2.6.2: Demand-side policies
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are demand-side policies used to achieve and how?
Macroeconomic objectives by influencing the level of aggregate demand within the economy
What is Fiscal policy?
Is conducted by the government and involves changing the levels of government spending and taxation to affect the level of aggregate demand
What do the main areas of government spending include?
grants, public goods & services, pensions, education, national defence
What is a budget deficit?
When the governnment spends more than it has collected in tax revenue
How are budget deficits funded?
by borrowing adding up over time to form the national debt
What is a budget surplus?
When the government spends less than it has collected in taxatrion
Draw a diagram of the cyclical budgetary position

What is a government’s fiscal stance?
Whether it aims to increase or decrease aggregate demand
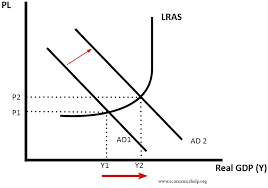
What does expansionary fiscal policy involve?
government spending exceeding taxation reciepts, would run a budget deficit to boost AD
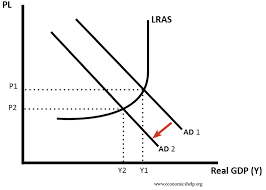
What does contractionary fiscal policy involve?
taxation reciepts exceeding gov spending, runs budget surplus to supress AD
What is a direct tax?
Taxes levied on the income of an individual or organisation and paid directly to HMRC
What is an indirect tax?
Taxes on expenditure levied on goods & services and bourne by producers, producers may pass on to consumers in form of higher prices
How do lower direct taxes affect AD?
raises disposable income of households/raises retained profits of firms, consumption and investment can increase, boost AD
How do lower indirect taxes affect AD?
lowers higher costs passed on by producers on goods & services passed onto consumers, raises discretionary income for households, boosts spending power, boosts AD. If indirect taxes aren’t passed onto consumers but absorbed as firm’s costs, it will increase their retained profits, used for investment, boost AD.
Draw a diagram of the effect of expansionary fiscal policy
draw a diagram of the effect of a contractionary fiscal policy
Examples of fiscal policy
Reduction in income tax
reduction in corporation tax
reduction in VAT
higher gov spending
how to evaluate fiscal policy
Time lags: tax changes take a year to take effect, large scale infastructure projects take 25+ years to complete
Crowding out: expansionary fiscal policy requires borrowing to fund gap between spending and taxation, increase loan costs, reduces private sector spending, limits magnitude of policy outcome
Size of the multiplier: Limits effect of fiscal policy
Ceteris Paribus: stage of economic cycle, spare capacit, output gap size, consumer confidence, MPC of the recipients of tax cut
Assumptions: Classical economists argue that because all markets clear then gov changes to AD only affect RGDP & unemployment in shortrun. Keynesians believe in existence of money illusions & that wages are sticky downwards such that the economy can remain below full capacity without gov intervention
What is monetary policy
Is conducted by the monetary policy comitteee of the Bank of England and involves the use of monetary instruments such as interest rates and the money supply to affect AD
What is loose monetary policy
When the aim is to boost AD
What is tight monetary policy
When the aim is to reduce AD
What is an interest rate
The cost of borrowing and the reward for saving
What is the base rate
It is the most influential interest rate in the entire economy which determines the level of interest that banks decide to pay to its savers and to charge to its borrowers
What is a spread
The difference between the rate that a bank borrows and the rate which they charge
What does a change in the base rate affect
retail bank rates
asset prices
confidence & expectation falls
exchange rate (hot money flows)
How do higher interest rates affect the demand for credit
Increases cost of borrowing,reduces demand for goods purchased using credit, fall in consumption, fall in AD
How do lower interest rates affect the housing market
decreases cost of borrowing a mortgage to buy property, can encourage first-time buyers/attract people to trade up the housing ladder, increases demand for new homes as well as consumer durables used in property/other related services, increases AD
How does higher demand for property from lower interest rates affect the wealth effect.
