1.1: Introduction to ecology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Ecology
studies the relationships among living organisms and their environment
Ecology Hierarchy
Biosphere (largest)
Biome
Landscape
Ecosystem
Community
Population (species)
Organism or Species (individual) (smallest)
Ecosystem
A community of living (biotic) organisms interacting with the non-living (abiotic) components of their environment as a system through various nutrients and energy cycles.
Abiotic factors
are the nonliving parts of an ecosystem.
Rocks, air, water, sand, etc.
Biotic factors
are living things in an ecosystem.
Plants, animals, bacteria, etc.
Population
Organisms of the same species that interact with each other and occupy a specific area
Community
Population of different species.
Species
Organisms that resemble each other, are similar in genetic makeup, chemistry, and behavior, and are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Specialists
species that have a narrow niche and can therefore only live in very specific areas/habitats
Generalists
species that have a broad niche, highly adaptable, can live in varied habitats
Niche
An animal's "niche" is a description of what an animal's role in an ecosystem. It includes:
Resources it uses
Habitat
food
Behavior
When are they awake/active?
When do they mate?
Interactions with other animals
What animals do they kill?
What animals kill them?
Competition
arises when 2 (or more) individuals of the same or different species are competing for resources in the environment.
Competition affects BOTH organisms involved in a negative way.
Interspecific Competition
Two different species compete for the same resource
Intraspecific Competition
Two organisms from the same species compete for a resource
Limited Resource Availability
When two species compete, they both have to share the same limited resources. This means each individual gets less of what it needs to survive and thrive.
Reduced Growth
Individuals may grow more slowly because they don't get enough food, water, or sunlight.
Decreased Reproduction
With fewer resources, organisms may not be able to reproduce as successfully, leading to lower birth rates.
Lowered Survival
Scarcity of essential resources can increase stress and make it harder for individuals to survive
The Principle of Competitive Exclusion (Gause’s principle)
States that two species or populations cannot inhabit the same niche: one will consistently out-compete the other
There are two ways you can avoid competition
Resource Partitioning
Niche
Resource Partitioning
Animals can choose to use these resources at different times to avoid other animals
Examples:
Hunt at different times of the day
Breed at different times of the year
Feed at different depths of water
Live in different parts of a tree
Niche
Animals can use different resources from other animals, so they don't compete for the same resources.
Examples:
Over time different species of birds in an area may evolve to eat different types of seeds and live in different trees to avoid competition.
Fundamental niche
the entire set of conditions under which an animal (population, species) can survive and reproduce itself.
Realized niche
the set of conditions actually used by given animal (population, species), after interactions with other species (predation and especially competition) have been taken into account.
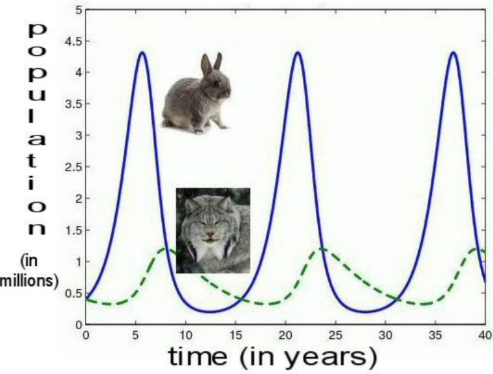
Predator-prey cycles
based on a feeding relationship between two species
If the prey species rapidly multiply, the number of predators increases until the predators eventually eat so many of the prey that the prey population dwindles again
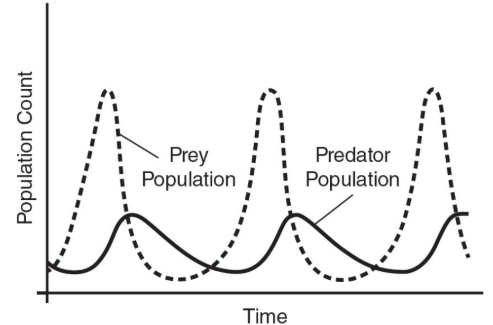
Boom-and-bust cycles
Prey populations rapidly increase. This is followed by an increase in the predator population.
As predators eat the prey, their population goes down because there is less to eat and the predator population also goes down.
Symbiosis
A close relationship between two different species
Mutualism (+/+): BOTH species benefit from each other in this interaction.
Parasitism (+/-): One species benefits and the other species is negatively affected.
Commensalism (+/o): One species benefits and the other species is not affected.
Ammensalism (-/o): One species is harmed while is other is unaffected!
Pathogen
A parasite that causes disease in its host.
Parasitoid
A specialized type of predator that lays eggs inside other organisms—referred to as its host