RADT146 Unit 4 - Radiographic Technique 2
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what are the 2 dual focus tubes and where are they located?
small and large focal spot sizes (filament wires); on the cathode side
what do microfocus tubes mean?
FSS of 0.3mm or less
what FSS is going to give you the best resolution?
the smallest
what is large focus used for?
normal imaging
does the large focus have high mA or small mA and why?
higher mA b/c it can be impressed for larger/denser body parts
does the large focus have high or low heat and where?
higher heat capacity at the anode
what is the advantage of a large FSS in relation to detail of an image?
shorter exposure times to minimize motion
what does having a high mA do to time and motion?
faster time and decreased motion/blur
when do you use the small focus
used for magnification radiography where detail is required;
ex: mammo or angiography
does small focus use high or low mA?
low mA;
it CANNOT use high mA due to limited heat capacity
for small focus, a given amount of electrons cover a ____ area on the ____
smaller; anode
what body parts do we use the small focus for?
for smaller and thinner body parts where large quantity of xray photons are not necessary
2 terms for the varying energies of an xray beam
polyenergetic and heterogeneous
what is the purpose of filtration?
"hardens" the beam (by removing the lower energy / the softer rays)
what does having filtration do to PT exposure?
decreases PT exposure so they do not absorb the soft rays
what are the 2 filtrations?
1. inherent
2. added
what does the word "equivalent" mean?
Any material can act as a filter as long as it has the same attenuating properties as 0.5mm of Al equivalent.
what is the thickness and material for an inherent filter?
glass or metal envelope; 0.5mm Al equivalent
what is the first added filtration's material and thickness?
mirror in collimator box; 1.0mm Al equivalent
what is another added filtration and where was it added?
another 1.0mm Al equivalent; added btwn the xray tube housing and the collimator
what is the total for the INHERENT filtration?
0.5mm Al equivalent
what is the total amount of ADDED filtration? name them and add them
2.0mm Al equivalent;
- 1.0mm from the mirror in collimator box
- 1.0mm from the added filtration btwn xray tube and the collimator box
what is total AMOUNT of filtration?
2.5mm Al equivalent
- what does the half-value layer improve?
- The amount of material that reduces the ___ of the x-ray beam to ___ its original value
- improves the quality of the beam
- intensity; half
- the HVL is used for both ___ and ___
- an increase in HVL ____ the quality of the xray beam
- shielding and filtration
- increases
how does increasing the HVL increase the quality?
b/c we removed the softer rays, making the beam HARDER, and reducing PT exposure
compensation filter:
- different shapes of Al mounted under ___
- Balances ___of x-ray beam for a more uniformed exposure to the __ __
collimator; intensity; IR
what are the 2 compensation filters?
1. wedge filter
2. trough filter
describe the thickness and thinness of a wedge filter
thin at one end and thick at the other end
describe the thickness and thinness of a trough filter
thick on both sides and thin in the center
just read :)
- Compensating filters slide over collimator box; an accessory you can slide in and out
- Do not confuse with inherent and added filters; these are a part of the system already
pretend we take a foot xray WITHOUT a wedge filter.
- how does the thicker end of the heel appear?
- how does the thinner end (toes) appear?
explain for both
- thicker end (heel) absorbs the xrays b/c the xrays do not penetrate it and reach the IR; appear LIGHTER
- thinner end (toes) allow more xrays to penetrate right through because it is so thin; appear DARKER
how do we avoid the uneven density from the toe to heel? we use a wedge filter. where do we place each end of the foot now?
- place the THICK part of the wedge towards the TOES; b/c there are less xrays interacting with the toes
- place the THIN part of the wedge towards the HEELS; allows more xrays to interact with the heel
the trough filter is good for what type of xrays?
chest xrays
remember that the trough filter is thin in the middle. why do we use this for chest xrays?
