BIOL 1031 - Lab Practical Exam #1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
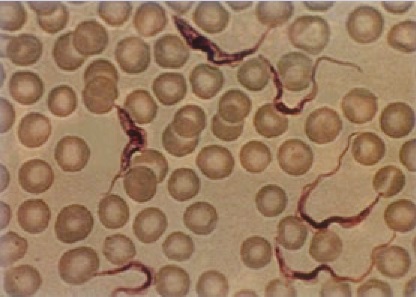
The organism pictured belongs to phylum:
Euglenozoa
Apicomplexa
Foraminifera
Radiolaria
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Organism: Trypanosoma

The red dot pictured at the top of this organism (Euglena) is called a/an:
Eyespot
Flagellum
Cilium
Clitellum
Eyespot
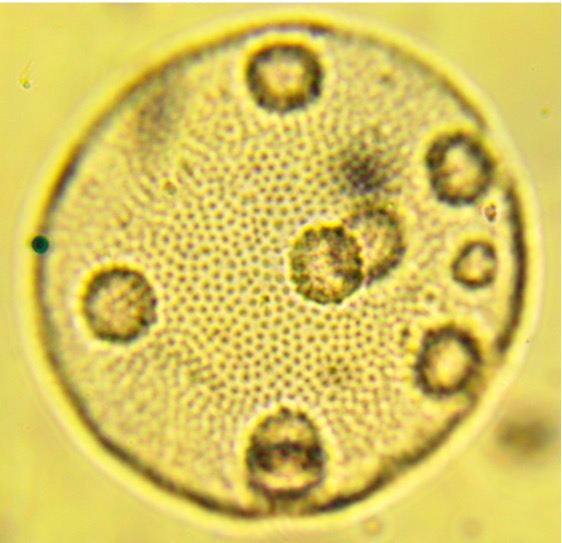
This organism (phylum Foraminifera) produces a _______ test.
Calcerous
Siliceous
Glass
Chloroplast
Calcerous
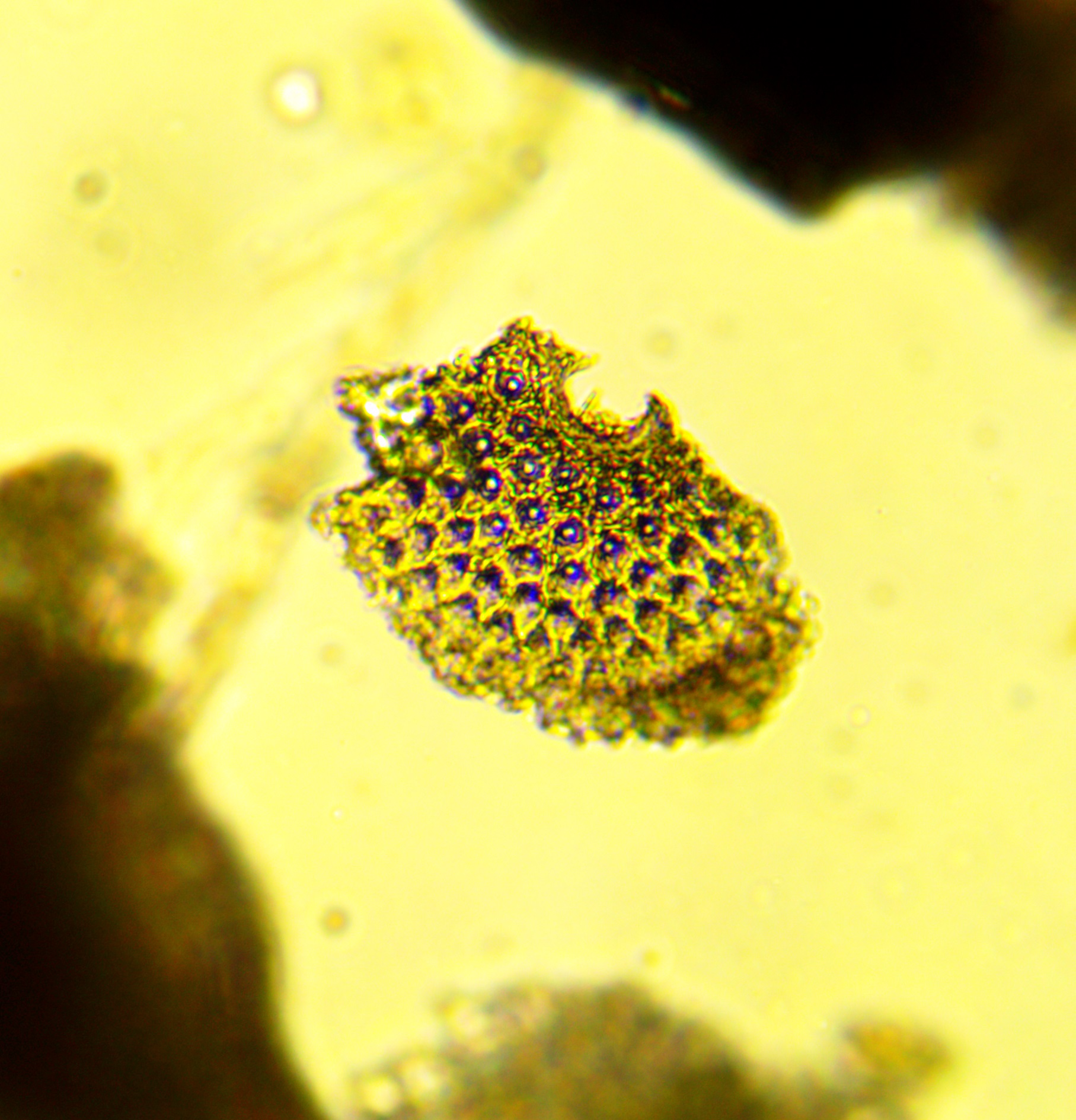
What species is this?
