TherapyEd - neuro terminology, CVA, TBI
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
agnosia
inability to recognize familiar objects w/ 1 form of sensation
akinesia
inability to initiate movement (found in PD)
apraxia
inability to perform previously learned movements despite no loss of strength, coordination, sensation, or comprehension
ideational apraxia
ideomotor apraxia
ideational apraxia
impaired concept of how to do a routine task (unable to sequence steps)
ideomotor apraxia
understands the concept of how to do a routine task but unable to execute the right action on command
astereognosis
inability to recognize objects by touch alone
damaged somatosensory association cortex
asynergia
inability to move mms together in a coordinated manner, associated w/ cerebellar dysfunction
ataxia
uncoordinated movement, esp. gait
athetosis
slow, involuntary, worm-like, writhing motions
causalgia
painful burning sensation, often associated w/ CRPS
chorea
rapid, involuntary, jerky movements seen in Huntington’s chorea
decerebrate rigidity
involuntary contraction of UE & LE extensor mms
damage to brainstem (pons) above vestibular nucleus & below red nucleus
decorticate rigidity
involuntary contraction of UE flexor mms & LE extensor mms
damage to motor tracts above red nucleus (midbrain)
dysdiadochokinesia
impaired RAM, associated w/ cerebellar dysfunction
dysmetria
