Chapter 15: Blood Flow, Blood Pressure Control, and Cardiovascular Regulation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the two separate systems of the cardiovascular system?
The right and left sides of the heart.
What is the primary function of arterioles?
They are the most adjustable blood vessels in terms of diameter, determining blood flow to tissues.
What do arteries primarily carry?
Blood away from the heart, usually high in oxygen.

What is the main function of veins?
To bring blood back towards the heart.

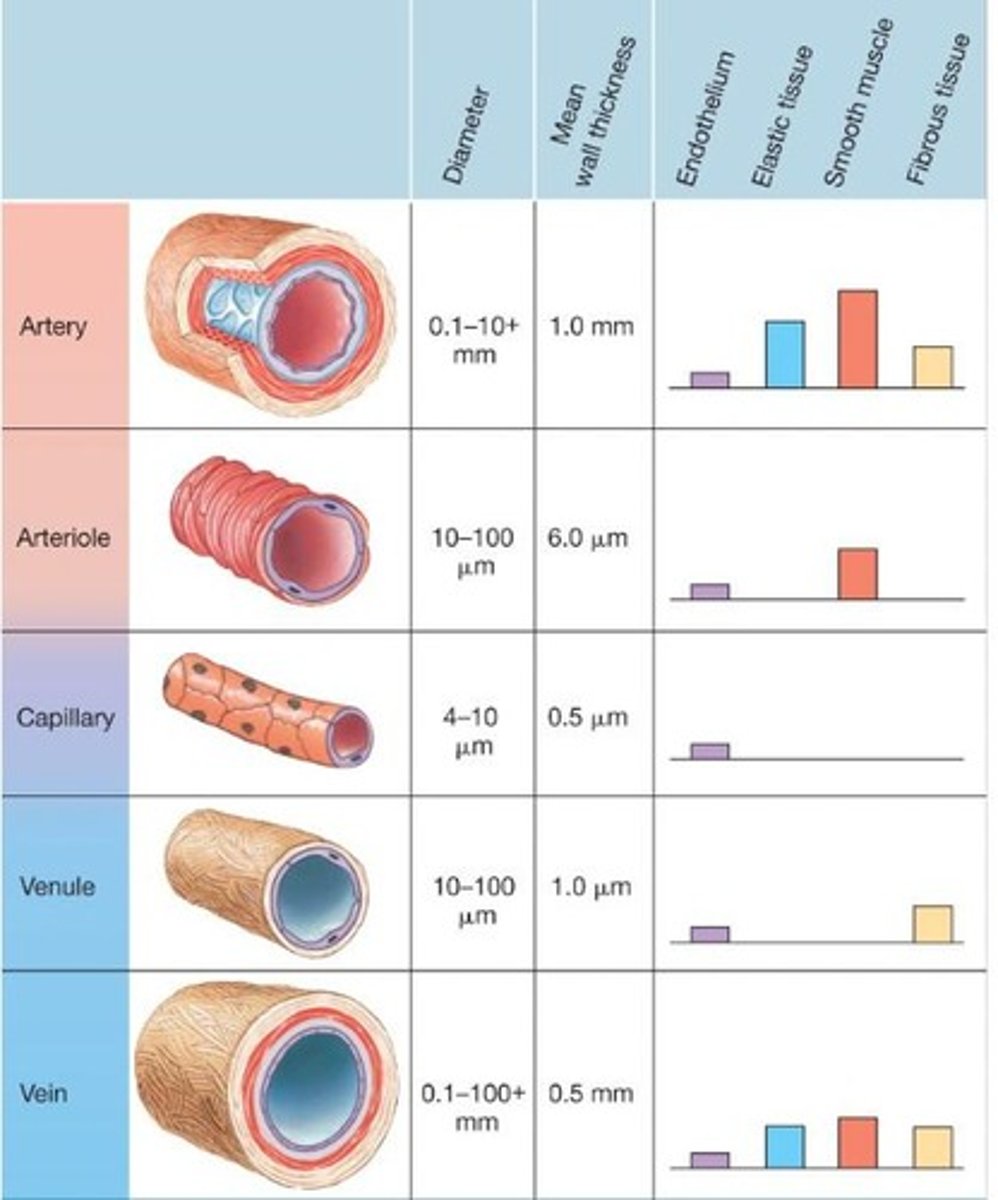
How do arteries and veins differ in structure?
Arteries are more muscular and elastic, while veins are more compliant and expandable.
What is the role of the endothelium in blood vessels?
It secretes paracrine factors and regulates blood pressure and vessel growth.
What is angiogenesis?
The formation of new blood vessels.
What is the significance of vascular smooth muscle in blood vessels?
It allows for vasoconstriction and vasodilation, regulating blood flow.
What is the primary site of exchange between blood and interstitial fluid?
Capillaries.
