D1.1 DNA Replication
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is DNA replication?
Process of producing exact copies of DNA
this process ensures that genetic info is passed on
Why is DNA replication important?
reproduction: in all organisms dna replication is essential before cell division to ensure that full genetic code gets passed down
growth: new body cells require exact copies of DNA
tissue replacement: Damaged or old cells can be replaced with new ones that have the same DNA
What is semi-conservative replication?
Each new molecule of DNA contains an original (parental) strand of DNA, and a newly synthesized strand
uses complementary base pairing to create new strand
Why is a high accuracy mechanism, like complementary base pairing, important?
It allows for DNA sequences to have the right amount of nucleotides and be very accurate when copying the DNA.
What is the role of Helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase unwinds the hydrogen bonds that are found between complementary base pairs
unwinds double helix, and separates the 2 strands
creates replication form where new strands can be synthesized
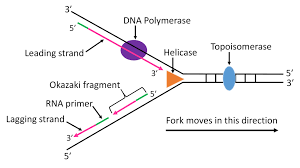
What is DNA polymerase role in DNA replication?
adds new nucleotides to exposed single strand (old strand), and uses it as a template to add these new nucleotides
catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds, and links nucleotides to the new strand
works in the 5’-3’ direction to build DNA strand
What is the polymerase chain reaction?
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a technique to amplify specific dna segments
has 2 main components: primers (short dna sequences that bind to target regions on dna, marking the start points for replication) and taq polymerase (heat-stable enzymes that synthesizes new dna strands)
What are the different temperatures that control the stages?
denaturation (~95 degrees): dna strands separate by breaking hydrogen bonds
annealing (~50-65 degrees): primers bind to target sequences
extension (~72 degrees): taq polymerase adds nucleotides to build new strands
cycle repeats 20-40 times
What is gel electrophoresis?
Technique that separates DNA fragments by size. Does this by placing dna samples on gel matrix and electric current is applied, then they apply a negative charge and dna moves to the opposite electrode.
smaller fragments travel faster through the porous gel
How can the PCR and Gel Electrophoresis be used?
DNA profiling: in forensics, they are able to identify individuals from biological samples
Medical diagnosis: they detect diseases by amplifying specific dna sequences
Biological research: studies gene mutations and analyzes genetic diversity in populations
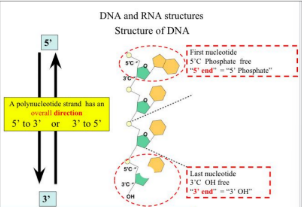
What are the 2 ends of DNA strands?
5’ end with phosphate group
3’ end with hydroxyl group
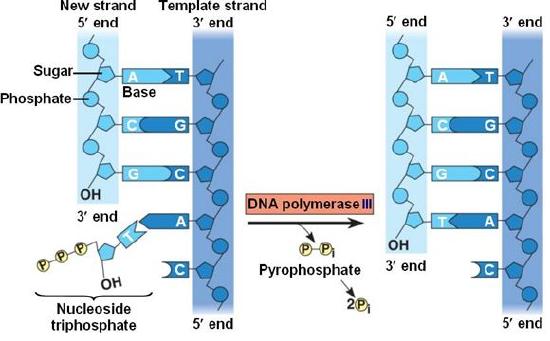
How does DNA polymerase work?
