Chapter 3- Enthalpy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what does system mean?
all the chemicals- both reactants and products
what does surroundings mean?
everything else in the universe, outside of the system.
energy can be transferred between the system and surroundings in both directions
energy meaning?
the ability of a system to do work
work meaning?
the energy transfer that is the result of a force moving an object through a distance
what is heat?
the energy transfer that is a result of a temperature difference between system and surroundings
what is enthalpy change?
the amount of heat energy taken in or given out during any change in a system
provided the pressure is constant
bond enthalpy meaning?
the enthalpy change needed to break that covalent bond into gaseous atoms
bond enthalpies are always positive because it will always require energy to overcome the attractive forces in the bond
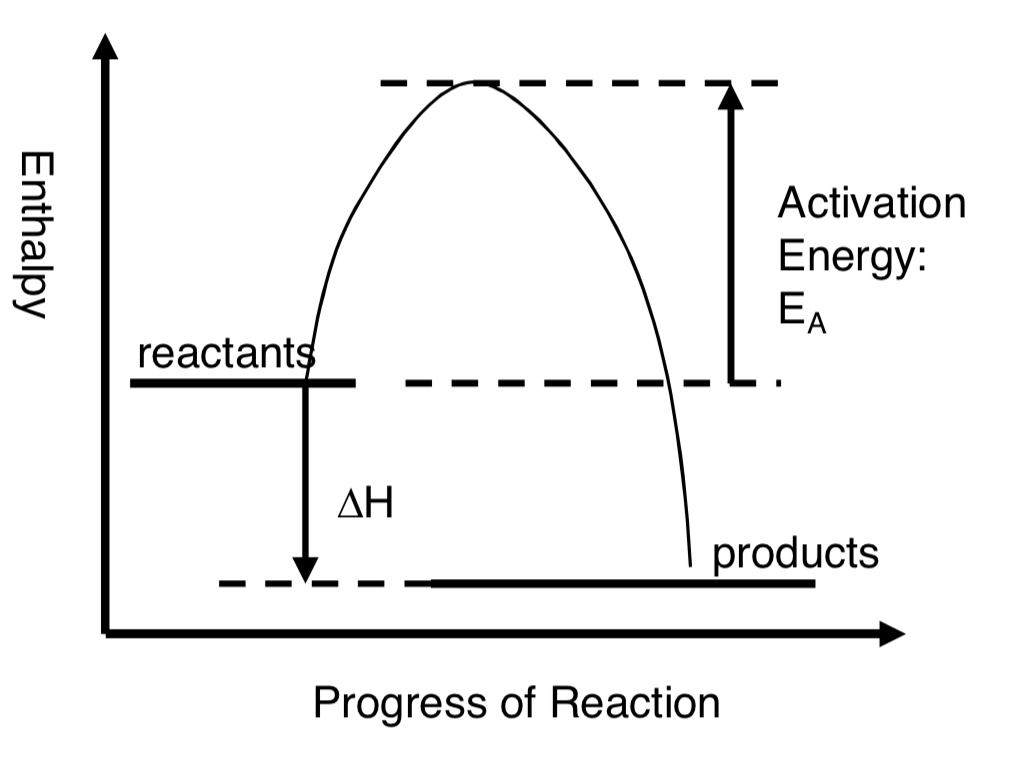
exothermic reaction?
heat energy is transferred from the system (chemicals) to the surroundings
the products have less enthalpy than the reactants
in an exothermic reaction, the enthalpy change is negative
why do exothermic reactions release heat?
because more energy is released forming new bonds in products than is absorbed breaking bonds in the reactants
exothermic diagram?
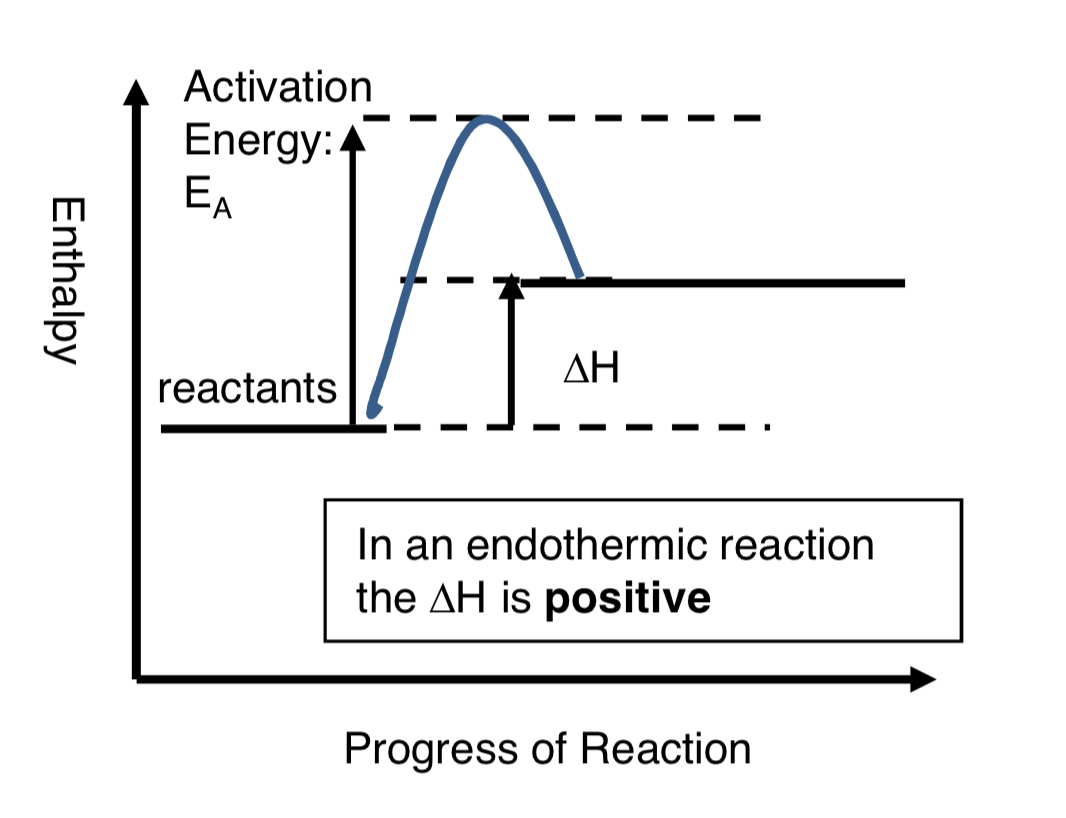
endothermic reaction?
heat energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system (chemicals)
the products have more enthalpy than the reactants
in an endothermic reaction, the enthalpy change is positive
why do endothermic reactions absorb energy (take in energy)?
because more energy is needed to break reactant bonds than is released forming product bonds
endothermic reaction image?
examples of exothermic reactions?
combustion of fuels
oxidation of carbs such as glucose in respiration
example of endothermic reaction?
thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate
how to remember which reaction breaks/makes bonds?
BENDO MEXO
Breaking bonds- ENDOthermic
Making bonds- EXOthermic

