Bone/Cartilage
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
compact bone
forms dense, hard outer casing of all bones
composted of osteons
resists forces from weight and movement
spongy bone
forms light, thin inner network of bone
can resist stress in multiple directions, found within flat bones and at the ends of long bones
hematopoiesis
protection in blood cells
occurs in red bone marrow in some spongy bone
adult
red bone marrow restricted to axial skeleton
yellow bone marrow in long bone shafts
child
red bone marrow in some spongy bone
long bones
lever, joints, and pivots for body movement
cylindrical bone shaft
short bones
distribute and transfer forces across multiple bones
flat bones
broad surface for muscle attachment and provide protection
irregular bones
varied function including attachment and protection
diaphysis
cylindrical shaft
compact bone with medullary cavity
epiphysis
ends of the bone
outside layer of compact bone surrounding spongy bones
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage on the epiphyses
supports, provides smooth surface for join movement
osteoartritis
articular cartilage wear down, bone rubs against bone
epiphyseal plate
hyaline cartilage plate between diaphysis and epiphysis
epiphyseal line
thin plate of compact bone between epiphysis
periosteum
dense irregular CT and cell layer that covers outside of bone
NOT found on articular surfaces of bones
grows in bone width
perforating fibers
very vascular, lots of nerves to anchor periosteum to bone
osteoblasts
immature bone cells that create bone
secrete osteoid
osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain one matrix
osteoclasts