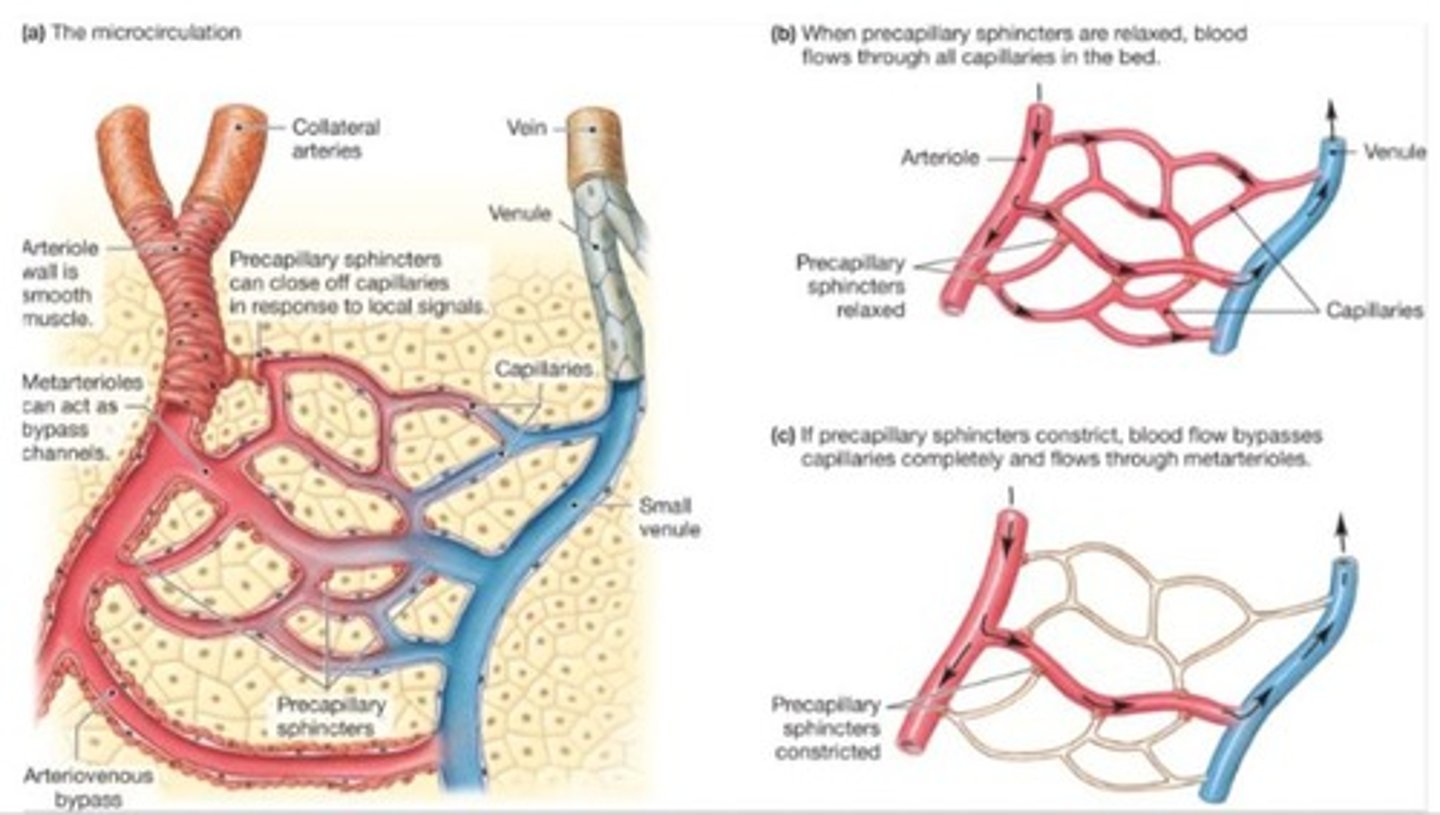
What are pericytes and their function?
Contractile cells associated with capillaries that contribute to capillary impermeability and promote vascular growth.
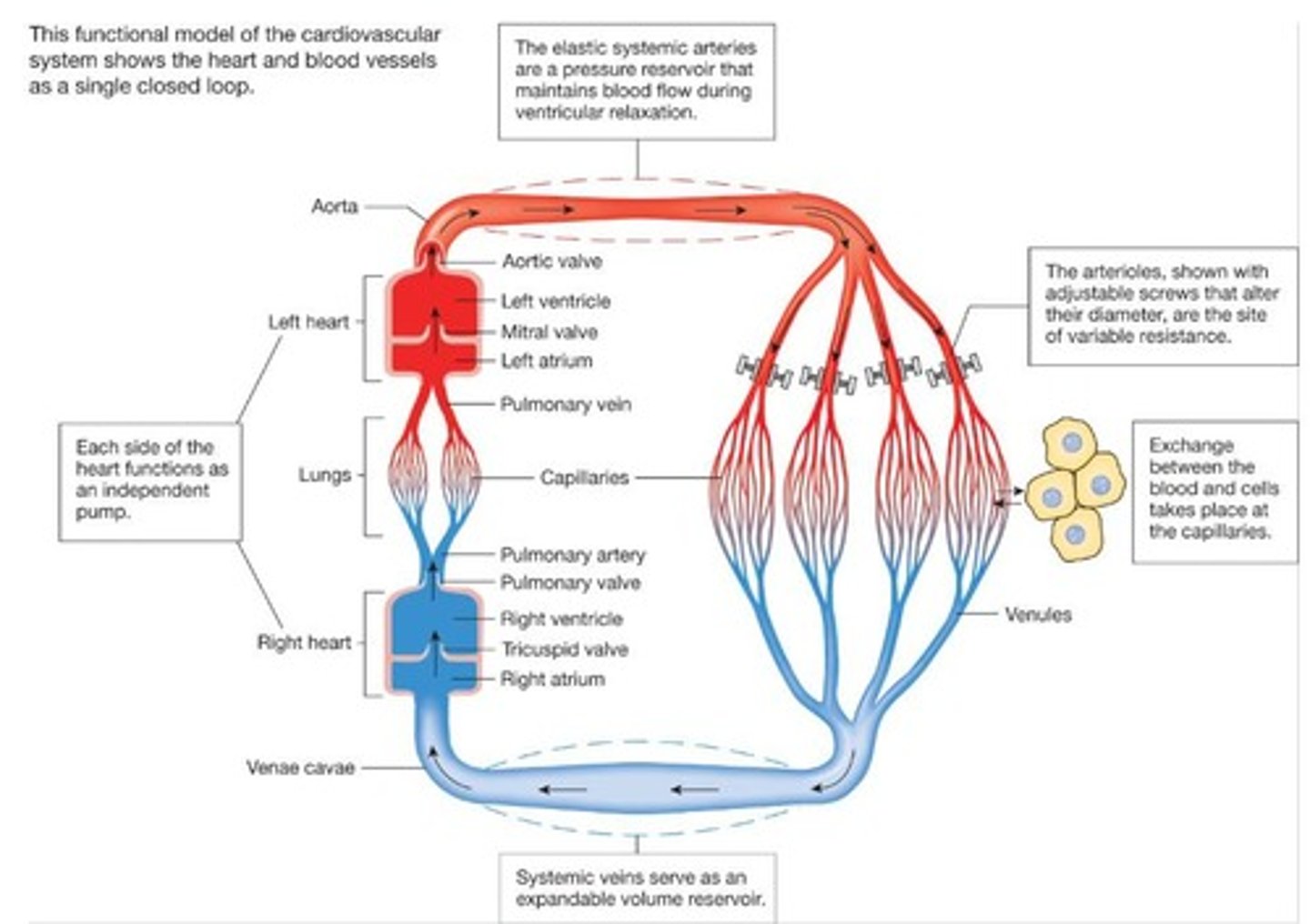
What is the pathway of blood flow from the left ventricle?
