Normative development of fears
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
how are childhood fears assessed?
directly (and often retrospectively)
via interviews, questionnaires, parent/teacher reports
characteristics of normal childhood fears
commonly experienced
relatively mild
appear and disappear spontaneously
follow a predictable pattern
decrease with age
what did Gullone (2000) find in 4-19 year olds?
average number of fears is 2-5 per child
tend to elicit general themes e.g. animals, death/injury, the unknown, social concerns
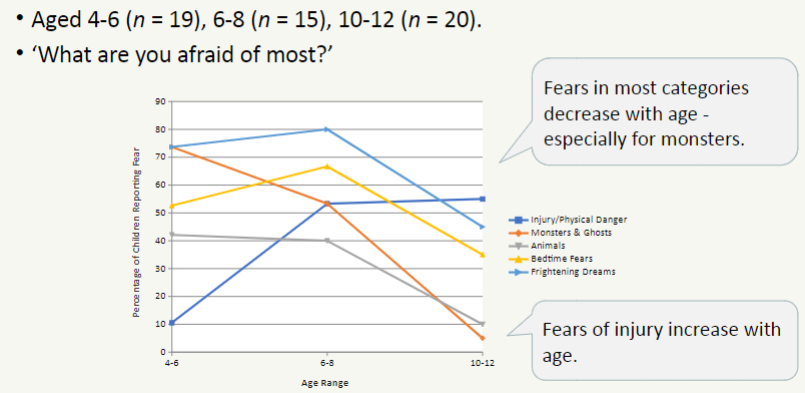
what did Baur (1976) find about childhood fears?
fears in most categories decrease with age (especially for monsters)
fears of injury increase with age
what is one of the most commonly used questionnaires to assess fear in children?
Fear Survey Schedule for Children (FSSC) (Ollendick, 1983)
key characteristics of the FSSC
80 item measure of children’s fear in response to a range of specific stimuli/situations
measures number, severity, and type of normal fears children experience
what are the reliable factors of the FSSC?
fear of danger and death
fear of failure and criticism
fear of the unknown
fear of animals
stress and medical fears
what are some of the methodological issues with the FSSC?
some of the items are quite outdated and contemporary threats are not included
may not accurately capture cultural variation in childhood fears
can only measure what is include so not an exhaustive list
might not index actual frequency of fears
what are the moderators of childhood fears?
gender
cultural variation
socioeconomic effects
what are the gender effects on childhood fears?
girls report more fears than boys and fear for death/danger was highest (Ollendick, King & Frary, 1989)
items that most strongly discriminated between boys and girls included: rats, spiders, snakes, mice, creepy houses, being alone, bad dreams (Gullone & King, 1993)
high femininity and low masculinity associated with greater anxiety and avoidance
gender role orientation stronger predictor of fear than child’s biological sex
how does cultural variation affect childhood fears?
across ‘western’ countries there is lots of consistency (number of fears decreases with age, girls are more fearful than boys, content of fears show similar developmental pattern)
fear levels may vary as a function of cultural group membership
cross-cultural differences have been found within-countries
what are the socioeconomic effects on childhood fears?
lower SES children report more fears
differences in fears (low SES children = abandonment by parents, death, violence, knives, middle/upper SES children = heights, ill health, roller-coasters, pet’s safety)
children in low SES environments are exposed to more specific threats and enhanced general feelings of fear and anxiety
what are some observed developmental patterns in terms of childhood fears?
infants: environmental stimuli (loud noises, separations, unusual stimuli)
4-8 years: ghosts, imaginary creatures, and animals
10-12 years: social fears, self-injury
what are the theoretical approaches to development of childhood fears?