Volvox
Oedogonium
Chlamydomonas
Plasmodium
Volvox
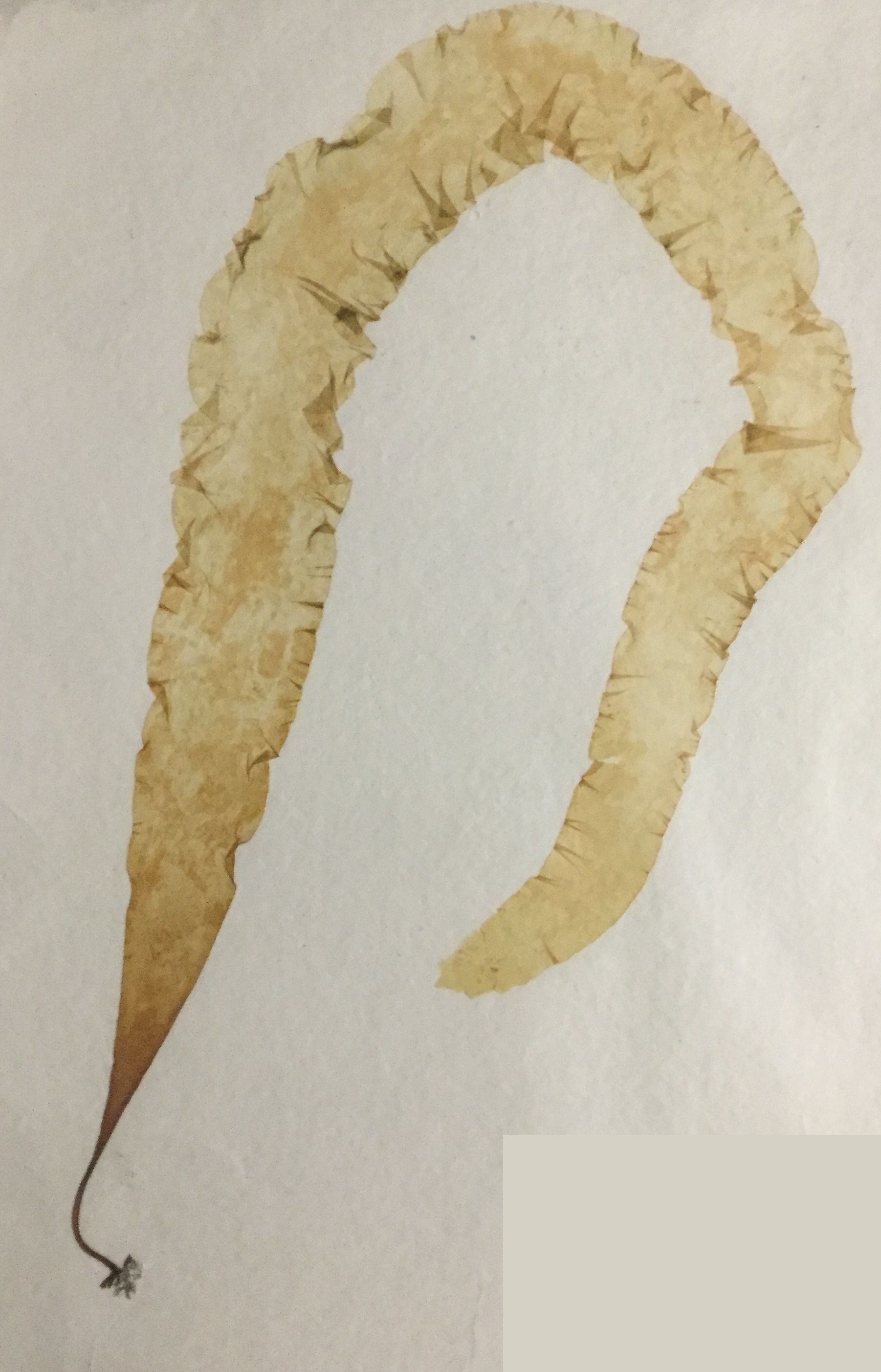
This organism belongs to the phylum:
Phaeophyta
Rhodophyta
Chlorophyta
MyxogastridaWha
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Phaeophyta
Organism: Brown algae
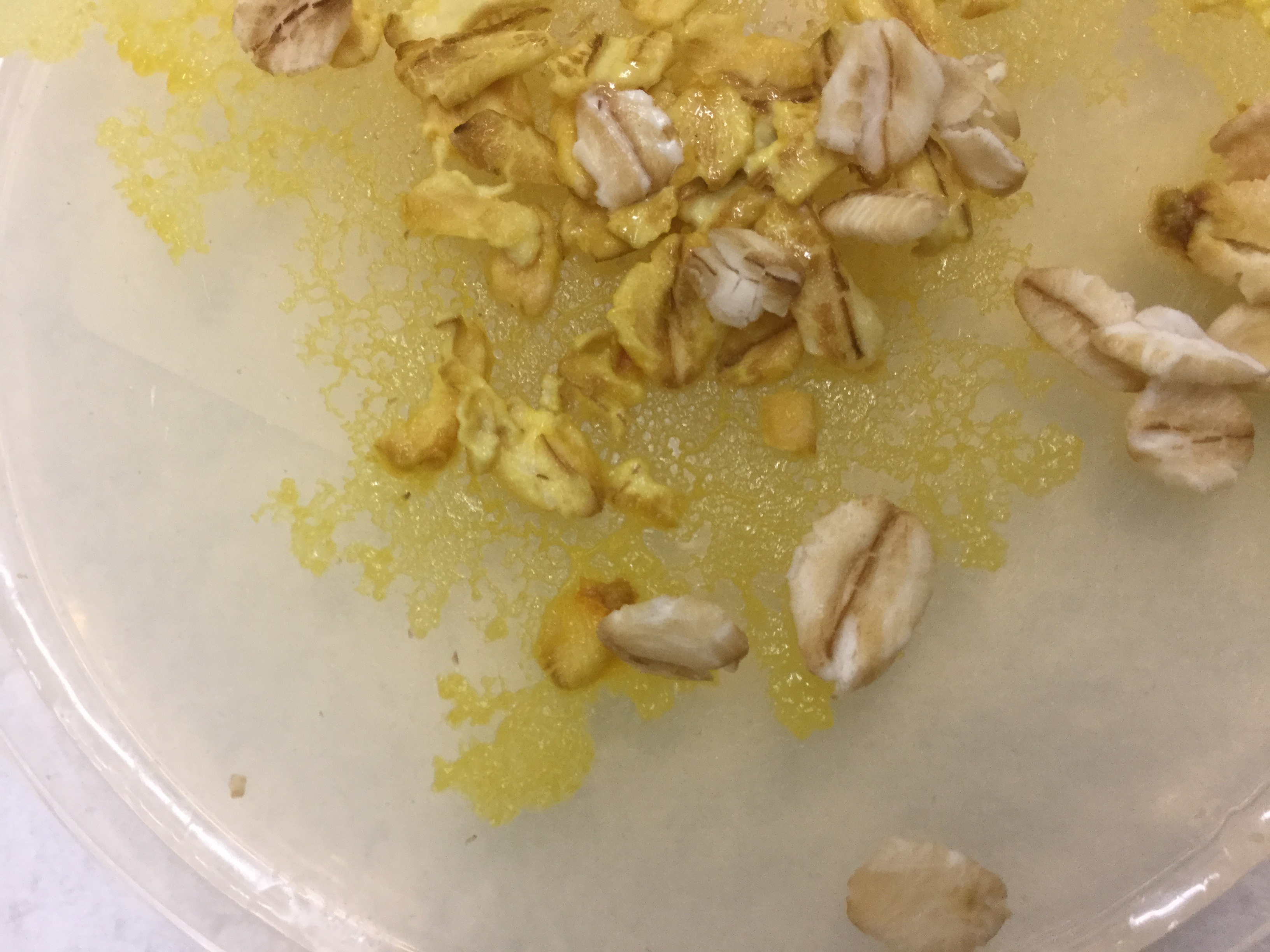

This organism falls within phylum:
Myxogastrida
Ciliophora
Euglenozoa
Rhodophyta
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Myxogastrida
