Neuro History and Physical
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
myelopathy, radiculopathy, neuropathy, myopathy
Localizing the Lesion
-An issue within the spinal cord itself would result in a ____________
-An injury to the nerve root would cause a _____________
-A peripheral nerve injury is also known as a ___________
-Problem with the muscle is known as a __________
deficits, localize, pathologic, location
Process of Developing a Neurologic Diagnosis
-Define the ________ → describe the functional impairments on the patient’s neurological exam
-________ the lesion → identify a location(s) that accounts for as many deficits as possible
-Identify → the __________ condition that accounts for the _________ and progression of her symptoms
attention, language, thought
Mental Status Examination: Components
-__________/concentration
-Memory
-____________
-Executive function
-_______ content and processes
-Praxis
Orientation
What are you assessing by asking these questions?
-Can you tell me your name?
-Can you tell me where we are?
-Can you tell me the day, month, and year, date of the week, season?
-Can you tell me why you are here?
Attention and concentration
What are you assessing by asking these questions?
-Are you losing track of thoughts?
-Can you follow a conversation?
-Do you get distracted easily?
-Can you follow a TV show or movie?
brainstem, digit, subtractions, months
Attention and Concentration
-What does poor attention mean → _________ lesions, toxic-metabolic encephalopathy, or nonspecific
-What to test → _____ span forward, reverse digit span, serial _____________, Go-No-Go testing, spell "WORLD” backward, and _______ forward and backward
Memory
What do these questions assess for?
-Do you forget names easily?
-Do you misplace objects?
-Do you find yourself repeating questions or conversations?
-Are you using more reminders?
-Are you missing appointments?
-Do you have any delinquent bills?
blurred, limbic, recall, family
Memory Function
-What does impaired memory mean → immediate could be _________ with poor attention, and delayed could indicate damage to _____ structures
-What to test → 3-5 object ______ after 3-5 minutes, tell them a simple two sentence story and ask them to repeat the gist of it, ask how they got to the hospital or what they did (requires ______ to validate)
Language
What are these questions assessing the function of?
-Word finding difficulties?
-Word mispronunciations?
-Issues with comprehension?
-Reduced speech?
-Loss of word meaning?
fluent, command, repetition, generation
Tests for Language Function
-_____ speech? → paraphrasic errors, prosody, word content
-Comprehension → issue a written or verbal ________
-____________ → “No ifs and or buts”
-Naming → confrontational and word ____________
-Reading and writing
Broca’s Aphasia
Nonfluent, expressive
-Unable to produce speech but can comprehend and follow commands
-Poor naming and poor repetition
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Fluent, receptive
-Able to produce speech but often void of meaning, inappropriate word substitutions and cannot repeat or follow commands
-The patient can speak, but they probably won’t make any sense
Global Aphasia
Poor comprehension and speech production
-See in dominant L MCA stroke
Dysarthria
Slurred speech due to weakness of muscles involved in speech
fluent, thiamine, global, nonverbal, decreased
Important Causes of Aphasia
-Wernicke’s Encephalopathy → ______ aphasia (receptive aphasia), gait ataxia, ophthalmoplegia due to __________ deficiency
-Dominant hemisphere MCA stroke → often _______ aphasia but may be expressive/receptive or mixed picture
-Nondominant hemisphere MCA stroke → decrease prosody, rhythm of speech and loss of _________ aspects of communication
-PPA or FTD variants → can cause insidious onset of ___________ speech production
Executive Function
What are these questions investigating?
-Issues with decision making?
-Able to make decisions?
-Prepare meals?
-Do laundry?