break down and reabsorb bone
formed from fused red bone marrow cells; large
osteons
compact bone is made up of…
spongy bone is not made up of…
central canal
opening that contains blood vessels/nerves
concentric lamellae
concentric rings of bone matrix
lacunae
spaces where osteocytes reside
canaliculi
tiny channels that radiate from lacunae
perforating canal
run perpendicular to the central canals; connect multiple central canals
interstitial lamellae
incomplete remnants of osteons
circumferential lamellae
rings of bone that run the entire circumference of the shaft
ossification
formation and growth of bone tissue
intramembranous ossification
pre-existing tissue is mesenchyme into flat bones
endochondral ossification
pre-existing tissue is hyaline cartilage to form most bones
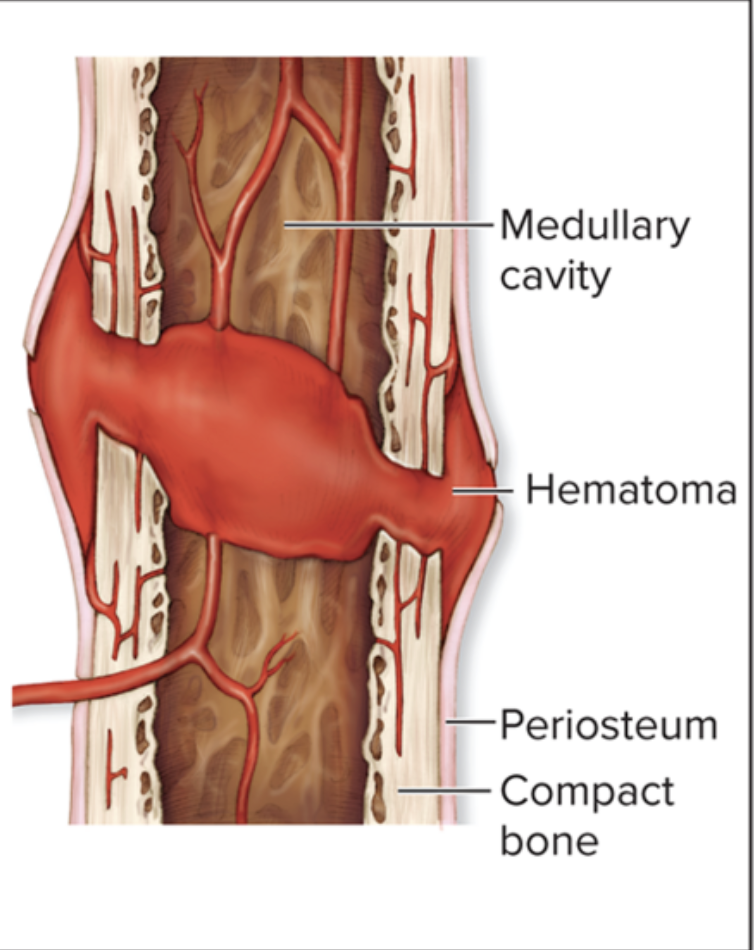
