atomic sturtcure - maths
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
how to calculate relative atomic mass
how to calculate unknow relative abundance
assign one realtiev abundance as x
Assign other relative abundance as 100 - x
If we are given one reactive abundance and are asked to deduce the other relative abundances
If the two relative abundances sum to 100%, then we can solve the equation by letting one relative abundance be x, and letting the other relative abundance be 100-x
If we are given one reactive abundance and are asked to deduce the other relative abundances
Return to our equation of relative atomic mass
Substitute out unknown values in
Plug in the relative atomic mass of one substance (given in the question)
Solve to find x
Multiply both espressions by 100
Expand brackets
Collect like terms
Rearrange to find x
speed and kinetic energy
The higher an object’s speed, the higher kinetic energy
speed mass and kinetic energy
For a given mass, the higher an object’s speed, the higher its kinetic energy
State the formula for kinetic energy.
Mass = kg
V = m/s-1
Ke = Joules
rearranging kinetic enegry formual
Write the equation for calculating the mass from kinetic energy, distance, and time of flight.
M = kg
Ke = J
Time = s
Distance = m
practice rearranging equation
pratice rearranging equaiton
four stages of a mass spectrometer.
Ionisation
Acceleration
Ion drift
Detection
ionisation/electron impact
One way of ionising an atom is to fire an electron gun at it, knocking out electrons, and therefore creating a positive ion.
Acceleration
The positively-charged ions accelerate to a plate carrying a negative electrical charge.
The ions all get the same kinetic energy, regardless of their mass
ion drift and detection
The ions are drift a known distance (ion drift)
When the ions reach the end of their flight tube they hit a metal plate called a detector.
At this point, the 1+ ions each gain an electron from the detector.
This movement of electrons is an electrical current, which is then recorded by a computer.
what happens after detection
After ions are detected by the mass spectrometer, the computer produces a mass spectrum.
mass spectutrum - what does the hieght represent
The mass spectrum tell us the abundances of each atom in the sample
The hight of eahc bar on a mass spectrum shows us relative abundance. E.g in this graph ½ our sample if helium -4 so the bar goes up to 50%
The x axis label of a mass spectrum is…mass to charge ratio. Charge = lower case z. So mass to charge ratio can also be represented as m/z ratio
Assumption to make in the exam about mass spectuturm
In your exam you can assume that the ma/z ratio is the mass number
For example, an ion with a mass to charge ratio of 20
E.g an ion with a mass to charge ratio of 20 has a mass number of 20
In the exam you might be asked to predict an ions time of flight based on the ions mass and the mass and time of flight of another ion. The question will say the two ion have the same kinetic energy and went down the same flight tube. What equation do you use to answer this question?
Rearrange the formula
Substitute in the values
Noe we don't need to use kg here because whatever unit we use it gets cancelled out anyway
Evaluate
describe electronspray ionisation to represent electronspray ionisation

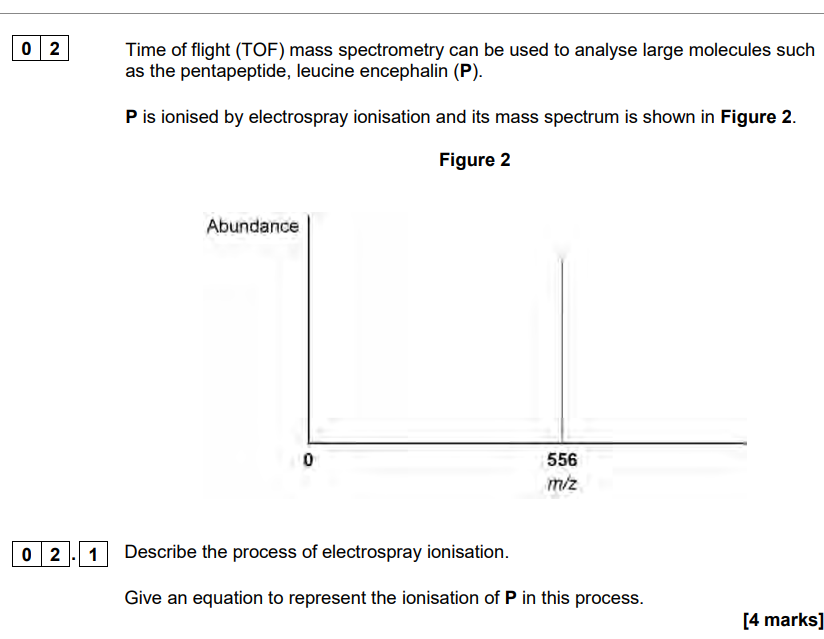
electrospray ionisatiom