inability to judge distances, associated w/ cerebellar dysfunction
hypermetria = overshooting
hypometria = undershooting
Herpes zoster (shingles)
painful inflammation of DRG d/t virus → vesicle formation along course of nerve in dermatomal pattern
Horner’s syndrome
ptosis (droopy eyelid), miosis (constricted pupil), & anhidrosis (lack of sweating) of ipsilateral face d/t damage to sympathetic tract (e.g. sympathetic chain)
somatagnosia
lack of awareness of the relationship of one’s own body parts or the body parts of others
visual acuity
sharpness of vision that generally decreases w/ age or diabetes
may need glasses, increased color contrast on walls/floors/stairs
reduced ability to adapt to very dark/bright environments
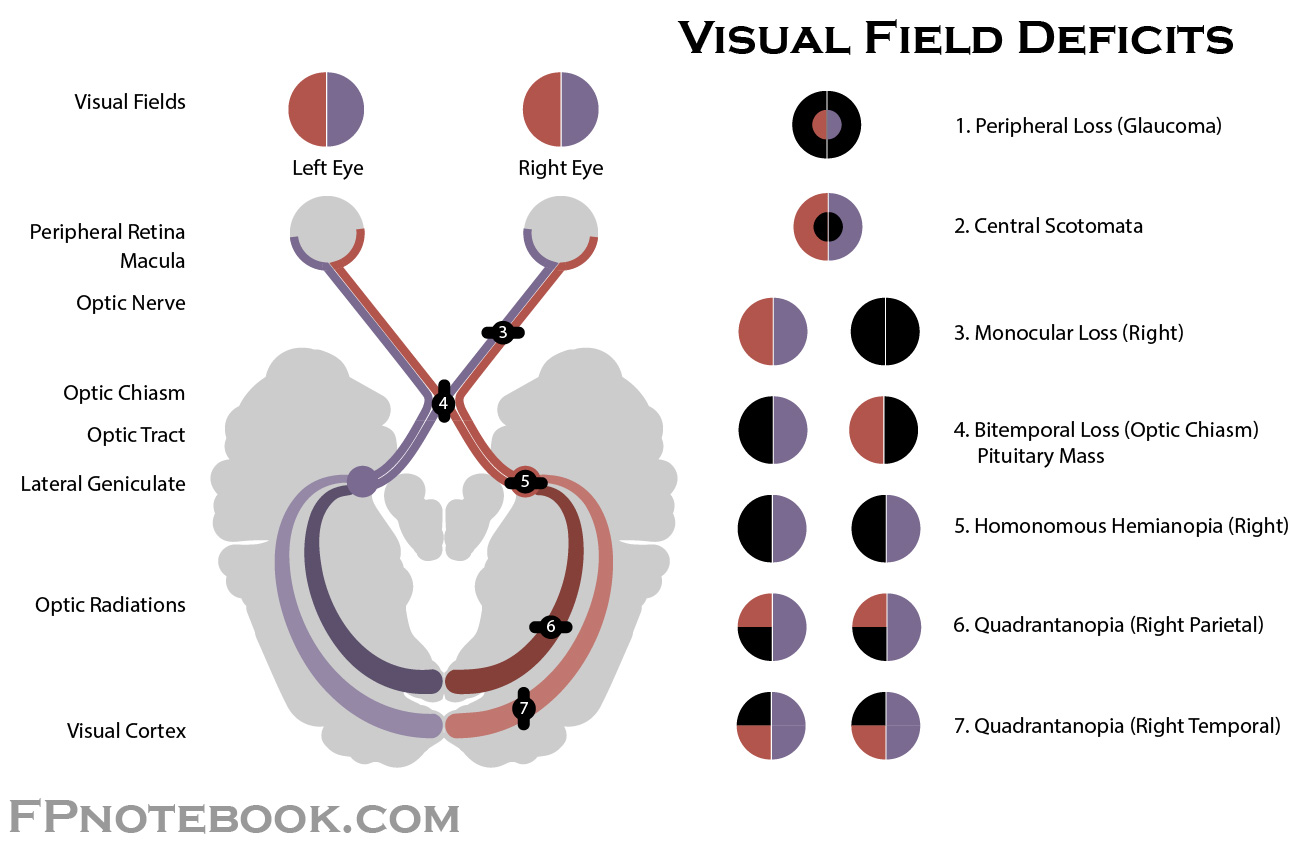
homonymous hemianopsia
deficit of either the R or L halves of the visual field
damage to contralateral optic tract
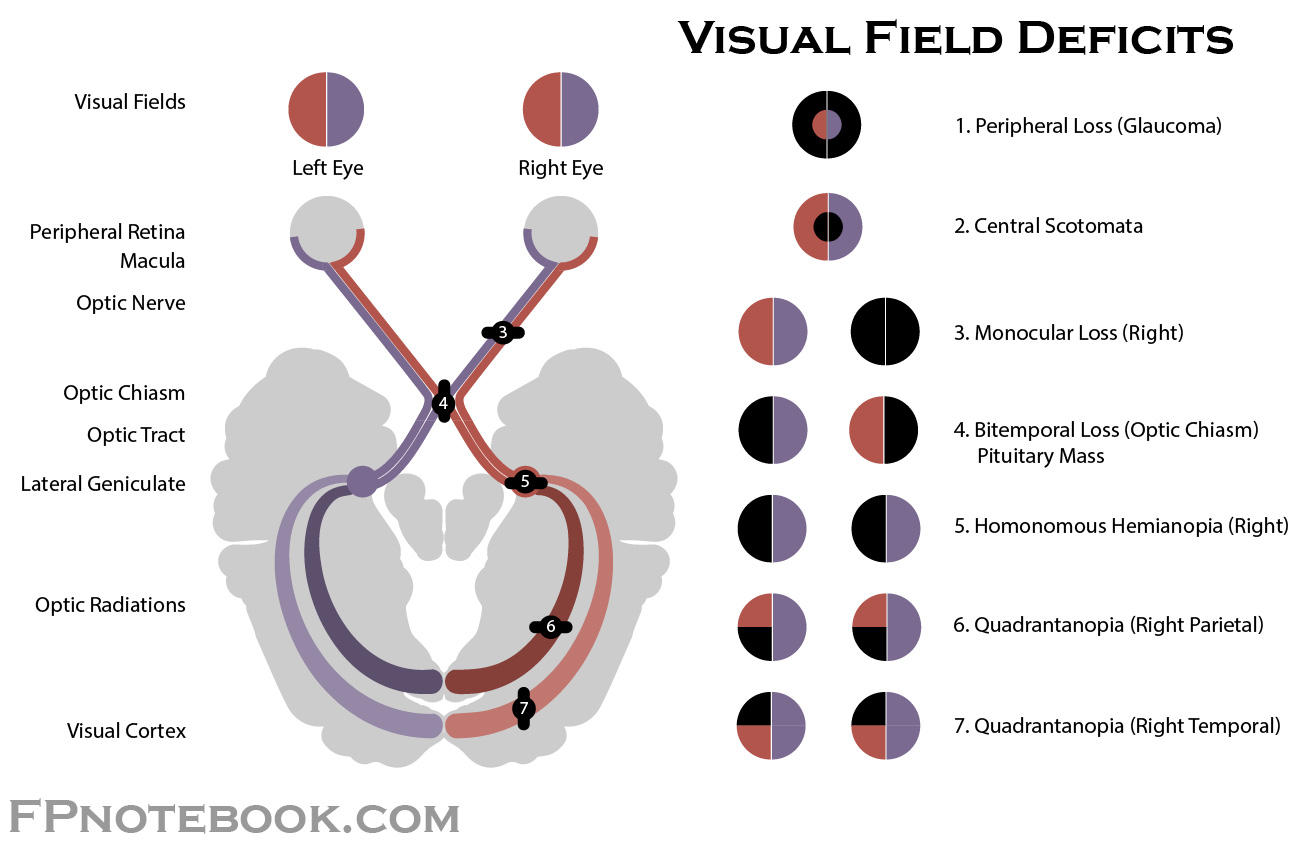
bitemporal hemianopsia
deficit of the temporal or peripheral visual fields (tunnel vision)
damage to optic chiasm
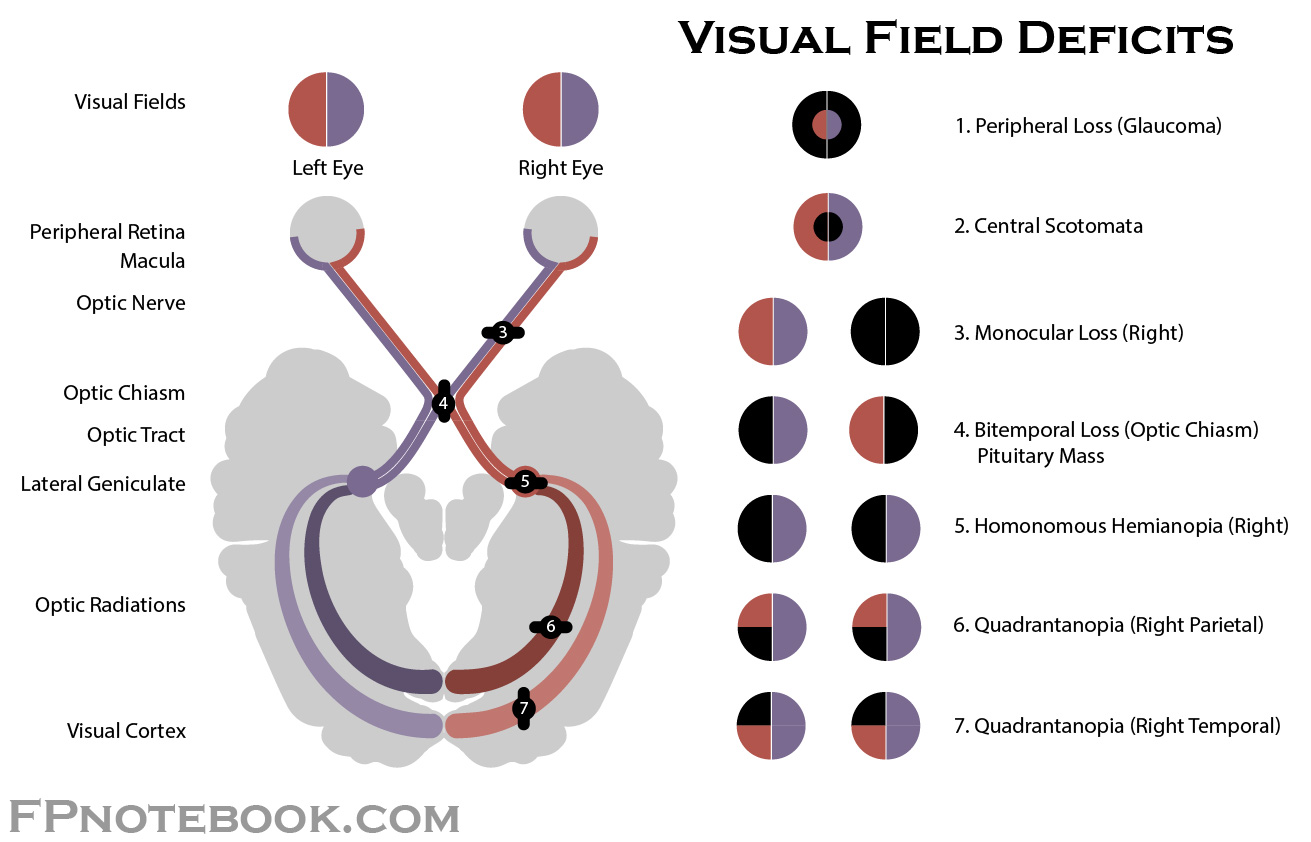
monocular blindness
blindness of one eye
damage to optic nerve
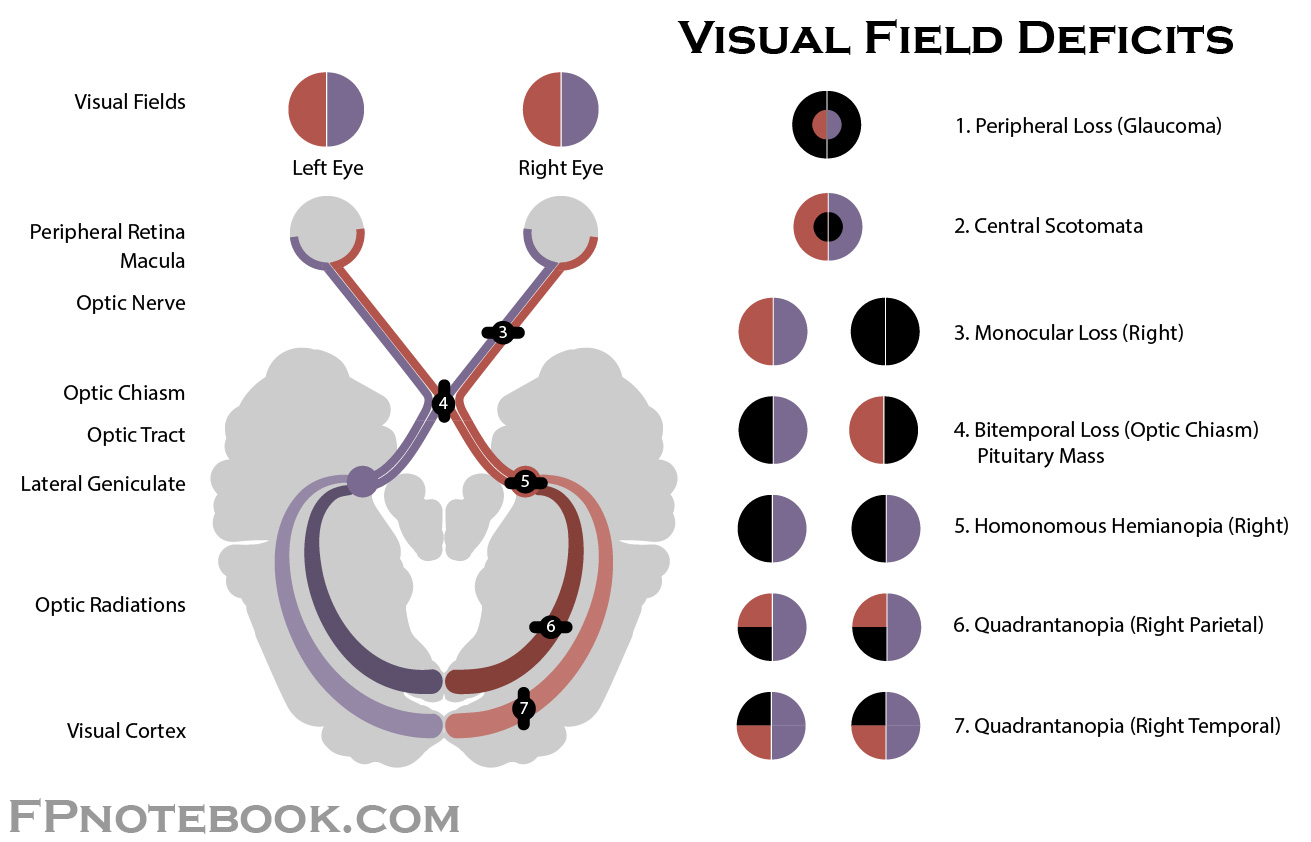
inferior quadrantanopia
pie on the floor (contralateral)
damage to parietal lobe
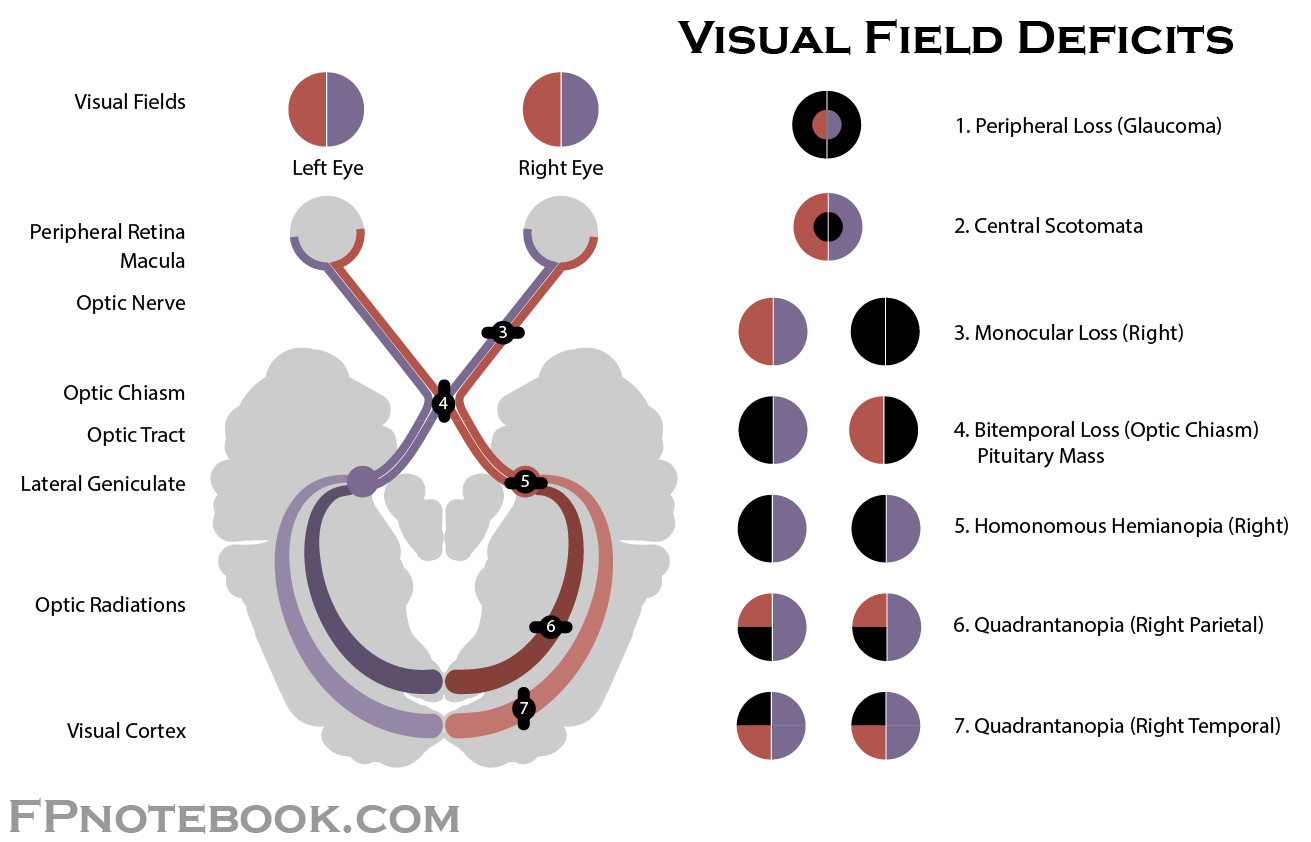
superior quadrantanopia
pie in the sky (contralateral)
damage to temporal lobe
What is the difference between ischemic & hemorrhagic stroke?
