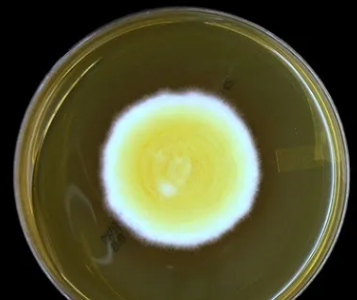
What sp is this? At what temperature?
Blastomyces dermatitis; 22C
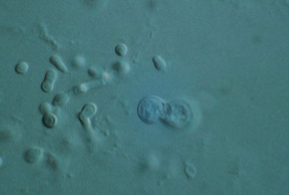
Which sp is this? What phases is this on?
Blastomyces dermatitidis; Yeast form
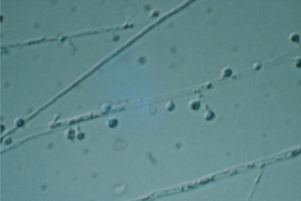
Which sp is this? What phase is this on?
Blastomyces dermatitidis; Mold form
What is a hyaline?
Species that are nonpigmented or lightly pigmented
Quick way to check is reversing the colony, if the back side is any color besides brown or black!
What is dematiaceous?
Species that are darkly pigmented
Officially due to the melanin production in the cell wall
Therefore most reverse cultures look either DARK BROWN or BLACK
What is Septae?
The separation of fungal filaments into individual cells by internal cross-walls
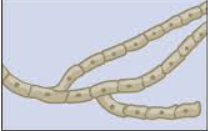
What is this?
Septate
What is aseptate hyphae?
The absence of a cross wall / septa

What is this?
Aseptate hyphae
What is pseudohyphae?
Looks like hyphaes but its just a bunch of elongated clusters that are coming together to look like hyphaes

What is this?
Pseudohyphaes
What are blastospores / blastoconidia?
Blastoconidia is the budding spore from a blastospore
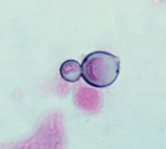
What is this?
Blastoconidia
What are arthrospores or arthroconidia?
Barrel-shaped fungal spores that are produced by the segmentation and fragmentation of septate hyphae
Think of scotch tape!
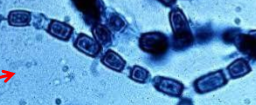
What is this? (Bonus pt of which sp it comes from)
Arthroconidia ; Coccidioides
What is sporangiospores?
Spores that form within a sac (sporangium)
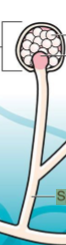
What are the white balls within the sac called?
Sporangiospores
What are dermatophytes?
Fungi that causes superficial skin, hair or nail infections
What are some dermatophytes species?
Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and microsporum
Which dermatophytes create macroconidia?
Epidermophyton floccosum and microsporum canis
What is the difference between microconidia and macroconidia?
The sizing
Macroconidia usually being large, multi-cell that are curved or sickle
microconidia usually small, single-celled (oval to spherical)
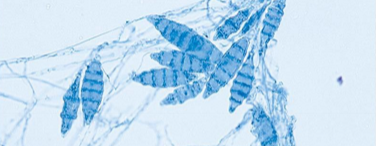
What is this? (Bonus points for species)
Macroconidia; M. gypseum
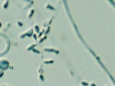
What is this?
Microconidia
Which species create microconidia?
Trichophyton mentagrophytes, trichophyton rubrum, trichophyton tonsurans
Easy way to remember the difference between mold and yeast?
If it bores a spore then let it mold but if it buds a yeast then it becomes a feast!
How can you tell the difference between mold and yeast?
The way they reproduce
Molds —> via spores
Yeast —> via budding or fission
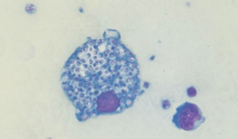
Which sp is this? What is it encapsulated by? What temperature is it at?
Histoplasma capslatum; Monocyte; 37C
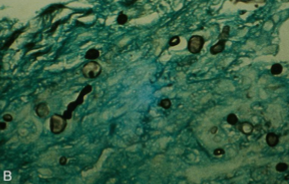
Which sp is this? What type of specimen is this? What temperature is it at?
HIstoplasma capsulatum; Tissue; 22C
What is a key feature of Histoplasma capsulatum in mold form?
It can be spikey!