Visual Imagery
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Last updated 11:36 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
**What are you experiencing when you visualize an image?**
visual imagery
2
New cards
**What are you experiencing when you daydream?**
mental imagery
3
New cards
**What was the debate where people’s thinking can be thought without images?**
imagery thought debate
4
New cards
**What experiment included pairing with words and the recall of a word that was paired?**
paired associate learning
5
New cards
**What happens when participants pair another word with an image and then it is presented and then image is remembered later?**
conceptual peg hypothesis
6
New cards
**What was measured in the mental rotation experiment?**
mental chronometry
7
New cards
What is visual imagery?
Seeing in the absence of visual stimulus
8
New cards
What is mental imagery?
Ability to recreate sensory world in the absence of physical stimuli used to include all senses
9
New cards
**What is the Imageless Thought Debate?**
Link between imagery and thinking
10
New cards
**What is paired associate learning?**
Participants paired with pairs words → presented during test period with first word for each pair → recall word that was paired
11
New cards
**What is the conceptual peg hypothesis?**
Concrete nouns create images that other words can “hang” onto
12
New cards
**What is mental chronometry?**
Determines amount of time needed to carry out cognitive tasks
13
New cards
**What did Kosslyn’s island and boat experiment where the participant had to look for a particular point of the image?**
mental scanning
14
New cards
**What is mental scanning?**
Participants create mental images and scan them in their minds
15
New cards
**What was the debate about whether imagery is based on spatial mechanisms (involved in perception) or propositional mechanisms (language)?**
imagery debate
16
New cards
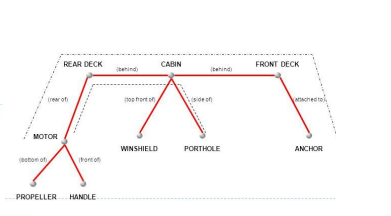
**This image is an example of?**
propositional representation
17
New cards
**What are known as epiphenomenon?**
spatial representations
18
New cards
**What is an epiphenomenon?**
Something that accompanies a real mechanism, but not actually apart of a mechanism
19
New cards

**“The cat is under the table is an example of what?”**
spatial representation
20
New cards
**What are propositional mechanisms?**
Representations in which relationships can be represented by abstract symbols
21
New cards
**Symbols and abstract language are associated with what?**
propositional representations
22
New cards
**Realistic pictures are associated with what?**
depictive representations
23
New cards
**What are depictive representations?**
Spatial representations involve parts of representation correspond to part of object
24
New cards
**What is NOT a reason cognitive scientists think perception and imagination are similar?**
Finding far apart items and discriminating more or less rotated objects is just as fast as nearby ones
25
New cards
**What is automatic and stable?**
perception
26
New cards
**What requires more effort and is fragile?**
imagery
27
New cards
**This example: Participants image what they were walking towards their mental image of the animal --> estimating how far away they were from the animal and when they experienced "overflow" --> when image filled visual field or became fuzzy is what task?**
mental walk task
28
New cards
**What task involved participants to judge whether pictures were two views of the same-objects or mirror-image?**
mental rotation task
29
New cards
**If the image is ambigious?**
it is difficult to flip due to difference in experience of perception and imagery
30
New cards
**What neurons are involved in responses of single neurons** \n **in a person’s medial temporal lobe that responding to the perception and imagining of a baseball?**
imagery neurons
31
New cards
**What are imagery neurons?**
Neurons responding in same way to perceiving an object and to imagining it
32
New cards
**How is the parts of the brain activate in response to imagery and perception?**
complete overlap with the front, but in the back, it’s different
33
New cards
**What is the response of brain activity in response to imagery?**
something may not be happening & it may not cause imagery
34
New cards
**What happens to other senses when the brain activity is responding to imagery?**
deactivates so mental images are more fragile so other things stop interfering
35
New cards
**What happens to brain functioning in TMS?**
Decreases brain functioning in a particular \n area of the brain for a short time
36
New cards
**How does brain functioning effect behavior in TMS?**
If behavior is disrupted, the deactivated \n part of the brain is causing that behavior
37
New cards
**Kosslyn’s experiment to TMS to visual area during perception and imagery task indicated what?**
Brain activity in visual area of brain plays a causal role in both perception and imgery
38
New cards
**This example of patients RM (where he could copy pictures, but not draw from memory) & CK (where he could not name objects in picture, but COULD draw from memory) is what?**
double dissociation
39
New cards
**When a patients ignores objects in one half of visual field in perception and imagery?**
unilateral neglect
40
New cards
**What is double dissociation?**
When some patients have imagery deficit but intact perception, but other patients have perception deficit but intact imagery that indicates a separate mechanism for both processes
41
New cards
**What happens in the pegword technique?**
associate items to be remembered with concrete words → pair these things with pegword -→ create vivid image of things to be remembered with the object represented by the word
42
New cards
**When eating only the food on one side of the plate is an example of?**
unilateral neglect
43
New cards
**What did Paivio belief about imagery to improve memory?**
memory for words that evoke mental images is better
44
New cards
**This is an example to watch This is Us on TV imaging picture an elliptical trainer inside a shoe, and the word US in a tree.**
pegword technique
45
New cards
**What is the method of loci?**
A method in which things to be remembered are placed at different locations in a mental image of a spatial layout
46
New cards
**Remembering a shopping list and imagine each product at a different spot on a familiar street is an example of what?**
method of loci