Organism: Slime
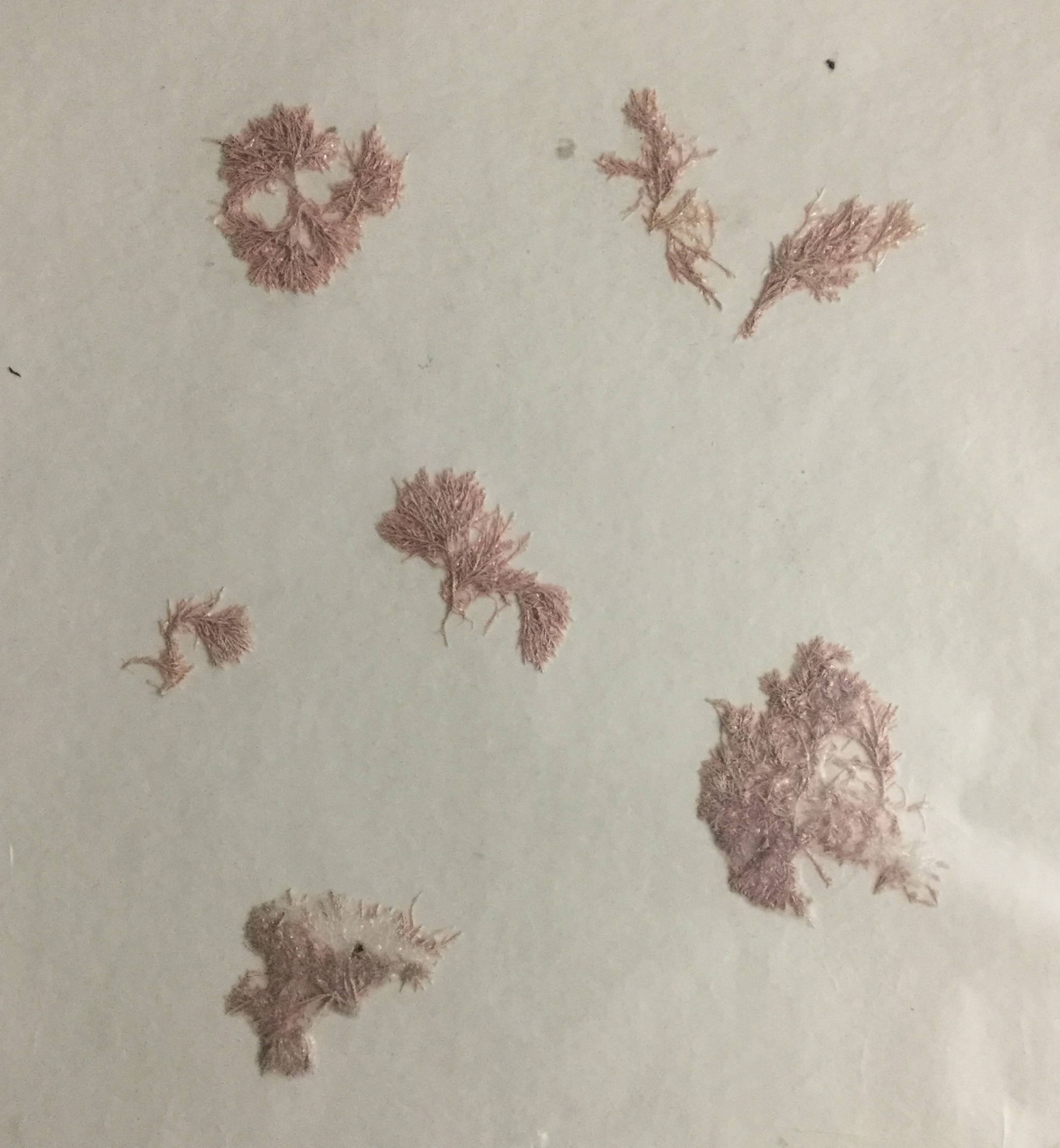

This organism belongs to the phylum:
Rhodophyta
Phaeophyta
Chlorophyta
Ascomycota
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Rhodophyta
Organism: Red algae
In the gametic meiosis life cycle, in what type of cell does mitosis occur? (Remember that a 1N cell has one set of chromosomes per nucleus, and a 2N cell has two sets of chromosomes per nucleus).