Left ventricle → aorta → arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins → superior/inferior vena cava → right side of heart.
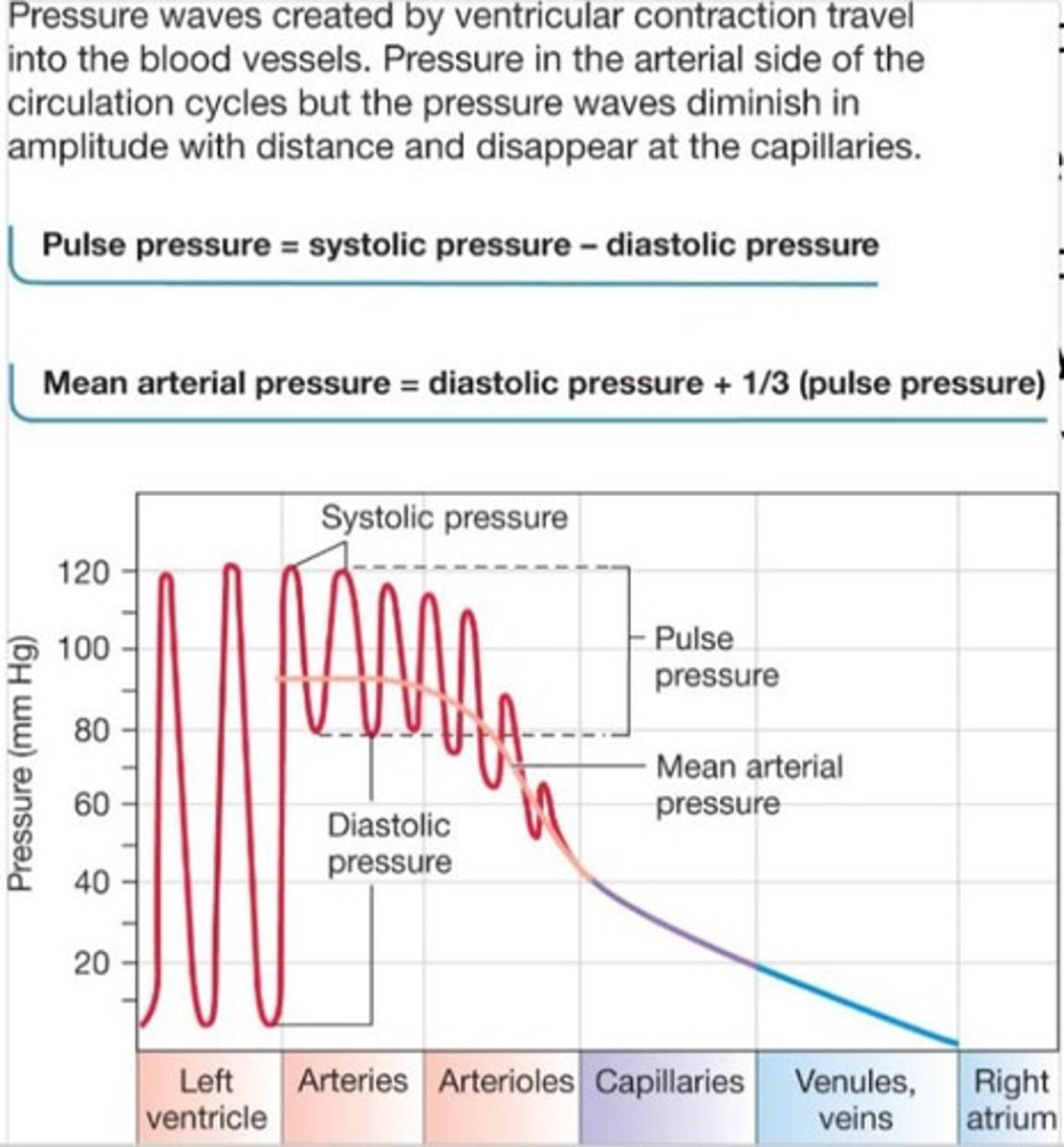
What is pulse pressure?
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
What factors affect blood flow in the cardiovascular system?
Pressure gradient (∆P) and resistance (R) of the system.
