Biology - Exam 3
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
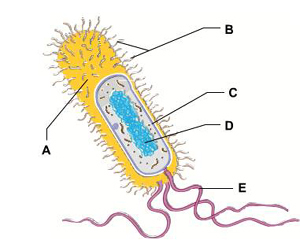
Fimbriae
surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface
Protection
The function of a bacterium’s capsule
D
DNA containing region
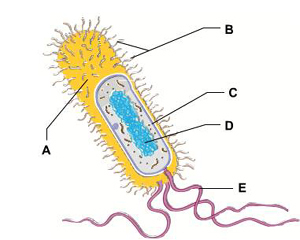
Nucleoid region
where is a bacterial cell’s DNA found
Ribosomes
In a bacterium, where are proteins synthesized
Cell Wall
Rigid structure, found outside the plasma membrane, that surrounds and supports the bacterial cell. made from cellulose fibrils
Plasma membrane
The bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to leave the cell
C
The structure that regulates the passage of material into and out of the bacterial cell
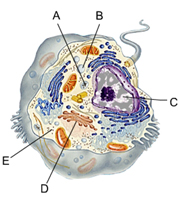
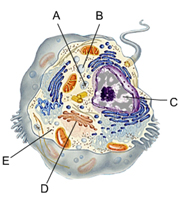
Mitochondrion
H
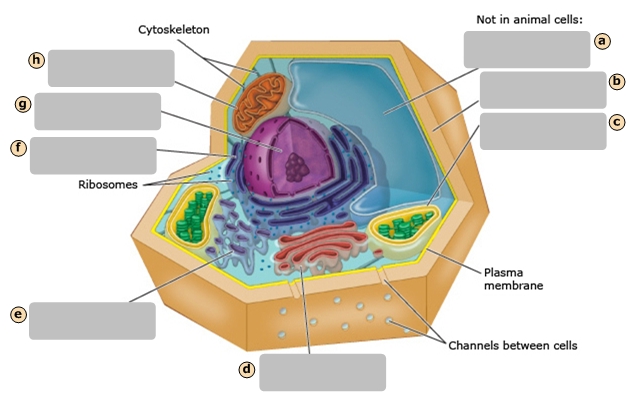
Nucleus
G
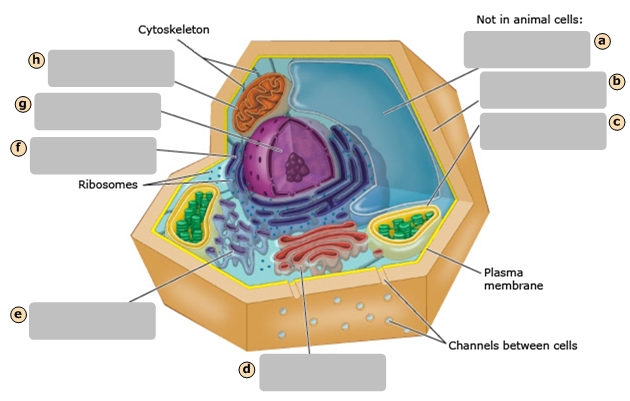
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
F
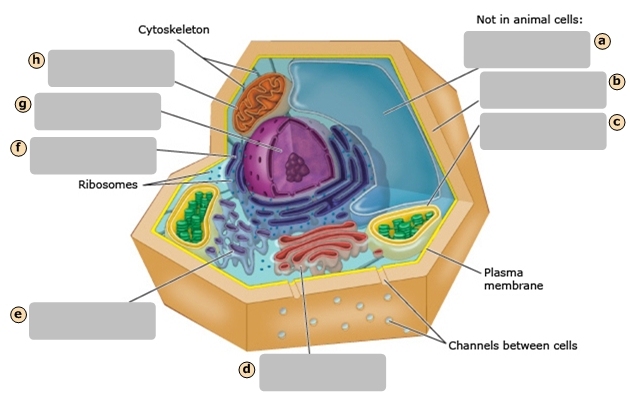