2n (diploid) cells only
1n (haploid) cells only
Both 1 n (haploid) and 2n (diploid) cells only
Mitosis does not occur in this life cycle
2n (diploid) cells only
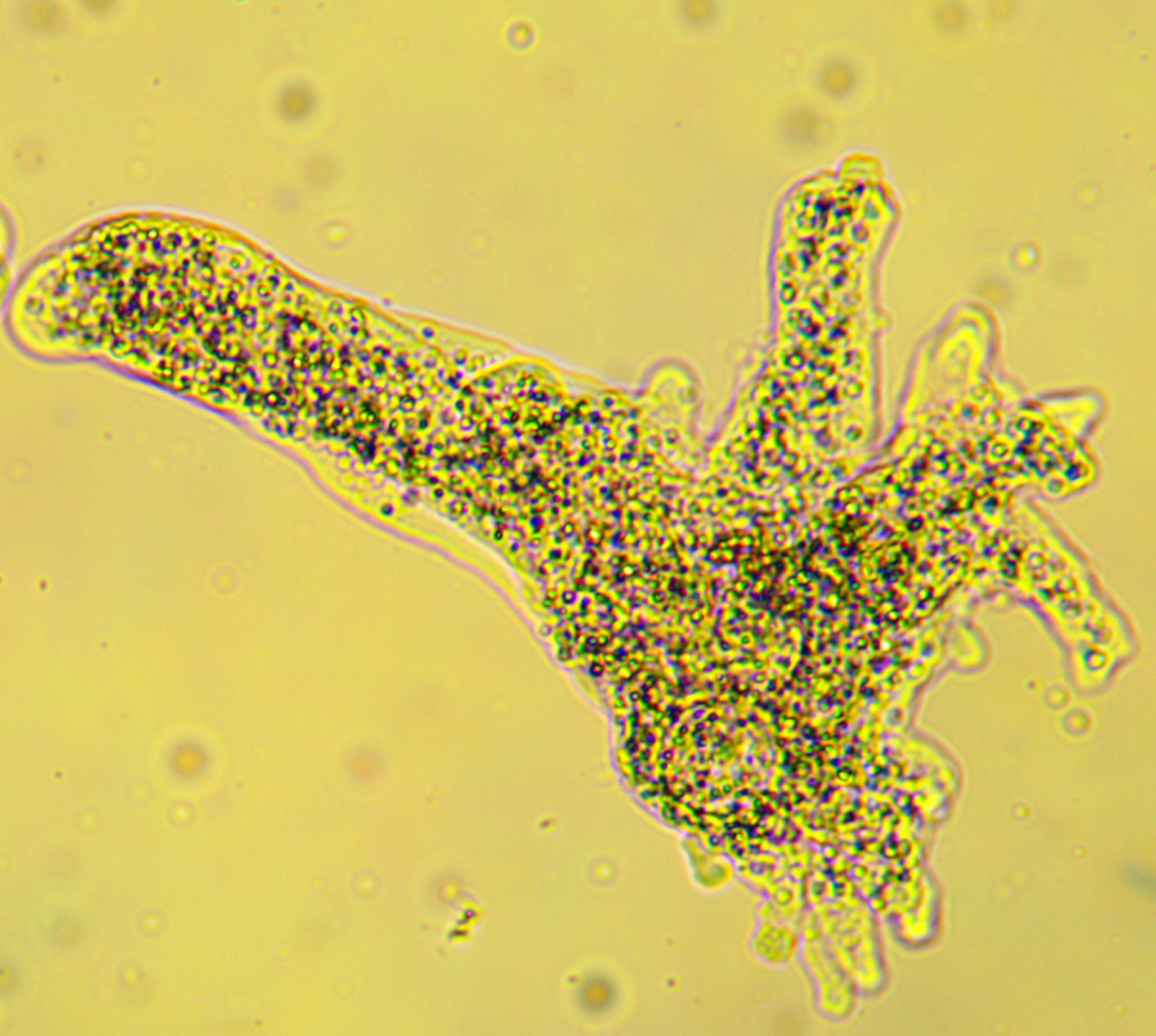
This organism belongs to the phylum ___________ and possesses pseudopodia.
Gymnamoeba
Euglenozoa
Radiolaria
Ciliphora
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Gymnamoeba
Organism: Amoeba

This organism falls within phylum:
Apicomplexa
Euglenozoa
Radiolaria
Chlorophyta
And what is the organism?
Phylum: Apicomplexa
Organism: Plasmodium vivax
Living organism can be either classified as __________ or __________.
1) Prokaryotic
Archaea
Bacteria
2) Eukaryotic
Eukarya
Protista
Plantae
Fungi
What is the classification of living organisms? (Mnemonic: “Dear King Philip Came Over For Great Soup”)
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
What are the 3 life cycles seen in eukaryotes?
Zygotic meiosis
Gametic meiosis
Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations)
What is the phylum Foraminifera?
Marine; secrete a calcerous shell (“test”) that often forms spiral patterns.
What is the phylum Radiolaria?
Marine; secrete siliceous (glass-like) tests that are often fragile and only seen as fragments.
What is the phylum Euglenozoa?
Trypanosomes live in the blood of vertebrates; causes African sleeping sickness; carried by the Tsetse fly.
What is the phylum Apicomplexa?
Plasmodium is a parasite living in blood of mammals and birds that causes malaria; carried by Anopheles mosquitoes.
What is the phylum Chlorophyta?
Largest phylum of algae; often “look” like plants because some possess a thallus (a vegetative body but no true roots, stems, or leaves).
What is Chlamydomonas and what phylum is it in?
2 anterior flagella; cup-shaped chloroplast; pigmented eyespot
Phylum Chlorophyta
What is Volvox and Gonium and what phylum are they in?
Motile, colonial; Gonium are flattened and held together by gelatinous material; Volvox are large spheres; usually within the sphere are several daughter colonies.
Phylum Chlorophyta
What is Hydrodictyon and what phylum is it in?
Non-motile; colonial; branched; multinucleate cells separated by cross walls.
Phylum Chlorophyta
What is Oedogonium and what phylum is it in?
Non-motile and colonial; filamentous and unbranched filaments.
Phylum Chlorophyta
What is Ulva and what phylum is it in?
Multicellular; relatively large; mature body is a flattened, tissue-like sheet; “sea lettuce”.
Phylum Chloropyhta
Cotyledons, radicles, and hypocotyls can all be found in:
Seeds
Spores
Flagella
Cilia
Seeds
Which of the following is a reason for the evolution of vascular plants we see today?
Relocation from water to land.
Relocation from land to water.
Decreased vascular plant genes.
Increased vascular plant diseases.
Relocation from water to land.
In sporic meiosis, plants alternate between a __________ (haploid) generation and a _________ (diploid) generation.
Gametophyte; sporophyte
Sporophyte; gametophyte
Microglia; macroglia
Thallus; Procambium
Gametophyte; sporophyte
True or false
Plantae is a phylum.
False
True or false
Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts are all vascular plants.
False
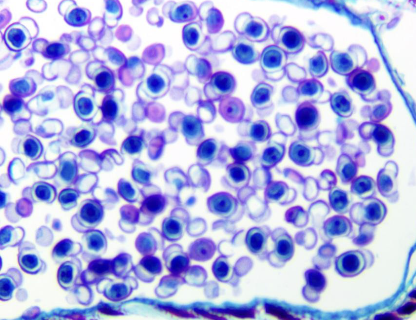
This is a cross-section of a pollen cone. what are the circular structures called?