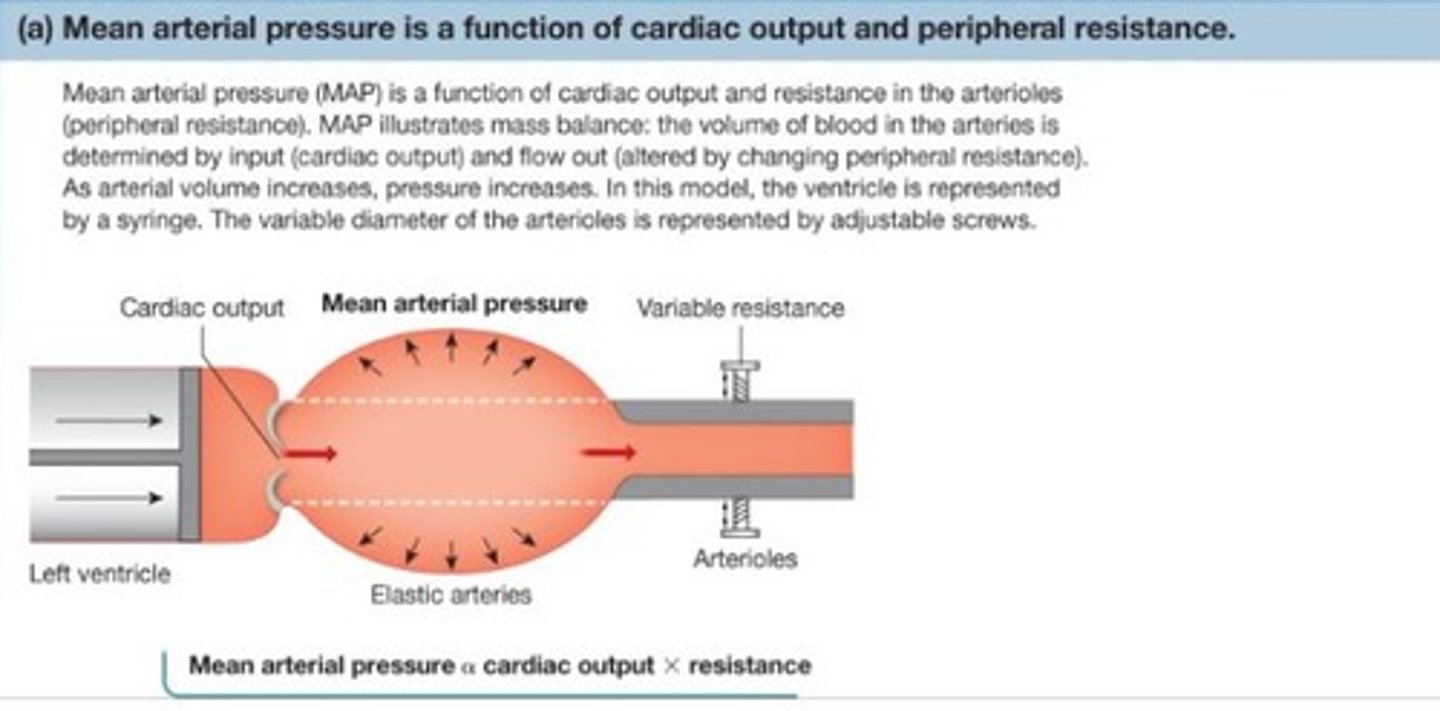
What is mean arterial pressure (MAP) and how is it calculated?
MAP is the driving pressure for blood flow, calculated as diastolic pressure + 1/3 (systolic pressure - diastolic pressure).
What is the role of valves in veins?
They prevent backward flow of blood, especially important in leg veins.
What is the difference between arteries and arterioles?
Arteries are pressure reservoirs with thick muscular walls, while arterioles are sites of variable resistance.
What happens to blood pressure as it moves through the circulatory system?
Blood pressure decreases due to friction from blood vessels.
What is the function of the skeletal muscle pump?
It aids venous return by squeezing blood vessels during movement.
What is the significance of the respiratory pump in venous return?
