Chem 103 Exam
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Enyzmes are all?
Globular Proteins that are used in cells
(Substrate + Ase) - Examples: Pepsin, Tryspin, Lysoenzyme.
Oxidoreduction
Acid Reduction (NAD-NADH) - O+ but takes away 2H
(Lactic Dehydrogase)
Transferase
Transfer of functional group from molecule to another
(Kinase)
Hydrolases
Catalyzes by adding H2O to break bonds
(Maltose, Amylase, Surcose, Lactose)
Lyase
Removes a group without hydrolysis
(fermentation) - CO2-
Isomerase
One isomer to another (CIS to Trans) - (Glucuse to Fructose)
Ligase
Synthesis - NEED ATP
2 small molecules to one large molecule
Isoenzymes
Catalyze on rx, slightly different structure depending on tissue
(LDH)
H4 Subunit - LDH
Heart + Kidney
M4 Subunit - LDH
Liver + Muscle
H3M Subunit - LDH
RBC + Brain
H2M2 Subunit - LDH
WBC + Liver
Catabolic Metabolism
Exothermic Rx
Breaks down large fuel molecules
bond energy (smaller ones)
Hydrolysis, Oxidation
Anabolism
Endothermic Rx
Synthesizing molecules (need energy)
Metabolism
Small molecules - CO2 + H2O “in cell”
Starch → Dextrins → Maltose (Carbonhydrates)
Mouth (Amylase)
Monosaccharides
Protein Channels (active transport)
Enzyme Binding
Temporary - Salt Bridge/H-Bonding
Apoenzyme (Protein) + Cofactor (Metal Ions or co-enzymes)
Holoenzyme = Organic New protein made from vitamins
Riboflavin
FAD Vitamin
Niacin
NAD Vitamin
Thromin
TPP Vitamin
Allosteric Enzyme
Several Binding Sites = Substrate, Regulate molecule
Proenzyme (Zymogen)
Synthesized in inactive form (protein digesting enzymes) - Blood clotting enzyme
Phosphorylation
Putting in a phosphate to enzyme
Plasma
Fibrinogen = can clot
Serum
None to clot
Vitamin E
This vitamin is anti-coagluant
Vitamin K
this vitamin can blood clot
Embolism
A clot that is moving
Thrombsis
Clot with B.V
Glycogen
Ready Energy source from the Liver + Muscle
Glycogen Phosphoryose
Activated by epinephrine (Liver + Muscle)
Glucagon
inhibited by insulin
Glycogenelysis
Break down of glycogen to glucose
Glycogenesis
Creation of glycogen from glucose
Glycogen Synthetase
Activated by insulin (Muscle Liver) - Enzyme
Glycolysis
All cells go through glycolysis
Pyruvic Acid
Energy process that goes into metabolism or fermentation (krebs cycle)
Examples of Metabolism
Lactic Acid - Analbolic
Glycerol - Lipid
Some Amino Acids → protein
Acteyl CoA
Can be turn into Fatty Acids through Insulin but the main process to enter krebs cycle
Glucogenesis
Activated by cortisol, epinehrine/glucagon but inhibited by insulin
Hyperglycemia
High Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia
Low Blood Sugar
Insulin
Feast Hormone
Activates glycogenesis (making glycogen)
Inhibits glycogenolysis (Glycogen no longer makes glucose)
Entry of glucose into liver/adipose tissue
Stimulates the glucose - aidpose synthesis (F.A in triglycerides)
Fat Metabolism is cancelled
Inhibits glucogenesis
New glucose from non-carbonhydrates
Diabetes
Insulin Dependent - (No production from pancreas)
Insulin = protein = cant give orally (must be peptides)
Glucagon
“Famine Hormone”
Protein hormone from pancreas
Act as liver + adipose tissue
stim glycogenesis (glycogen → glucose)
stimulate liver glucogenesis (Lactic Acid, Glycerol, A.A)
Stimulates Hydrolysis of trig (adipose)
Epinehrine
Stimulate glycoygenesis (Production of glycogen)
stimulate glucogenesis in liver
+ Heart rate / BP
What happens in Step 1,3 in Glycolysis
Kinase
Slow down enzyme activity
Active Site for glucose + ATP → product
Activator Site for ADP = Activate Enzyme
Complete Oxidation of Glucose
686 Kcal
% of energy (2 ATP + 7kcal = 14 kcal)
% saved = 14/686 × 100 = 2%
Anaerobic Conditions
Not enough O2 or Mitochondria
NAD is done in step 6
Aerobic Conditions
Oxygen is avalible and cell mitrochondria
Krebs cycle - Acetyl CoA
Which Usually forms a covalent bond with an amino acids side chain in the active site of the enzyme?
