Micro Exam 1 🍄
1/174
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
study of microorganisms 🤏
(too small to be seen w/o magnification)
Microbiology
List the 6 microorganisms & their respective fields
🌱 Algae (phycology)
🧫 Bacteria (bacteriology)
🍄 Fungi (mycology)
🪱 Helminths (helminthology)
🦠 Viruses (virology)
🧬 Protozoa (parasitology)
How long has bacteria existed
~3.5 billion years
Nucleus, & simple or complex
prokaryotes
eukaryotes
prokaryotes: pre-nuclei simple cells
eukaryotes: true nucleus complex cells
Compare prokaryotes & eukaryotes
what are they
unicellular or multicellular or both
lacks or has mem bound organelles?
prokaryote:
microorg,
only unicellular,
lacks nuclei & membrane-bound organelles
eukaryote:
microog,
uni & multicelullar,
has nucleus & membrane bound organelles
Microbes that do harm are _
Pathogens
Define photosynthesis
sunlight 🌞fueled conversion of CO2 to organic material
breakdown of matter & waste into simple compounds
Decomposition
food, drug, vaccines using living organisms
Biotechnology 💉
manipulating organism genes to make new product
Genetic Engineering
using living organisms to remediate environmental problem
Bioremediation
Biological Insecticides 2 functions
alternates to chemical pesticides
use microbes pathogenic to insects, but not humans
Name of natural crystal insecticide
(toxic to insects but not humans)
Bacillus thuringiensis ⚡️
Microorganisms are usually (3)
free,
harmless
beneficial
live in the body of other organisms (host) & damages them 👹
Parasites
What do you call Microbes normally present in human body
what do they prevent
what do they produce
Normal Microbiota
prevent pathogen growth
produce growth factors like folic acid & vit K
chemicals produced by bacteria & fungi to kill microbes
Antibiotics 💊
Robert Hooke’s accomplishment?
first to observe cells
first to observe living microbes/’animal cues’
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek
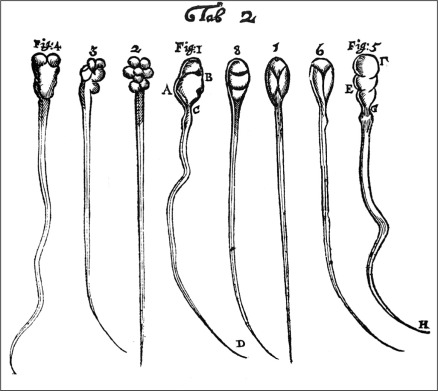
How does Louis Pasteur relate to these theories
Spontaneous Generation
& Theory of Biogenesis?
His experiment
Disproved Spontaneous Generation (life could arise from nonliving decomposed matter)
Proved Theory of Biogenesis (living things only arise from other living things)
🦢 flask (broth) heated (open=microbe growth, closed=no growth)
process of high heat (short time!)
to kill microbes that cause wine to go bad
Pasteurization (Pasteur)
Wine going bad
what it has & function
what bacteria does what
waste product
Alcohol (aka ethanol- makes yeast during fermentation)
Acetic acid bacteria eat alcohol for energy
Acetic acid is aka vinegar, as to why sour taste
Conversion of sugar🧁 to make alcohol🍻
Fermentation
Golden Age of Microbiology
~ when?
began w who?
what did they study during this time?
1857-1914
began with Pasteur
studied microbes, disease, immunity
1st to use chemical disinfectant to prevent
surgical wound infections 🩸🧼🧪🩹
Joseph Lister
Robert Koch:
what 2 diseases identified
Kochs’ __ & what it is
Anthrax (ulcers, proved caused by bacterium)
& Cholera 💩
Koch’s Postulates: criteria to establish relationship btwn microbe & disease🦠👩❤💋👨🤒
Alexander Fleming:
discovered
name & how?
when approved?
discovered 1st antibiotic🥇💊
he found Penicillin fungus killed his S. Aureus 🧫
1940s, Penicillin tested & mass produced
What did Edward Jenner do?
Injected his gardeners’ son with cowpox virus,
making him immune to smallpox 👨🏻🌾💉
Where does the word vaccination come from?
Vacca (cow!) 🐮
What does Phylogeny study?