It helps return blood to the heart by creating pressure changes in the thoracic cavity during breathing.
What is hypotension and hypertension in terms of mean arterial pressure?
Hypotension is below normal MAP, while hypertension is above normal MAP.
What is the relationship between cardiac output and peripheral resistance?
Cardiac output is proportional to the product of cardiac output and resistance in arterioles.
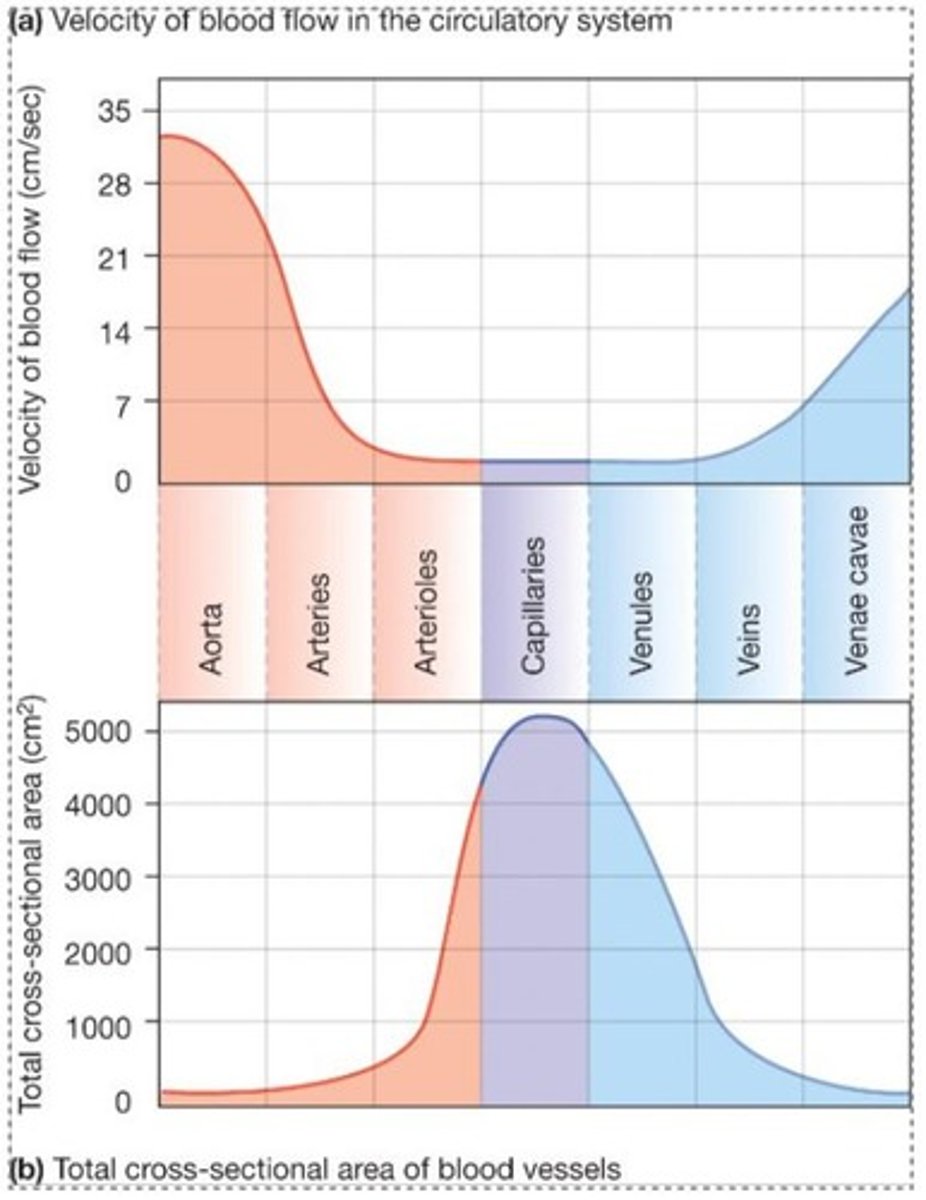
How does blood flow relate to the cross-sectional area of blood vessels?
The total cross-sectional area of vessels is the primary determinant of flow velocity when flow rate is constant.
What is the role of smooth muscle tone in blood vessels?
It maintains a state of partial contraction, allowing for regulation of blood flow.
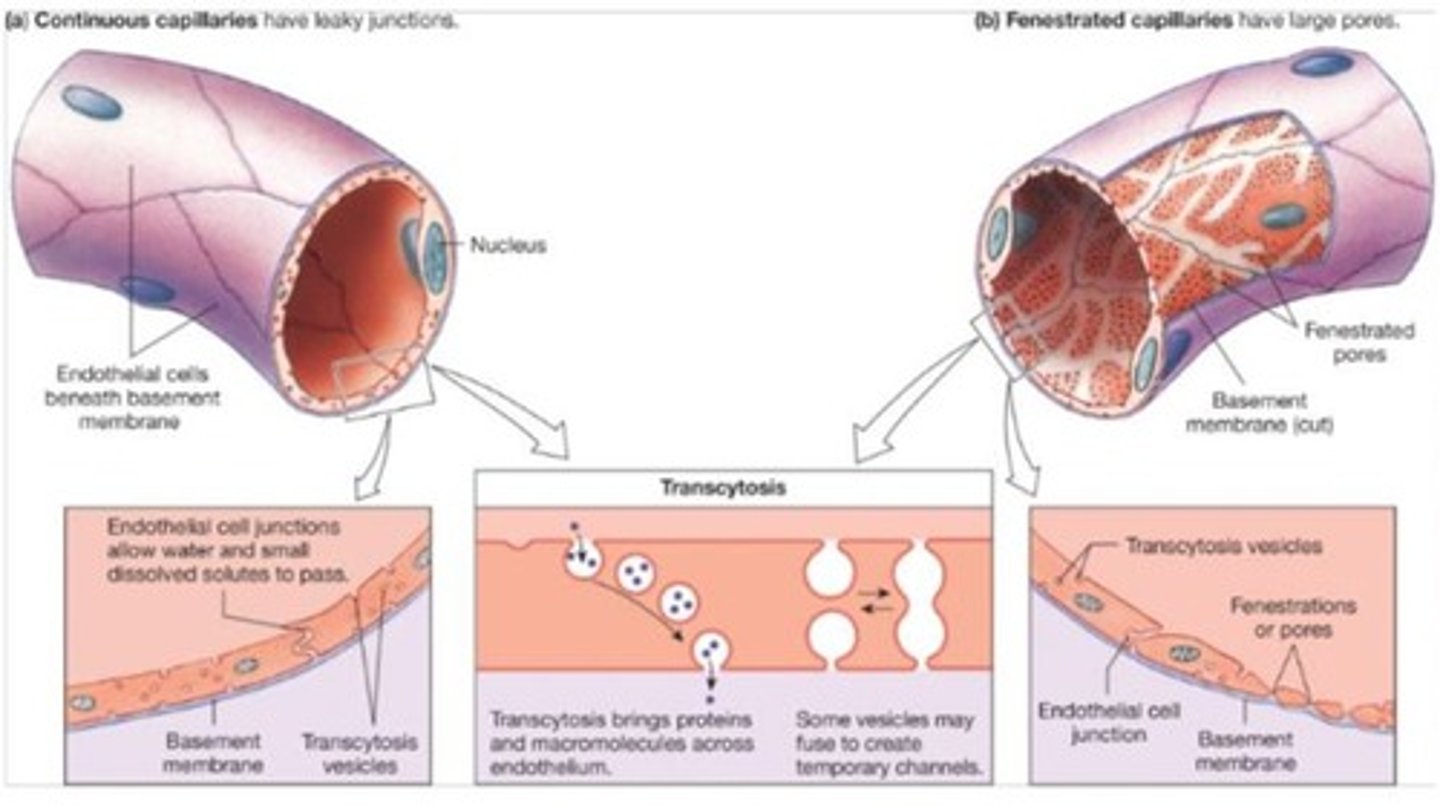
What is the structure of capillaries?