we want more xray penetration b/c we want to shoot through the spinal column and the heart
- put the THICKER part of the trough in areas where its ____ ___
- put the THINNER part of the trough in areas where its ____ ___
- highly penetrating
- not as penetrating
the anode heel effect is a:
phenomenon in which the ___ of the x-ray beam is greater towards the ___ side of the tube. The loss of ___ is a result of the ___ traveling farther to the ___ heel portion of the target
intensity; cathode; intensity; electrons; anode
absorption by heel of target results in ___ xray intensity on ___ side of the beam
decreased; anode
ex: for a foot xray, place the thicker part of the body at the ___ end
cathode; heel at the cathode
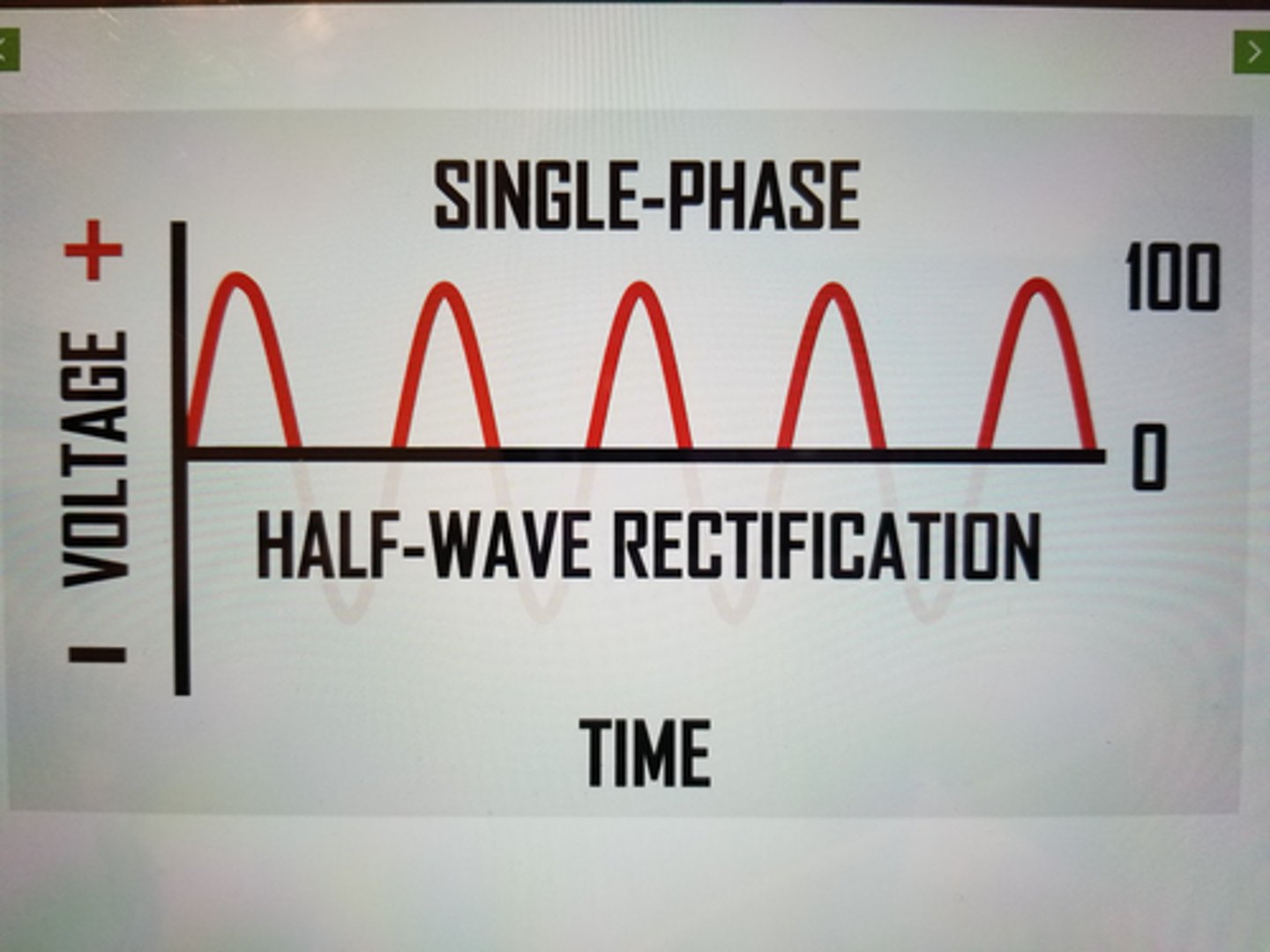
traits of Single Phase Half Wave rectified generator
- half of the cycle is wasted
- xray produced only HALF of the time
- 100% ripple
- used in mobile radiography and dental
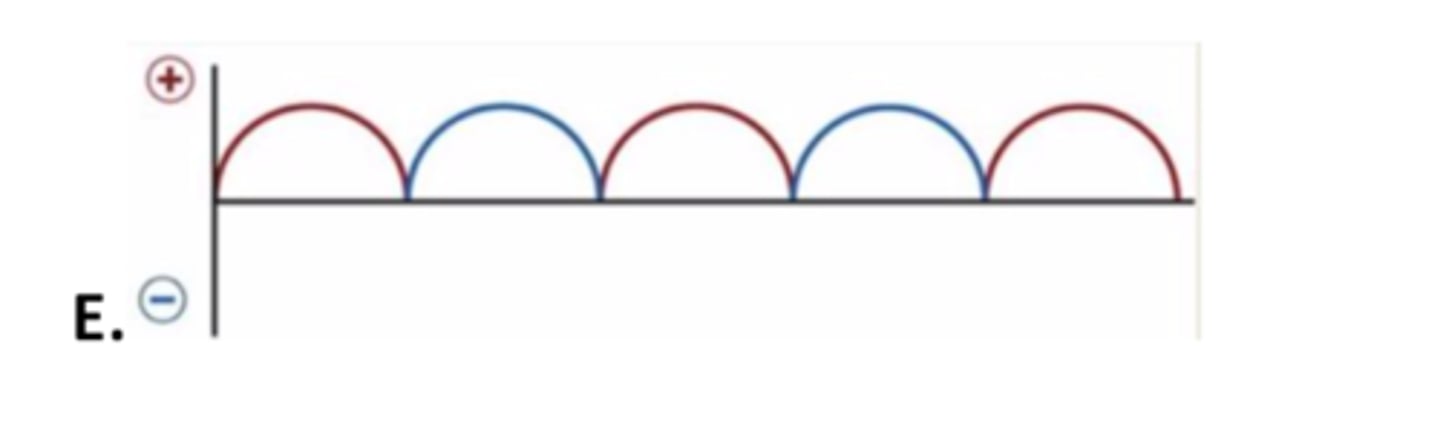
traits of Single Phase Full Wave rectified generator
- no dead time
- xrays are emitted continuously as a pulse
- 100 % ripple still b/c it peaks and comes back to 0
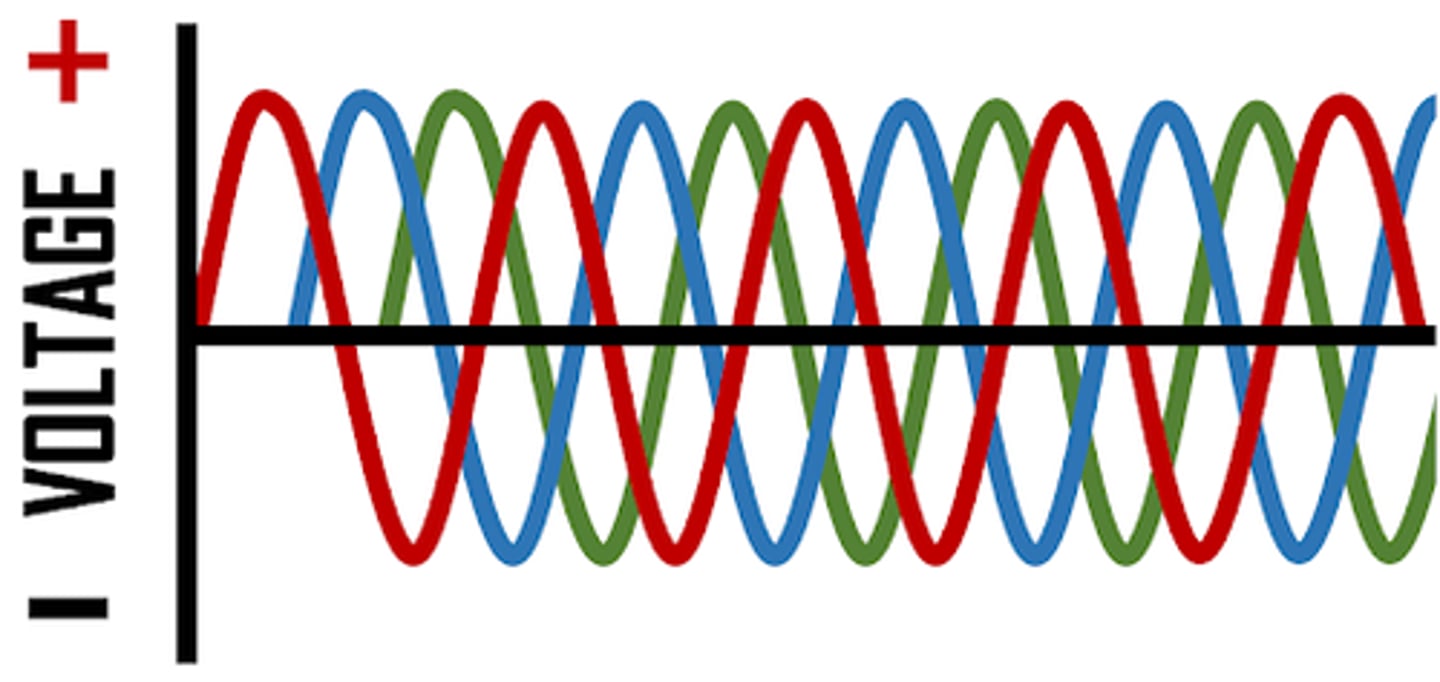
traits of Three Phase Half Rectified
- 3 phase / 6 pulse
- phases are 120 degrees apart