Pollen grains
Sori
Megasporangia
Gemma Cups
Pollen grains
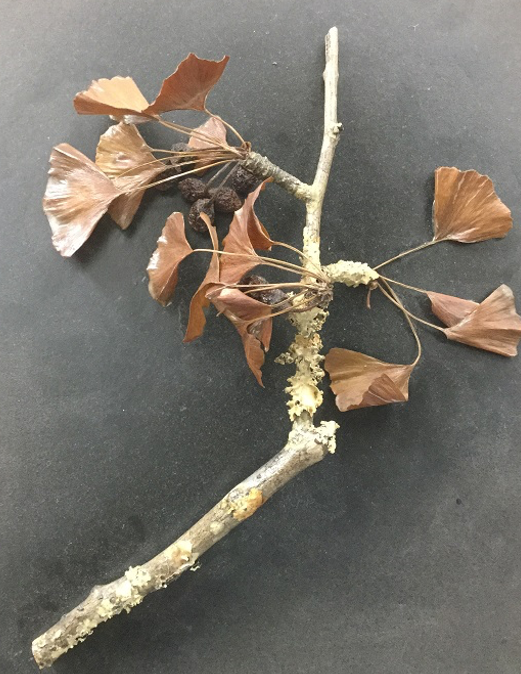

This organism is:
Ginkgo biloba
Ephedra
Equisetum
Oedogonium
Ginkgo biloba
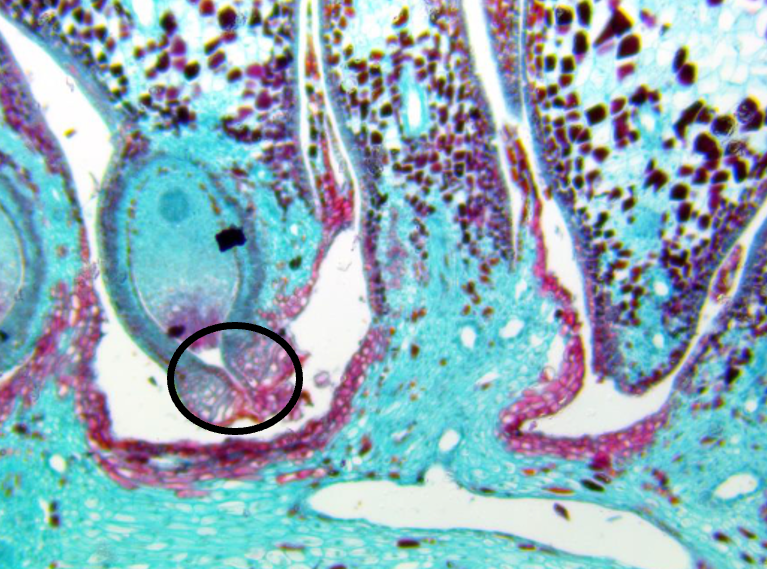
the opening indicated in the ovulate cone cross-section is the:
Micropyle
Pollen tube
Hypocotyl
Integument
Micropyle

Everything EXCEPT the horn-like structures in this organism represents the ________ generation.
Gametophyte (n, haploid)
Gametophyte (2n, diploid)
Sporophyte (2n, diploid)
Sporophyte (n, haploid)
Gametophyte (n, haploid)
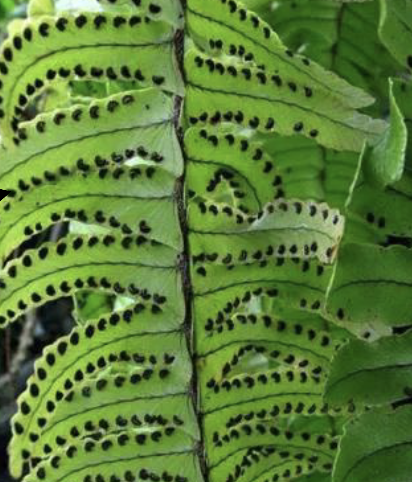

This organism belongs to phylum:
Pterophyta
Anthocerophyta
Psilophyta
Bryophyta
Pterophyta
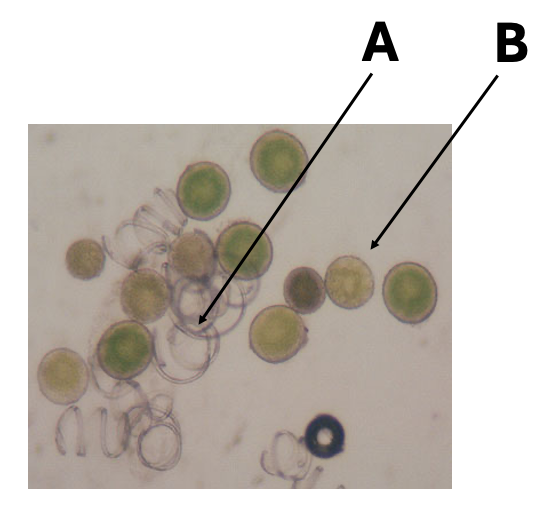
Elaters are indicated by the latter:
A
B
A
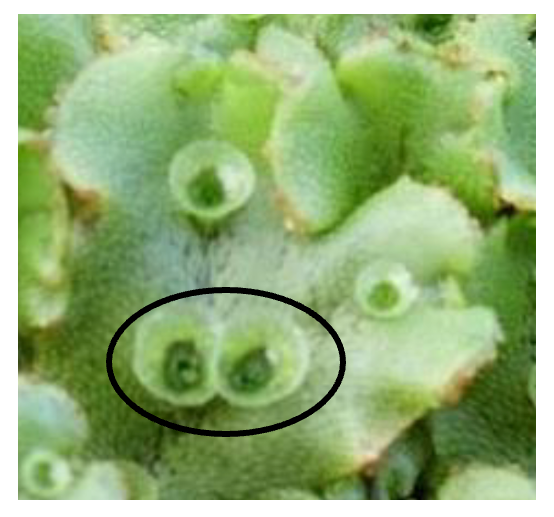

The circled structures are called:
Gemma ccups
Micropyles
Megasporangia
Microsporangia
Gemma cups
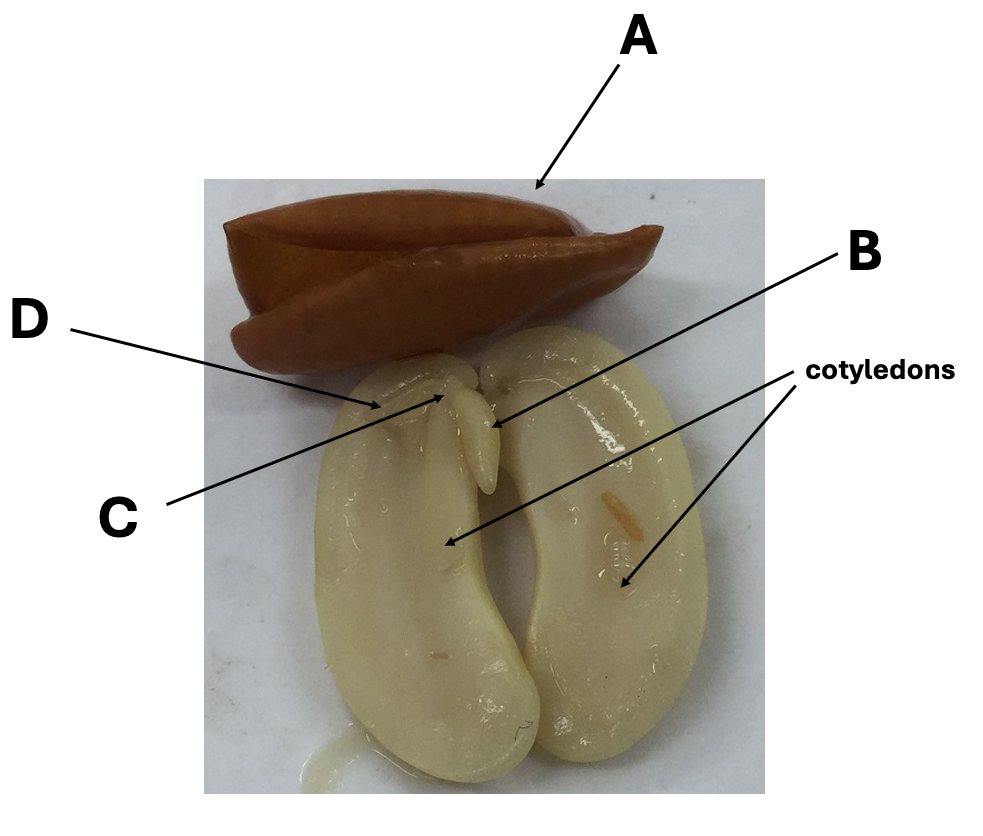
Structure ____ is the hypocotyl