They consist of a single layer of endothelial cells with a lumen for blood flow.
How do veins differ from arteries in terms of elasticity?
Veins are more compliant and expandable, while arteries are more elastic and can recoil.
What happens when blood flow into the aorta exceeds blood flow out?
Blood volume increases and mean arterial pressure (MAP) increases.
What is the role of the kidneys in blood volume regulation?
The kidneys remove excess fluid volume but cannot compensate for lost volume.
What compensatory mechanisms occur when blood volume decreases?
Pressure decreases, compensated by drinking, IV infusion, vasoconstriction, and sympathetic stimulation of the heart.
How does skeletal muscle pump affect venous return?
It increases venous return, leading to greater end-diastolic volume (EDV) and stroke volume.
What is the significance of arterioles in blood flow regulation?
Arterioles are the site of variable resistance and can regulate their own flow, compensating for changes in other arterioles.

What is the primary determinant of blood flow velocity in capillaries?
The total cross-sectional area of all capillaries.
What are the two main types of capillaries?
Continuous capillaries and fenestrated capillaries.
What is the difference between filtration and absorption in capillaries?
Filtration is fluid movement out of capillaries, while absorption is fluid movement into capillaries.
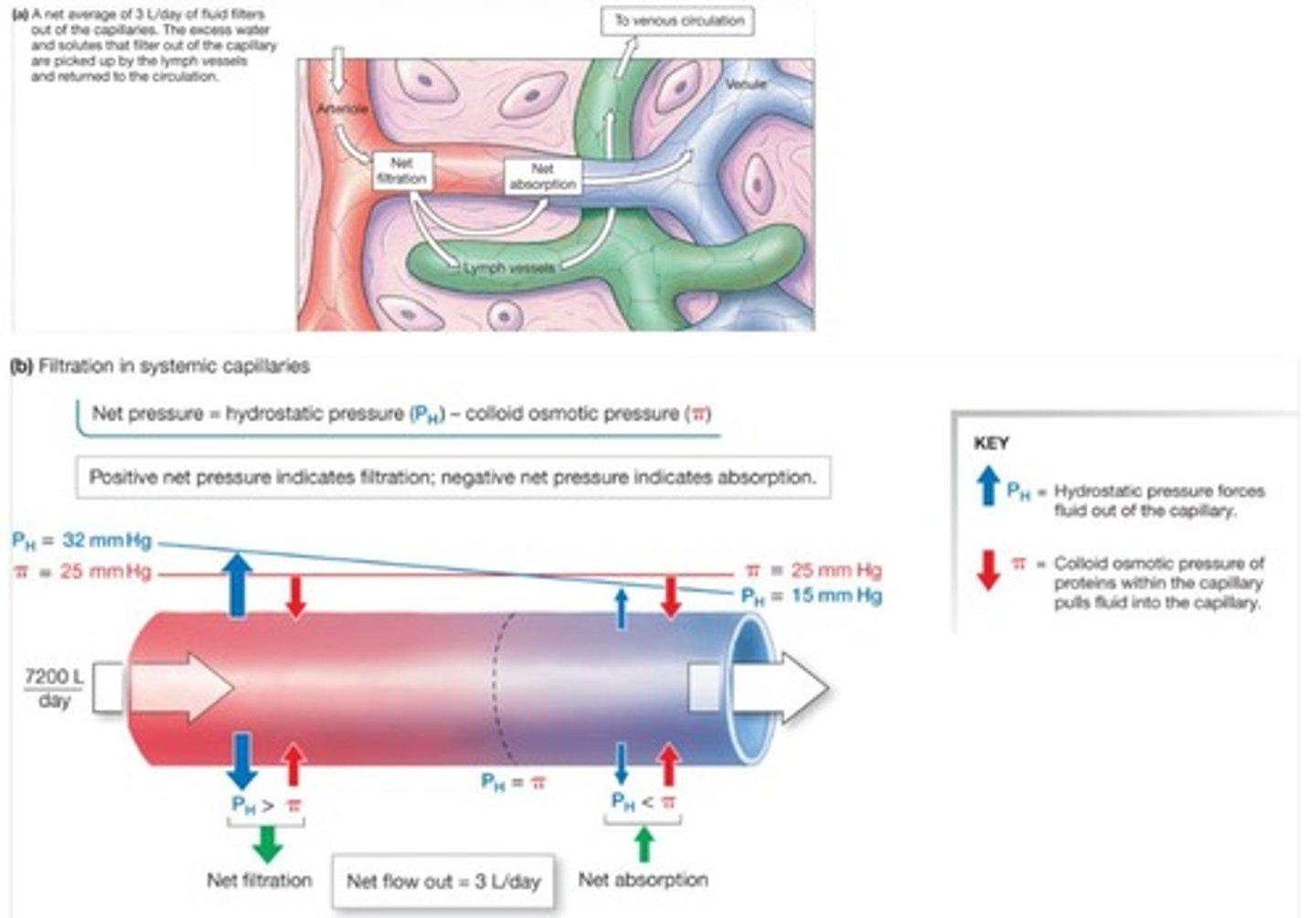
What causes ascites and how is it related to protein levels?
Ascites is abdominal edema caused by low protein levels in the blood, leading to greater filtration than absorption.