Irreversible Inhibition
Which inhibition can be reversed by adding an excess of the substrate
Competitive Inhibition
In which inhibition does the inhibitor resembles the substrate
Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor binds to the enzyme at a different site than substrate, but it can be removed
Non-competitive inhibition
An example is ethanol as an antidote for methanol posioning
Competitive Inhibition
Allosteric enzyme inhibitors are examples of what types of inhibition
Non-competitive inhibition
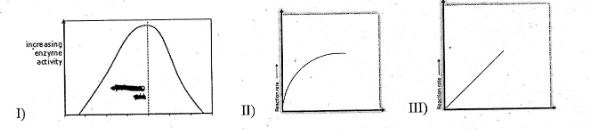
Temperature
Substrate Conc
Enzyme Conc
What is true of pepsin
It is a peptidase/Stomach acid catalyzes the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin
What type of enzyme would be synthesized first as a zymogen
Protein digesting enzyme and blood clotting enzymes
What factors affect the activity of enzymes?
The substrate saturation, genetic control, and temperature
What type of bond can hold a substrate to the active site of an enzyme?
Salt bridge
What is true of cofactors?
Without it, the enzyme would not be active, many of it is made from vitamins, and it can be metal ions
Which of the following physiological activity (without adding any group)
Holoenzymes
What is true of a zymnogen
The other name is apoenzyme, synthesized with more amino acids than active enzyme, and its active active site is blocked by several a.a
What is true of about denaturing an enzyme?
Severe pH changes will cause perm denature and heavy metals can denature an enzyme
Which of the following statements are true concerning enzymes vs hormones
Enzymes and hormones are all proteins and enzymes are used in the cells where they are made
Which is true concerning Trysinogen and Trypsin?
Trypsin has catalytic ability while Trysinogen is not
Which is true of blood clotting mechanism?
Actual clot is protein called fibrin
True of acetylcholine?
Ester linkage, Neurotransmitter, and a molecule that blocks its receptor site can be used as an muscle relaxant
Which is true of acetylcholineteraste
It can convert millions of substrate molecules to product within minutes, if permanetly inhibited, it can cause overstimulation of muscles, convulsions, and death
True of digestion?
It is mostly hydrolysis reactions that break down food into smaller molecules.
Which is the following is not stored?
Amino Acids
Which product of digestion does not need a protein channel to get into the blood?
Glycerol
Which is true of glycerol
Produced from triglyercides, soluble in blood, and all cells use it for energy
Which product of digestion is not soluable in blood?
fatty acids
What is true of diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin. In some cases, the pancreas does not synthesize enough insulin or lack of receptor sites for the insulin molecule on the target cells
What is true of glycogenolysis?
It is done in the liver and muscle and the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rxaction of converting glycogen to glucose-1-phosphate, which can then be transformed into glucose for energy.
What is true of gluconeogenesis?
Done in the liver, activated by glucagon and inhibited by insulin
What are possible starting materials for gluconeogenesis
such as lactate, glycerol, and amino acids.
What is true of glucagon?
A protein hormone that raises blood glucose levels, promotes gluconeogenesis, and inhibits glycogen synthesis.
Which processes are activated by insulin
Fatty acid synthesis
What cell need insulin to faciliate glucose entry
Muscle Cells
Process stimulated by epinephrine (adrealine)
Glycogenolysis in the liver, Glycogen to G1P, and gluconeogenesis in the liver
What is true of glycogen synthetase
Found in liver and muscle and activated when blood sugar is high
How does glucagon affect the liver cell?
It promotes glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, increasing blood glucose levels. (cAMP system)
Muscle cells have no receptor sites for which hormone?
Glucagon
What hormone will stimulate glycogenolysis in muscle?
epinephrine
Which is true of the conversion of G1P to glycogen?
Energy needed to synthesize the glycogen comes from breaking high energy phosphate bonds on glucose
Which of the following acn get out of a cell using protein channels?
Glucose
What hormones uses the cAMP system?
most protein hormones
Which process needs alot of ATP?
Muscle work, synthesis rx, and active transport processes.
C
Which contrains the highest energy? (All in Mitochondria)
One NADH
Which of the following reactions are exothermic?
Which of the following is endothermic?
Glucose to glycogen and ADP and Pi → ATP
Which is true of glycolysis?
All cells can do it, often done in the cytoplasm, and can be done aerobic and anaerobic conditions
Starting of the point of glycolysis for a brain cell
is glucose, which is phosphorylated to form glucose-6-phosphate and is the first step in the glycolytic pathway.
Starting point of glycolysis for a muscle cell
Glycogen and blood sugar after its glycogen is used up
Which is true concerning the enzyme phosphatase?
Converts G6P to glucose.