-Decrease in complex tasks previously able to do?
skilled, deficit, mimic, comb, dominant, parietal
Cortical Deficits: Apraxia
-Inability to perform _________ action that is not caused by a motor or sensory ______
-Ask the patient to _______ a complex motion like brushing your teeth, ____ your hair, suck through a straw, blow out a candle, stand in the posture of a boxer ready to fight, figure 8s
-Apraxia is often due to injury to the _________ temporal and/or _______ lobe and with aphasia
hemisphere, unaware, half, clock, right, stroke
Cortical Deficits: Neglect
-Inability to recognize one ____________ of input or stimuli
“Half of the world”
________ that one side of their body belongs to themselves and will not see or be aware of ____ of their environment. May not be aware of profound motor deficits
-Exam → “Whose arm is this?”, cancellation tests, _____ drawing
-Neglect is typically associated with _____ (nondominant) parietal lesions due to _______
higher, failure, sensory, visual, finger
Cortical Deficits: Agnosia
-Disorder of ______ sensory processing resulting in ________ of recognition not due to “low level” ________ function
-Examples:
Alexia = inability to read
_______ agnosia = can’t recognize things with vision
Astereognosia = can’t tell what something is in your hand
Prosopagnosia = inability to recognize faces
______ agnosia = inability to feel things
left, right, speech, finger, contralateral, nonverbal
Basic Concepts of Cerebral Localization
-_____ hemisphere is dominant in 95% of ______ handed individuals and around 60% of left handed individuals
-Left hemispheric lesions associated with _______ changes, skilled motor actions, dyscalculia, right-left disorientation, and _______ agnosia
-Right hemispheric lesions associated with inattention to ____________ side (neglect), loss of normal prosody and __________ aspects of speech
CN I
What cranial nerve is tested by asking the patient about sense of smell and appetite or using cinnamon, coffee, or lemon?
Snellen, fovea, cones, fields, not, scotoma, homonymous, bitemporal
Optic Nerve: CN II
-Visual acuity is tested with the _________ eye chart
Test each eye independently and together
Assess the central field including the ______, area within the macula with highest resolution due to high concentration of _______
-Visual _____ by finger confrontation to assess the peripheral field of vision
-Visual field deficits tend to ___ affect visual acuity
-________ → well circumscribed region of visual loss
-___________ hemianopsia → affects the same VF in both eyes
-__________ hemianopsia → affects temporal fields in both eyes
Left oculomotor nerve
Where is the lesion here?
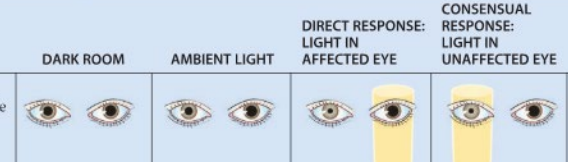
Left afferent pupillary defect
What type of defect is this?
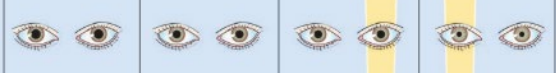
Aniscoria
different size pupils
retina, increased, disc, color, hypertension, meningitis
Fundoscopic Exam
-Visual inspection of _______, vessels, and optic disc
-Papilledema/optic disc edema indicates ___________ ICP
-Look for sharp optic _____ margins, smoothness of vessels, observe the ______ of the disc and look for hemorrhages and exudate
-Differential diagnosis → idiopathic intracranial ___________, venous thrombosis, intracranial mass lesion, hydrocephalus, __________, and optic neuritis
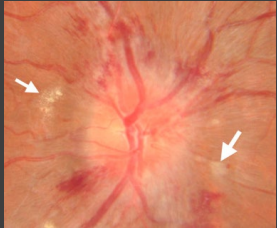
down, dilated, aneurysm, abduction
Eye Movement Abnormalities