A
B
C
D
C
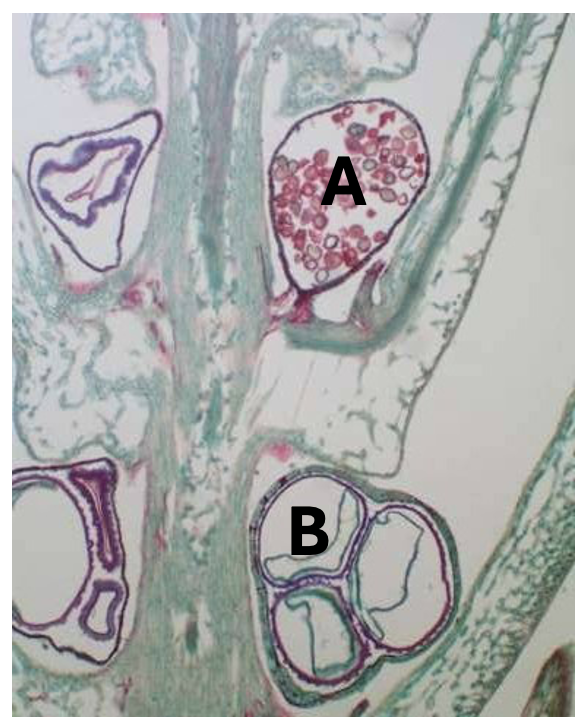
In Selaginella, structure “A” is the:
Microsporangium
Megasporangium
Micropyle
Macropyle
Microsporangium
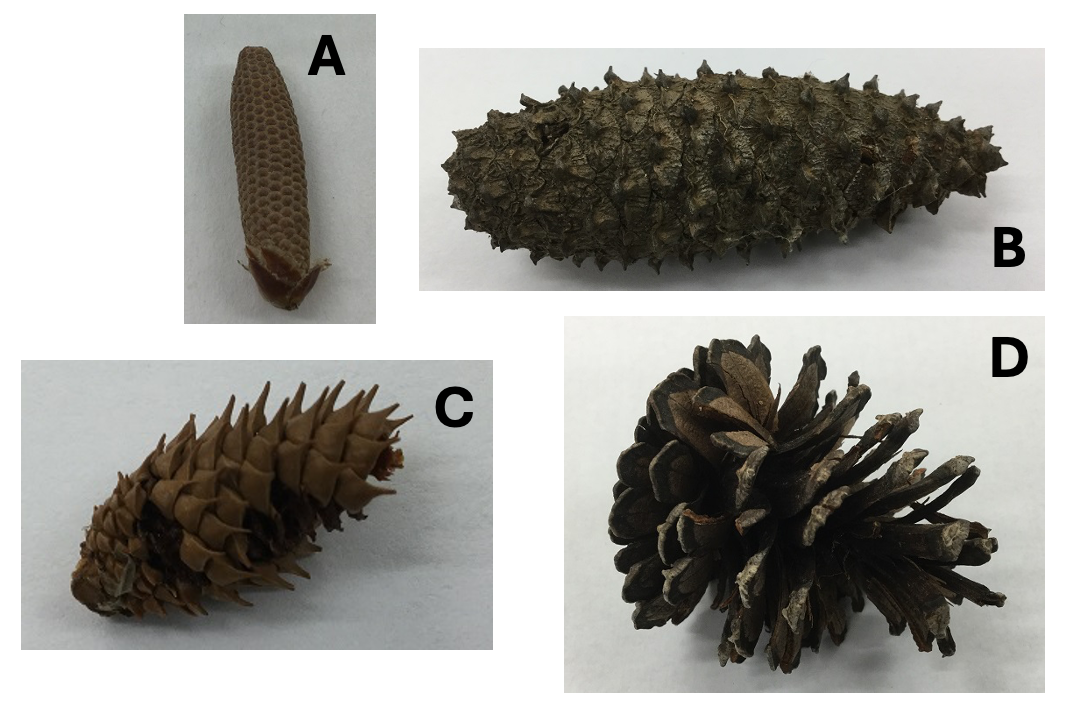

Structure ____ is an ovulate cone in its first year and can receive pollen:
C
A
B
D
C
What ix xylem and phloem?
Vascular tissues in seedless vascular plants.
Xylem: For water and mineral transport; flow occurs only up from roots, rest of plant (the “shoot”).
Phloem: For photosynthate and other nutrient transport; flow is in whatever direction is needed (up or down).
What is homospory and heterospory?
Homospory: sporophytes (structures that produce spores) only produce one kind of spore.
Heterospory: sporophytes produce two different kinds of spores called microspores and megaspores.
For flowering plants, the primary role of fruits is to:
Feed animals
Disperse and protect seeds
Feed young plant seedlings
Feed developing plant embryo tissue.
Disperse and protect seeds.