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
E
Golgi Apparatus
D
Central Vacuole
A
Cell Wall
B
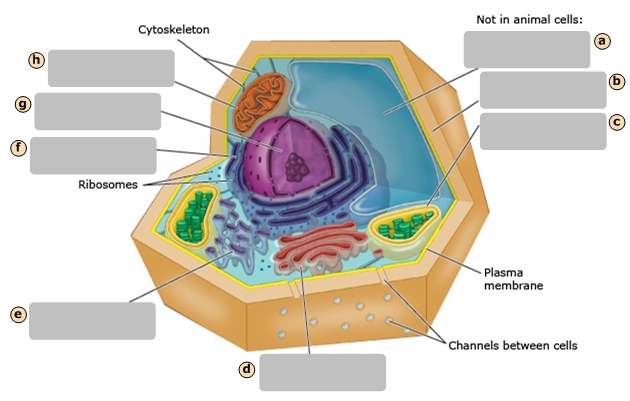
Chloroplast
C
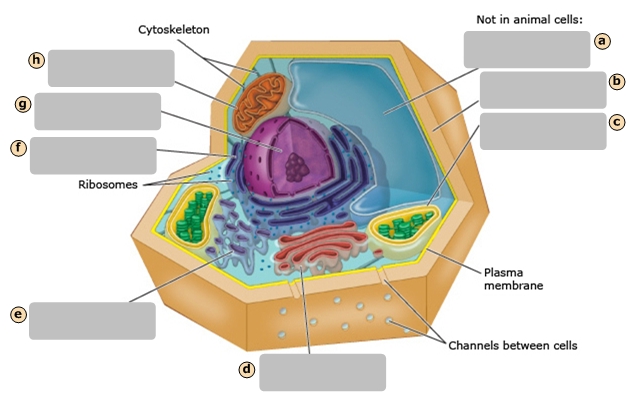
Central Vacuole
Regulates cytoplasm composition, creates internal pressure and stores cell compounds
Chloroplast
Makes food by converting light energy into chemical energy
Mitochondrion
Converts chemical fuel into packets of chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies and packages proteins
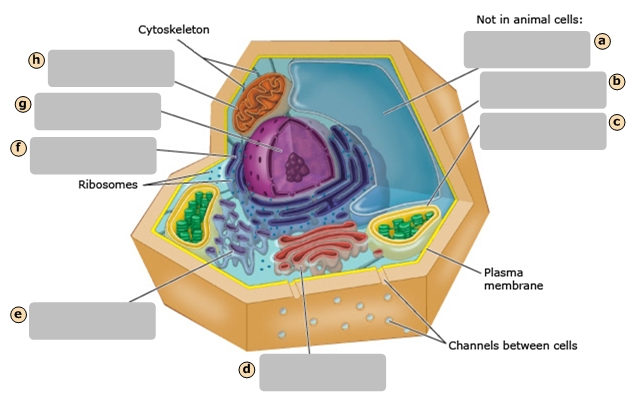
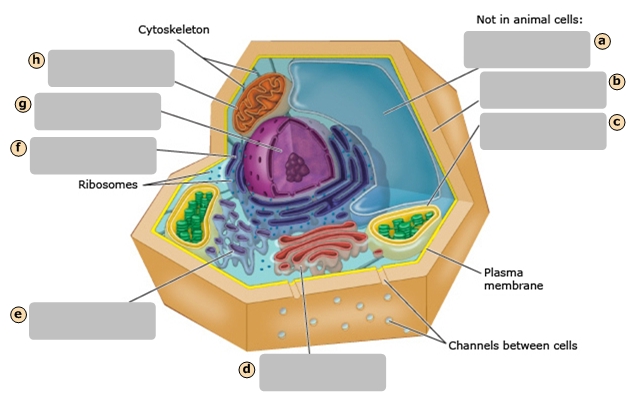
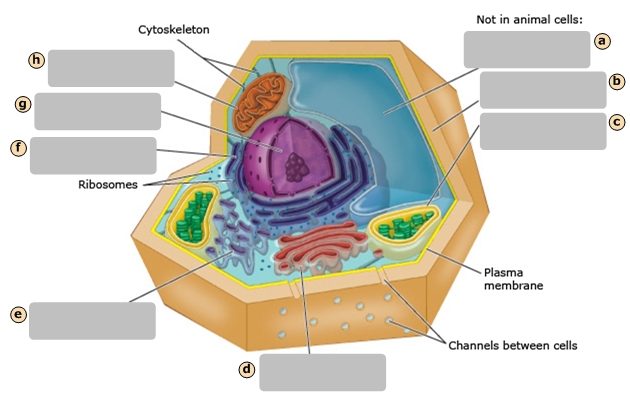
Cytoskeleton
A
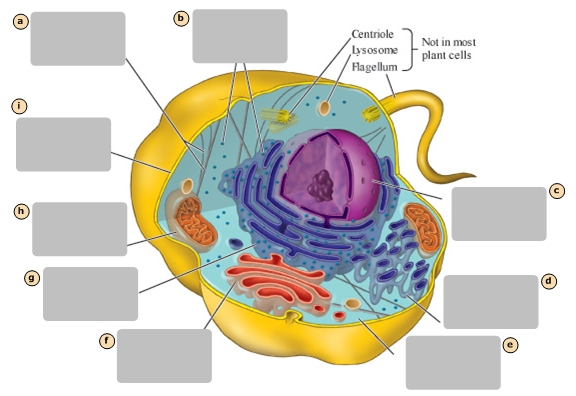
Ribosomes
B
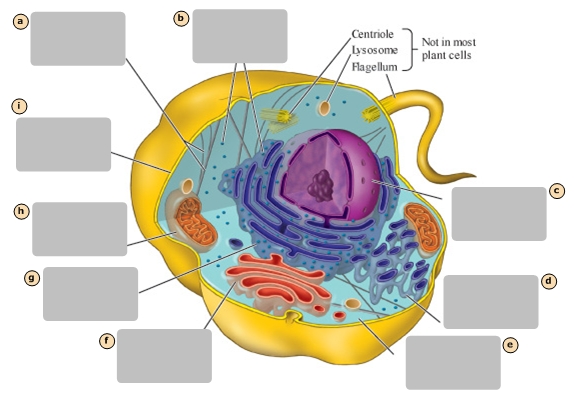
Nucleus
C
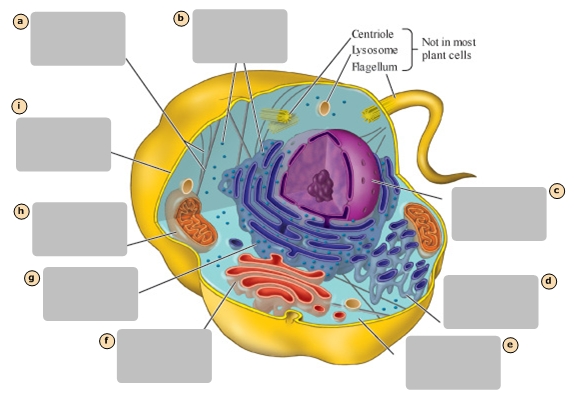
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
D
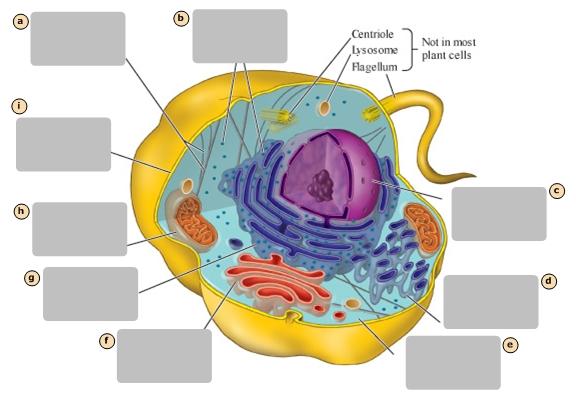
Cytosol
E
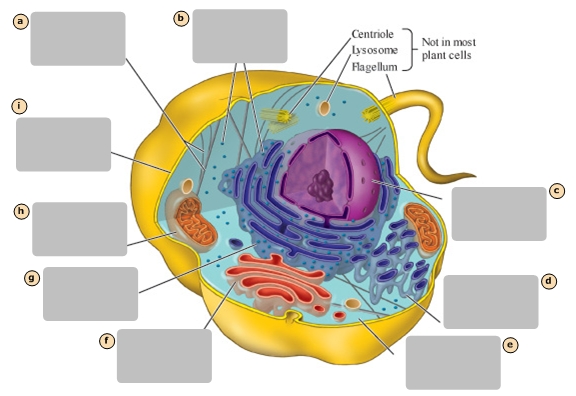
Golgi Apparatus
F
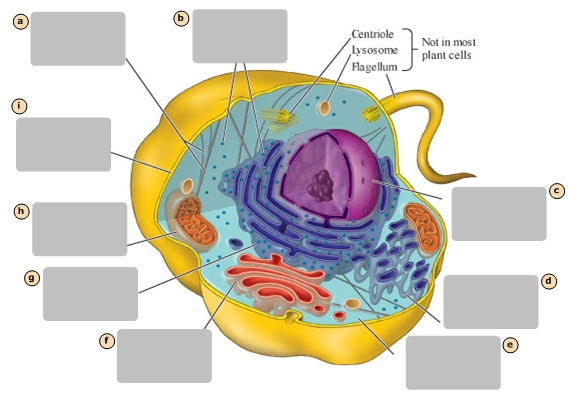
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
