Exercise 41 Gelatin hydrolysis KTTK (MB. LAB)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Know what substance gelatin was derived from
collagen found in vertebrate connective tissue
Know what gelatinases do and why this is important to the gelatinase
test
hydrolyze gelatin
Gelatinases are family of enzymes certain microorganisms produce and secrete to break down gelatin extracellularly; amino acids are then absorbed
Know what type of molecule is the final result of gelatin hydrolysis
amino acids
Know how nutrient gelatin differs from most other solid media
the solidifying agent (gelatin) is also the substrate for enzymatic activity.
Know which technique is used to inoculate nutrient gelatin
stab inoculation
Know why (application) the gelatinase test is used
• Used to determine ability of microbe to produce gelatinases
• Can be used to differentiate members of a genus
• Positive Staphylococcus aureus from negativeStaphylococcus epidermidis
• Positive Serratia and Proteus species from negative members of Enterobacteriaceae
• Positive Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus and otherBacillus species
• Positive Clostridium tetani and Clostridium perfringens
Gelatin Hydrolysis test results and interpretations
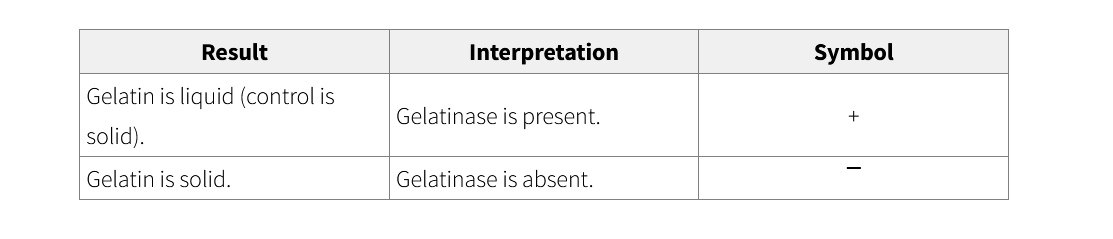
why it is extremely important to use an uninoculated control to interpret your results
uninoculated control used to verify that any liquefaction is not either temperature related or due to presence of gelatinase
