L 7 Breast Disorders - benign
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
2nd most common cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer death in US women
breast cancer
what population has the highest incidence rate of BC and what population has the highest mortality of BC?
Non-Hispanic White women have highest incidence
non-Hispanic Black women have the highest mortality rate
what age does biennial screening (mammogram) start?
40 - 74 years
what 2 biennial screening tools (mammogram) are there?
- Digital mammography (2D)
- Digital breast tomosynthesis (3D)
Digital breast tomosynthesis (3D) can generally offer __________, but it is slightly a higher ________ dose
more detailed view of breast tissue
radiation
screening starts at 40, but how often are breast screening follow ups?
q1-2 years
an average risk woman = what r/f?
no risk factors
<15%
High risk women includes any 3
- Personal history of breast ca
- Breast cancer gene (BRCA1/2, PTEN, TP53)
- History of chest radiotherapy between ages 10-30
when to start bc screening for average risk pts?
40-years-old
when to start bc screening for moderate risk pts?
same as Average risk
*can discuss supplemental screening but evidence is not conclusive
what type of screening is done for high risk pts?
– screening mammogram AND supplemental MRI (higher sensitivity than mammography/US) per ACOG
what are 2 main supplements screening modalities (for mod - high risk pts)?
- Breast Ultrasound
- MRI, breast with contrast
Increased breast density refers to a higher proportion of ____________ compared to _________ in the breasts
fibroglandular tissue
(skin, blood vessels, ductal/stromal elements of glands)
fatty tissue
what is the only way to identify breast density?
Radiologic
how does fibroglandular tissue appear on a radiograph?
radio-opaque/white
how does fat tissues appear on radiograph?
radiolucent/black
BI-RADS classification (A-D)
A - almost entirely fatty
B - scattered areas of fibroglandular density
C - heterogeneously dense (may obscure small masses)
D - extremely dense (lowers sensitivity of mammography)
what is the first-line imaging to evaluate breast mass in patients younger than 30-years-old?
Breast ultrasound
also used to investigate abnormalities or masses seen on mammography
what are the benefits to a breast ultrasound?
- Easy, available
- No radiation exposure
- Not as expensive
what is the routine screening in asymptomatic patients?
Mammography
if a pt is symptomatic, what diagnostic modality is used
mammography
a diagnostic mammography gives a higher ___________and _________ than screening mammogram
abnormal interpretation rate and higher cancer detection rate
Order a ____________, digital, even if only evaluating abnormality of one breast.
bilateral diagnostic mammogram
an MRI is a supplemental screening tool used with or without contrast?
with!!
what else can an MRI w. contrast be used for other than supplemental screening?
-Further evaluation of abnormalities detected by mammogram
-Further evaluation of breast cancer
-Assess for leakage in breast implants
what modality is this?
used to remove small amount of breast tissue or fluid to evaluate for malignancy
needle aspiration
needles aspiration imaging precedes _________
biopsy
what else can a needle aspiration for the breasts be used for?
- Can be therapeutic in relieving pain from a cyst
- Used to drain breast abscesses
- Evaluate axillary lymph nodes
T/F
breast pain = malignancy
False
breast pain is common, rarely sx of malignancy in absences of corroborating PE/imaging findings
3 types of breast pain (Mastalgia, Mastodynia)
cyclical, non-cyclical, extramammary
what should make you order imaging for breast pain?
- Noncyclical, unilateral, or focal breast pain that is not extramammary may benefit from breast imaging
T/F
Cyclical or bilateral diffuse breast pain usually DOES NOT require imaging
T
tx of breast pain
reassurance, acetaminophen/NSAIDs, physical support
- If refractory 6+mths conservative tx: tamoxifen x 1- 3mths during luteal phase (breast pain greatest)
In general, mastalgia has a natural history of __________
remission and relapse
Common, benign changes that give breasts a lumpy or ropelike texture
Fibrocystic Changes of the Breast
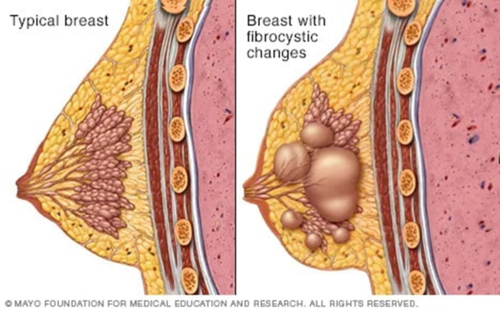
Fibrocystic Changes are rare in ___________
menopause
what is the pathophys of fibric changes?
