Unit 3: Electricity Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Smallest unit of electrical charge
electron
One coulomb is how many electrons?
6.3 x 10^18
Electrostatics
The study of electric charges at rest
Electrification
Too few or too many electrons
Methods of Electrification
friction, contact, induction
Negative charges pull _____, positive charges push ______
Inward, Outward
1st Law of Electrostatics
like charges repel, unlike charges attract
2nd Law of Electrostatics
Electrons travel outside of a conductor(wire)
3rd Law of Electrostatics
Electrical charges are concentrated on the sharpest curvature of a conductor.
4th Law of Electrostatics
Electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and are inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
Electrodynamics
The study of electric charges in motion
Conductor
A material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it.
Insulator
A material that does not allow heat or electrons to move through it easily.
Semiconductor
A substance that can conduct electricity under some conditions
Superconductor
a material that has almost zero resistance when it is cooled to low temperatures
Current
Measured in amperes (A)
Potential Differences- volts(V)
EMF (Electro Motor Force)
Resistances(R)
Measured in Ohms
Length of the Wire
Longer the wire, more resistance
Cross-section of the wire
Thinner the wire, more resistance
Material the wire is composed of
Gold is a better material than wire
Temperature of the wire
Higher temperature has more resistance
Ohm's Law
V = I(R)
Power (Measured in Watts)
P = I(V) or P = I^2(R)
Open switch symbol
The circuit is switched OFF
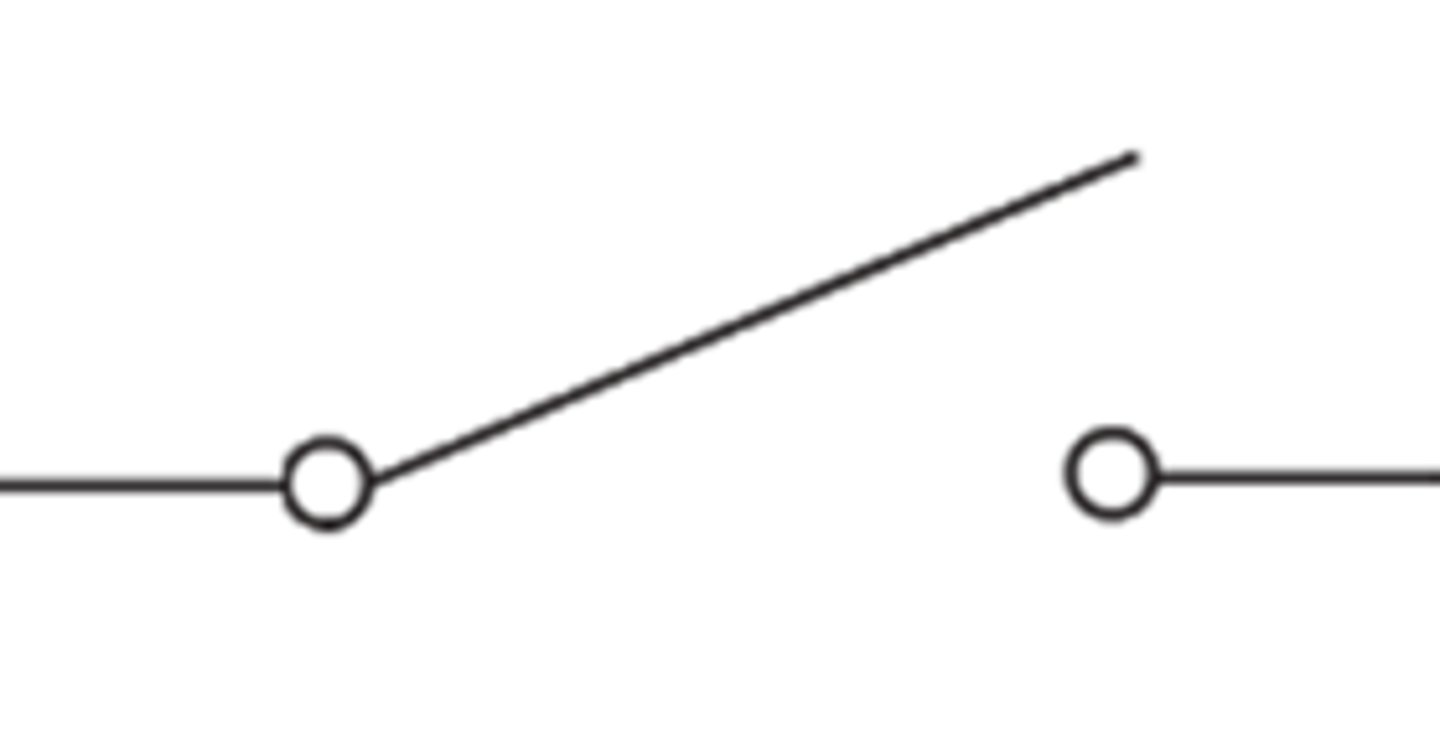
Closed Switch
The circuit switch is ON

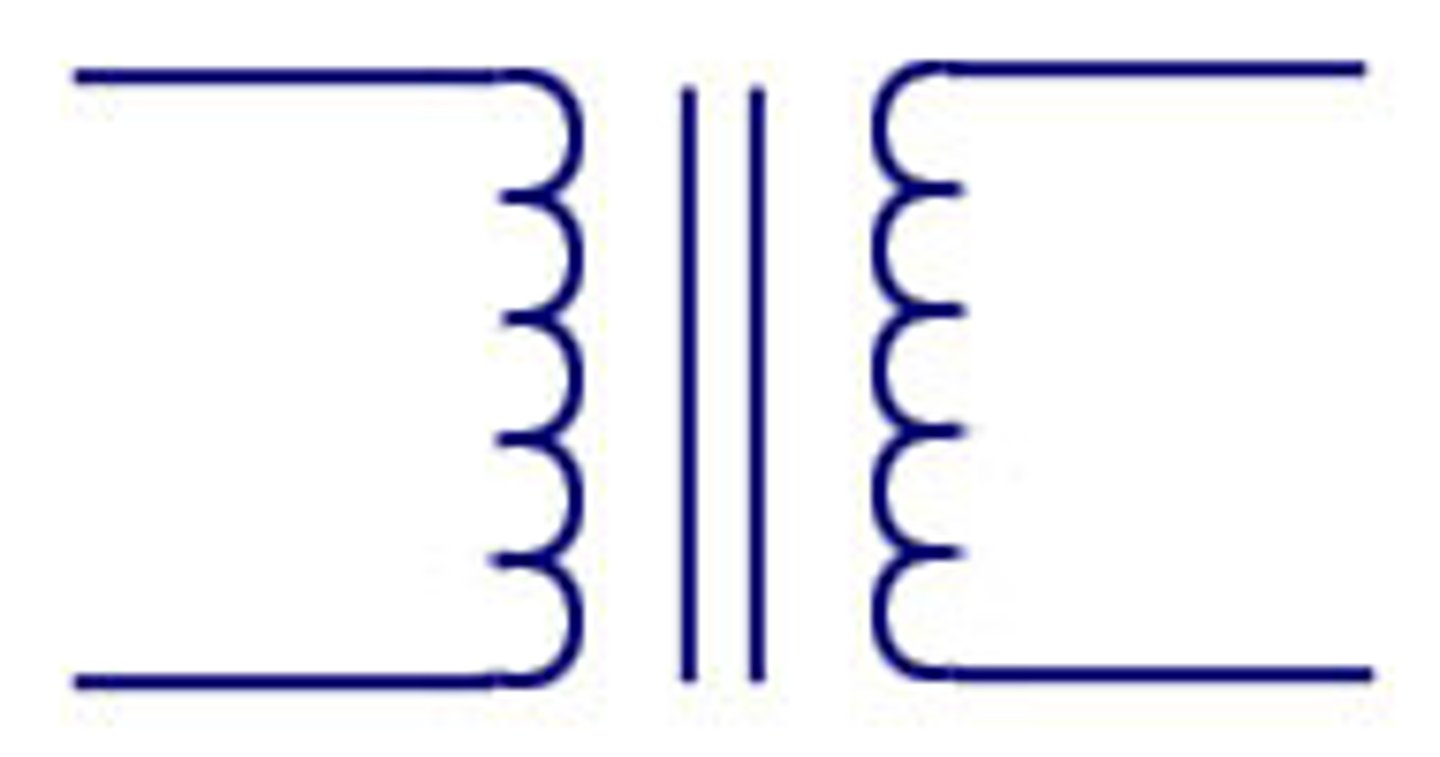
Transformer
A device that increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current
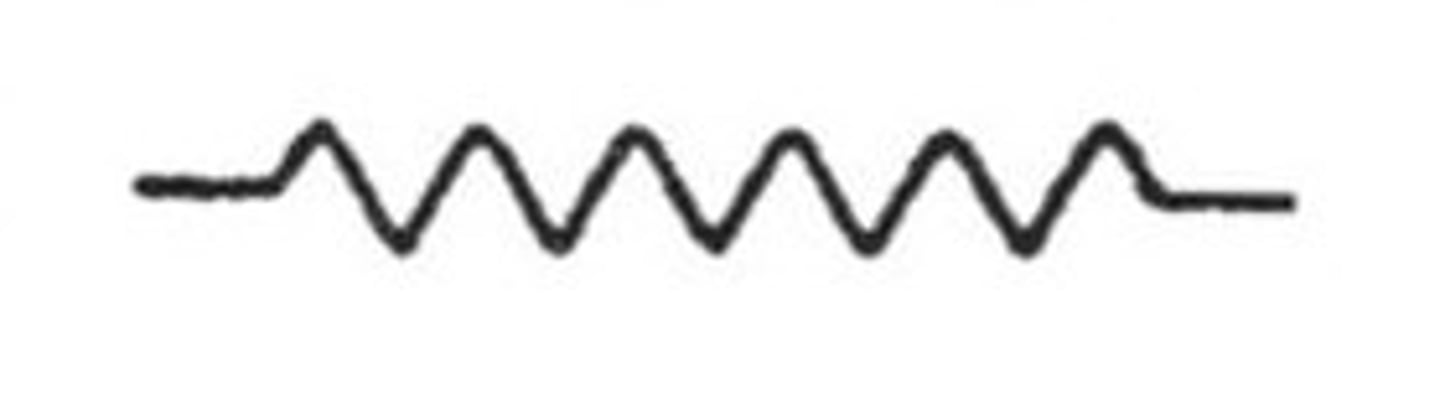
Resistor
An electrical device that resists the flow of electrical current

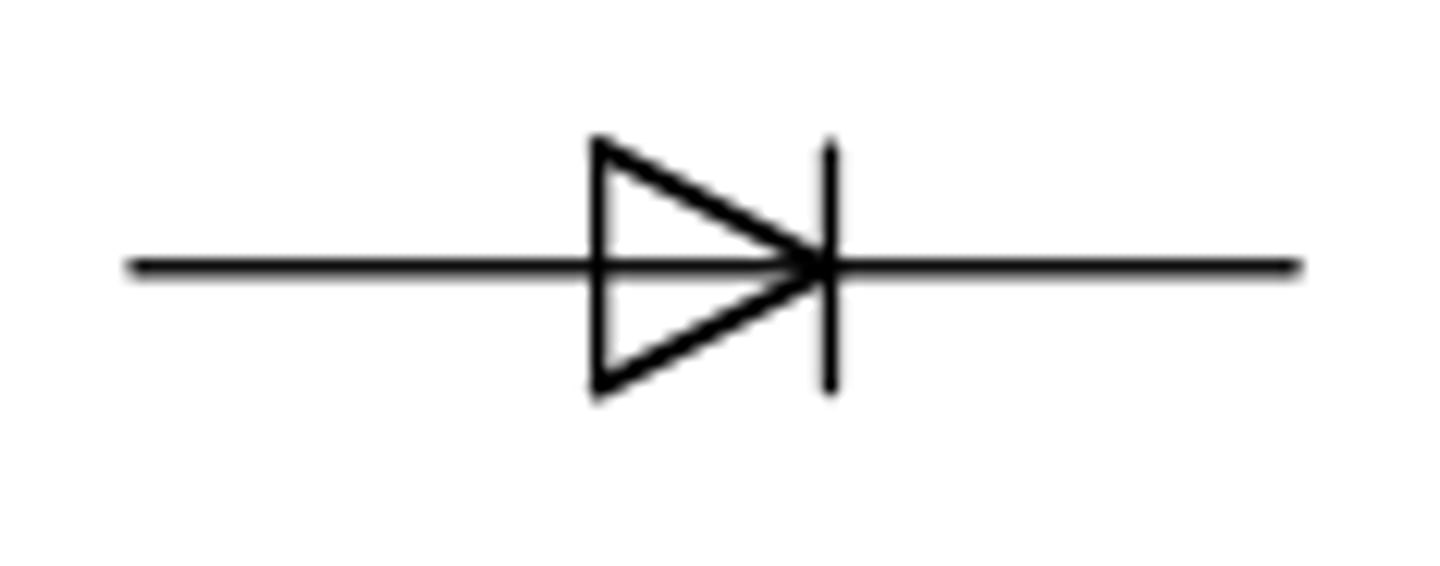
Diode
A device that permits current to flow through it in only one direction.