definition of the standard enthalpy change of formation?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of the compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions (298k and 100kPa)
and all reactants and products are in their standard states
symbol for enthalpy change of formation?
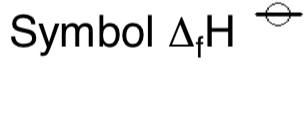
definition of standard enthalpy of combustion?
the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of a substance is combusted completely in oxygen under standard conditions (298K and 100kPa),
alll reactants and products being in their standard states

symbol for enthalpy change of combustion

definition of the enthalpy change of reaction?
the enthalpy change when the number of moles of reactants as specified in the balanced equation react together
definition of the enthalpy change of neutralisation?
the enthalpy change when solutions of an acid and an alkali react together under standard conditions to produce 1 mole of water
enthalpy changes of neutralisation are always exothermic
what are the standard conditions?
298Kelvin
1 mol dm-3
101 kPa
specific heat capacity equation:
energy transferred (J) = mass of water (g) x specific heat capacity (4.18J g -1 K -1) x temperature difference (°C)
q = mc t
how to calculate enthalpy change?
energy transferred / moles in reaction
what is activation energy?
the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
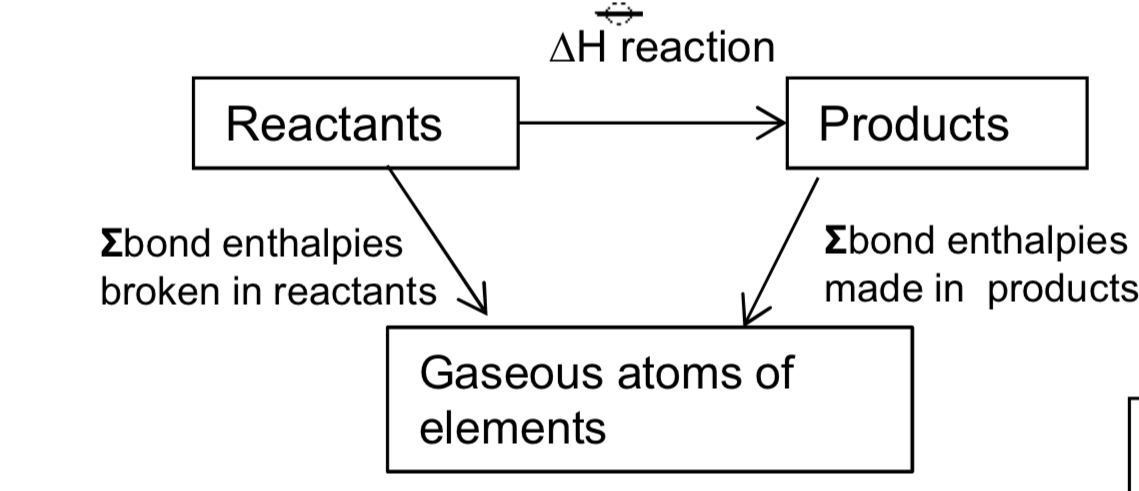
what is hess law?
the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route it takes
exam question: Explain why this value of ΔcH is different from the data book value and suggest how the experimental design could be modified to improve the accuracy of the ΔcH value obtained.
difference from data book value:
Heat losses
Incomplete combustion
Data book uses standard values
Evaporation of alcohol from wick
Evaporation of water from beaker
how to improve:
burn in plentiful oxygen
draft shield
add lid to beaker
heat for longer to reduce percentage uncertainty in mass/temp measurements
use standard conditions
digital thermometer OR 3 DP balance