Week 1: Fluid Balance & Electrolytes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
ADH and vasopressin
-The collecting ducts of the nephrons respond to ADH by increasing the reabsorption of water
-decrease excretion of urine
Potassium expected range:
3.5-5 mEq/L
Sodium expected range:
136-145 mEq/L
Calcium expected range:
9-10.5 mEq/L
Magnesium expected range:
1.3-2.1 mEq/L
Potassium functions:
-intracellular electrolyte
-support the transmission of electrical impulses of the body's nerves and muscles
-conduction of nerve cells within the heart
Hypokalemia
-muscle weakness/cramping, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory weakness/paralysis
-never give IV push K
-put patient on cardiac monitoring
Hyperkalemia
-most common cause is renal failure
-paralysis, dysrhythmias or palpitations
-place on cardiac monitor/ECG
-decrease K intake
-remove K via dialysis or kayexalate (BMs)
-treated with dextrose
Sodium functions:
-extracellular electrolyte
-supports proper neurologic and neuromuscular function
-seizure precautions
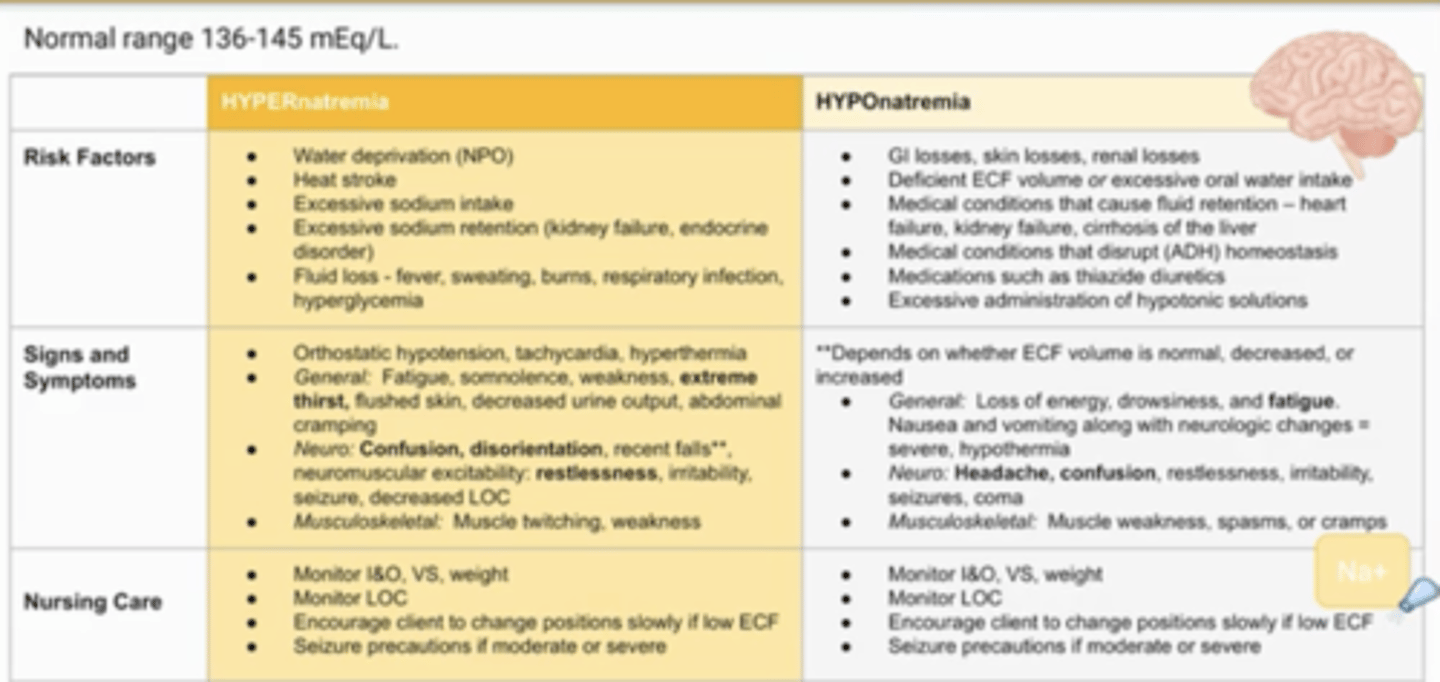
Hyponatremia
-Neuro symptoms: loss of consciousness, seizures, and coma, headache due to swelling in brain
-rapid increase in fluids/fluid retention
--think kidney or heart failure
-focus on I and O and seizure precautions
Hypernatremia
-causes by dehydration or increase in sodium intake
-extreme thirst, some neuro, restlessness
-seizure precautions
-treat w/hypotonic fluids
Hypocalcemia
-numbness and tingling, muscle spasms, hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
-positive Chovostek and Trousseau sign
-causes by hypoparathyroidism after surgery or excess diarrhea or laxative misuse
-keep emergency tracheostomy equipment standby