fracture hematoma
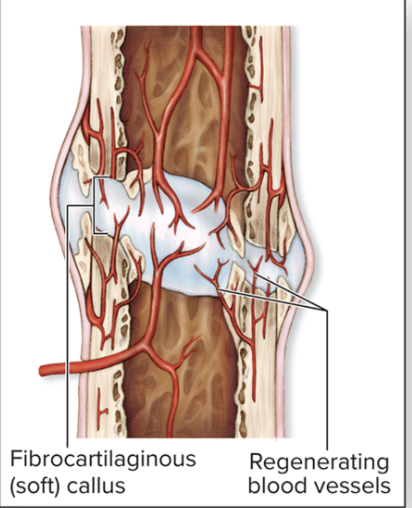
fibrocartilaginous callus
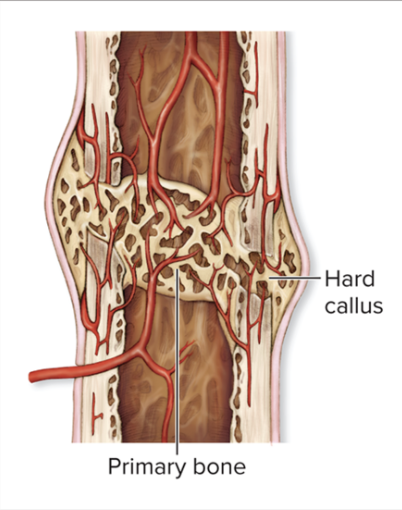
bony callus
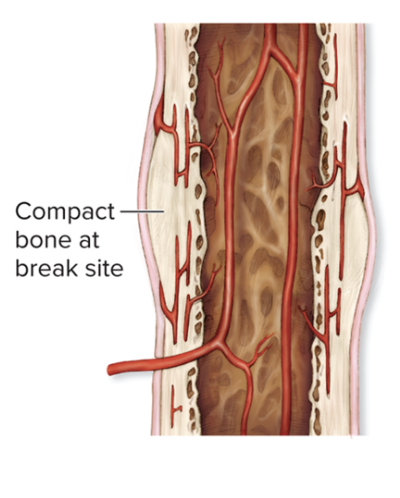
remodeling
periosteum
covers the outer surface of the bone, except for areas covered by articular cartilage
osteocyte
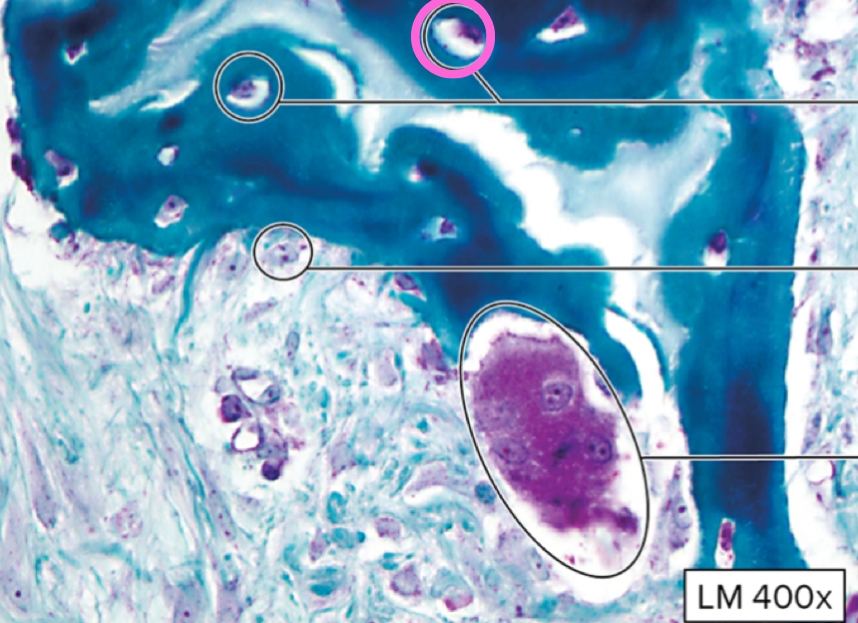
osteoblast
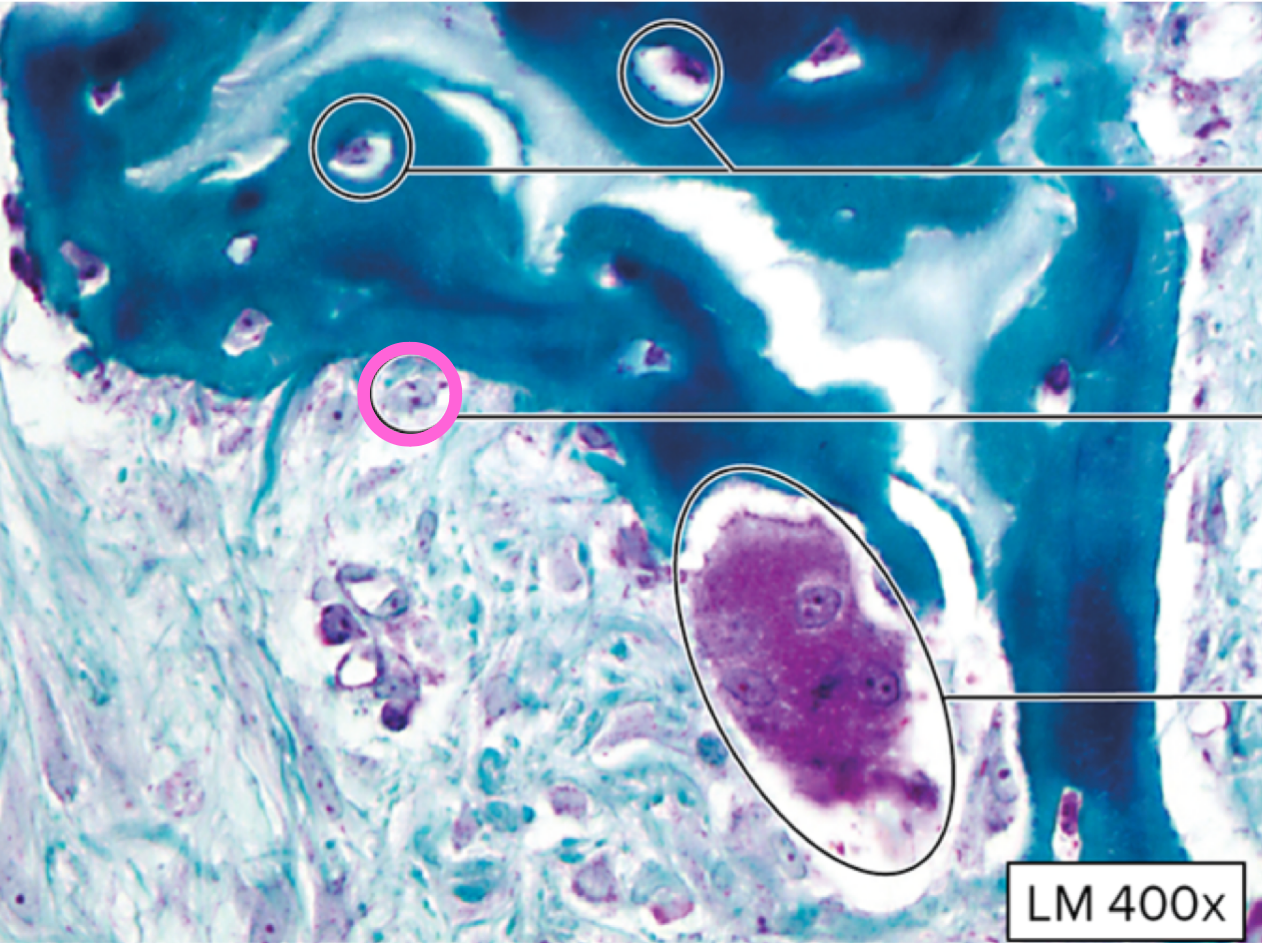
osteoclast
