HC Ch 8: Revenue Cycle Management: Cost Estimation and Rate Calculations
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what is the equation for calculation of total costs?
total costs = fixed costs + total variable costs OR
total costs = fixed costs + (variable cost rate x volume)
what is activity based costing?
it is a costing approach that analyzes the individual units of work performed that contribute to the total cost of a process - it is a 6 step process
identify the activities
identify the activity costs
identify the cost drivers
identify volume or utilization
calculate allocation rates
calculate process totals
what is a workload calculation?
it is an estimate of the anticipated labor expense for a project or process
tasks that compromise the project or process
completion time for each task
frequency and duration of the tasks/project
pay rate of the employee completing the tasks
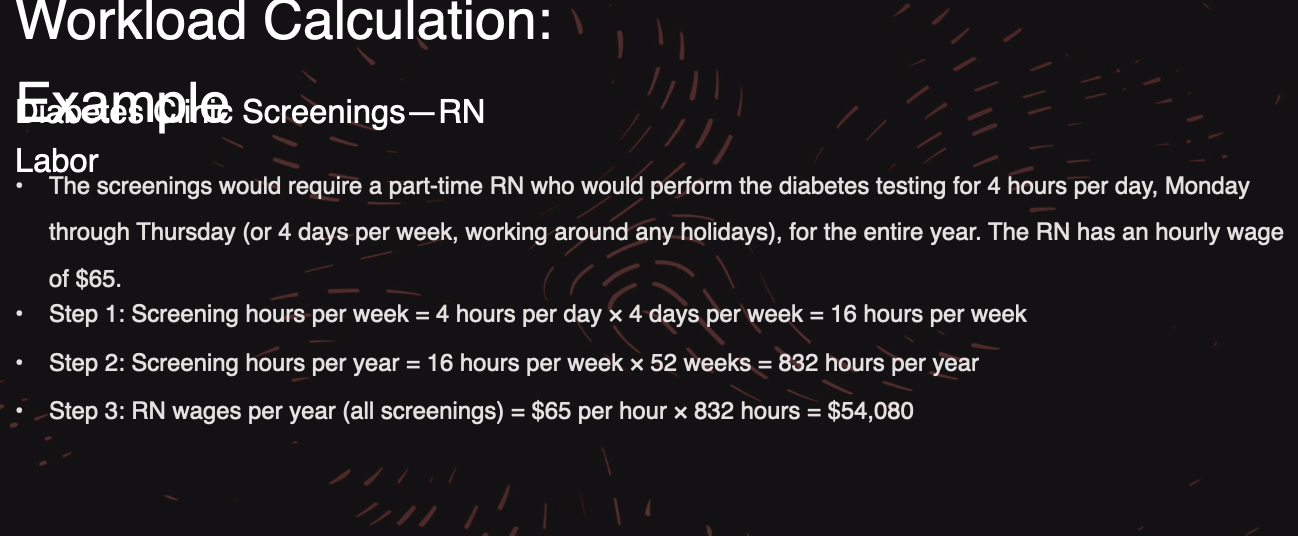
workload calculation example
what are rate calculations and price?
price is the amount the organization will charge consumers or patients to utilize the services provided
ex: fixed costs (rent & salary), variable costs (medical supplies & single use items), profit (percentage & specific amount)
what are pricing strategies and profit analysis?
Full cost pricing
marginal cost pricing
price shifting
what is full cost pricing?
this is establishing a price that covers direct fixed costs, direct variable costs, and overhead (indirect)
what is marginal pricing?
marginal pricing is pricing that covers additional units of service only, but not all costs incurred
what is price shifting?
the process of charging higher pricing to one group of consumers to cover the financial shortfall of another group of consumers
what is breakeven are what are the types of breakeven?
a point where total revenue (price x volume) - total costs (foxed costs) (total variable costs) = profit. they are used for profit analysis
economic breakeven: covers costs incurred and includes profit margin
accounting breakeven: covers costs incurred with no profit margin
what is capital structure?
the determination of the ideal financing, by comparing equity financing return on equity (ROE) and the debt financing ROE
every organization has its own unique equity and debt mix
this comparison is done by completing a balance sheet and income statement based on the desired equity and debt percentages
what is the corporate cost capital?
this is calculated using the debt and equity percentages and the required interest rate or rate of return for each
CCC = (equity percentage x equity cost) + (debt percentage x debt cost) x (1-tax rate)
what is the equity percentage?
the percentage of equity to be used in the financing decision
what is equity cost?
the required rate/cost of financing using quality
what is the debt percentage?
the percentage of debt to be used in the financing decision
what is the debt cost?
the required rate/cost of financing using debt and tax rate
what is tax rate?
the organizations tax rate
what are the decision making and data capturing sources?
accounting, budgeting & forecasting, investments, and patient & stakeholder experience
in this case how is accounting used?
this records all financial activity coming in and going out of the organization this data helps decision makers to visualize what financial resources we have now and how we are sending them
in this case how is budgeting and forecasting used?
after the actual financial activity is recorded, decisions must be made on preparing for the future, efforts to maintain the organizations operations must begin with proper planning
in this case how are investments used?
data capture helps to determine what, how, and when to invest in projects and services by providing the much needed detail on available alternatives. data for the “make or buy” decision, as well as the “expand or contract” decision allows leadership to utilize available resources for the appropriate investments
in this case how are patients and stakeholders used?
the needs of stakeholders must be managed, data capture through accounting methods and ABC provides decision makers with information at the transaction levels for patients, clinicians, insurer's and other stakeholders, allowing for continous improvement