why the nutrient gelatin is incubated at a lower temperature than most of the other tests you have run
Nutrient gelatin melts easily (@ 28 degrees C) so it can result in a false positive
to avoid liquefaction is related to temp.

gelatin hydrolysis test results
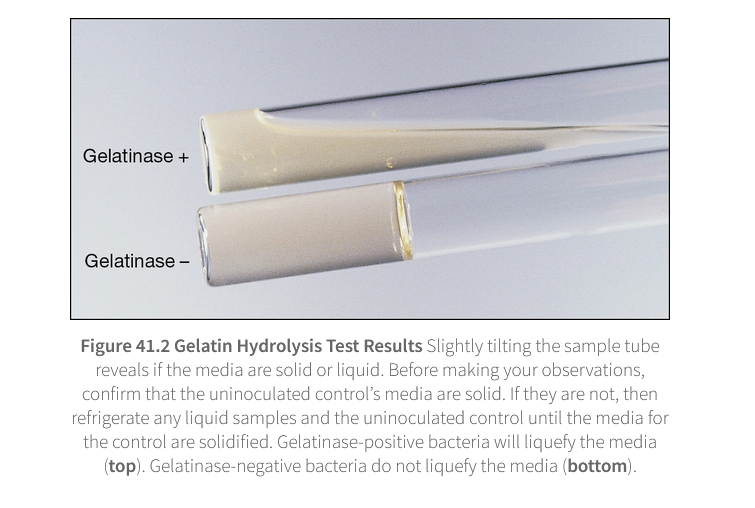

some organism can show crateriform liquefaction
does not completely liquefy gelatin
liquefies gelatin in crater formation
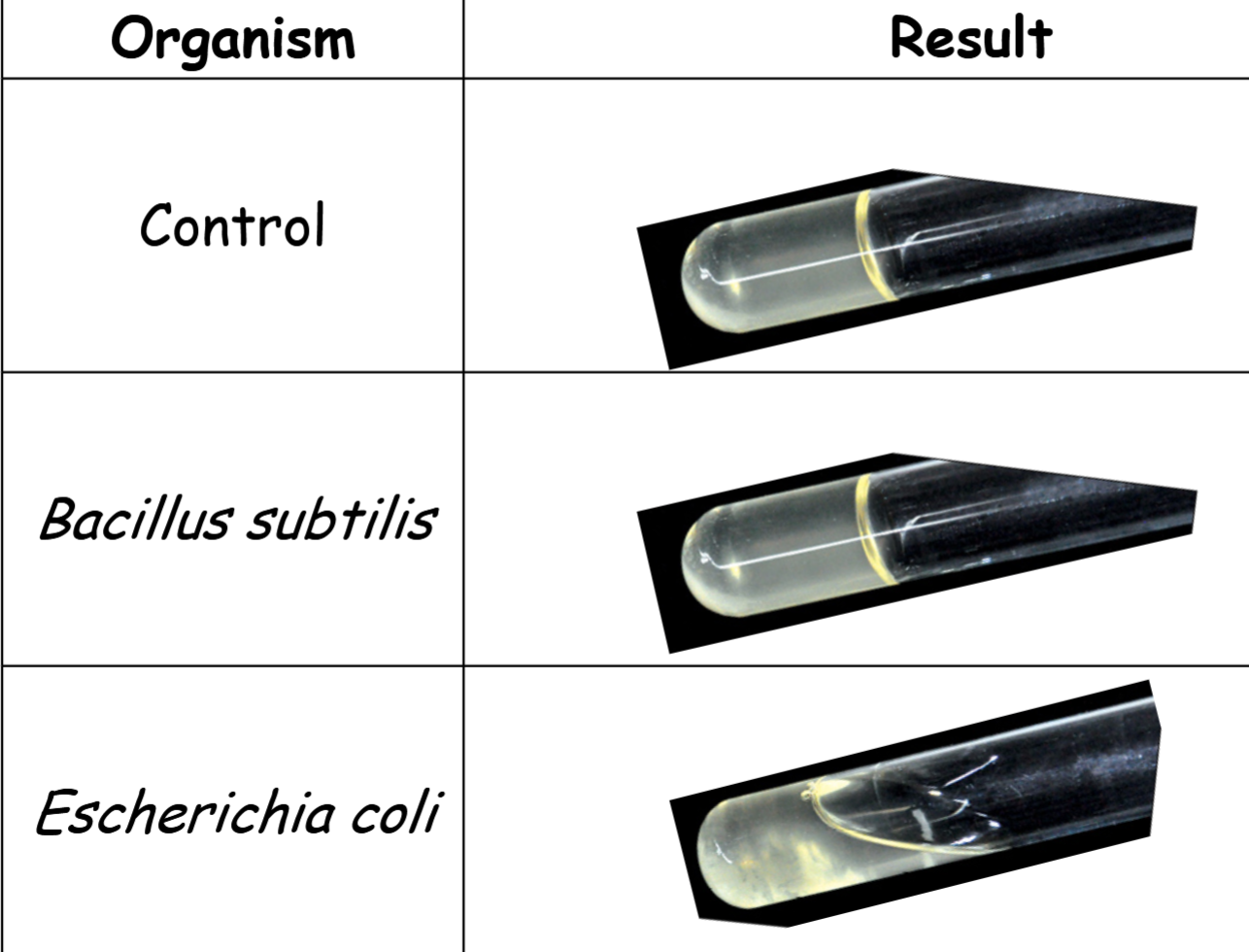
nutrient gelatin stabs - results 1
result 1:
control: gelatinase is absent -
Bacillus subtilis: gelatinase is absent -
Escherichia coli: gelatinase is present +
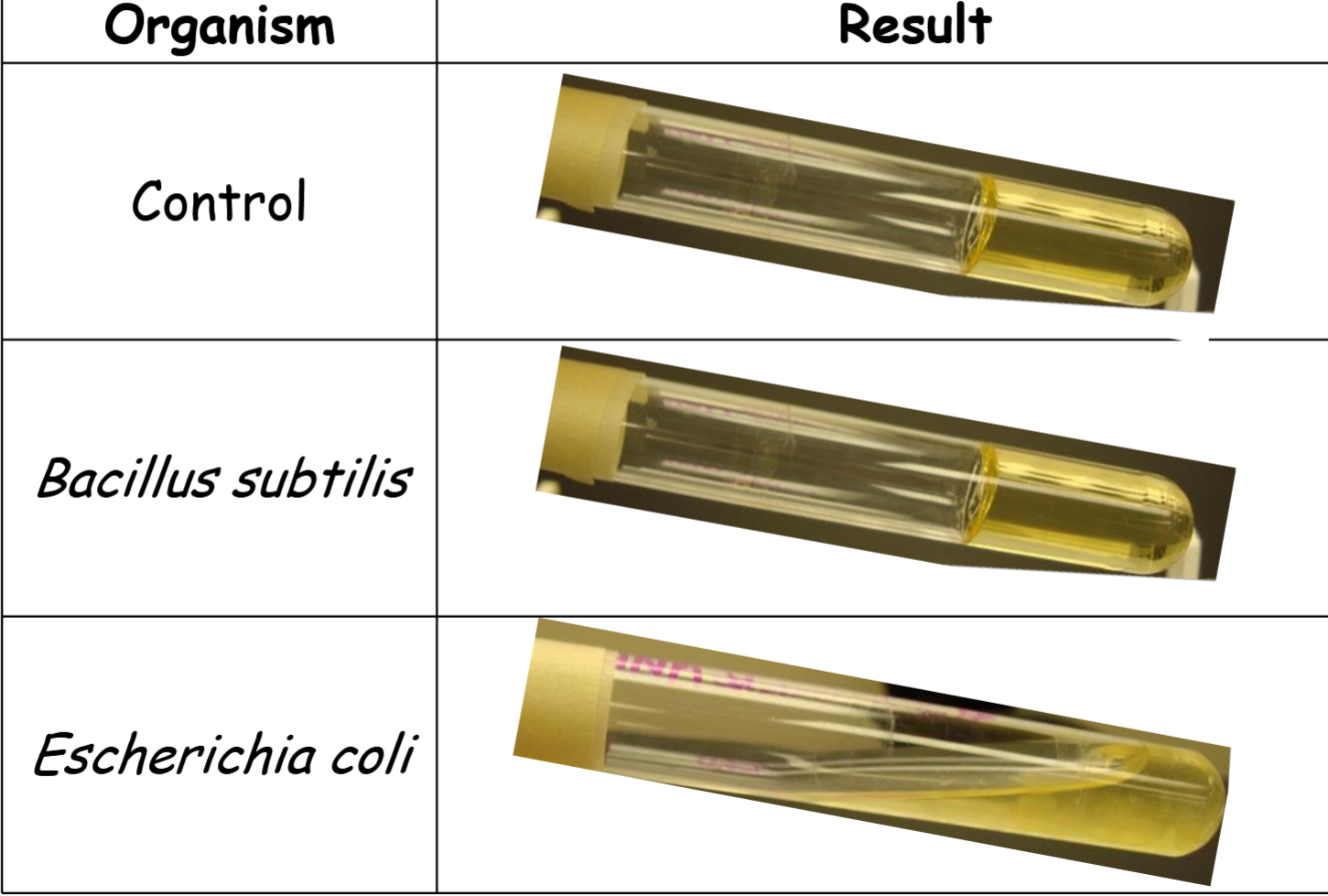
nutrient gelatin stabs results 2
control: gelatinase is absent -
Bacillus subtilis: gelatinase is absent -
Escherichia coli: gelatinase is present +