- more xrays produced for a given mAs, avg energy is greater
- xray production is near constant rather than pulsed
- 14% ripple
traits of Three Phase Full Rectified
- 3 phase / 12 pulse
- 4% ripple
- less ripple means less exp time means better for PT
traits of high frequency generators
- developed in 1980's, increasingly used
- near constant delivery of power
- LESS than 1% ripple
- used in highly sophisticated systems: mammo and CT; found in hospitals now
voltage ripple of:
- single phase
- 3 phase / 6 pulse
- 3 phase / 12 pulse
- high-frequency
- less ripple means greater __
- 100%
- 14%
- 4%
- LESS than 1%
- efficiency
four traits for 3 phase comparison to 1 phase
- more efficient
- requires more complex circuitry
- more expensive to install
- provides for shorter exposure times
what are 4 PT factors that influence the radiographic technique?
1. size and shape (body habitus)
2. anatomy density (thickness)
3. pathology
4. composition (chest v. abdomen)
sthenic body habitus traits
strong, active, avg size
hyposthenic body habitus traits
thin but healthy in appearance
hypersthenic body habitus traits
large framed and usually overweight
asthenic body habitus traits
small, frail, emaciated, and often elderly; sickly; everything sags inside too
the thicker the PT, the ___ xrays are needed to penetrate the body to expose the ___
more; IR
generally, kV is ___ while mAs is ___ to achieve optimum density on film
fixed; varied
how is subject contrast different from radiographic contrast?
subject contrast refers to the PT's body part and composition
is the chest high or low subject contrast?
high subject contrast: mostly black and white, with some grays in between
what is radiopague and 2 examples
difficult to penetrate; bone & metal
what is radiolucent and 2 examples
easy to penetrate; air & soft tissue
osteoporosis is an example where it's a ____ process causing ___ to be more ____
destructive; tissue; radiolucent
osteopetrosis is an example where bone is constructive in increase ____ ___ and ____
mass density; composition
if you have a PT with osteoporosis, what would you do to kV? why?
decrease kV
- low kV makes high contrast (mainly black and white). you want to see the black and white clearly
if you have a PT with osteopetrosis (stone bone - abnormally dense and brittle; super white), what would you do to kV? why?
increase kV
- high kV makes low contrast (mainly grays). since this condition appears super white on the image, you want to have more grays to distinguish the different parts