Flowering plants all fall within Phylum:
Coniferophyta
Gnetophyta
Florophyta
Anthophyta
Anthophyta
The typical life cycle of a plant is best described by:
Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations)
Zygotic meiosis
Gametic meiosis
Mitosis only
Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations)
The word “angiosperm” quite literally means:
“Contained seed” or “vessel seed”
“Naked seed”
“Same seed”
“Different seeds”
“Contained seed” or “vessel seed”
True or false
In a typical flowering plant, the endosperm is triploid (3n).
True
True or false
The stamen is the female portion of a flower.
False
The ovary wall is also known as the:
Pericarp
Cotyledon
Endosperm
Fruit
Pericarp
There are 3 groups of fruits. ________ fruits derive from separate carpels on one flower.
Simple
Aggregate
Accessory
Multiple
Aggregate
True or false
An incomplete flower has one or more whorls absent.
True

Which of the following categories most completely describes a magnolia fruit?
Multiple, fleshy
Aggregate, dry
Simple, dry
Simple, fleshy, accessory
Aggregate, dry
Monocots have _________ seed leaf(ves).
One
Two
Three
Four
One

The flower pictures here exhibits _______ symmetry.
Radial
Bilateral
Radial

Which of the following fruit categories most completely describes a pineapple?
Multiple, fleshy
Simple, fleshy, accessory
Aggregate, dry, accessory
Simple, fleshy
Multiple, fleshy
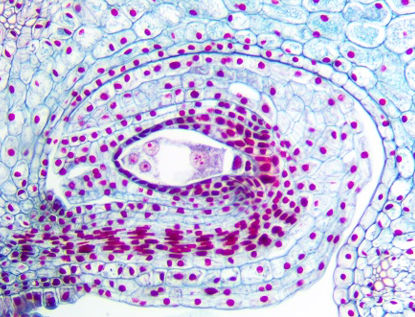
The structure pictured here is a/an:
Embryo sac
Cotyledon
Pollen grain
Aggregate fruit
Embryo sac
True or false
Fusing between whorls is connation.
False
If you were to describe the general life cycle of a plant, you would say:
Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations)
Gametic meiosis
Zygotic meiosis
Mitosis only
Sporic meiosis (alternation of generations)
What are the 2 groups of angiosperms?
Monocots: 1 cotyledon (seed leaf); flower parts typically multiples of 3; leaves with parallel venation of vascular tissue.
Eudicots (previously “dicots”): 2 cotyledons; flowers parts typically in multiples of 4 or 5; leaves with netlike or branched venation of vascular tissue.
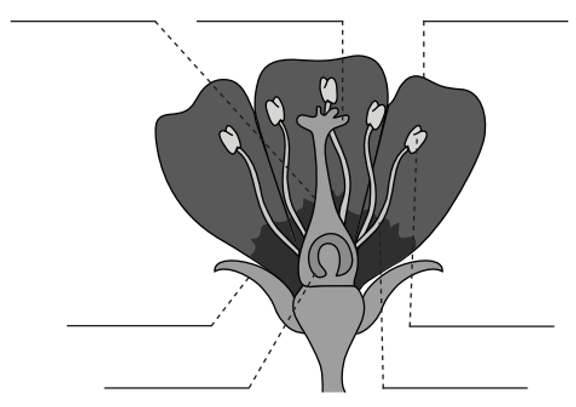
Label the parts of the flower from left to right.
Pistil ← Carpels more or equal to 1, part of Carpel (female)
Stigma ← part of Carpel (female)
Petal ← neither male or female
Sepal ← part of Carpel (female)
Ovary ← part of Carpel (female)
Anther ← part of Stamen (male)
Filament ← part of Stamen (male)
What are the 4 different whorls of a flower?
Calyx → sepals (calyx means “cover”)
Corolla → petals (“corolla car has pedals”)
Androecium → stamens (Andro [like androgen] = male)
Gynoecium → carpels (Gyn [like gynecologist] = female)
What does it mean for a flower to be complete or incomplete?
Complete = flower has all 4 whorls
Incomplete = at least one whorl is absent
What does it mean for a flower to be perfect or imperfect?
Perfect = flower has both androecium (stamen) and gynoecium (pistil)
Imperfect = flower is missing either androecium (stamen) or gynoecium (pistil)
What is connation and adnation?
Connation = fusing WITHIN a whorl.
Adnation = fusing BETWEEN whorls.
What is radial and bilateral symmetry and asymmetry?
Radial = flower can be sliced like a pie and each slice looks the same.
Bilateral = can only splice a flower in half to make them look the same.
Asymmetry = is not symmetrical in the first place, so cannot slice the flower in a way to make it symmetrical.
What are the 3 different parts of the pericarp (ovary wall where fruit are formed from)?
Exocarp = outer wall
Mesocarp = in the middle
Endocarp = inner wall; next to seed
What is an accessory fruit?
A fruit that contains tissue from parts of the flower other than the ovary.
Ex. apple, strawberry, cucumber
What are the 3 different groups of fruits?
Simple = derived from one pistil
Ex. acorn, maple, tomato, orange, lemon, apple, cucumber
Aggregate = from separate carpels on one flower
Ex. magnolia, strawberry
Multiple = from multiple flowers
Ex. pineapple
What are the 2 characteristics of pericarp?
Fleshy = pericarp is fleshy/soft
Ex. berries, eggplants, pineapple, tomato, orange, lemon, apple, cucumber
Dry = pericarp is not fleshy
Ex. nuts, magnolia, strawberry, acorn, maple
Xylem and phloem are best described as:
Vascular tissue
Organelles
Plasma cell membrane components
Animal tissue
Vascular tissue
When the terminal bud of a plant prevents the development of axillary buds, this is called:
Apical dominance
Axillary dominance
Cptyledon impairment
Phloem phylogeny
Apical dominance
The primary water conducting tissue that you would see in a stem cross-section is the:
Xylem
Phloem
Collenchyma
Cambium
Xylem
The “seed leaves” that are leaves that are part of a dormant embryo in a seed are called:
Apical meristems
Radicles
Receptacles
Cotyledons
Cotyledons
The growing tips of stems and roots are called:
Cotyledons
Apical meristems
Receptacles
Petioles
Apical meristems
What was the effect of auxin on axillary bud growth in Phaseolus?
Auxin inhibited the growth of axillary buds.
Auxin promoted the growth of axillary buds.
Auxin made half of the plant tissue fall off.
Auxin made xylem and phloem transport different photosynthates.
Auxin inhibited the growth of axillary buds.
True or false
When auxin was applied to Coleus, the petioles experienced abscission.
False
In general, pruned plants grow more ________, whereas unpruned plants grow more __________.
Yellow; green
Green; yellow
Vertically; laterally
Laterally; vertically
Laterally; vertically
A/an _______ is the stalk-like part of a leaf.