hormone driven; cyst development in lobules-> rupture, scarring, inflammation-> fibrotic changes
CP of fibrocystic changes
Cyclical, diffuse breast pain, lumpy-textured breasts
may reveal free-moving, lumpy masses +/-discomfort
what can intensify fibrocystic pain ?
hormonal fluctuation with menstruation can intensify symptoms
What is the management for fibrocystic changes?
NSAIDs
bra support
no alc, caffeine
stop HRT
what imaging is best for < 30-years-old
Ultrasound of breast - 1st line
what imaging is best for 30 - 39 -years-old
Diagnostic mammogram and/or US
what imaging is best for 40+ years-old
Diagnostic mammogram w/ US if needed
3 types of breast cysts
simple, complicated, complex
what cyst?
well circumscribed, anechoic, <2-3mm, w/o discrete solid components.
- Benign (BI-RADS 2)
simple
what is the intervention for a simple cyst?
No intervention needed
what cyst?
masses with homogenous low-level internal echoes due to echogenic debris, w/o solid components, thick walls or thick septa, and w/o vascular flow
- Usually benign (BI-RADS 2-3)
complicated
what is the intervention for a complicated cyst?
Continue with imaging q 6 months for 1 year to show stability
what cyst?
masses with thick walls and/or septa greater than 0.5 mm, presence of cystic and solid components, and absence of posterior wall enhancement. Can demonstrate anechoic and echogenic components
- Need to be biopsied (BI-RADS 4-5)
complex
what is the intervention for a complex cyst
- biopsy
- If benign, monitor with imaging q 6 - 12 months for 1-2 years to document stability
Benign proliferation of the glandular tissue of the male breast diagnosed clinically by the presence of a rubbery or firm mass extending concentrically from the nipple(s)
Gynecomastia (Male)
who is gynecomastia common in?
common in infancy and adolescence (puberty), and middle-aged to elderly men
why does gynecomastia occur?
imbalance in androgen-to-estrogen concentrations due to decreased androgen production, increased estrogen production, antiandrogen, or estrogenic drugs or compounds
what can cause gynecomastia?
idiopathic
persistent pubertal
med induced
cirrhosis or malnutrition
male hypogonadism
testicular tumors
untreated hyperthyroidism
CKD
CP of gynecomastia
centrally located glandular tissue, symmetrical in shape, usually bilateral, tender (early phase)
what imaging for gynecomastia?
Imaging not recommended UNLESS concern for possible cancer
Diagnosis for gynecomastia is clinical based on finding of a palpable mass at least _______ in diameter underlying the nipple that is a __________ directly beneath the areola that can be "_________" to locate edge of rubbery tissue.
0.5cm
concentric, rubbery-to-firm mobile disk of tissue
flipped up
who do you just treat gynecomastia with simple observation?
- Adolescents (80% regress spontaneously)
- Adults with recent onset (<6-12mths) AFTER meds and underlying medical disorders have been addressed
pharm tx for gynecomastia for adolescents (severe, tender, significant embarrassment)
Tamoxifen 3mo, then re-eval
pharm tx for gynecomastia in adult males without hypogonadism (no identifiable cause, breast tenderness > 3mths)
Tamoxifen 3mo, then re-eval
pharm tx for gynecomastia in adult males with hypogonadism
testosterone therapy
when is sx indicated for gynecomastia
persistent gynecomastia causing considerable psychological distress
present >12mths, and the nontender
fibrotic stage has been reached
Inflammation of the breast tissues with or without infection
Lactational Mastitis
What is lactational mastitis?