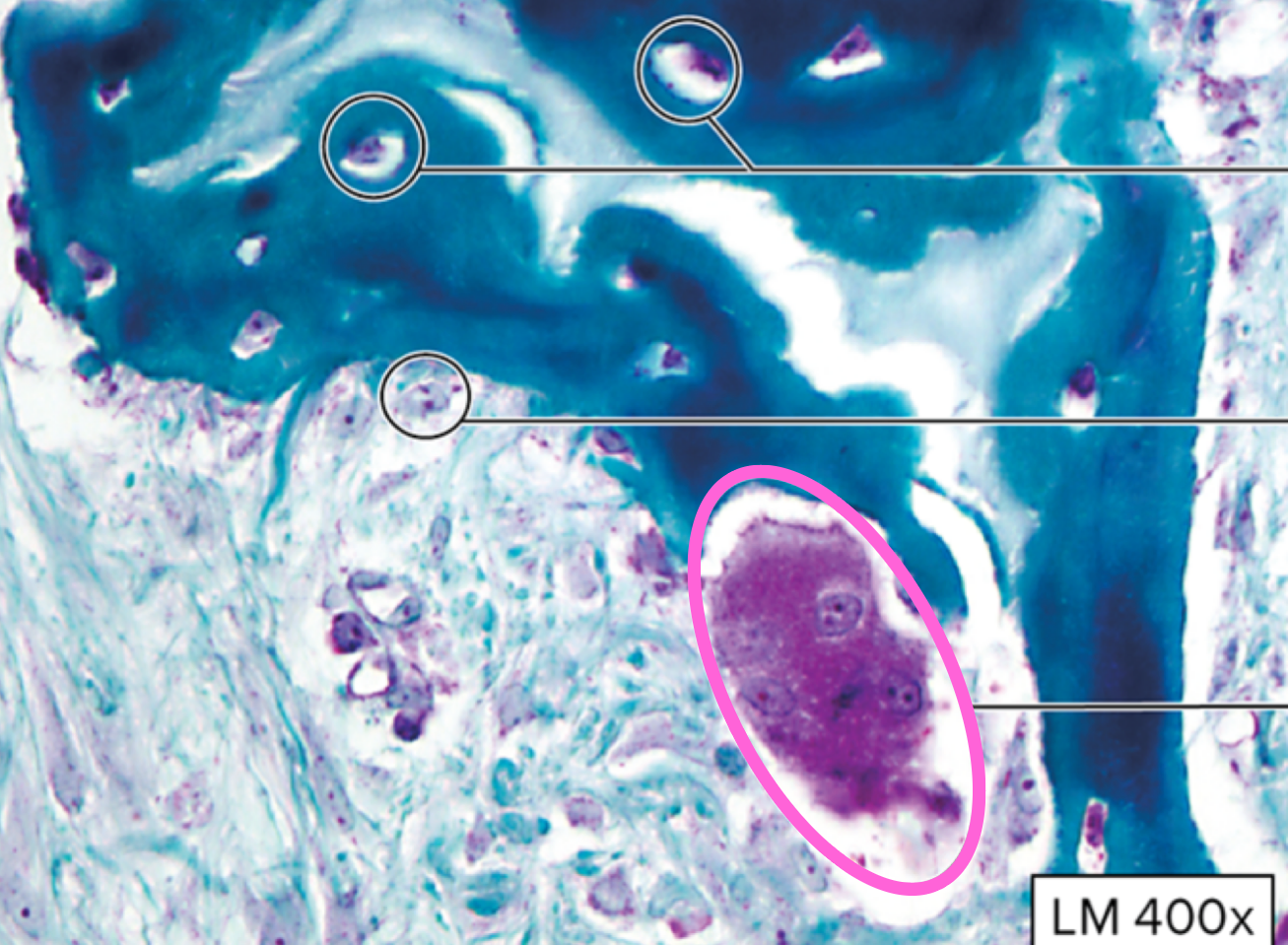
lacunae
space
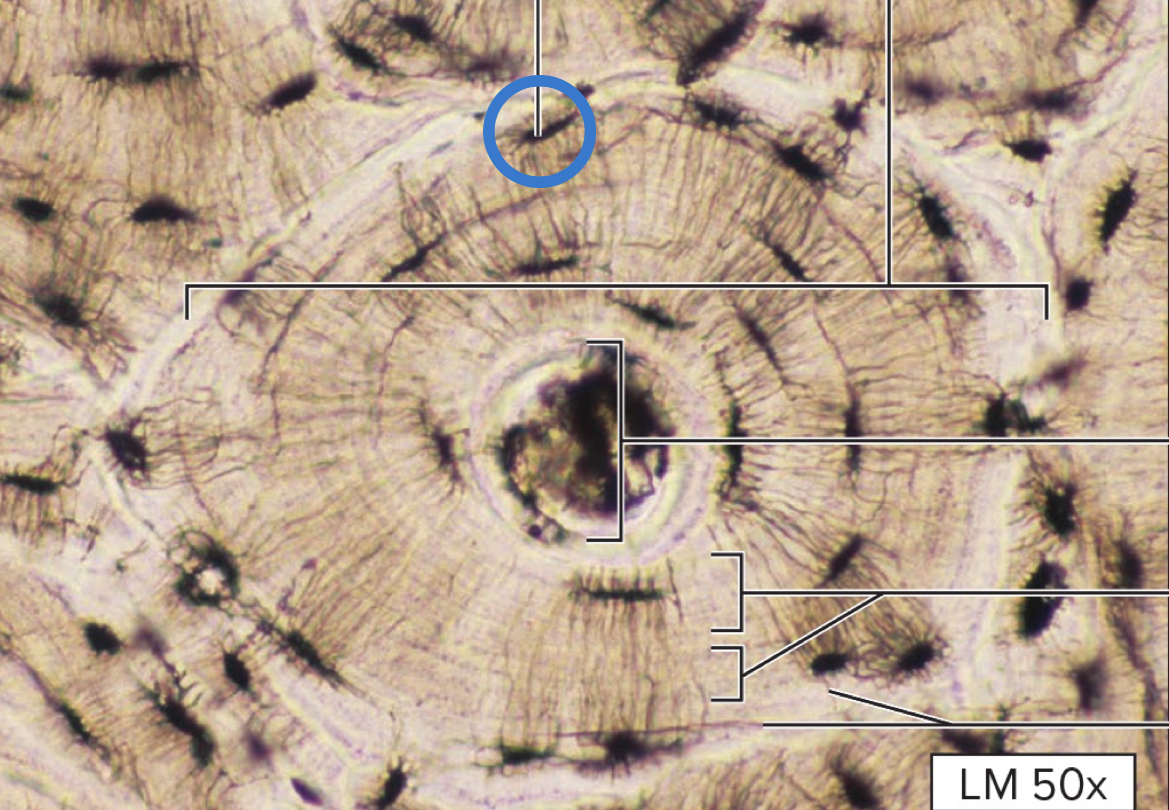
osteon
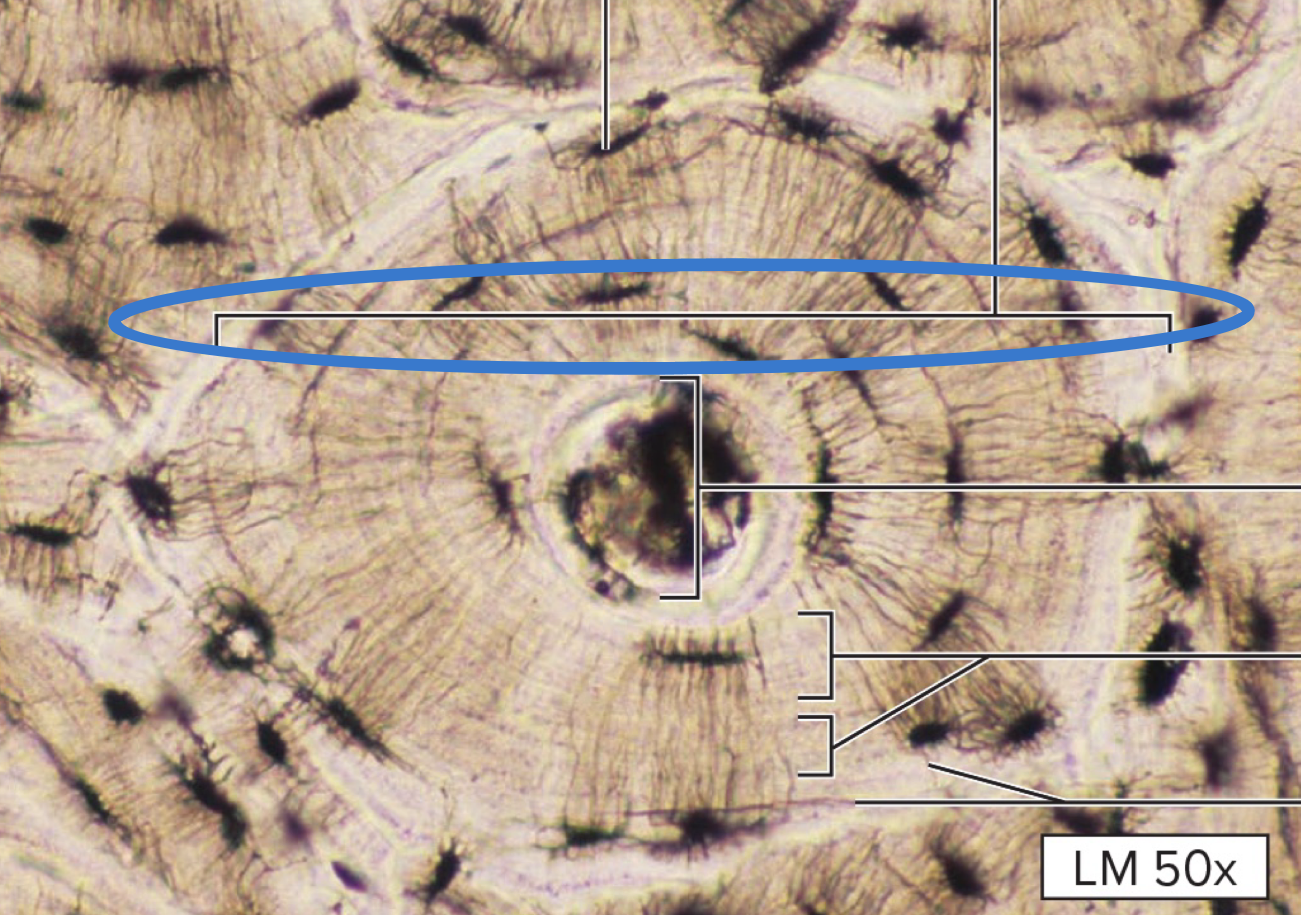
central canal
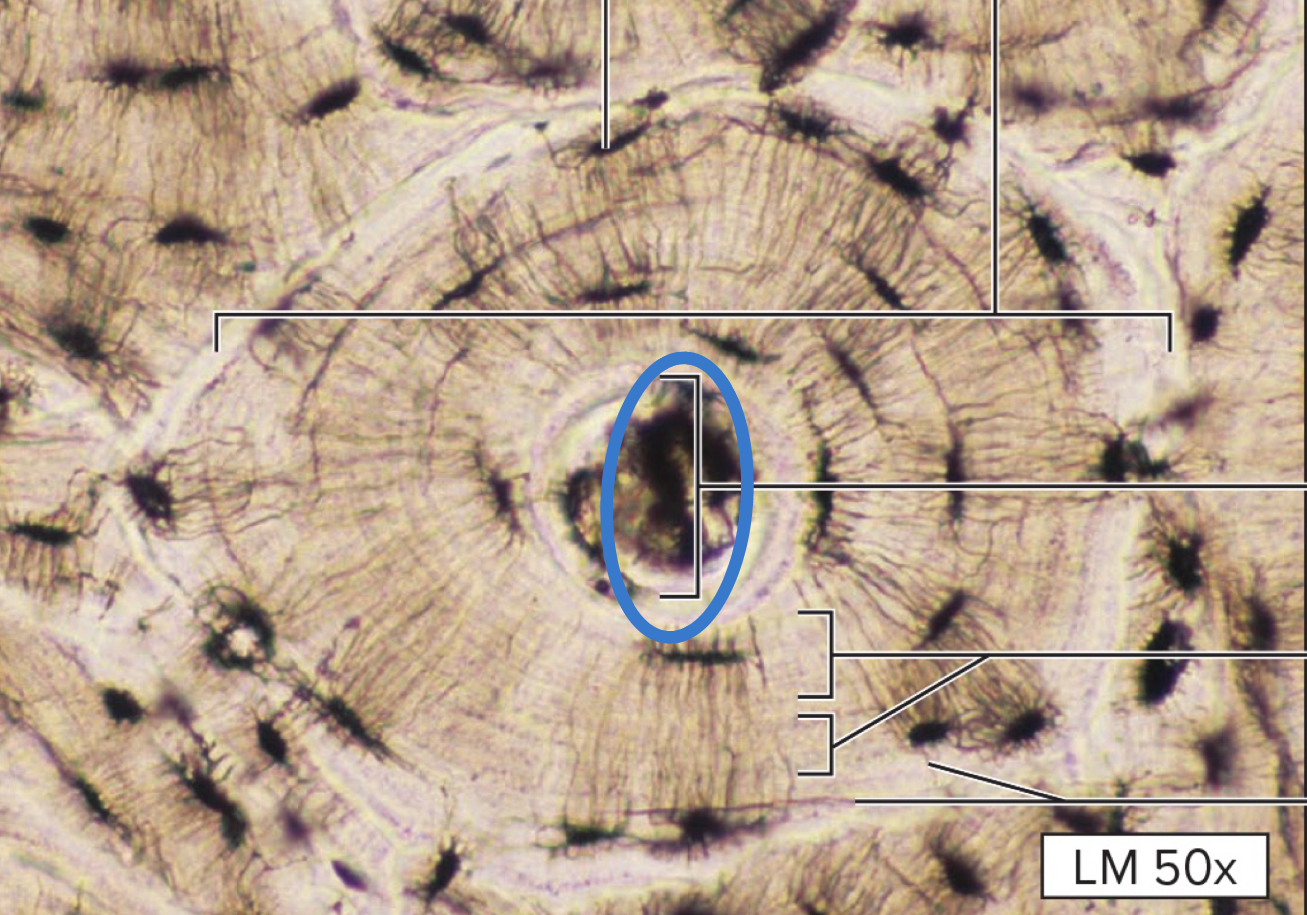
lamella
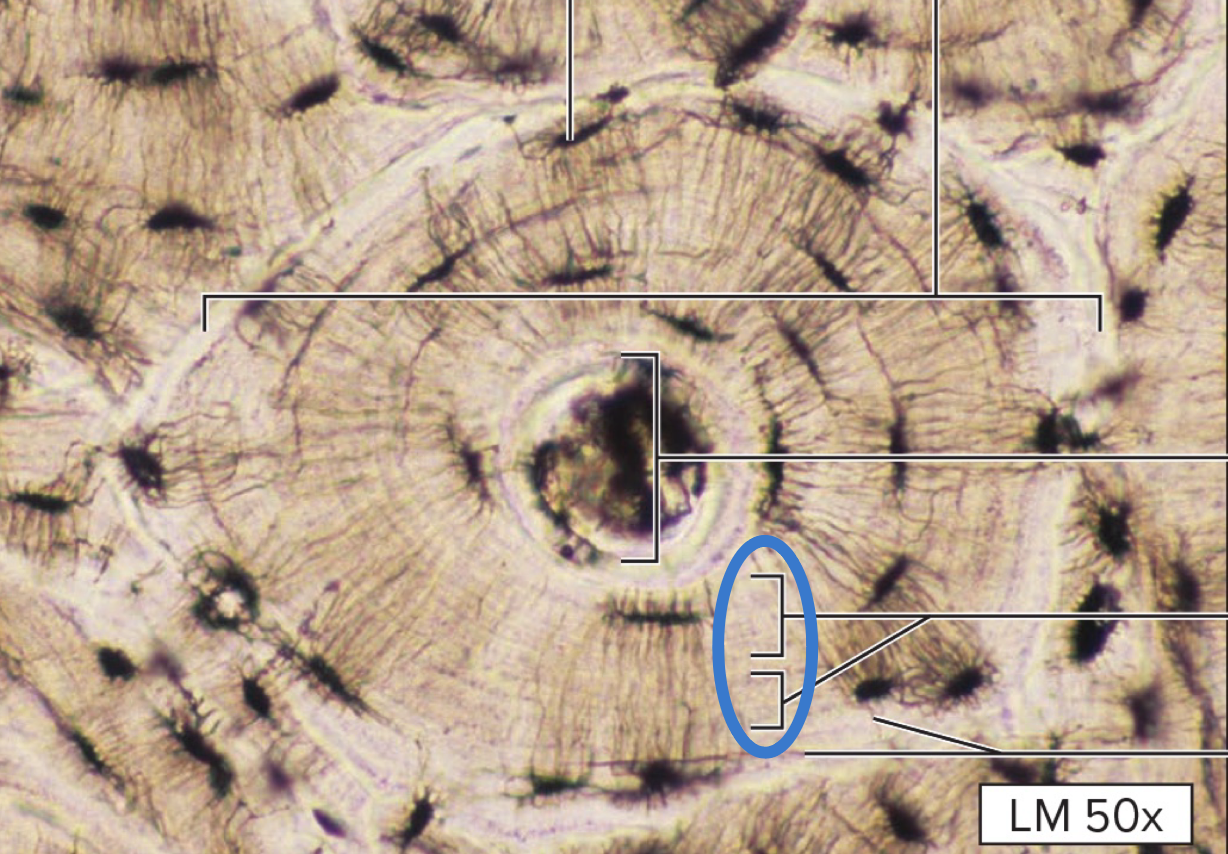
canaliculi
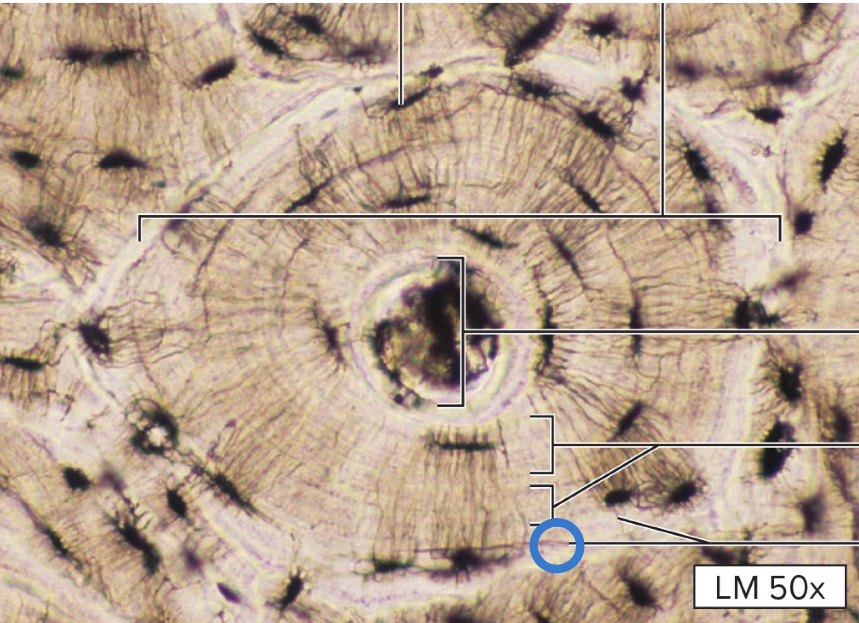
osteocyte
cell
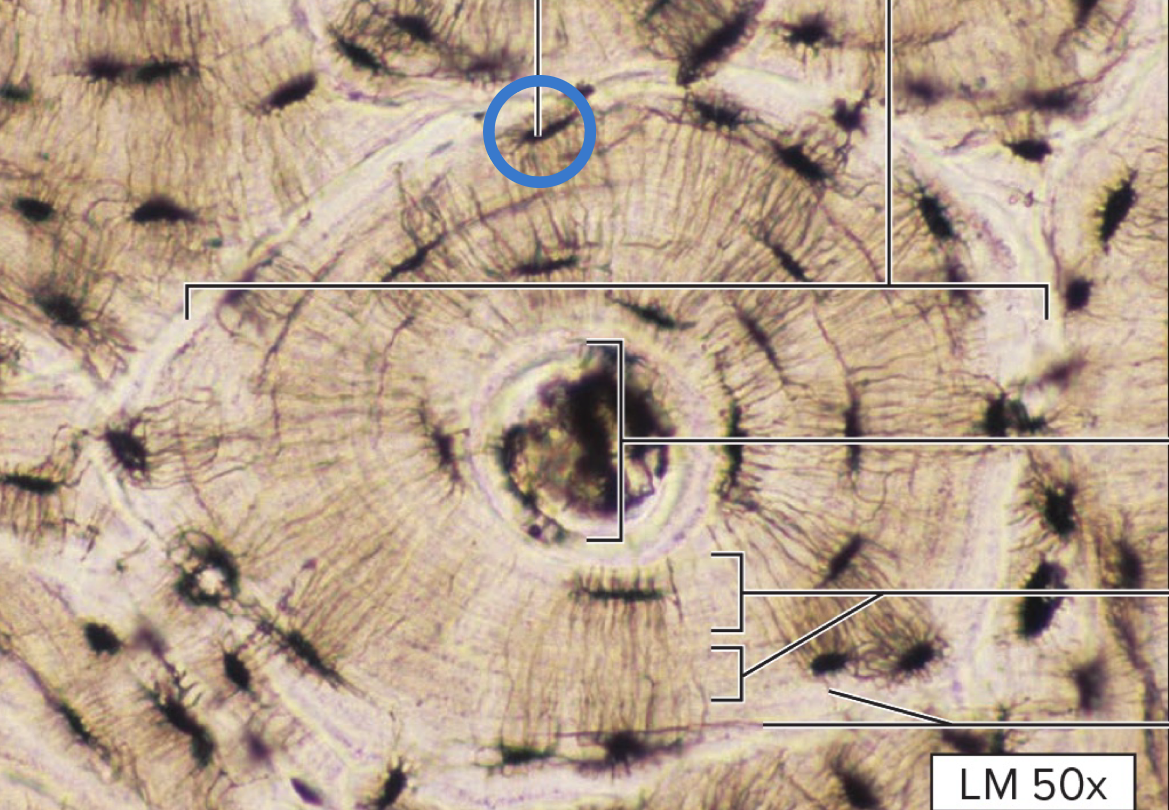
endosteum
cover all internal surfaces of the bone, such as medullary cavity