Axillary bud
Petiole
Apical bud
Cotyledon
Petiole
What is auxin?
A plant hormone
A structural part of a plant
A cell type found in xylem
A cell type found in phloem
A plant hormone
What does leaf abscission means?
When leaves produce sori
When leaves stop growing their xylem and phloem
When leaves fall/drop from trees or other plants
When leaves grow too big for the plant to support
When leaves fall/drop from trees or other plants
Which of the following terms is NOT associated with fungi?
Heterotrophic
Autotrophic
Zygotic meiosis
Mycelium
Autotrophic
The sac fungi are characterized by having the products of meiosis formed in a sac-like structure called the:
Ascus
Annulus
Septum
Basidium
Ascus
The sexual life cycle of all fungi known to have sexual reproduction is _______ meiosis.
Zygotic
Sporic
Gametic
Alternation of generation
Zygotic
The term _________ refers to when plants grow long and pale due to growing in the darkness.
Etiolation
Gigantism
Apical dominance
Karyogamy
Etiolation
A lichen is a symbiotic partnership of at least 2 different organisms. One of them is a fungal component called the:
Mycobiont
Photobiont
Lichobiont
Symbiont
Mycobiont
________ plants applied with gibberellic acid (GA3) appear like their normal, _________ counterparts.
Dwarf; non-dwarf
Non-dwarf; dwarf
Gymnosperm; angiosperm
Angiosperm; gymnosperm
Dwarf; non-dwarf
How are dwarf plants and gibberellins related?
Dwarf plants are mutated to the point where they can’t make their own gibberellins
Dwarf plants are mutated to the point where they make too many gibberellins
Dwarf plants are mutated to the point where they make gibberellins instead of auxin
Dwarf plants are mutated, but they can still produce comparable amounts of gibberellins compared to normal plants
Dwarf plants are mutated to the point where they can’t make their own gibberellins
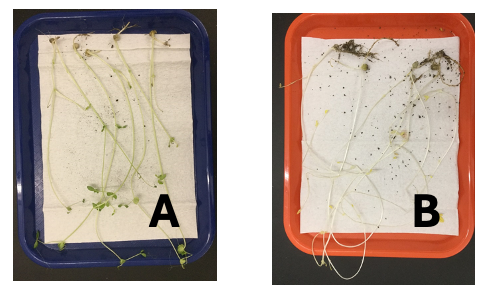
Simply by looking at the coloration of these 2 speciments, which one do you predict was grown in the light?
A
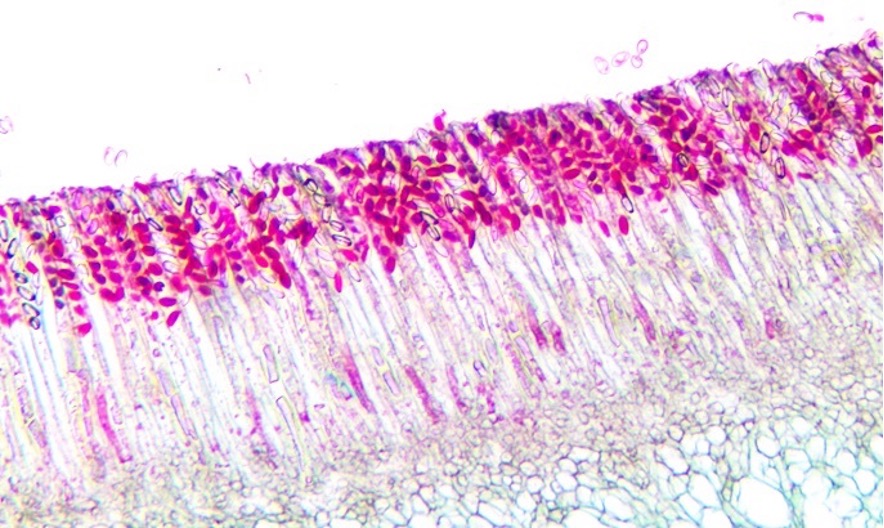
The dark pink structures located toward the top of this Peziza ascus are called:
Ascospores
Basidiospores
Conidiospores
Sporangia
Ascospores
You’re reading about a phylum that ends in -mycota. You can confidently predict that it is a/an:
Fungus
Plant
Animal
Protist
Fungus
Fungi primarily rely on _______ for reproduction.
Spores
Pollen
Roots
Lichens
Spores
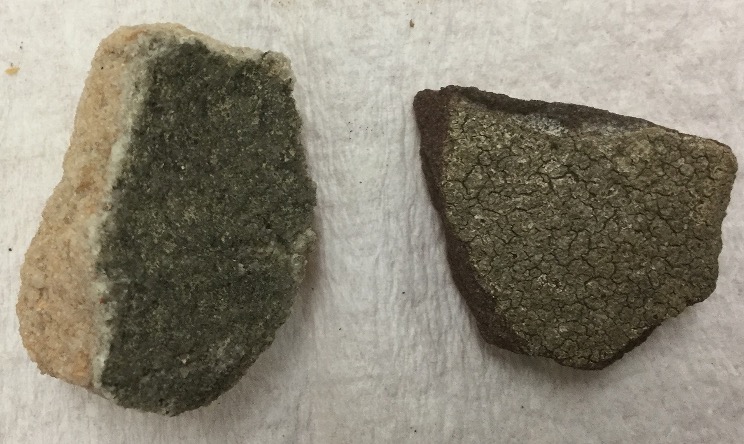

This is a ________ lichen.
Crustose
Foliose
Fruticose
Sucralose
Crustose
Which of the following is NOT an effect of plants grown in the dark?
Longer internodes
Shorter internodes
Limited leaf expansion
Pale coloration
Shorter internodes
Gibberellins can:
Increase shoot growth
Promote cell division
Promote cell elongation
All of these
All of these
What are dwarf mutants?
Don’t respond to auxins or cytokinins (plant hormones that promote growth), but when gibberelic acid is applied to these plants, they become indistinguishable from normal, tall varieties.
What is etiolation and the results?
Refers to plants that have been growing in the dark (greatly reduced amount of light).
Results: increased stem elongation; poor leaf development; lack of chlorophyll
What is phylum Ascomycota?
Sac fungi
Defined by ascus
What is phylum Basidiomycota?
Club fungi
mushrooms, toadstools, shelf fungi, stinkhorns, puffballs
Defined by a basidium
What are lichens?
Symbiotic relationship between a heterotrophic fungus (mycobiont) and an autotrophic alga or bacterium (photobiont)
Usually a mutualistic relationship (both benefit)
What are the 3 types of lichens?
Crustose = crustlike
Foliose = leaflike
Fruticose = shrublike