Inflammation of the breast tissues with or without infection.
When is lactational mastitis most common?
In the first 4-6 weeks of breastfeeding.
What are some risk factors for lactational mastitis?
Breastfeeding difficulties, nipple injury, breast pump use, hyperlactation, history of mastitis.
What is the most common causative organism of lactational mastitis?
Staphylococcus aureus > Group B streptococci.
What is the pathophysiology of lactational mastitis?
Nipple injury and ductal narrowing lead to milk stasis and poor draining, resulting in inflammation, edema, and infection of breast tissue.
What are common clinical presentations of lactational mastitis?
Erythematous, swollen, tender region of breast; may include induration, fever, chills, tachycardia, and axillary lymphadenopathy.
What laboratory test is sometimes used for lactational mastitis?
Milk culture (not routine).
When should an ultrasound be considered in cases of lactational mastitis?
If there is no response to treatment within 24-48 hours.
What is a common management option for lactational mastitis?
Topical warm/cold compresses
What medications are recommended for pain relief in lactational mastitis?
NSAIDs or APAP (avoid ASA)
Should breastfeeding continue during lactational mastitis?
Yes, continue to breastfeed or express milk
What is the recommended treatment of bacterial lactational mastitis?
Cephalexin
What should be considered if MRSA is suspected in lactational mastitis?
Bactrim DS or Clindamycin
What is a contraindication for using Bactrim DS in lactational mastitis?
Avoid in newborns < 1 month or G6PD-deficiency
Less common, inflammation of breast tissue +/- infection
Non-Lactational Mastitis
What is Non-Lactational Mastitis?
An inflammatory condition of the breast that occurs outside of lactation.
What is Periductal Mastitis?
An inflammatory condition of subareolar ducts presenting with peri-areolar inflammation.
What can occur as a secondary infection in Non-Lactational Mastitis?
Duct rupture and abscess may occur.
What is needed if there is purulent nipple discharge in Non-Lactational Mastitis?
GRAM STAIN & CULTURE.
Is Non-Lactational Mastitis usually an acute or chronic problem?
Usually a chronic problem.
What surgical treatment may be required for Non-Lactational Mastitis?
Ductal excision.
What is idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM)?
A rare benign inflammatory disease of unknown etiology.
Who is most commonly affected by idiopathic granulomatous mastitis?
Parous young women, typically within a few years after pregnancy.
How is idiopathic granulomatous mastitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made via core needle biopsy.
What is the management for localized infection in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis?
Antibiotics and drainage are recommended.
Is surgery recommended for idiopathic granulomatous mastitis?
No, surgery is not recommended.
What is the goal of managing idiopathic granulomatous mastitis?
To reduce inflammation and manage symptoms, as there is no known cure.
What is the typical demographic for Tuberculosis mastitis?
UNCOMMON, reproductive age women +/- lactation.
What type of biopsy is essential for diagnosing Tuberculosis mastitis?
Core needle biopsy.
What histological feature is associated with Tuberculosis mastitis?
Langhans' giant cells.
What is the treatment for Tuberculosis mastitis similar to?
Treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis.
*ALWAYS CONSIDER ____________ IN YOUR DDx! BIOPSY IS SO IMPORTANT
BREAST CANCER
What is a common complication of breast mastitis?
Breast abscess
r/f for breast abscesses (lactating vs nonlactating causes)
Lactating – over 30 y/o, 1st pregnancy, gest age>=41 w, tobacco use
Nonlactating- AfrAm, obesity, smokers
what labs should you order for a breast abscess if pt is lactating?
milk culture
what dx procedure should you order for breast abscess either lactating and nonlactating
ultrasound showing fluid collection
how to tx a breast abscess? Non severe vs severe abscess
- Draining with needle aspiration or surgical drainage
- Empiric antibiotic tx:
non-severe = Cephalexin
severe infection = Vanco