Studies the evolutionary relatedness
btwn organism groups 🧍🏻♂️🦍
George Beadle & Edward Tatum
showed genes encode a cell’s enzymes 🦔 👩🏻💻🧬🪲
Paul Ehrlich responsible for?
used arsenic drug called salvarsan (rat poison☠🐀)
to treat syphilis (sexually transmitted)
Oswald Avery, Colin Macleod, Maclyn McCarty
showed DNA was hereditary 🧬🧑🧑🧒🧒
Jacques Monod & Francois Jacob
discovered role of mRNA💌 in protein synthesis💌
Beutler, Hoffman & Steinman
dendrites (immune cells recognize pathogens) 🧠
Von Behring nobel
Diphtheria Antitoxin 👄
Ross nobel
Malaria Transmission 🦟🩸
Koch nobel
TB bacterium🫁😷
Chain, Florey, Fleming nobel
Penicillin ⛓💥💊
Waksman nobel
Streptomycin🚶🏻♂️
Prusiner nobel
Prions (misfolded protein cause neurodegeneration)
Marshall & Warren nobel
H. Pylori (stomach gastritis) & its Ulcers 🍔
Rebecca Lancefield 👵🏻
proposed immunology could identify bacteria 💉!!
How worked together:
John Tyndall
Ferdinand Cohn
Tyndall: saw some microbes were heat-resistant 🥵🔥
Cohn: identified them as endospores (bacteria resist structure💪)
What is Taxonomy?
the organization, classification (into groups), & naming of living things
Order the 8 Levels of Classification
Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
*king philip came over for good soup
What are the 3 domains of life?
Archaea,
Bacteria (true),
& Eukarya
What are archaea?
odd bacteria that live in extreme
environments high salt, heat, etc 🔥🦠🌋🧂
Binomial (2) Nomenclature for microbes & example :)
Genus: Capitalized
Species: lowercase
*both italicized*
(i.e. Staphylococcus aureus)
Eukaryotes
when appeared
came from _ through which process?
2B yrs ago
came from prokaryotes thru symbiosis
Name Function of Ribosomes?
Sedimentation rate?
Protein Synthesis (make protein thru mRNA and tRNA)
50s+30s ≠ 70s
What are endospores?
Resting😴cells resistant to drying, heat, & chemicals
Cells that forms endospores & 2 examples?
Nucleoids!:
Bacillus
Clostridium 🚪
Sporulation
Process/formation of endospores by nucleoids
Germination
When dormant endospores return to vegetative, active state 🌷
3 Inclusions of energy reserves
Polysaccharide Granules
Sulfur Granules
Lipid Inclusions
Phosphate reserve inclusion?
Metachromatic Granules (volutin)
What does the Carboxysome inclusion store & its function?
1.5-diphosphate carboxylase
fixation of CO2 🐮
Gas Vacuole Inclusion has:
Protein-covered cylinders
What does the inclusion of Magnetosomes store & its function ?
Iron oxide
(destroys H2O2)
Macroscopic vs Microscopic Fungi examples
micro: mold, yeast
macro: mushroom, puffballs, gili
What are the 2 morphologies of fungi?
If both _
Yeast & Hyphae
Dimorphic
Describe yeast:
appearance
reproduction
round & ovoid
asexual reproduction/budding
What are hyphae
long filamentous fungi

What are Mycelium?
what does it give fungi?
A mass of hyphae
gives fungi a cottony, hairy, or velvety texture.

What are the two types of hyphae
& what they do?
Vegetative hyphae: digest/absorb nutrients🍔
Reproductive hyphae: make spores for reproduction.
What structure divides hyphae?
cell walls called septate
Nutrition of Fungi AND Protozoa?
Heterotrophic (feed off other microbes/organic matter)🧛🏻♀️
What are saprobes/saprophytes?
Fungi that live off dead plants or animals 🐸
What are parasitic fungi?
Fungi that live off living organisms.
What is mycosis?
A fungal infection
How do most Fungi primarily reproduce?
Through ___ on ___
Through Asexual Spore Formation on reproductive hyphae.
Sexual Reproduction:
how/what occurs?
result
3 examples
2 diff strains fuse (💭parents fusing)
Genetically diff spores formed;
Ascospores, Basidiospores & Zygospores
Describe product of asexual reproduction in fungi.