-CNIII Palsy → “_____ and out” with _______ pupil and ptosis
Indicates and ___________ until proven otherwise
-CNIV Palsy → subtle head tilt and turn
-CN VI Palsy → estotropia of eye with limited ___________ of affected eye
sensory, motor, sharp, neuropathies
CN V: Trigeminal Nerve
-Chiefly _______ nerve for face with three divisions
-Also supplies ______ innervation to the masseter and temporalis
-Assess with light touch, ______ dull discrimination in all three divisions bilaterally
-Most trigeminal __________/disorders have subjective symptoms only
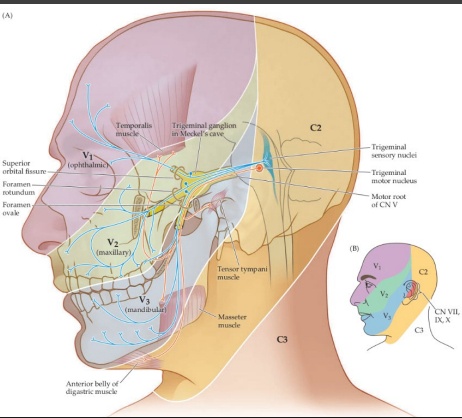
ipsilateral, expression, elevation, raise
CV VII: Facial Nerve
-Each facial nerve controls ___________ control of muscles of facial ___________
-Not involved in eyelid __________
-Bell palsy vs CNS pattern of facial weakness → ability to _____ eyebrows is spared in strokes
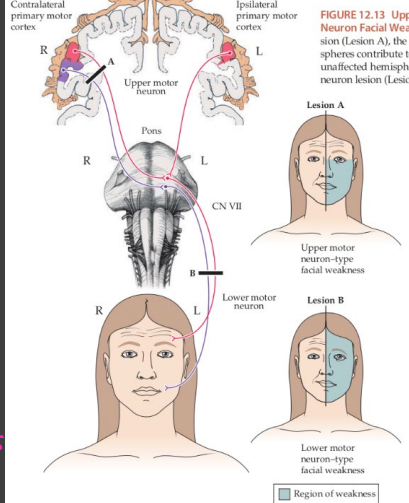
relaxed, no, brisk, CNV, efferent, cornea, closure, afferent, efferent
CN V and VII
-Jaw Jerk → gently tap on chin with mouth ________ and somewhat open. There should be __ response but _____ closure of the mouth indicates a “hyperactive jaw jerk”. Assesses the integrity of ___ which is both afferent and efferent
-Corneal reflex → gently stroke the _______ with wisp of cotton observing for ________ of eyelid. Assesses integrity of CN V (_______), CN VII (_______), and higher centers that modulate the reflex
hearing, closed
CN VIII: Vestibulocochlear Nerve
-Test ________ with finger rustle bilaterally with eyes _______
Peripheral
What type of vertigo is being described?
-Nystagmus: unidirectional, nearly always horizontal, often habituates
-Often associated with tinnitus and hearing loss
Central
What type of vertigo is being described?
-Nystagmus: changes direction with gaze, may be horizontal, vertical, or torsional, does not habituate
-Often associated with other neuro findings of limb ataxia or motor issues
BPPV, Meniere’s, neuritis, hemorrhage
Evaluation of Dizziness: Temporal Features
-Recurrent episodes of positionally provoked vertigo last seconds to minutes → ____
-Recurrent episodes of unprovoked vertigo lasting hours → _______’_ disease or migrainous phenomena
-Single prolonged attack of vertigo without marked neurologic deficit → vestibular _______/labyrinthitis
-Single attack of sudden vertigo associated with ataxia, weakness, nystagmus → vertebrobasilar ischemia/brainstem or cerebellar infarct or ___________
nystagmus, Romberg, dorsal, central, low
Evaluation of Dizziness: Physical Exam
-Cranial nerve exam with thorough EOM exam, looking for __________ and its character
-_________ assess ______ column sensory function and vestibular function
-Limb and gait exam → _______ lesions associated with weakness or ataxia
-Orthostatic BP → ____ BP important cause of “dizziness”
brainstem, speech, swallowing, speech, tongue
Bulbar Exam
-Bulbar muscles are innervated by CN IX, X, XII that leave the _________ at the medulla and are involved in ________ and swallowing
-IX: stylopharyngeus → elevated pharynx and larynx to facilitate __________
-X: pharyngeal muscles which control ___________ and laryngeal muscles which produce ________, also elevates soft palate controls upper portions of esophagus
-XII: intrinsic muscles of the ________
trapezius, ipsilateral, away
CN XI: Spinal Accessory Nerve
-Controls sternocleidomastoid and _________