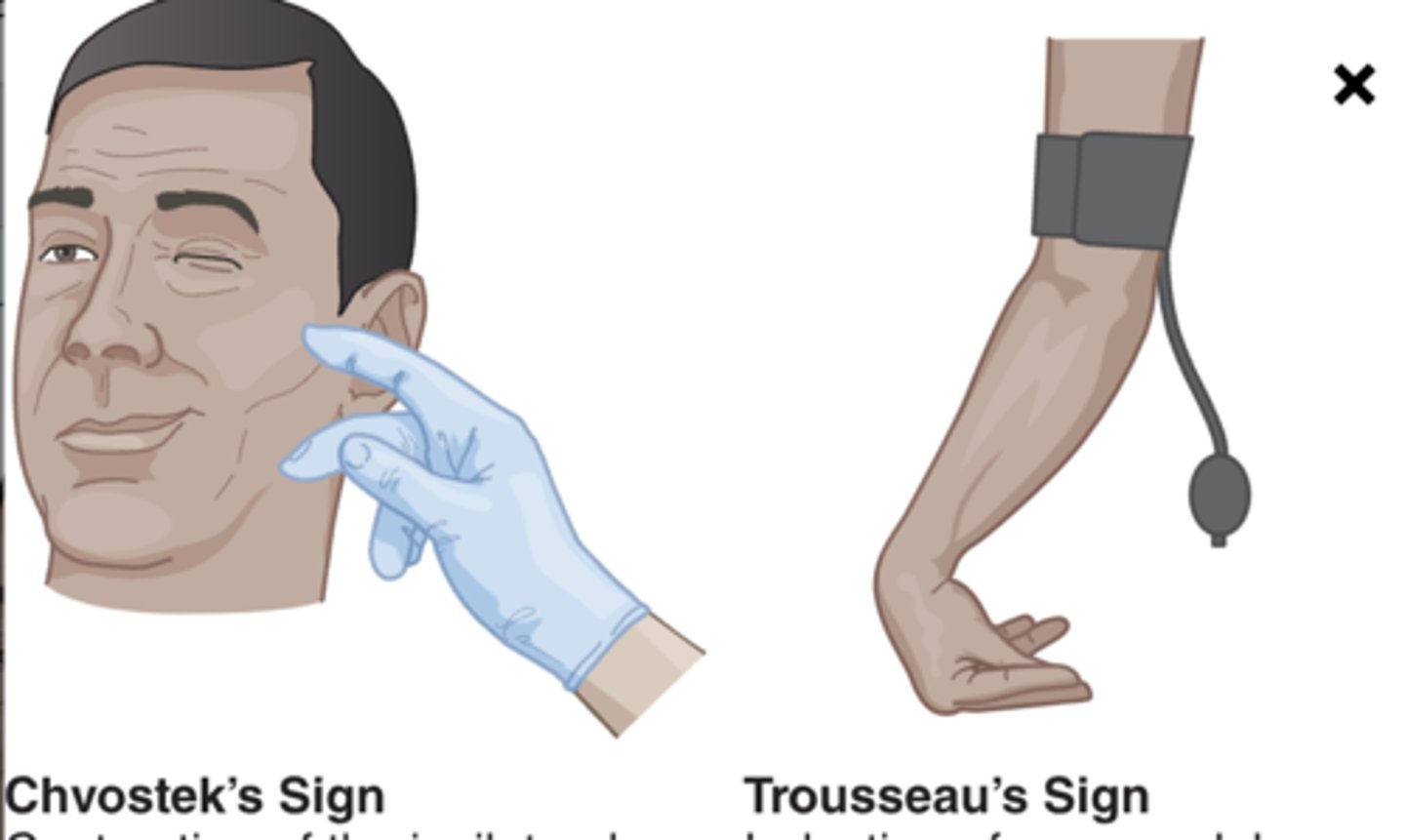
Chvostek sign
Test which may indicate low calcium or magnesium levels. A positive result results in a twitching response of the side of the face when facial nerves are tapped
Trousseau sign
Test that can indicate low calcium or magnesium levels and spasms in the wrist and hand when a blood pressure cuff is inflated above the systolic blood pressure
-more specific to hypocalcemia
Hypercalcemia
-kidney stones, bone pain, dysrthmias
-most common causes are hyperparathyroidism/thyroidism and cancer
-monitor for bone fractures/restrict Ca, increase fluids
Magnesium function:
-intracellular electrolyte, 50% to 60%, is located in the bones
-regulation of nerve and muscle function, maintain blood pressure and serum glucose levels, support bone and teeth health, and synthesize protein, DNA, and RNA
-social butterfly
Hypomagnesemia
-nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, fatigue, and weakness
-severe are neuromuscular changes, muscle cramps, spasticity, numbness, seizures, tetany, personality changes, cardiac dysrhythmias
-IV mg is high alert med
Hypermagnesemia
-most common cause is kidney disease
-nausea, dizziness, weakness, and confusion, confusion, sleepiness, blurred vision, headache, hypotension, bradycardia, dysrhythmias, decreased reflexes
-check patellar reflex if suspected
-long half life
-overuse of laxatives can cause this
Dehydration
-there is a loss of water or lack of water intake without a concomitant loss of sodium
-increased osmolality
-body water shifts from the inside of the cell to the extracellular space= cell shrink
-thirst, lethargy, dry mucosa, and oliguria
-severe is tachycardia, hypotension, lactic acidosis, shock
-increased urine specific gravity level, and all other labs!!