Thru what process
2 examples
Genetically identical spores formed
Budding or Mitosis
conidia & sporangiospores 🧽
4 characteristics of Fungi
eukaryotic
mostly unicellular
colonial
heterotrophic
3 Negative effects of fungi
allergies & mycosis
destruction of crops & food
produce toxins
3 Positive effects of fungi
decompose dead material
use in genetics & food production
produce antibiotics, alcohol, acids, vitamins! 💊
4 General characteristics of Algae
eukaryotic
mostly unicellular
colonial
autotrophic: chlorophyll photosynthetic 🧌
Micro vs Macro characteristics of Algae
Micro: unicellular, colonial, filamentous
Macro: multicellular, colonial
What are the two major functions of Algae?
serve as base of aquatic food webs
produce large amounts of O2
What are dinoflagellates? What do they release?
Algae that can cause red tides;
Release toxins affecting nervous systems.
4 Characteristics of Protozoa
eukaryotic
unicellular
lack cell wall ❌so they come in many shapes :>
heterotrophic
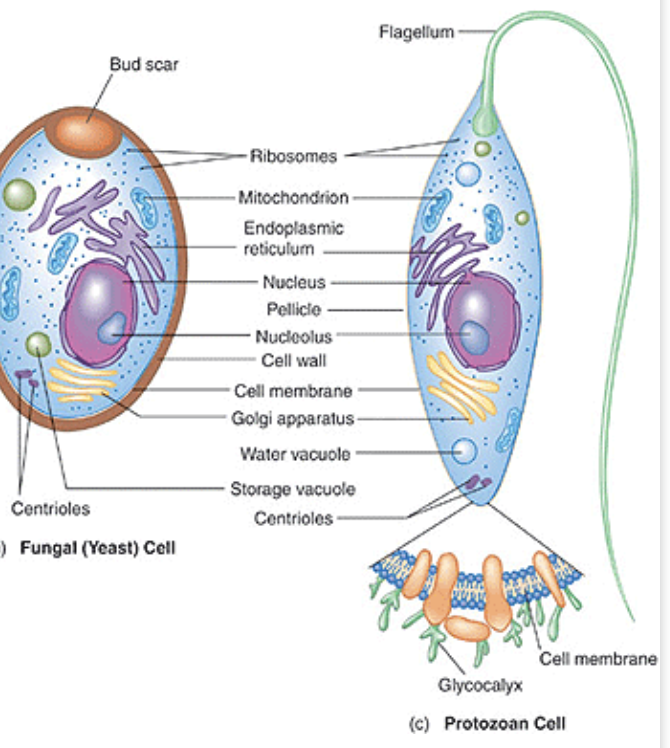
What are the two cytoplasmic layers of protozoa?
Ectoplasm (outer) &
Endoplasm (inner)
What are Trypanosoma Flagellates?
Pathogenic Protozoans!
2 Examples of Trypanosoma Flagellates? 🤗
(name → disease → place)
Trypanosoma brucei → Sleeping sickness → (Africa)
Trypanosoma cruzi → Chagas disease → (South America).
Name the protozoa amoeba that causes amebic dysentery (gastric infection)
Entamoeba histolytica 📜
What are helminths? What kingdom do they belong to?
Multicellular parasites of tissues and organs 🪱
Animalia
Most helminths have well developed __, that go thru _
🪱🥚sex organs to produce gametes (eggs & sperm)
these eggs go thru larval period in/out host
2 examples of flatworms
cestodes (i.e. tapeworm)
trematodes (have sucking mouthparts)
4 characteristics of flatworms?
shape
dig tract?
protection or no?
excretory & nervous sys?
flat
pouch dig tract
no body cavity
simple excretory & nervous sys
Characteristics of roundworms?
shape
dig tract?
protection or no?
excretory & nervous sys?
round
complete dig tract
protective surface cuticle
poorly developed excretory & nervous sys
Special characteristic in roundworms
Have spines & hooks on mouth (㇏(•̀ᵥᵥ•́)ノ)🧛🏻♀️
Most abundant microbes
what microscope needed to observe them
Viruses
Electron Microscope
Define Virus
what they’re made up of
Acellular parasites
Made of nucleic acid & protein
What is the term that defines viruses as only surviving in host’s cells
Obligated Intracellular Parasites
Damage to cells from Viruses
Cytopathic Effects
2 Examples of a complex virus?
Poxvirus
Bacteriophage
*peanut butter is complex 🥜
2 examples of enveloped viruses & their respective capsid
Mumps Virus (Helical Nucleocapsid)
HIV/AIDS (Icosahedral Nucleocapsid)
2 examples of non enveloped viruses & their respective capsid
Plum Poxvirus (Helical Nucleocapsid)
Poliovirus (Icosahedral Nucleocapsid)
What 2 things make up a nucleocapsid?
A nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
+ A Capsid