Carbonyl 5/6
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
The chemical process of converting aldehydes and ketones into alcohols.
Reagent for Reduction
A common reagent used for this process is sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
Limitation of NaBH4
only reduces ketones and aldehydes
Why is LiAlH4 a good reducing agent
It can reduce all carbonyl compounds
Nucleophilic Addition
A reaction where a nucleophile adds to a carbonyl compound, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Why do ketones and aldehydes partake in nucleophilic addition
As they have no leaving group with an electrophilic carbonyl carbon that it is susceptible to nucleophilic attack
Hydrolysis of Acid Chloride
The process by which an acid chloride reacts with water to form a carboxylic acid.
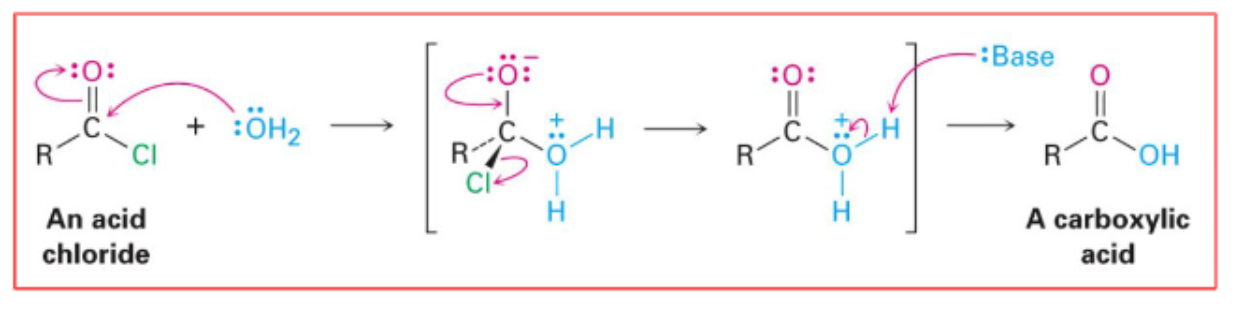
How does replacing water with amine/ alcohol/ thiol effect Acid Chloride hydrolysis ?
Replacing water with X can create an amide/ ester/ thiol from an acid chloride.
Acid-Catalyzed Esterification
A process where a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an ester.
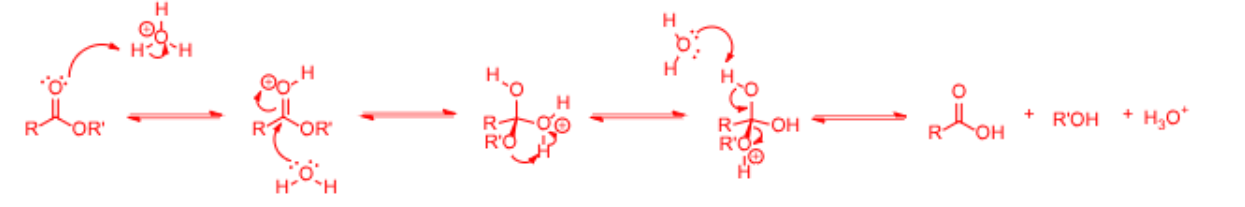
Base-Catalyzed Esterification
A process involving the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of a base.

Why are Carboxylic Acids more acidic than Alcohol
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols because the conjugate base (carboxylate anion) is resonance-stabilized.
allowing the negative charge to be delocalized over two oxygen atoms.
Spreading charge makes conj. base more stable and therefore a stronger acid.
Alcohols cannot resonate to stabilize the negative charge localised on oxygen atom, making them weaker acids.
What does it mean when a compound has a pKa higher than water
It means that the compound is a weaker acid than water, indicating that it does not donate protons as readily as water.
it will have a strong conj. base
and is less likely to dissociate in solution, resulting in lower acidity and is unionised in water.
the compound with a pKa higher than water will be deprotonated in water
Carbonyl Compound Interaction with Water
Carbonyl compounds can hydrogen bond with water, leading to increased solubility.
What is a HBD?
A molecule with a Hydrogen atom which attracted to an electronegative element
What is HBA ?
an electronegative atom with a lone pair that form a partial bond with a positive bond.
Reactants of Ester Formation
Carboxylic acid and an alcohol are reactants in the ester formation process.
Thioester
An organic compound formed where a sulfur atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
Acyl Halide
A compound derived from a carboxylic acid where the hydroxyl group is replaced by a halide.
Why do drugs contain carbonyl compunds
Due to large number of hydrogen bonds in the body
Carbonyl make HB and dipole interactions with receptors at binding sites in the body
increases binding affinity
Tertiary Amide
An amide where the nitrogen atom is bonded to three carbon atoms.
Lactone
A cyclic ester formed from the condensation of a hydroxyl and a carboxylic acid.
Ester
A compound formed from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, often with the elimination of water.
Why is acyl chloride most reactive
has a secondary dipole has a strong inductive effect
Weak resonance due to diminished overlap due to carbon being 2p and chlorine 3p hybridized
Chloride anion is a weak conj. base
Why does nucleophilic addition occur to carbonyl compounds?
Nucleophiles add to carbonyl compounds due to the electrophilic nature of the carbon atom in the carbonyl group.
What happens when a carbonyl compound hydrogen bonds with water?
The carbonyl oxygen can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, affecting properties like boiling point.
Draw the mechanism for nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group.
The mechanism involves the nucleophile attacking the electrophilic carbon, followed by protonation of the resulting alkoxide.
Draw the reaction mechanism for the hydrolysis of an acid chloride.
The mechanism includes nucleophilic attack by water, subsequent formation of the tetrahedral intermediate, and elimination to form the carboxylic acid.
Why do many drug compounds contain carbonyl groups?
Carbonyl groups are often involved in critical interactions such as hydrogen bonding, enhancing pharmacokinetics.
What is the typical geometric structure of a carbonyl group (C=O)?
Trigonal planar, with sp2 hybridization of carbon and oxygen.
What role do carbonyl groups typically play in chemical reactions?
They act as electrophiles in nucleophilic addition reactions.
How do aldehydes compare to ketones in terms of reactivity?
Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions.
What is the effect of protonation on the reactivity of carbonyl compounds?
Protonation increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
What is the acidity range (pKa) for typical carboxylic acids?
The pKa values for most aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids fall within the range of 3 to 5.
What kind of interactions do carbonyl groups typically participate in regarding drug molecules?
Hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions.
What is the mechanism for acyl substitutions in carboxylic acid derivatives?
Nucleophile adds to the carbonyl carbon, forms a tetrahedral intermediate, and then expels a leaving group. Nucleophilic substitution
What is the significance of the Bürgi-Dunitz angle in relation to carbonyl reactions?
It influences the steric crowding and approach of nucleophiles to the carbonyl carbon.
What is keto-enol tautomerization?
It is the interconversion between the keto form and the enol form of carbonyl compounds.
What are examples of biologically relevant carboxylic acid derivatives mentioned in the lecture?
Acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP).
What is the process called when a carboxylic acid form a carboxylate anion
deprotonation