G
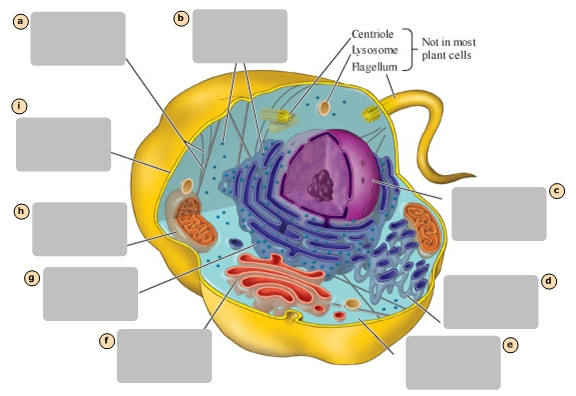
Mitochondrion
H
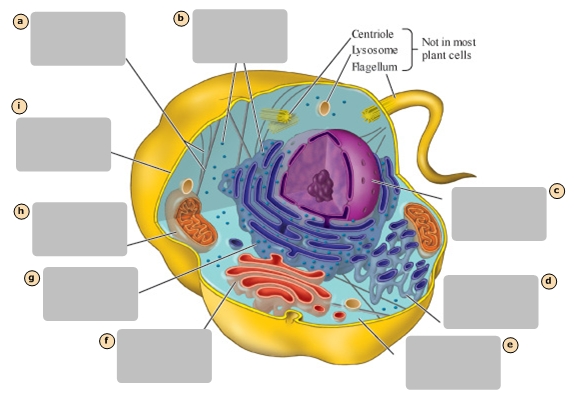
Plasma Membrane
I
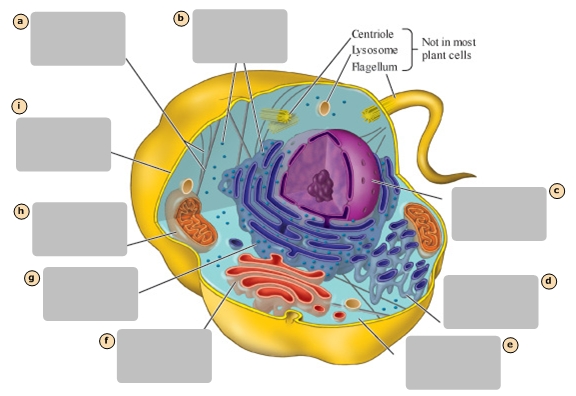
Nucleus
Stores the genetic information of the cell
Lysosome
Breaks down macromolecules using digestive enzymes
Mitochondrion
Converts chemical fuel into packets of chemical energy that can power the cell
Ribosome
Works with mRNA to synthesize proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of lipid synthesis
Mitochondrion
Which plant cell organelle converts chemical fuel into packets of chemical energy that can power the cell
Cytoskeleton
The structural framework in the cell
Mitochondria
Where in a cell is ATP made
mRNA
carries instructions for making proteins from the nucleus into the cytoplasm
Ribosomes
One of the ways smooth endoplasmic reticulum differs from rough endoplasmic reticulum is that rough ER is covered by
Endomembrane System
includes the ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles - manufactures, processes, and transports lipids and proteins