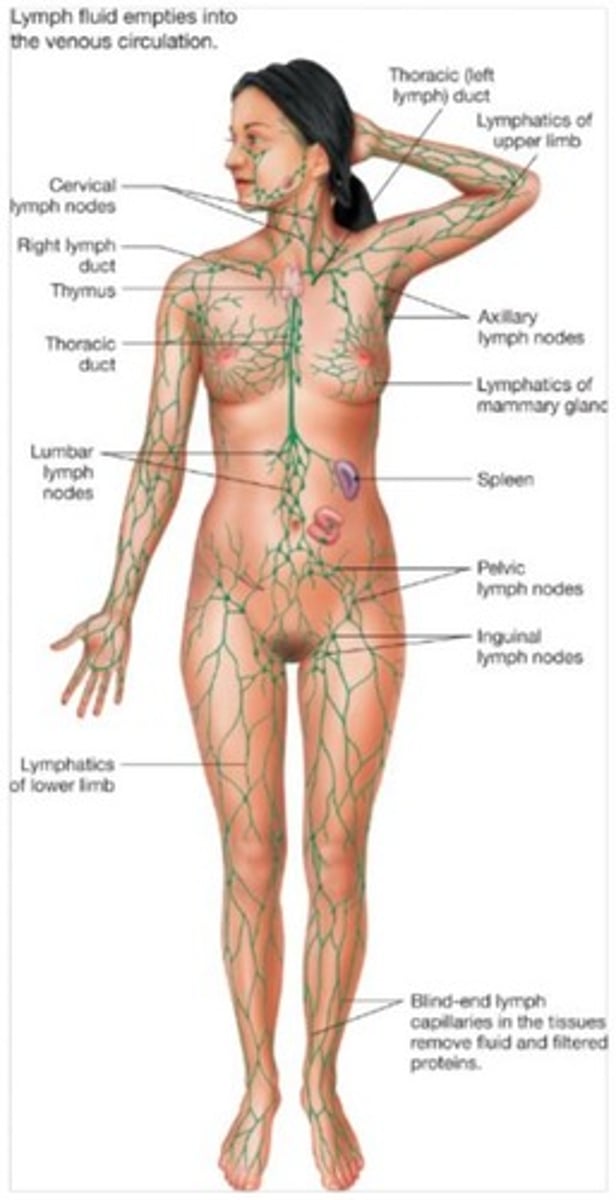
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
It returns fluid and proteins to the circulatory system, picks up fats from the digestive tract, and filters pathogens.
What are the risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
Risk factors include smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and untreated hypertension.
What is the difference between primary and secondary hypertension?
Primary hypertension has no clear cause other than hereditary factors, while secondary hypertension is due to underlying pathology.
What is heart failure and its two types?
Heart failure is the inability of cardiac output to meet body demands, with types being diastolic HF (trouble filling) and systolic HF (trouble pumping).
How does hypertension affect the risk of developing cardiovascular disease?
The risk doubles with each 20/10 mmHg increase over a baseline of 115/75 mmHg.
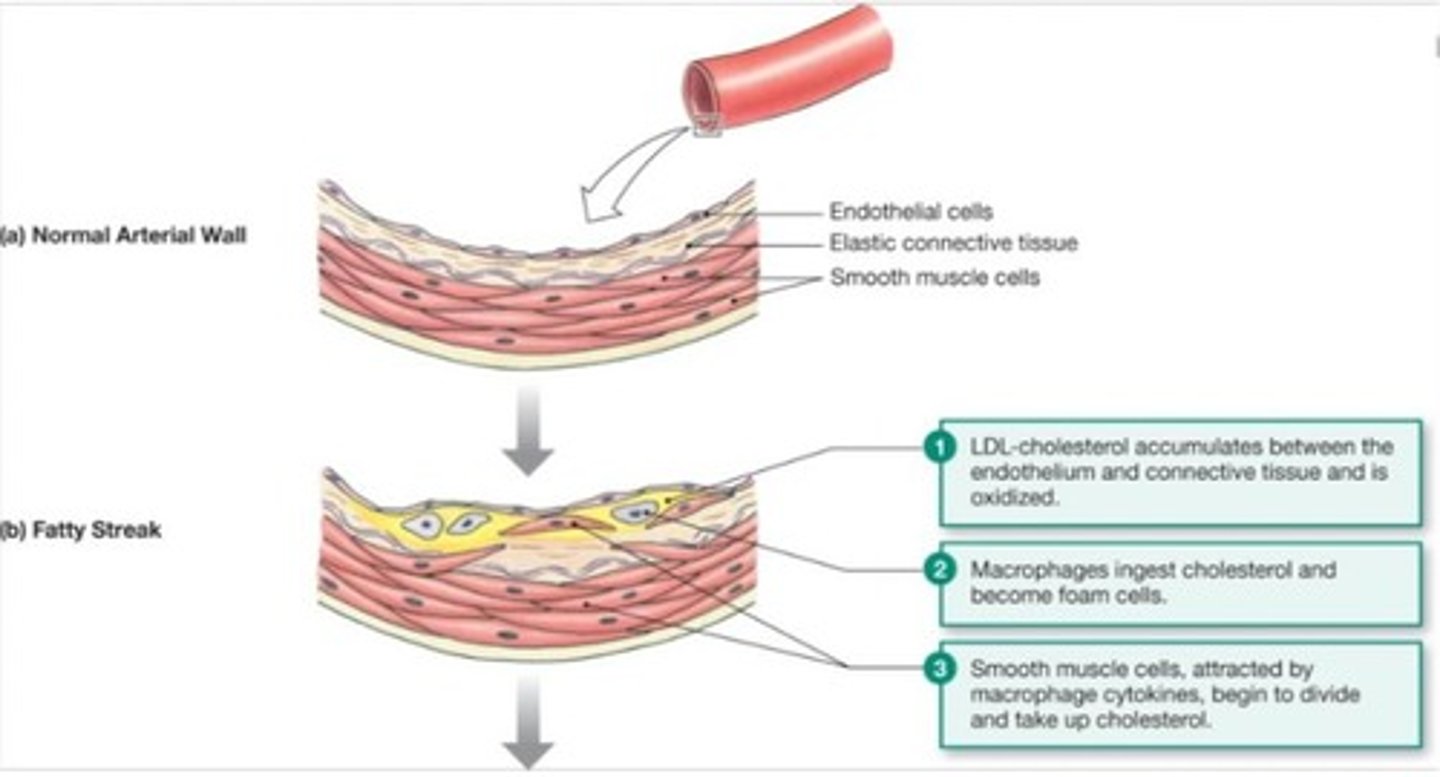
What is the role of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol?