ischemic: clot blocks or impairs blood flow → depriving the brain of essential O2 & nutrients (more common)
hemorrhagic: blood vessels rupture → bleeding in or around the brain (worse prognosis)
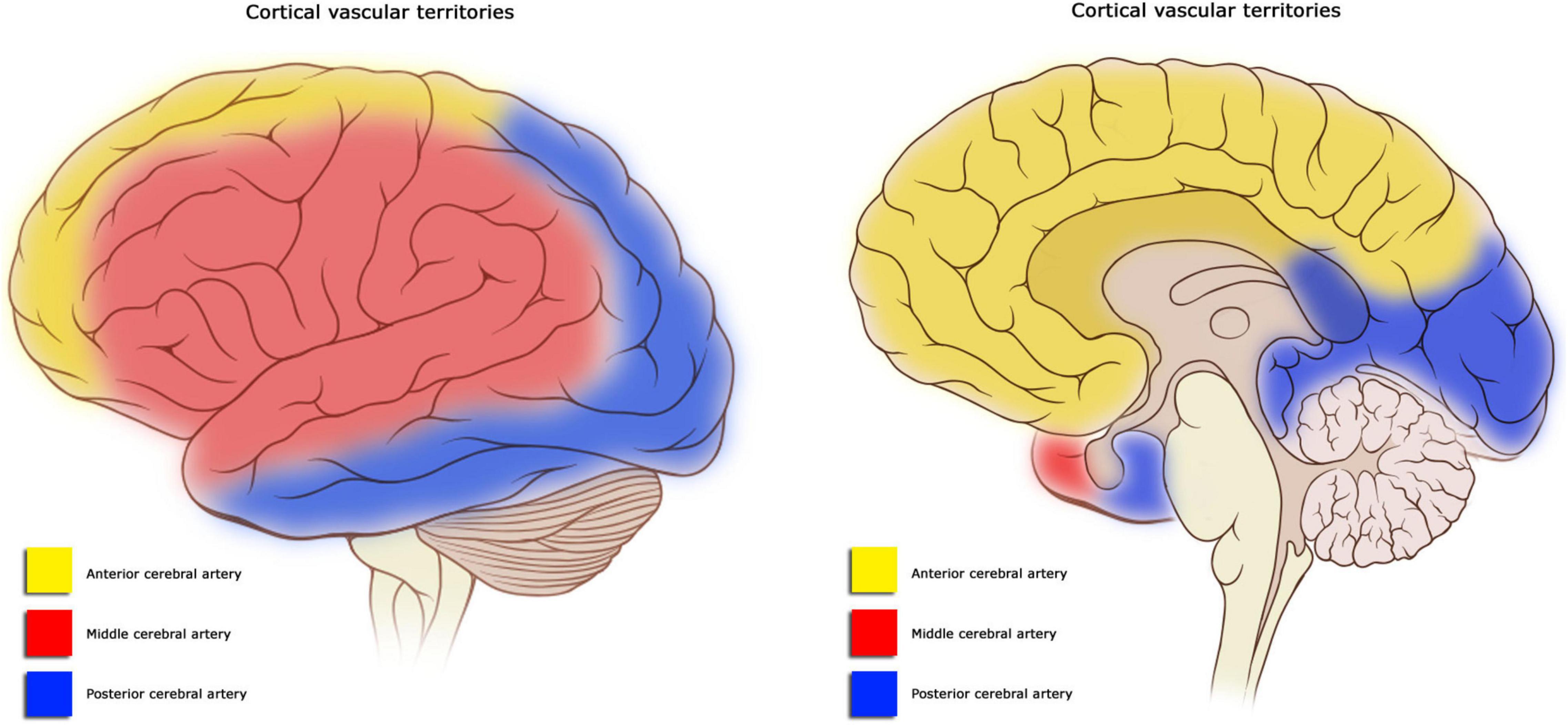
What are the effects of CVA on the middle cerebral artery (MCA)?