Lysosomes
breaks down worn-out organelles
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Where are lipids made in the cell
in the middle 1800s
when was the idea of the cell theory developed
Cytoplasm
all of the material contained within the plasma membrane of a cell, except for the nucleus.
Organelle
The nucleus is an example of a cell __________, one of a number of tiny membrane-enclosed structures found in many cells.
microtubule
A(n) ___________ is a small, hollow strand of the protein tubulin that enables movement of cell structures and is a major component of cilia and flagella.
lysosome
A(n) ___________ is a membrane-bound cell structure that digests worn-out cellular material and foreign matter that enters the cell.
prokaryotic
A(n) ___________ cell lacks a nucleus.
eukaryotic
A(n) ________ cell has a "true" membrane-enclosed nucleus.
endoplasmic reticulum
The ____________ ___________ is a system of membranes and channels where proteins and lipids are synthesized.
True
Prokaryotic cells do not have cilia
Prokaryote
What is the smallest living thing in the following list: frog embryo, mitochondrion, prokaryote, virus, atom?
Cell membranes
Where are phospholipids found
DNA
what provides the instruction code for making proteins
C
organelle that contains most of a cell’s DNA
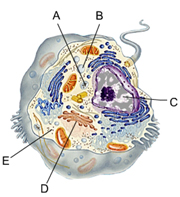
Mitochondrion
carries out cellular respiration
E
double membrane that encloses the nucleus
Chromatin
composed of DNA and protein
Nucleous
Ribosomal subunits are manufactured by the
Ribosomes
sites of protein synthesis
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
manufactures cellular membranes by adding membrane proteins and phospholipids to its own membrane
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Where is calcium stored
A
stores, modifies, and packages products
Microtubules
hollow rods that shape and support the cell
Basal bodies
identical in structure to centrioles
Peroxisome
Produces H2O2 as a byproduct
Microtubules
The cilia and flagella of eukaryotic cells are composed of