HDL is considered 'healthy' cholesterol, while LDL is termed 'lethal' cholesterol due to its association with atherosclerosis.
What is the relationship between blood volume and blood pressure?
An increase in blood volume leads to an increase in blood pressure, while a decrease leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
What is the effect of diuretics on blood pressure?
Diuretics reduce blood pressure by decreasing blood volume.
What is the significance of capillary filtration pressure?
Capillary filtration pressure (P_H) is responsible for pushing fluid out of capillaries.
What is the role of colloid osmotic pressure in capillary absorption?
Colloid osmotic pressure draws fluid into the capillaries due to the presence of proteins in the blood.
What happens during congestive heart failure?
There is a mismatch in pumping between the right and left ventricles, leading to pulmonary edema.
What is the impact of sympathetic stimulation on heart function?
Sympathetic stimulation increases heart rate and contractility.
What is the consequence of decreased ventricular compliance?
Decreased compliance results in reduced filling during diastole and decreased stroke volume.
How does hypoxia affect coronary blood flow?
Hypoxia causes myocardial cells to release adenosine, leading to dilation of coronary arteries.
What is the relationship between metabolic need and blood distribution?
Blood distribution varies according to the metabolic needs of individual tissues.
What is the effect of vasodilation on heart rate and cardiac output?
Vasodilation can lead to a decrease in cardiac output and heart rate.
What is the primary function of capillaries?
Capillaries facilitate the exchange of materials between blood and interstitial fluid.
What is the significance of capillary density?
Capillary density is related to the metabolic activity of cells, with more active tissues having higher density.
What is the role of the basal lamina in capillaries?
The basal lamina supports the single layer of endothelial cells in capillaries.
What is the consequence of increased total peripheral resistance (TPR)?
Increased TPR can lead to elevated blood pressure.
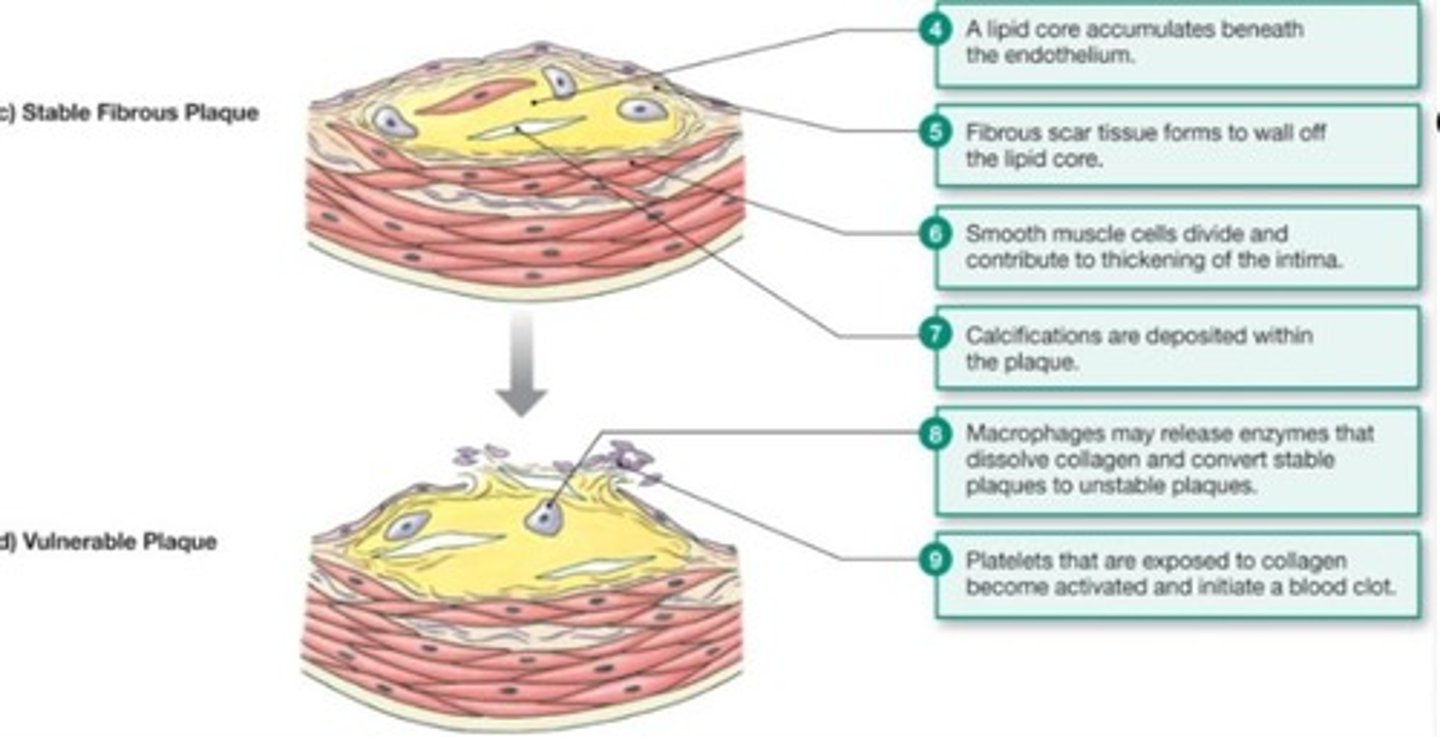
What is the primary cause of atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is primarily caused by an inflammatory process associated with increased blood cholesterol and triglycerides.