adds nucleotides to only the 3’ end (new nucleotides are added to the phosphate group) because strands are antiparallel meaning that the 3’ end of the original strand is the 5’ end of the new strand
DNA replication keeps proceeding in the 5’ to 3’ direction along the new strand
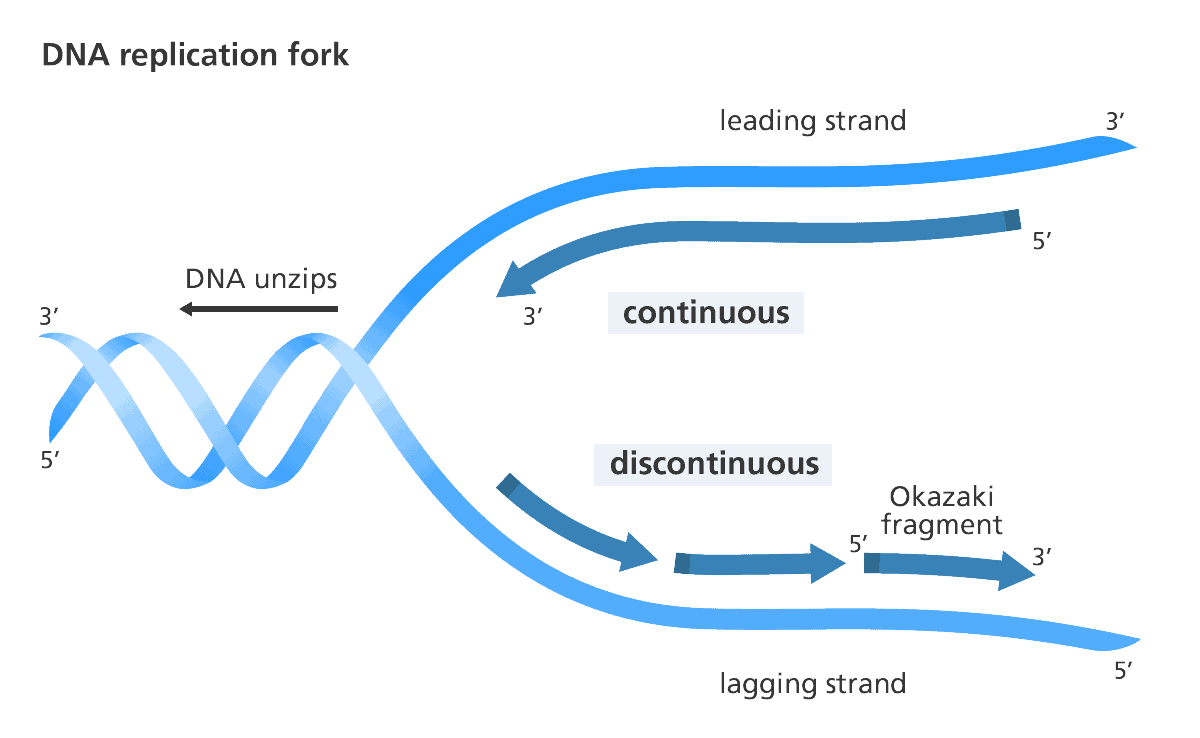
What is leading strand replication?
continuous synthesis of dna polymerase, which moves in the same direction of the replication fork
dna is made smoothly since only one primer is needed
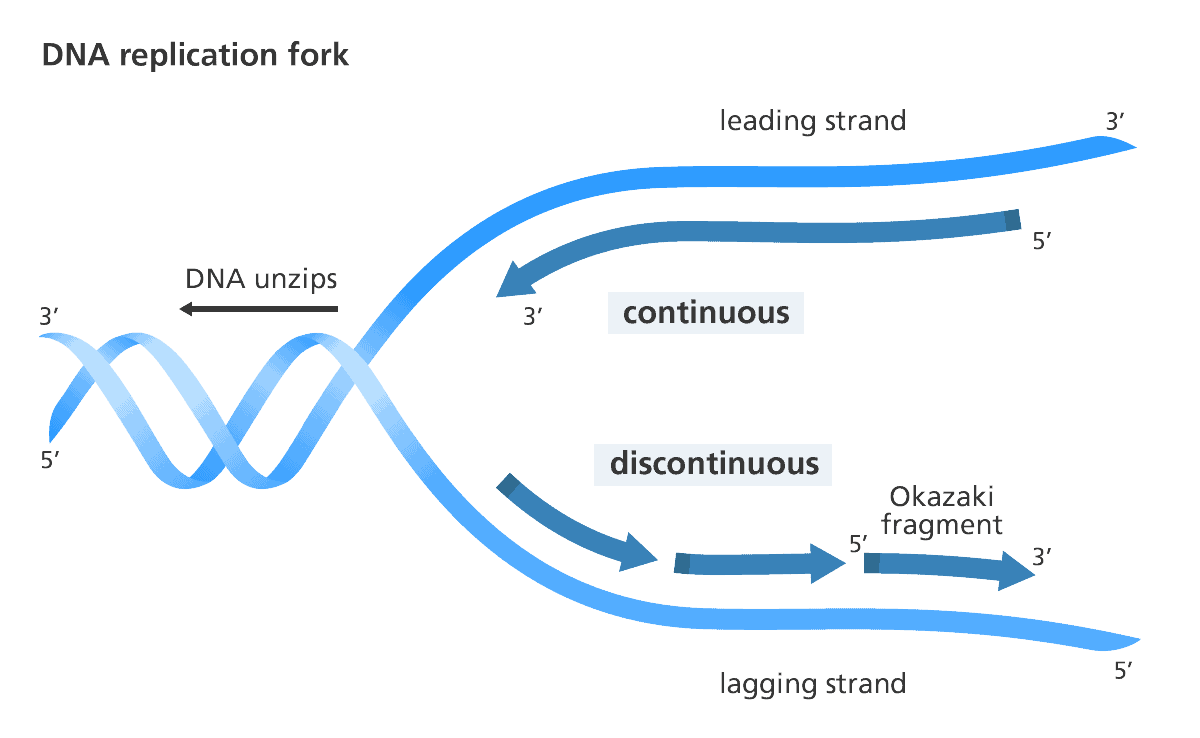
What is lagging strand replication
discontinuous synthesis, polymerase moves in opposite direction of replication fork
because it has to restart every couple nucleotides, it synthesizes dna in short fragments called Okazaki fragments
requires multiple rna primers (each for every okazaki fragment) because it has to start and stop
okazaki fragments are latter joined by dna ligase
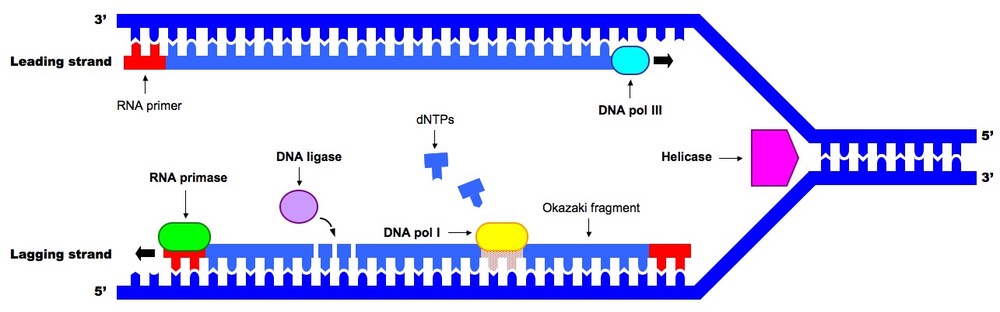
What is the role of DNA primase?
because it is an rna polymerase enzyme it synthesizes short rna primers on the dna templates (on leading strand it is only one, on lagging it is multiple)
this primer acts as a starting point for dna polymerase III (which is for only synthesizing new strands of dna)
DNA polymerase III
main enzyme for DNA synthesis
adds dna nucleotides to 3’ end of the new strand and works in 5’-3’ direction of old nucleotide
has a proofreading function
synthesizes dna continuously on leading strand and discontinuously on lagging strand
DNA polymerase I
Removes rna primers from new dna strand
replaces rna primers with dna nucleotides
also proofreads to maintain accuracy
What is the main difference between DNA polymerase 1 and 3?
DNA polymerase I is used to create new dna strands
DNA polymerase III is used to remove rna primers from lagging and leading strand and replaces them with nucleotides
DNA ligase
selas the gaps between okazaki fragments on lagging strand
forms phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
ensures continuous dna strand
Why is proofreading important?
DNA replication is very accurate, but errors (like mutations) can happen, so it is important to reduce these errors to keep the genetic code intact
How does DNA polymerase proofread?
has a mismatch detection: dna polymerase III pauses when a wrong nucleotide is added
Exonuclease activity: removed the incorrect nucleotide from 3’ end of growing strand
utilizes backtracking
corrects the nucleotide and then resumed synthesis