Year 3
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
Diagnose - Weight gain of 11kg in 6 months, plethoric face, BP 180/120, serum potassium of 2.9mmol/L and fasting glucose of 11 mmol/L in 59 year old woman
Cushing syndrome
Diagnosis - A 46 year old woman with weight loss, fast arterial fibrillation and agitation
Thyrotoxicosis
Diagnosis - Loss of consciousness and falling in a 59 year old hypertensive man receiving nifedipine and frusemide, who has recently been started on an ACE
Postural hypotension
Diagnosis - A 52 year old woman with fatigue, malaise, weight loss and a serum sodium of 123 mmol/L, potassium of 5.9 mmol/L and pigmentation of her palmar skin creases
Addisons disease
Diagnosis - An 80 year old woman has been getting progressively more short of breath for 6 months. Recently she has been coughing up blood. Her Mantoux test is strongly positive
Tuberculosis
What medical condition might someone have if they experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the ankles or legs, and irregular heartbeats, often associated with a decrease in heart function over time?
Cardiomyopathy
What condition is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, frequent urination, increased thirst, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue, often requiring careful management of diet, medication, and insulin injections to maintain proper control?
Diabetes mellitus
What medical condition shares symptoms such as excessive thirst, excessive urination (even at night), dehydration, and potentially electrolyte imbalances, yet differs from diabetes mellitus in its underlying cause related to insufficient production or ineffective response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Diabetes insipidus
What condition might result from an insufficient production of one or more hormones by the pituitary gland, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, decreased libido, menstrual irregularities in women, and decreased bone density, often requiring hormone replacement therapy for management?
hypopituitarism
What medical condition is characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, constipation, depression, and a general feeling of sluggishness, often stemming from an underactive thyroid gland and requiring thyroid hormone replacement therapy for management?
Hypothyroidism
Oral manifestations of thyroid disease- Associated with salivary gland enlargement and dysguesia
Hashimoto's disease
Oral manifestations of thyroid disease- In the severest form, it can cause enlargement of both jaws and such cases are known as osteitis fibrosa cystica
Hyperparathyroidism
Oral manifestations of thyroid disease- Associated with abnormal lip pigmentation, halitosis, periodontitis and candidaisis
Chronic kidney disease
Oral manifestations of thyroid disease-Signs and symptoms include increased susceptibility to caries and increased risk of burning mouth syndrome
Hyperparathyroidsm
Oral manifestations of thyroid disease- Dental signs include anterior open bite, delayed eruption and enamel hypoplasia
Hashimotos disease
The decline in stroke mortality in the USA since 1973
Demographic trend
The national health service breast cancer screening program
Secondary disease prevention
Prescription of statins to everyone aged over 50
Primary disease prevention
Action to reduce the prevelance of risk factors for a disease
Primary disease prevention
A cardiac rehabilitation programme
Tertiary disease prevention
What study - Post surgical clinical monitoring of soft tissue wound healing in periodontal and implant surgery
Narrative review
What study - Type II diabetes mellitus with oral abscess and obesity
Clinical case report
What study - PRF1 is a prognostic marker and correlated with immune infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Cross sectional study
What study - The relationship between oral and cardiovascular disease
Systematic review
What study- Manifestation of hypothyroidism
Clinical case report
Changing your preferred candidate to agree with the senior partner
Authority bias
Choosing between qualified candidates on the basis of culture fit
Affinity bias
Meeting as a team to review all the applications and draw up a short list
Conformity bias
Dismissing a candidate because their interview was worse that the person before them
Contrast effect
Shortlisting a candidate on the basis of the school they they attended
Halo effect
_____ is the healing that occurs when a clean laceration or a surgical incision is closed primarily with sutures, Steri-Strips or skin adhesive
Primary intention healing
____ closely resembles endochondral ossification
Secondary intention bone healing
_____ refers to healing of an open wound, from the base upwards, by laying down new tissue
Secondary intention healing
_____ is the reestablishment of the cortex without the formation of a callus. It occurs when reduction, immobilisation and rehabilitation are appropriate.
Primary intention bone healing
______ nvolves the classical stages of injury, haemorrhage inflammation, primary soft callus formation, callus mineralisation and callus remodelling.
Secondary intention bone healing
A granulocyte with very tiny light staining and difficult to see granules. The nucleus is frequently multi-lobed with lobes connected by thin strands of nuclear material. Capable of phagocytosing foreign cells, toxins and viruses. Can account for 50-70% of leukocytes or more in the face of acute infection.
Neutrophil
A granulocyte with large acidophilic granules that stain pink or red. The nucleus usually has two lobes connected by a band of nuclear material. Capable of phagocytosing antigen-antibody complexes and are particularly effective against the larval form of parasitic worms. Usually <5% of the WBC count but may increase if actually infected with parasitic worms.
Eosinophil
A granulocyte packed full with large granules that stain deep blue to purple and which may be so dense as to obscure the nucleus. The granules contain histamine and heparin. A key player in inflammatory reactions and allergies. Generally <1% of the WBC, but likely to increase if infected with chicken pox.

Mast cell
A relatively small agranular cell with very little cytoplasm and a big nucleus. A key player in the adaptive immune response. Generally contributes 25-35% of the WBC. Numbers will increase in response to chronic infection and decrease if HIV infection progresses to stage 3.

