CS Physical computing
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Open source hardware
Open to the public to see design specification of a physical object
Open source software
Source code available to everyone without price
Digital
Digital systems are based on discrete signals
What is an analogue system based on?
Analogue systems are based on continuous signals
What is an interface?
An interface is a point which two computer systems communicate
What is an IDE?
An IDE is a software program written in an integrated development environment, for example IDLE for Python and PyCharm
What is a USB?
A USB is a universal serial bus, a serial communication protocol. It is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cable and connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply
Tell me about the features of USBs
older types of USB had asymmetric connectors, whereas USB-C has a symmetric connection which makes it easier to connect
USB-C can provide more power than previous types
Almost all modern protocols can run over USB-C which makes it more versatile
What are the two types of port?
A hardware port and a software port
What is a hardware port?
A hardware port is a connection point or interface between a computer and an external/internal hardware device
What is an internal port?
An internal port provides connections to hard drives or DVD drives
What is an external port?
An external port may connect printers, mice and other devices
What is a software port?
A software port is a virtual point where network connections start and end
these ports are software-based and managed by a computer's operating system
What is a driver?
A driver is a program that enables the communication between an OS and a hardware component or software application
What is a bootloader?
The bootloader on Arduinos is a tiny piece of software that lets you upload the code you write to the Arduino itself
What is an OS?
An OS is an operating system
What are logic gates?
Fundamental building block of digital electronics that allow computers to transform 1s and 0s from input wires into more complex operations
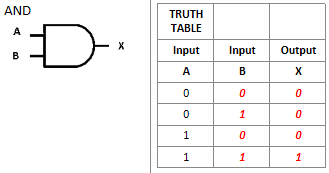
What is this logic gate?
AND logic gate, provides 1 only if both numbers are 1
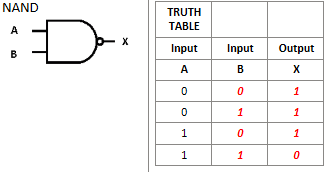
What is this logic gate?
NAND logic gate, opposite of AND gate
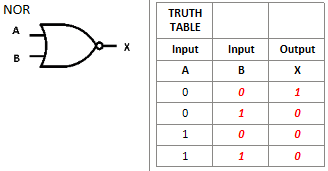
What is this logic gate?
NOR logic gate, opposite of OR logic gate
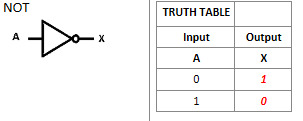
What is this logic gate?
NOT logic gate, shows 1 if input is 0
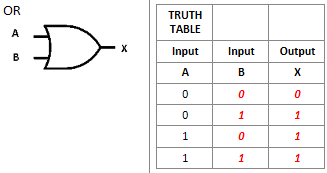
What is this logic gate?
OR logic gate, shows 1 when one of the inputs is 1
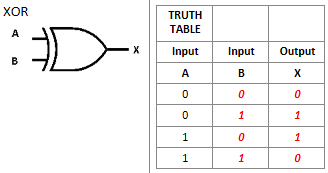
What is this logic gate?
XOR logic gate, shows 1 when ONLY one of the inputs is 1
What is a CPU?
A CPU (central processing unit) executes programs
What is a RAM?
A RAM (random-access memory) holds data and instructions that the CPU is currently using
Say what you know about microprocessors:
used in similar general purpose computers such as the ones in your phones and watches
central chip of a microprocessor has several peripheral chips for memory, input and output, timers, and interfaces
uses an operating system to control and manage multiple processes at the same time
Say what you know about microcontrollers:
tiny, single purpose computers, do one thing well
embedded inside other devices so they can control the features/actions of the product
run one specific program
low-power devices, does not use many watts of electricity
microcontrollers have a dedicated input and output device
usually small and low cost
Give examples of high level code
Python, Java, C
What are advantages of high level languages?
closer to natural language (than binary)
easier for a human to understand
source code are the instructions written in a high level language
What is the difference between the two types of low level languages?
Machine code is the set of instructions that a CPU understands directly whereas assembly language uses mnemonics: short abbreviations which correspond to a machine code instruction, easier for a programmer to understand than machine code
What is all programming ultimately converted to?
All programming is ultimately converted to machine code
What are the three types of translators?
Compilers, interpreters, assemblers
What does a compiler do?
A compiler takes the whole source code and translates it into machine code in one go. This products object code which can run unassisted at any time
What are the advantages of compilers?
Compiled programs run quickly as they’ve already been translated
A compiled program can be supplied as an executable file - a file that is ready to run
Compilers optimise code. Optimised code can run quicker and take up less memory space
What are disadvantages of compilers?
The source code must be re-compiled every time the programmer changes the program. Source code compiled on one platform will not run on another - machine code is specific to the processor’s architecture
What is an interpreter?
An interpreter translates source code into machine code one instruction at a time. The resulting machine code is then executed immediately
Advantages of interpreters?
Instructions are executed as soon as they are translated
Errors can be quickly spotted - once an error is found, the program stops running and the user is notified at which part of the program the interpretation has failed
Disadvantages of interpreters?
Interpreted programs run slowly as the processor has to wait for each instruction to be translated before it can be executed
The program has to be translated every time it is run
Interpreters do not produce an executable file that can be distributed. As a result, the source code program has to be supplied, and this could be modified without permission
Interpreters do not optimise code - the translated code is executed as it is
Tell me about assemblers
Assemblers translate assembly language into machine code
Whereas compilers and interpreters generate many machine code instructions for each high-level instruction, assemblers create one machine code instruction for each assembly instruction
What is serial communication?
Serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel
What is the difference between synchronised and asynchronous serial communication?
Synchronised serial communication is when the timing of each bit is synchronised by the oscillations of the clock, whereas asynchronous communication is when files are broken up into many packets and reassembled at the receiving end (more common)
What is parallel communication?
Parallel communication describes several bits being sent at the same time, on a link with several channels in parallel with each other
Pro and con of parallel communication?
Pro: as many bits are sent over many channels at the same time, parallel communication is faster than serial
Con: Can be unreliable over long distances, so is mainly found on the very short communication channels of printed circuit boards
What is a transducer?
Transducers are any device that converts between an electrical quantity and a real-word quantity
What is an actuator?
Actuators can be referred to as output transducers
responsible for moving or controlling a mechanism or system
An actuator is the mechanism by which a control system acts upon an environment
mechanical output device that produce movement
What do actuators do?
Actuators take an electrical signal and convert it into a physical form - they apply movement through the use of energy which is converted to motion. Control signal provided by a microcontroller and energy from a battery
What movements can actuators cause?
Rotate, open, close, push, pull, etc
Examples of actutators?
Speakers, solenoids, relays, motors
Speaker definition
A diaphragm is vibrated to create sound waves
Solenoid definition
A solenoid is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical current into mechanical motion. When energised, the solenoid can control plungers, or arms. These can control triggers or locks, etc
Relays definition
act as switches or signal amplifiers
Motors definition
if the motor movement needs to be smooth, the signal from the microcontroller is put through a DAC to supply a smooth analogue signal, rather than the discreet steps of a digital signal
What is a DAC?
A digital-analogue converter