-Causes weakness of __________ shoulder shrug and weakness turning head ______ from lesion
voluntary, horizontal, against, only, active, normal, relax, ROM
Motor Exam Components
-Strength or power: Graded 0-5
0 = no ______ movement
1 = flicker but no productive movement of the limb
2 = can move limb in the __________ plane but not ______ gravity
3 = can hold limb against gravity _____
4 = can hold limb against some _____ resistance
5 = _______ strength against examiner
-Muscle Tone and Bulk
Encourage patient to _____ and examine tone of limb throughout ___
no, normal, brisk, clonus, adduction
Muscle Stretch Reflexes: 0-5
-0 = __ reflex elicited
-1+ = trace reflex
-2+ = _______ reflex
-3+ = _____ or “jumpy”
-4+ = brisk with sustained ______
-Look for cross _________ and pathologic spreading
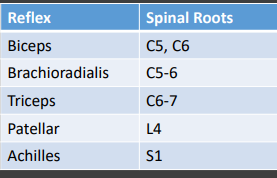
Babinski, beating
Special Reflexes
-_________ → a normal reflex in infants, shows injury to the brain or spine
-Hoffman
-Ankle clonus → _________ of the ankle as a nonspecific marker of injury in the motor center
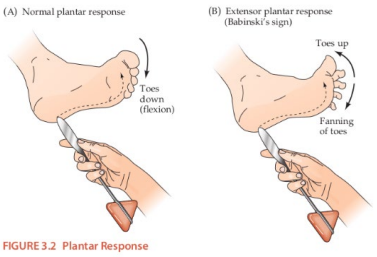
Upper
Is the upper or lower motor neuron pattern of injury being described?
-Weakness = ±
-Tone = spastic/stiff
-Atrophy = none
-Fasciculation = none
-Muscle stretch reflexes = hyperactive
-Pathologic reflexes = present (Babinski, Hoffman, etc.)
Lower
Is the upper or lower motor neuron pattern of injury being described?
-Weakness = present
-Tone = flaccid or decreased
-Atrophy = present
-Fasciculation = present
-Muscle stretch reflexes = decreased
-Pathologic reflexes = absent
dorsal, spinothalamic, cortical
Sensory Function
-JPS and vibration → ______ column function
-Sharp-dull discrimination and temperature sensation → ___________ tract
-Light touch
-_______ sensation → cortical function
numbers, objects, where, parietal
Cortical Sensation
-Graphesthesia → identify ________ drawn on palm of hand
-Stereognosis → identify ________ placed in hand
-Point localization → with patient’s eyes closed, touch their face, arm, or leg, and ask them to tell you ______ you touched them
-Extinction → perception of touch on one side of the body while also appreciate similar stimulus on other side of the body simultaneously. Indicative of _______ injury
Coordination
What do the finger to nose, finger to finger, rapid alternating movements, overshoot, and heel to shin tests look at?
stand, assistance, wide, short, drop, cortical
Truncal Coordination and Gait
-Ability to ______ from seating chair without ____________ from hands, ability to stand or walk on heels and toes
-Look for ____ based gait (ataxic gait due to cerebellar disease), ______ choppy shuffling steps (parkinsonian gait), look for weakness or spasticity (UMN lesion), foot ____ (steppage gait from LMN lesion)
-Look for decreased arm swing (Parkinson’s), _______ posturing (cerebral palsy, stroke, UMN lesion)
-Stress their cerebellar function with tandem gait exam/heel-toe walking
ipsilateral, double
Localization of Cerebellar Lesions
-Cerebellar lesions usually cause ____________ ataxia due to “______ decussation”
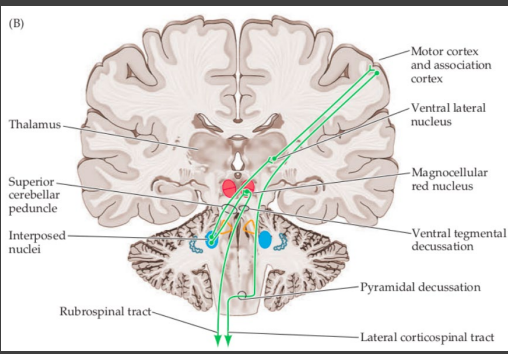
cerebellar, sides, station, sensory
Romberg Testing
-Standing/walking is a highly integrated function mediated by visual, vestibular, sensory, ____________ and motor functions
-Have patient stand with arms at _____, feet together and have them close their eyes
-Breaking _______ means vestibular or _______ dysfunction