T Lymphocyte
A large agranular leukocyte with a kidney bean shaped nucleus. A key player in the innate immune system. These cells differentiate when they leave the circulation. Capable of phagocytosis. Usually between 3-9% of the WBC and more if infected with malaria.
Monocyte
The neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli
Nociception
A frequently encountered patient complaint that can present with a number of associated factors including erosion and abrasion

Dentine Sensitivity
Most commonly caused by nerve compression by, for example, a blood vessel
Trigeminal neuralgia
Most likely carried by the lateral spinothalamic pathway
Lancinating pain
Neuropathic pain involving non-nociceptive neurones
Allodynia

Phenoarbital

Benzodiazepine
Fluconazole

Metronidazole

Phenytoin

Asthma

Syncope
HYpoglycaemia

Epilepsy

Anaphylaxis

Basic

Urgent

Essential

Advanced

Emergency

Confirmation Bias

Horns Effect

Authority BIas

Affinity Bias

Gender Bias

Histamine

Acetylecholine

Gamma-aminobutyric acid

Glutamate
Serotonin

RCT

Experimental

Systematic Review

Case Control

Narrative Review
The reduced form of a coenzyme that acts as a redox agent. An excess is associated with alcohol metabolism and fatty liver disease

NADH
A production of both glycolysis and beta oxidation that carries CH3CO into the citric acid cycle where it is oxidised to carbon dioxide and water
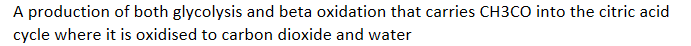
Acetyl CoA
At the branch point of the catabolic sequence of oxidative metabolism in the TCA cycle and the gluconeogenic pathway from C3 precursors

Pyruvate
Present in the blood as an ester in association with glycerol and a major component of adipose tissue

Fatty acid
An inhibitor and activator of enzymes located at the entrance and/or at the exit of glycolysis, TCA cycle, gluconeogenesis and fatty acids synthesis
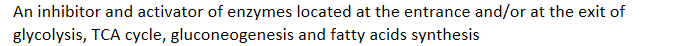
Citrate
Acts to lower the circulating glucose activity by reducing the renal transfer maximum for glucose via reversible inhibition of SGLT2
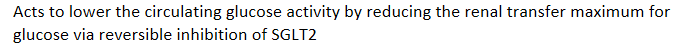
Dapagliflozin
A first-line glucose lowering medication that has been available in the BNF since 1958 whose mechanism of action remains unclear. May be used prophylactically in those at high risk of type II diabetes
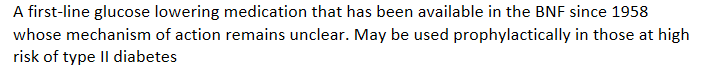
Metformin
A second-line glucose lowering medication that ats by blocking starch metabolism and which is commonly used in China when lifestyle interventions can no longer achieve HbA1c targets -

Acarbose
A sulfonylurea first developed in the 1960s that acts to increase insulin release by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) in beta cells of the endocrine pancreas

Glibenclamide
An oral medication that may be used in conjunction with sulfonylureas that acts on nuclear (steroid) receptors in muscle, adipose tissue to reduce insulin resistance

Pioglitazone
Individual pain thresholds may determine the relationship between this and seeking therapeutic treatment

Onset
May be achieved by stimulating activity in A beta neurones that branch in the dorsal horn before entering the dorsal columns
Exacerbation
May be difficult to determine if pain is of neuropathic origin
Site
The description of neuropathic pain using terms such as shooting, burning, stabbing or electric shock-like

Character
May be described in terms of duration and using words such as mild, distracting, moderate, etc

Severity
An aspect of what is potentially the most cost-effective mechanism to reduce the burden of disease across multiple morbidities. Shahab NCSCT briefing 2012
Nicorette
Efforts to manage this have led to improved health-related quality of life (standardised mean difference 0.37, 95% Cl 0.14 to 0.61) and objectively measured physical function and reduced depression and anxiety symptoms. Bricca et al Br.J.Sports Med. 2021 55.1

Sloth
May be determined using sensitivity analyses, when accounting for the severity of the conditions, at 45 years, participants with poor health and multimorbidity had 9.00 (95% Cl 8.47, 9.53) years lower life expectancy compared to those with good health without multimorbidity. Chudasama et al BMC Med 2019 17, 108

Longevity
Exacerbated by frailty syndrome associated with multimorbidity in older adults and may lead to permanent disability. Apathanasiou et al Front.Genet. 2021 24 430

Physical Trauma
Multimorbidity may cause increase beyond the sum associated with each individual condition. Vetrano et al Nat Commun 2020 11, 3223
Stochastic Events
Made more difficult by the need to clearly identify patients with multimorbidity and to develop cost effective and specifically targeted interventions that can improve health outcomes. Smith BMJ 2012, 345

Health Seeking Behaviour (Zola 1973)
May lead to under-reporting of aspects of multimorbidity particularly when associated with depression. Eyowas et al BMJ Open 2021 11
Stigma (Goffman 1968)
A way of evaluating the poor quality of life (QoL), disability, functional decline and high health care costs that are major consequences of multimorbidity. Makovski et al Ageing Research Reviews 2019 53
Biographical Disruption (Bury 1991)
Future developments in this area to improve health outcomes must accommodate individuals who are already symptomatic. Murray et al Psych.Rep. 2020

Illness Behaviour (Mechanic 1978)
May be employed, along with newer concepts, such as the 'Behaviour Change Wheel' to help individuals with multimorbidity manage the accompanying polypharmacy. Byrne et al Imp.Sci 2015 10

Transtheoretical (Prochaska and Di Climente 1983)