Lysosome
plays a role in intracellular digestion
Central Vacuoles
found only in plants and provides internal support for the plant
E
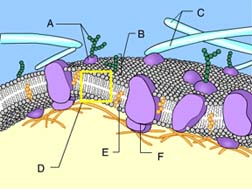
Which structure’s function is stabilization of the phospholipids
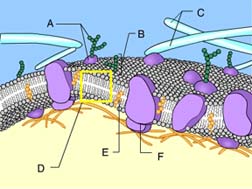
Phospholipid bilayer of membrane
D
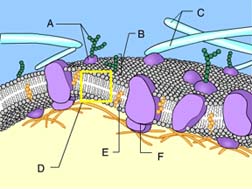
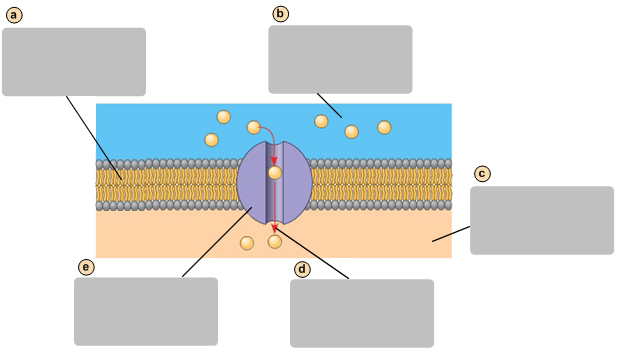
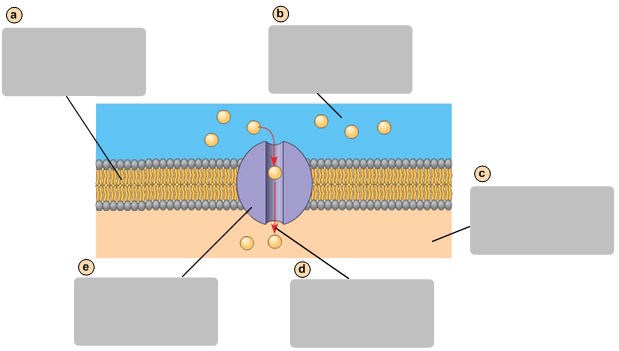
glycoprotein
A
Side with lower concentration square molecules
A
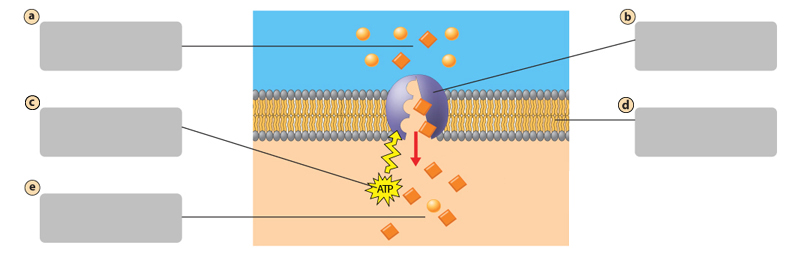
Transport protein
B
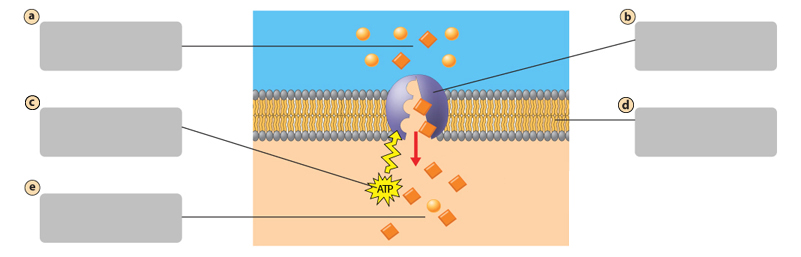
Energy input from the cell
C
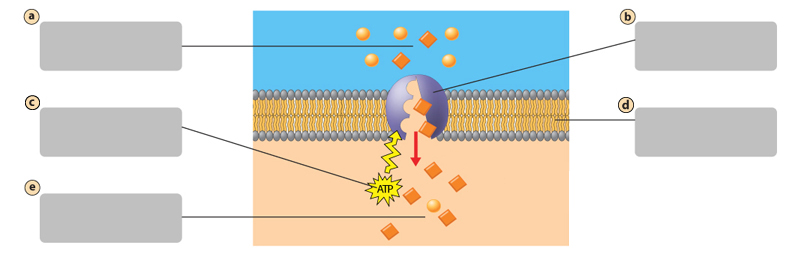
Plasma membrane
D
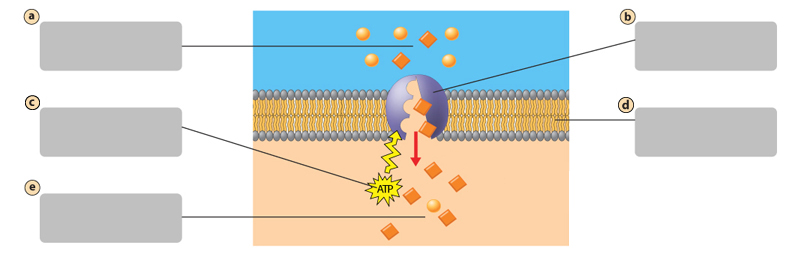
Side with higher concentration of square molecules
E
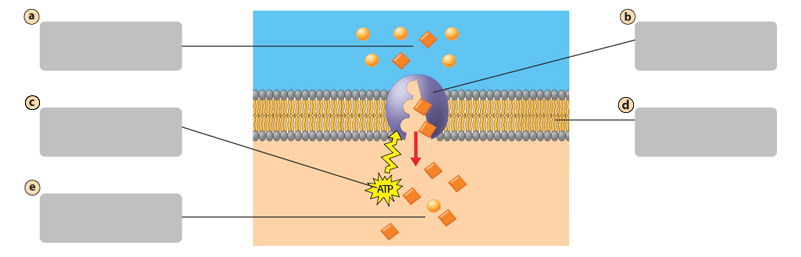
Side with higher concentration of molecules
A
Plasma membrane
B
Side with lower concentration of molecules
C
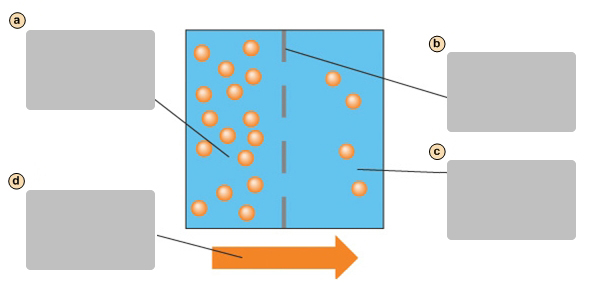