Fluid volume deficit (hypovolemia)
-thirst, dryness of mucosa, decreased skin turger, flat neck veins, dark urine, sudden weight loss, orthostatic hypotension, increased HR
-all labs go up EXCEPT FOR NA+
-similar to dehydration, but decrease in fluid AND electrolytes
-treat w/isotonic solutions
Fluid volume excess/overload (hypervolemia)
-sudden weight gain, edema, full neck veins, crackles in lungs, bounding pulse, pulmonary edema, increase in RR, decrease 02
-all labs go down
Interventions for fluid excess:
-weigh daily in the morning, same clothing (get patient to void)
-edema in legs--> elevate legs
-edema in lungs--> elevate HOB, possible IV diuretics, dialysis, supplemental 02
Interventions for fluid deficit:
-treat with isotonic solutions
-mild: oral rehydration w/electrolytes
-moderate to severe: isotonic, 0.9 or lactated ringers
Hematocrit (Hct)
-proportion of RBC in the blood
-males: 42-52%
-females: 37-47%
Importance of thyroid:
-controls Ca+ homeostasis via Calcitonin and PTH
Do we administer IV push potassium?
NO NEVER
-only use IVPB or oral routes (no crushing)
How to treat hyperkalemia?
-remove K via dialysis or kayexalate (BMs)
-treated with dextrose
BUN reference range:
10-20 mg/dL
Creatinine reference range:
0.5-1.1 mg/dL
Urine specific gravity:
1.005-1.030
Dextrose/insulin is used to treat which imbalance?
Hyperkalemia
-insulin increases re uptake
Phosphorus reference range
3.0-4.5 mg/dL
S/S of hypophosphatemia
-respiratory muscle weakness
-hypotension, arrhythmias
-bone pain, bone fractures
-bleeding, thrombocytopenia
S/s of hyperphosphatemia
same as hypocalcemia
-fatigue, anxiety
-hyperrelexia, tetany
-seizure
-positive Chvostek's sign, positive Trosseua's sign
Nursing considerations for hypophosphatemia:
-monitor cardiac rhythm and BP
-place patient on seizure and fall precautions
-administer oral replacement
Nursing considerations for hyperphosphatemia:
-ASSESS FOR HYPOCALCEMIA (tetany, twitching, seizures)
-place patient on cardiac monitoring
-administer phosphate binders
Fluid distribution in body
Intracellular fluid- inside the cell, 2/3 of body water; contains potassium, magnesium, phosphates, and proteins.
Extracellular fluid- outside of the cell, 1/3 of body water
Crystalloids
water and electrolytes (water soluble molecules)
-simple
-cost effective
-no immune response
Colloids
large insoluble molecules
-higher osmotic pressure
-more expensive
-immune response
Isotonic
-wont shift between ECF and ICF
-normal saline, lactated ringers, PlasmaLyte, D5W
Hypertonic
greater amount of solutes--> greater osmotic concentrate
-results in fluids pulled from ICF to ECF (dehydrates cells)
-3% normal saline
Hypotonic
less amounts of solutes--> less osmotic concentration
-fluid moves ECF to ICF (cells swell)
-0.5 normal saline--> (dont use w/head injuries or admin fast)