Bioinformatics and protein engineering strategies BME 128
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Which database the structures of proteins usually are deposited in?
Protein Data Bank (PDB)
Understanding the concept of three common protein engineering strategies: comparative design, rational design, and experimental design
Comparative Design: using multiple sequence alignment to select mutations that alter protein properties
Rational Design: mutating protein in attempt to alter properties in predictable way (protein structure)
Experimental design: introducing mutations randomly to template protein and selecting improved fitness - usually requires high throughput methods and less demanding structural information
One case of comparative design for improved stability and solubility
Stability: Mutate sequence to consensus sequence by selecting positions in protein different from consensus and mutate to consensus sequence amino acid
Solubility: mutate sequence to consensus sequence by finding positions in your protein that are hydrophobic but where 1 more more homologs possess a polar residue and mutate to polar residue
One case of rational design for improved hydrophobic packing
Barnase ribonuclease increases stability and activity when hydrophobic core cavities are filled, Valine to Isoleucine or Leucine to Phenylalanine mutations
One case of directed evolution (experimental design); what two factors are important to design an efficient directed evolution platform?
mimics natural evolution in lab, but working at a lab level and focusing on human guided process that iteratively mutates biomolecules and selects variants for chosen function (fitness)
Two factors: mutagenesis, screening (user guided selection)
Understanding the three major ways to diversify the targeted gene with mutagenesis: random mutagenesis, directed mutagenesis, and DNA shuffling.
Random: creates a library of a gene that has been randomly mutated; create artificual condition that is conducive of polymerase base mispairing, results in library of randomly mutated genes, using Taq polymerase to substitute Mn 2+ to Mg 2+ : 1 error in 200 to 2000 bases
Directed: creates a library of a gene that has been randomly mutated specifically at one or more codons, design of degenerate primers for oligonucleotide mutagenesis, order set of primers whre wild type nucleotides in one or more codons are replaced by mixture of nucleotides
DNA shuffling: Recombination of two or more genes (usually homologous), makes a library of chimeric genes to combine existing diversity in new ways
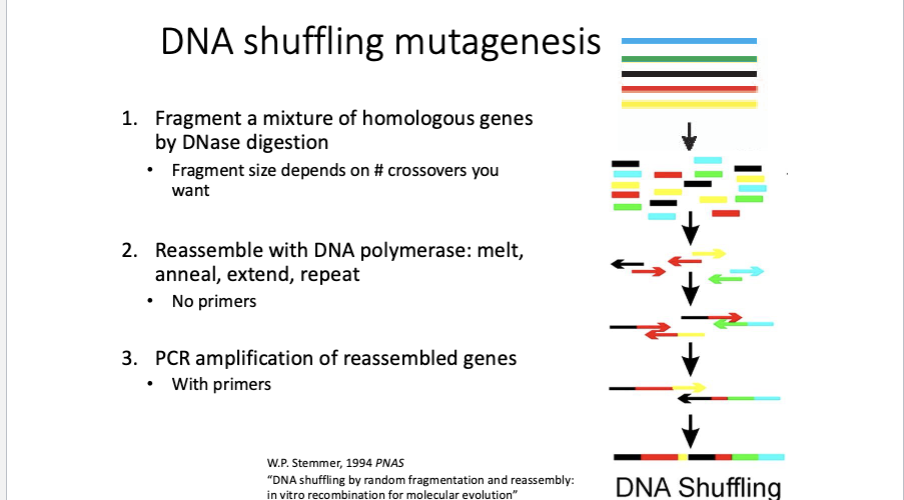
The general concept and comparison of phage and yeast display.
Phage display: A library of gene mutants is cloned into phage genome, usually M13 phage, phage displays mutant protein on its surface, fused to a virus coat protein, displayed protein can be tested for binding activites (large libraries, small proteins)
Yeast display: takes advantages of eukaryotic expression system available in yeast, including post translation modifications (complex proteins)
How to select codons based on the codon usage (abundant/rare codons)?
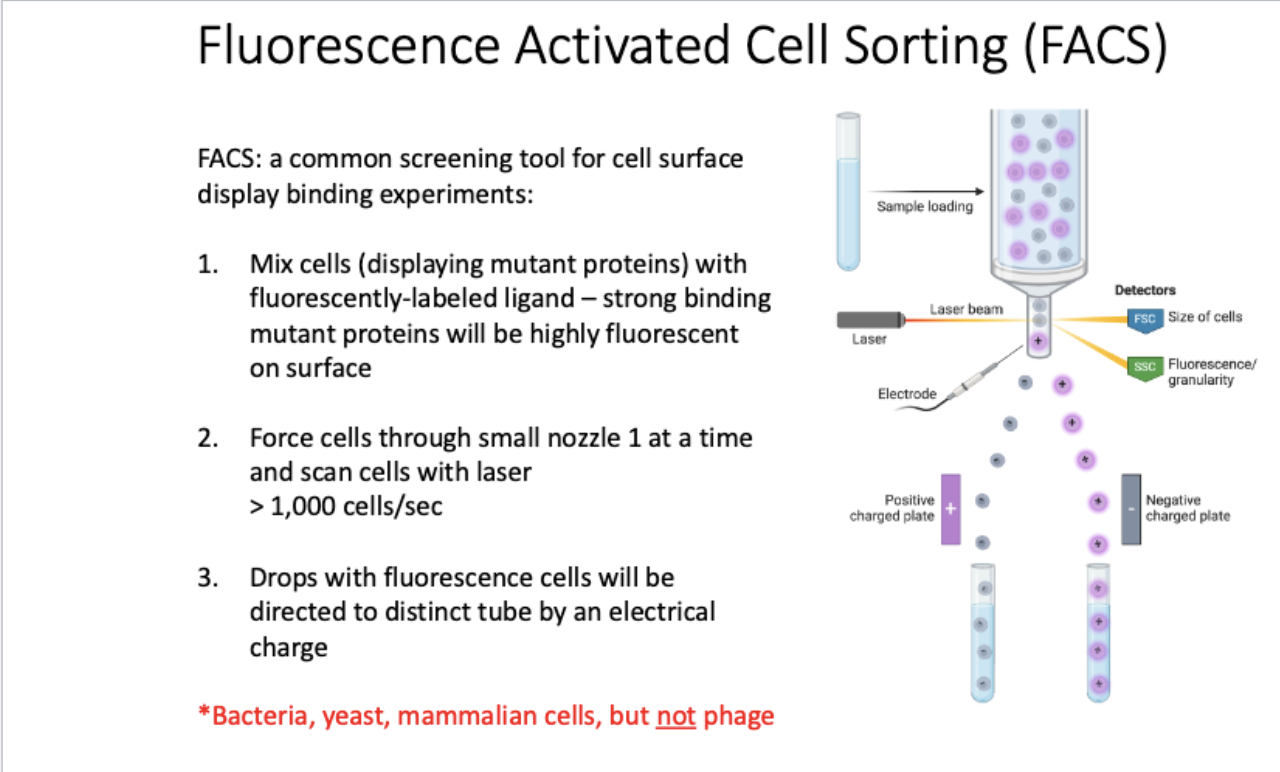
What is FACS, and how does it work?
Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting is a common screening tool for cell surface binding experiments.
mix cells with flourescently labled ligand - strong binding mutant proteins will be highly fluorescent on surface
force cells through small nozzle 1 at a time and scan cells with laser
drops with fluorescence cells will be directed to distinct tube by electrical charge