sensorimotor deficits in the contralateral face & UE
contralateral homonymous hemianopsia
L hemisphere → aphasia
superior division of MCA → Broca’s
inferior division of MCA → Wenicke’s
main stem of MCA → global aphasia
R hemisphere → perceptual deficits (unilateral neglect)
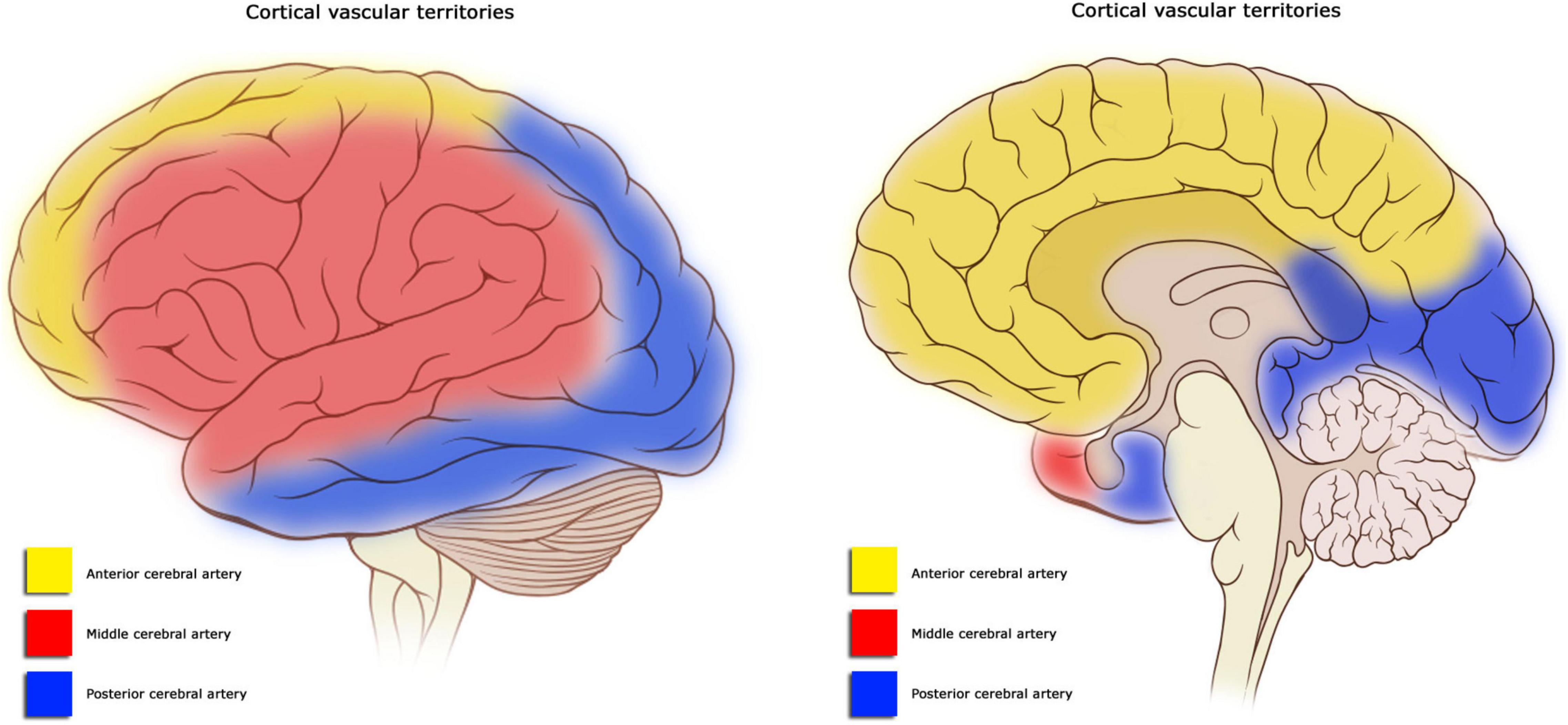
What are the effects of CVA on the anterior cerebral artery (ACA)?
