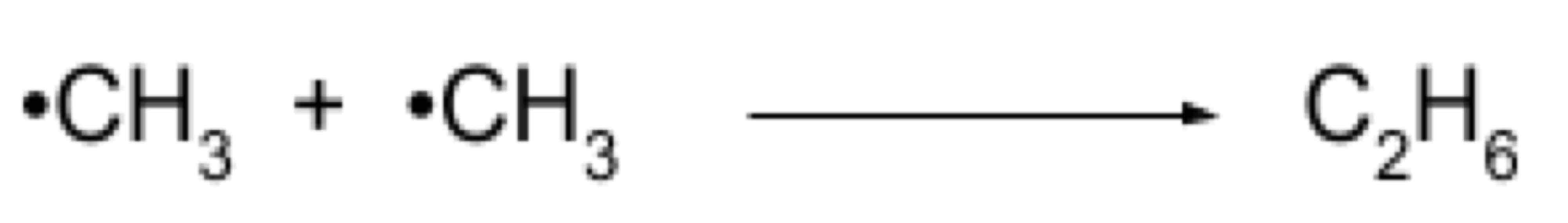3.2.4 - Chlorination Of Alkanes
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
When do alkanes react with halogens
In the presence of UV light producing Halogenoalkanes
UV light breaks down the halogens binds producing reactive intermediate (appears in the mechanism of the reaction but not in the overall balanced equation) called free radicals
Free radicals attack the alkanes resulting in a series of reactions initiation, propagation and termination
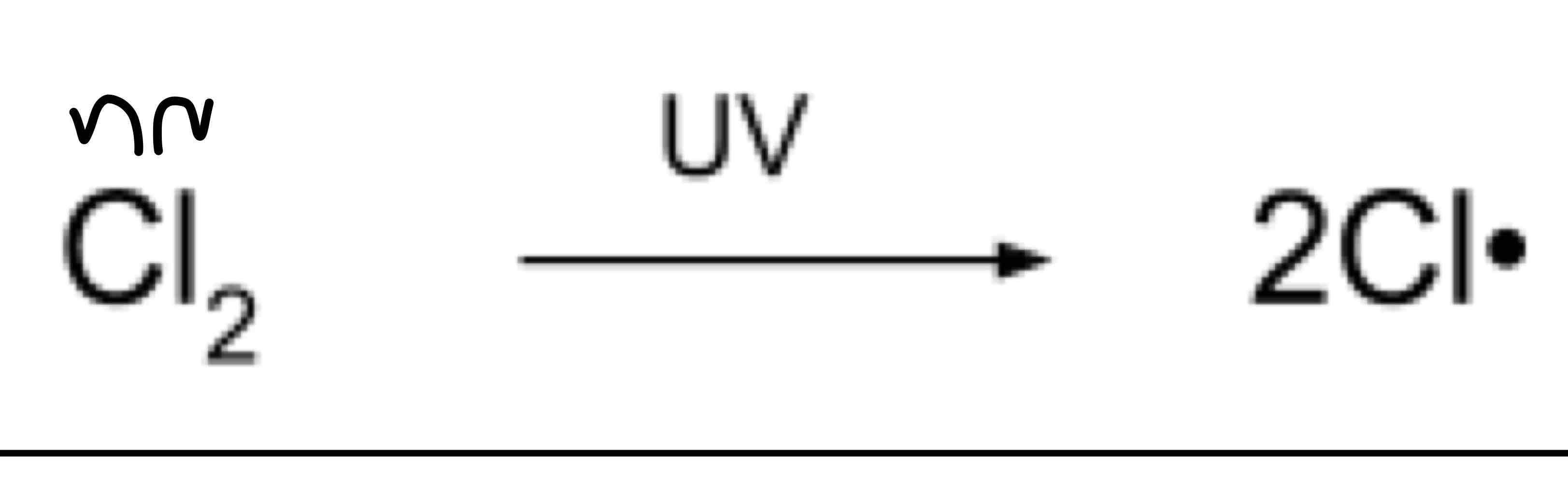
Initiation
The halogen is broken down
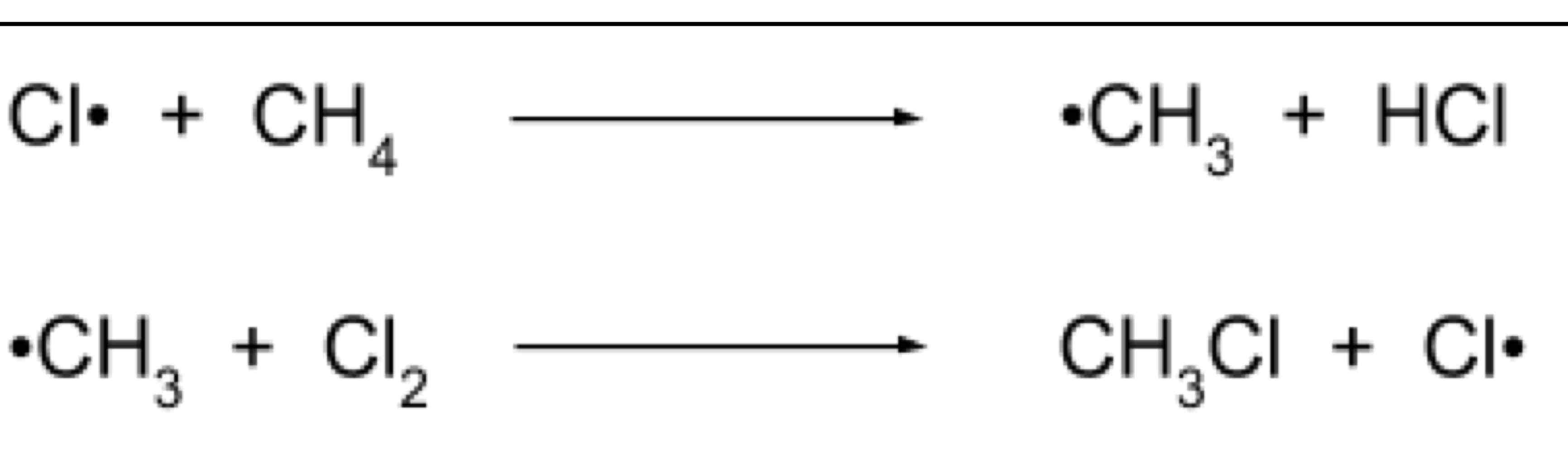
Propagation
A hydrogen is replaced and the Cl• radical reformed as a catalyst
this step can continue many times to result in multiple substitutions → this is a chain reaction
Conditions of the reaction can be altered to favour the termination step and limit the no. Of substitutions
Termination
2 radicals join to end the chain reaction forming a stable product