evolutionary
cognitive development
describe the evolutionary approach to development of childhood fears
natural selection favours individuals who learn rapidly about threats that pose danger to self (facilitates survival)
fear system evolved to focus on threats at ages at which those threats would have been greatest risk to our ancestors
some fears may be innate and may not need to be learned
we may be prepared to rapidly acquire some fears with little or no prior learning
describe the cognitive developmental approach to development of childhood fears
fear and anxiety originates from conceptualisation of threat
conceptualisation of threat depends on a child’s cognitive and physical abilities
as cognitive abilities develop, fear and anxiety become more sophisticated
range of fear-provoking stimuli broadens and cognitive features of anxiety become more prevalent
what are common fears in infancy?
environmental stimuli
separation anxiety
results of the Muris, Merckelbach, Mesters & Van den Brand (2002) study
increased age and cognitive maturation lead to enhanced ability to elaborate on worries, in turn increasing risk for emergence of personal worry
describe the evolutionary case for snake and spider fear
from 8-10 months, evolutionary accounts argue that infants demonstrate negative responses and rapid detection indicative of innate fear of snakes and spiders
negative responses are universal across cultures
seen across a variety of nonhuman animals
evidence for the evolutionary accounts for snake and spider fear
infants form faster associations between snakes and fearful stimuli than between snakes and happy stimuli
infants rapidly detect and show greater attention to snakes and spiders than to control images

evidence against the evolutionary accounts for snake and spider fear
there is no corroborating evidence of fear
some studies suggest young children display evidence that they like snakes/spiders
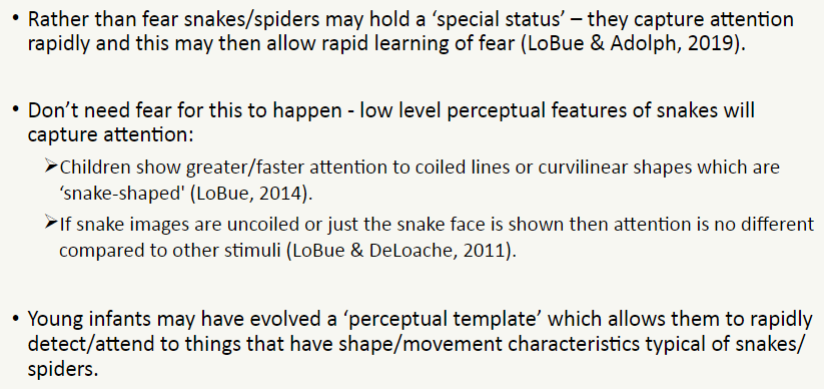
possible perceptual bias (low level perceptual features of snakes will capture attention)
young infants may have evolved a ‘perceptual template’ which allows them to rapidly detect/attend to things that have shape/movement characteristics typical of snakes/spiders
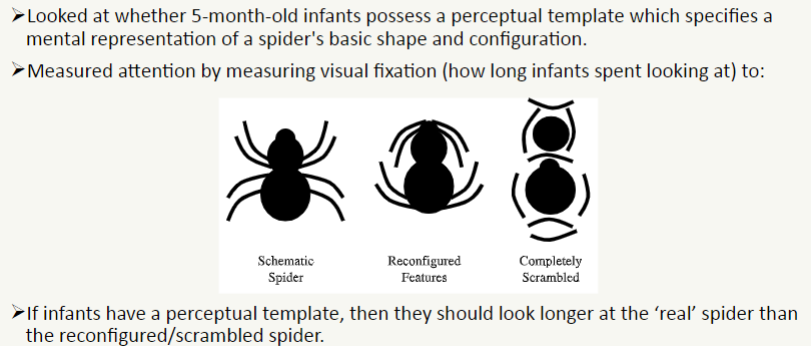
results of Rakison & Derringer (2007) perceptual template/rapid detection mechanism study
infants looked longer at the schematic spider than the reconfigured and scrambled spider – consistent with possession of an innate perceptual template
no significant difference in visual fixation times when spider images did not contain typical curvilinear body and leg shape
suggests perceptual template specifies the structure of spiders e.g. curved body and legs