sensorimotor deficits in the contralateral LE
urinary incontinence
mental impairments (confusion, amnesia, apathy, short attention span)
problems w/ imitation, bimanual tasks, apraxia
slowness, delay, motor inaction
contralateral re-emergence of grasp reflex, sucking reflex
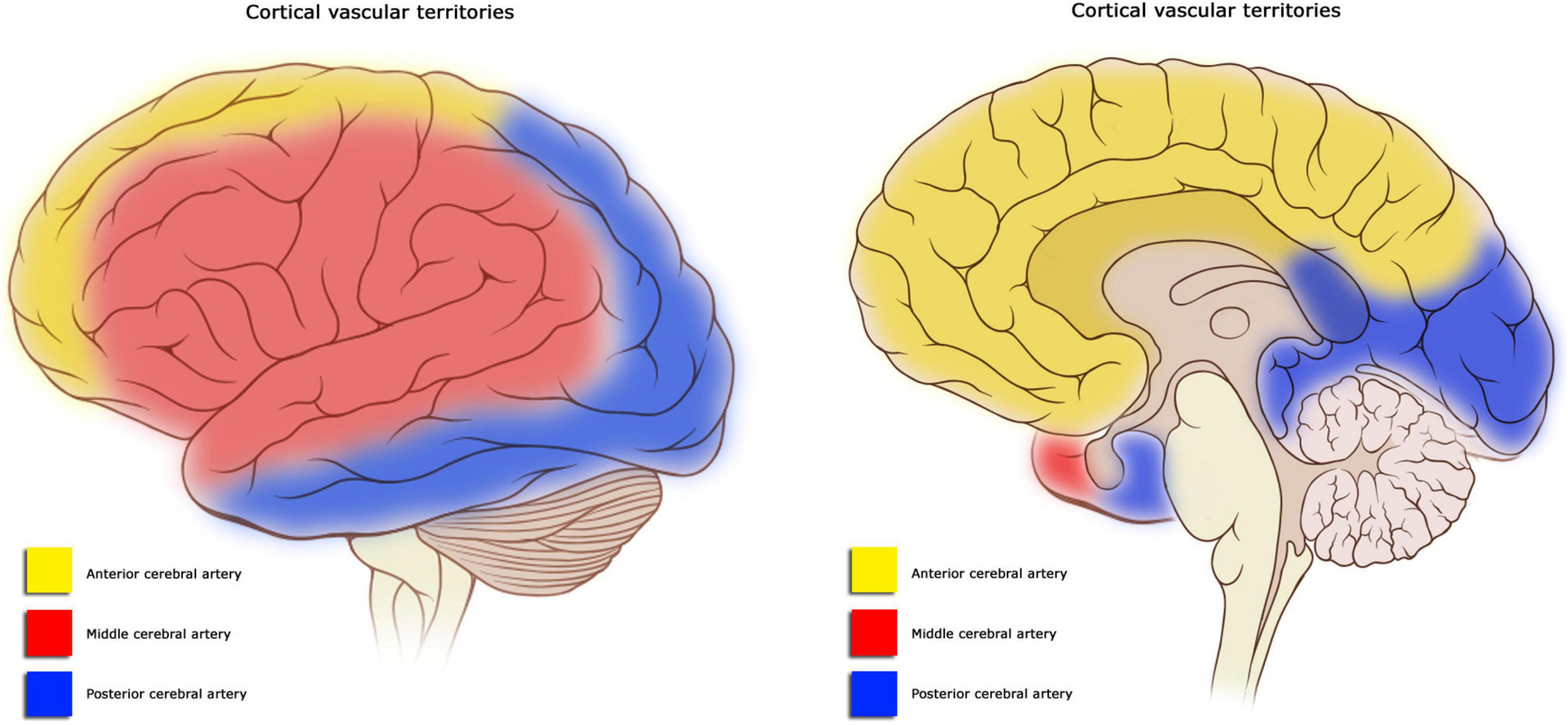
What are the effects of CVA on the posterior cerebral artery (PCA)?
contralateral homonymous hemianopsia
visual agnosia → prosopagnosia (difficulty naming familiar faces)
dyslexia w/o agraphia
difficulty w/ color discrimination
memory deficits
topographical disorientation (difficulty w/ directions)
aphasia
hemiplegia if cerebral peduncle of midbrain involved
central territory: thalamic pain syndrome
What are the effects of CVA on the vertebrobasilar artery?
often results in death from the edema
quadriparesis & bulbar palsy → locked-in syndrome (pt can only communicate by eye blinking)
vertigo, coma, diplopia, nausea, dysphagia, ataxia, CN impairments
What are the effects of CVA on the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)?
unilateral deafness
contralateral loss of pain & temperature
paresis of lateral gaze
unilateral Horner’s syndrome
ataxia, vertigo, nystagmus
What are the effects of CVA on the superior cerebellar artery (SCA)?
severe ataxia
dysarthria
dysmetria
contralateral loss of pain & temperature
What are the effects of CVA on the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)?
Wallenberg’s syndrome
nausea
vertigo
hoarseness
dysphagia
reduced sensation of ipsilateral face
reduced sensation of contralateral torso & limbs
Horner’s syndrome
What are the characteristics of hypotonicity?
How can you treat this?
low or flaccid tone
risk of joint subluxation or dislocation
hypoactive reflexes
shallow breathing
Treatment:
isometrics
quick stretching
tapping of mm belly or tendon
high-frequency vibration
light touch
quick icing
fast spinning or rolling
joint approximation for co-contraction
What are the characteristics of hypertonicity?
How can you treat this?
spastic, high tone
risk of contractures & deformity
hyperactive reflexes
decreased thoracic mobility
∆s in body positioning can affect tone
Treatment:
inhibit reflex activity via postures, positioning, or relaxation training
reciprocal inhibition (facilitation techniques to nonspastic mms)
prolonged static stretching
inhibitory casting
slow repetitive rocking or rolling
very low-frequency vibration
reflex inhibiting postures
limb movements emphasizing rotation
slow stroking
neutral warmth
prolonged icing
deep pressure to tendons
What are the perceptual problems associated with R hemisphere CVA?