Diffusion causes a net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient
D
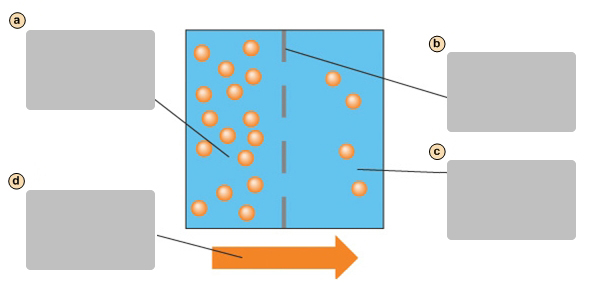
Plasma membrane
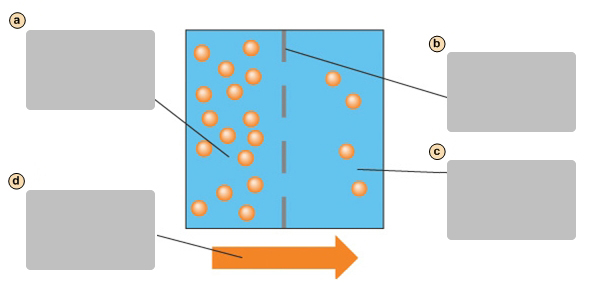
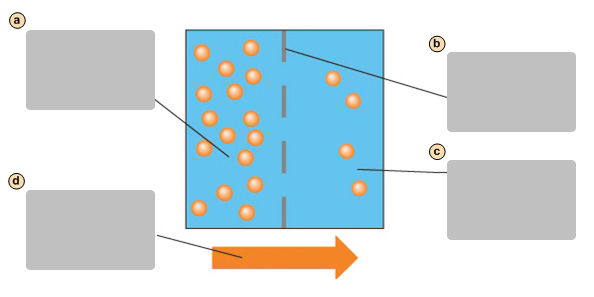
A
Side with higher concentration of molecules
B
Side with lower concentration of molecules
C
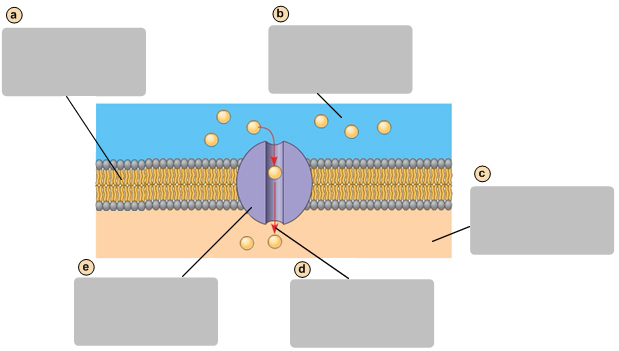
Facilitates diffusion causes a net movement of molecules down their concentraion gradient
D
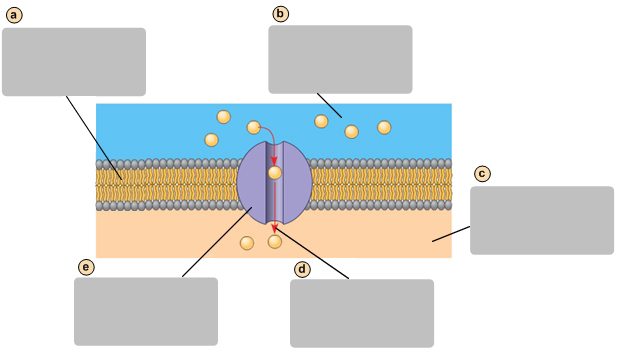
Transport protein
E
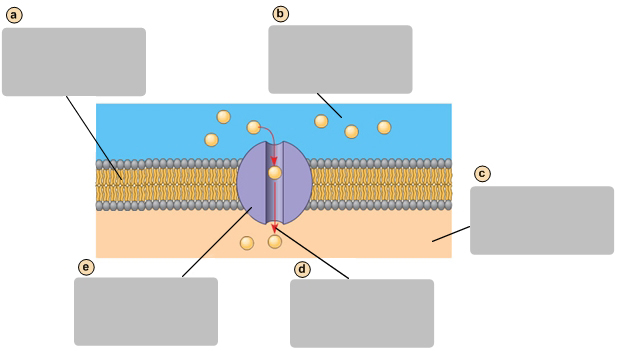
Exocytosis
A vesicle inside the cell fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents outside the cell
Facilitated Diffusion
A form of passive transport. Molecules move across the plasma membrane using a transport protein
Endocytosis
The plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell
Diffusion
A form of passive transport. Molecules move across the plasma membrane by crossing the lipid bilayer
Active Transport
Requires energy from the cell. Molecules move against their concentration gradient
active transport
molecules move across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradient.
endocytosis
The plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell.
Tight junction
Which of these cell junctions form a barrier to the passage of materials?
Desmosomes
The primary role of _____ is to bind animal cells together
Gap junctions
aid in the coordination of the activities of adjacent in animal cells
isotonic
A(n) _________ solution has the same concentration of dissolved particles as an adjacent solution.
Phagocytosis
________ is the movement of large materials into a cell by wrapping extensions of the plasma membrane around the material and engulfing it by fusing the extensions together.
transport proteins
Embedded within the phospholipid bilayer surrounding a cell are ________ _______, which regulate the movement of hydrophilic molecules from one side of the plasma membrane to the other.
hypotonic
A(n) _________ solution has a lower concentration of dissolved particles than an adjacent solution