higher demand for property increases average house price, increases personal household wealth, generates positive wealth effect, increased notional demand
How do higher interest rates affect discretionary incomes of mortgage payers
reduces discretionary income of variable rate mortgaeg payers, reduces their purcasing power, lowers consumptions, lowers AD
How do interest rates changing affect consumer confidence
lower interest rates indicates MPC may me trying to avoid recession which might boost confidence & consumer spending, boosts AD
Lower rates may signal an econoic slowdown causing confidence to fall
how do higher interst rates affect savings
increases reward for saving, increases opportunity cost of spending, spending falls, edmand or goods & services fall, AD falls
How do lower interest rates affect the demand for credit
Lowers rate of borrowing for firms which increases the profitability of some investment projects at the margin, increases demand for capital goods for projects funded by borrowing to boost AD
How do lower interest rates affect business expectations
it indicates to firms that consumer spending is likely to rise in the future, improves firms optimism, shifts out MEC curve, increases investment, boosts AD
How do higher interest rates affect the exchange rate effect
increases attractiveness of the UK to international savers, generates hot money inflows which increases demand for sterling, increases strength of pound, Uk exports become more expensive & imports becomes cheaper, reduces net exports, lowers AD
What may cause the use of QE
credit crunch: sudden reduction in the general availability of loans/tightening of the conditions required to borrow
liquidity trap: saving rates remain stubbornly high, despite low-interest rates, driven by a lack of confidence on behalf of consumers and firms
Zero-lower bound: interest rates are so low that any further reduction is no longer possible or will have no real impact on the level of lending and borrowing
What is QE
The process of the central bank buying financial assets such as previously issued bonds and guilts in exchange for newly created electronic money with the purpose of injecting liquidity into the financial system to facilitate increased borrowing and lending in the economy.
how does QE affect the economy
MPC of bank of England purchases financial assets (mostly gov bonds) using newly created electronic money, this increases the asset’s price and and reduces their yield, encourages sellers of the financial assets to use the money they recieve from the Bank to switch into other financial assets in pursuit of greater returns.
How does QE affect consumers
Houhseolds which owns bonds/shares enjoy a higher asset price, increases their wealth and sense of financial security, the positive wealth effect causes higher consumer confidence, increases consumption
How does QE affect firms
firms find it easier and cheaper to borrow from high street banks that have additional funds to lend from the money saved by those who have sold their higher financial assets. When bank of England purhases existing private sector bonds this increases liquidity within capital markets making it easier for companies to issue and sell new bonds to raise money for investment, boosts AD.
How does QE affect Net-exports
injection of new electronic money into financial system raises edmand for financial assets, causes their yeilds to fall, lowers interest rates, outflow of hot money from international savers, increases suppply on currency into FOREX, currency depreciates, exports cheaper and imports more expensive, increases net-exports, boosts AD
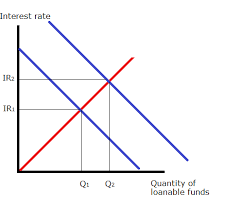
Draw a diagram modelling the impact of QE on the market for loanable funds
Injection of newly created electronic money by MPC increases supply of money (S1-S2)
Reduces interest rate (R1-R2)
Reduces cost of borrowing and prompt greater spending by consuemrs & firms
What is quantitative tightening
When Bank of England sells the financial assets previously purchased, reducing money supply, interest rates increase, increase cost of borrowing and increase reward for saving, consumption falls, AD falls
How can monetary policy be evaluated
A blunt instrument: It relies upon the confidence of the private sector and its willingness to borrow or spend
Lack of lending/higher reserve to asset ratio: QE is less effective if banks try to repair their finances and reduce their leverage instead of lending to the priavet sector. Households also may prefer to pay back accured debt rather than taking on more debt
Conflicting objectives: lowering bank rate may cause inflation
Time lags: there is an immediate rise in the interest rates by high street banks in response to a rise in the base rate but a delay in banks responding to a fall in the base rate.
Keynesians vs classical economists argument for speed for adjustment of demand side policies
Keynesians say economy may take decades to return to long-run equilibrium and the social harm suffered in the meantimes means the gov needs to actively use demand-side policies to stimulate the economy
Classical economists argue that failure to return to full employment equilibrium is caused by supply-side problems and demand-side policies will have no long-term effect when the economy is stagnant
Keynesians vs classical economists arguement for conflicting objectives of demand side policies
Keynesians argue that both expansionary fiscal policy and looser monetary policy approach should be used to get the economy back to growth
Cliasscal economists say use looser monetary policy but contractionary fiscal policy because fiscal deficits willl add to the national debts and the repayments of it in the future will cause more significant problems than in the short term boost to AD would overcome