L sensorimotor loss, homonymous hemianopsia
visual-perceptual deficits: L sided neglect, problems w/ spatial relationship & hand-eye coordination, difficulty w/ visual cues
irritability
short attention span, cannot retain info, difficulty learning individual steps
quick, impulsive, poor safety
rigidity of thought
difficulty w/ negative emotions
What are the perceptual problems associated with L hemisphere CVA?
R sensorimotor loss, homonymous hemianopsia
language deficits: aphasia, difficulty w/ verbal cues
apraxia
difficulty initiating & sequencing tasks
perseveration
irritability
cautious & slow
highly distractible
difficulty w/ positive emotions
What are some mobility activities to consider for a pt with CVA?
focus on using both sides of the body initially
active assisted movements
focus on bed mobility & transfers
control & stability in sitting & standing, add dynamic challenges
transfers to both sides to promote NM re-education
What are some respiratory activities to consider for a pt with CVA?
improve chest expansion w/ manual contacts, resistance, & stretch to chest wall segments
diaphragmatic breathing & coordinated breathing w/ movement
avoid Valsalva
What are some oromotor activities to consider for a pt with CVA?
establish sitting posture w/ hips well back, symmetrical WB, & feet flat on the floor
head in normal position (not extended or tipped back) to avoid aspiration or choking and promote normal swallowing
Describe the Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery
stage 1: flaccidity, no active limb movement
stage 2: beginning of minimal voluntary movement, some synergy w/ associated reactions, some spasticity
stage 3: voluntary control of movement synergy, spasticity at its peak
stage 4: some movement outside of synergy, less spasticity
stage 5: complex movement, greater selective control of movement from synergy
stage 6: individual joint movement, coordinated movement
stage 7: normal function
What is the difference between synergy & spasticity?
synergy: combined motion pattern w/ AROM
spasticity: increased tone w/ PROM, resting position, velocity-dependent
Describe the spasticity pattern
UE (chicken dance)
scapula: retraction, downward rotation
shoulder: ADD, IR, depression
elbow: flex
forearm: pronation
wrist: flex, ADD
hand: finger flex, clenched fist thumb, ADD in palm
LE (ballet dancer)
pelvis: retraction (hip hiking)
hip: ADD (scissoring), IR, ext
knee: ext
foot & ankle: PF, INV, equinovarus, toes claw (TMT ext, MTP flex), toes curl (TMT, MTP flex)
Describe both flexion & extension synergy pattern
Flexion synergy
scapula: retraction, elevation, or hyperextension
shoulder: ABD, ER
elbow: flex
forearm: supination
wrist & finger: flex (same as ext synergy)
hip: flex, ABD, ER
knee: flex
ankle: DF, INV
toe: DF
Extension synergy
scapula: protraction
shoulder: ADD, IR
elbow: ext
forearm: pronation
wrist & finger: flex (same as flex synergy)
hip: ext, ADD, IR
knee: ext
ankle: PF, INV
toe: PF
What is the Rancho Los Amigos Classification?
Response
1: no response
2: generalized response
3: localized response
Confused
4: confused & agitated
5: confused & inappropriate
6: confused & appropriate
Appropriate
7: automatic appropriate
8: purposeful appropriate
Describe RLA 1-3
How can you manage pts in these levels?
1: no response: coma
2: generalized response: non-purposeful, whole body, vocal, inconsistent response
3: localized response: purposeful, local & specific, inconsistent response; follows simple commands (close eyes, squeeze hands)
Management
head in neutral, prevent ulcer, sit if stable
gentle PROM for joint & skin integrity
postural drainage, percussion, vibration
family education on what to expect & how to be more involved
Describe RLA 4-6
How can you manage pts in these levels?
4: confused & agitated: heightened activity, coming out of coma, doesn’t cooperate, incoherent speech, confabulations (making up stories), no selective attention, no memory
5: confused & inappropriate: responds consistently to simple commands, inconsistently to complex commands, able to socialize for short period, impaired memory, inappropriate use of objects, can’t learn new task
6: confused & appropriate: responds consistently to simple commands, goal-oriented behavior w/ external input, carryover of previous skills present (self care)
Management
consistency: same therapist, same staff, family introduce themselves daily, establish a routine
orient the pt: calendar, clock
memory: no carryover, chart & graph to measure progress
agitated: calm behavior, no confronting, closed environment to prevent harm to others, give options, no yes/no or open-ended questions
Describe RLA 7-8
How can you manage pts in these levels?
7: automatic appropriate: oriented in home & hospital, daily routine but automatic & robot-like, impaired judgment, able to initiate social or recreational activity w/ structure
8: purposeful appropriate: carryover of new skills present, impaired judgment in an emergency situation, abstract reasoning, low tolerance for stress
Management
focus on re-entry to work & community
emphasize skills related to problem solving, social interaction
trial period of independent living
adaption at work or school to return to normal life