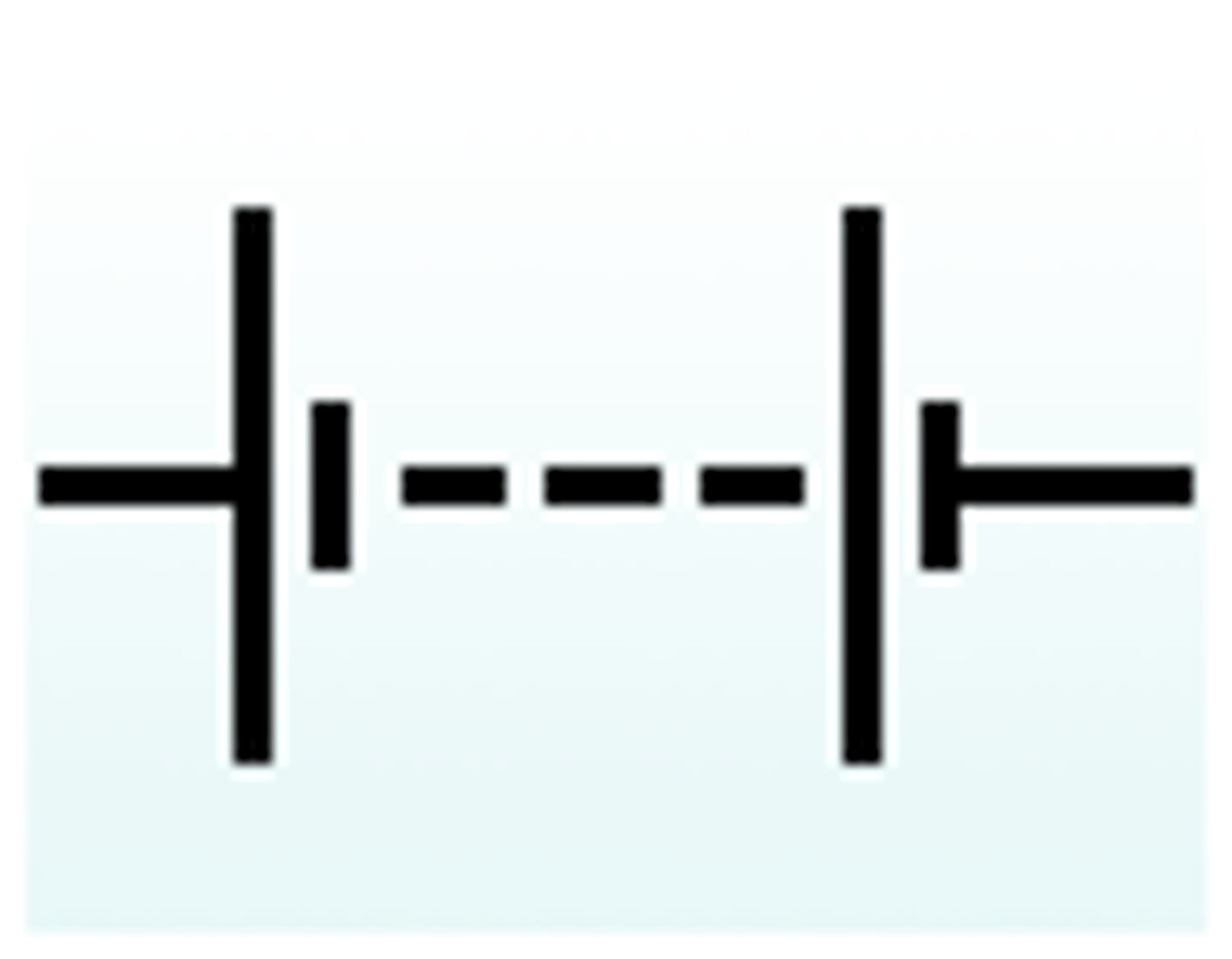
Battery
DC supply of voltage and current, usually made of many cells
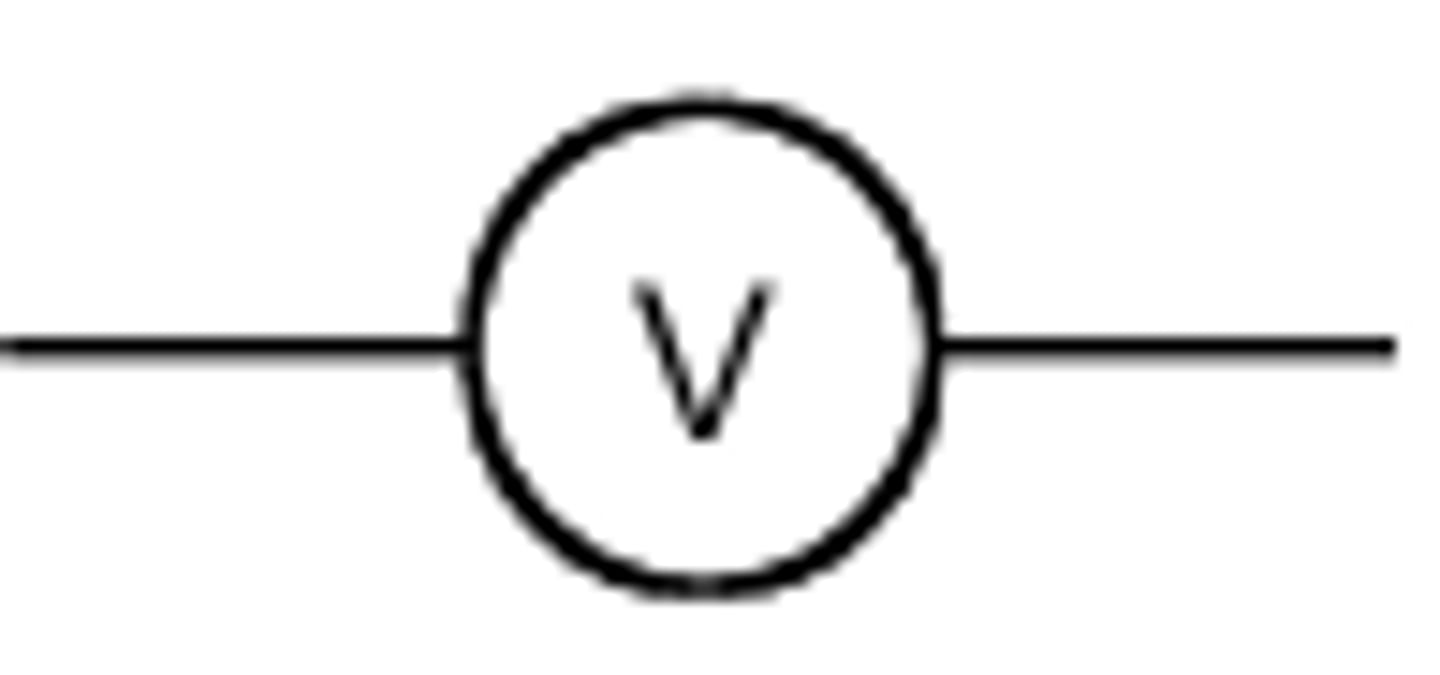
Voltmeter
A device used to measure potential difference, must be put in parallel
Anmeter
A device used to measure the current flowing through a circuit, must be in a series

Ferromagnetic
Substances that can become magnetized; iron, nickel & cobalt. Their atoms will form magnetic domains.
Paramagnetic
Slightly magnetic material
Diamagnetic
Material that cannot be magnetized
Susceptibility
The degree to which a material can be magnetized
Retentivity
the ability of a material to stay magnetized
Magnetic Flux Lines
Parallel lines of force that always go from the north pole to the south pole in a magnet, and surround a DC current-carrying wire.
Strongest point of magnetic flux is __ ___ _____?
At the poles
Electromagnetism
Acts like a magnet, but it's magnetic force is induced by electricity.
Oersted
magnetic field surrounds a moving electrical current
Faraday (1st Law)
current is induced by moving magnetic field
Helix
A coil of wire
Solenoid
a coil of wire with an electric current in it
Lenz Law (2nd law of electromagnetism)
induced current flows in the opposite direction of the applied current (self induction)
Mutual Induction
inducing current flow in a secondary coil by varying the current flow through a primary coil
Generator: _____ to ______ energy
Mechanical, electrical
Motor: _______ to ______ energy
Electrical, mechanical
Induction Motor
Powers the rotating anode of an X-ray tube
Self-induction
Utilizes one could which acts as a primary and secondary coil
Mutual induction transformer
Changes voltage and current in the secondary coil is caused by a change in the voltage/current of the primary coil
Open Core
-iron core is inserted
-leakage flux
-least efficient
Closed Core
-continuous path
-minimal leakage
-core is laminated
Shell Core
-most advanced
-wiring is insulated
-common in modern x-ray systems
-most efficient